|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1130038
2030年に向けた乗用車のCO2排出量規制に対応する欧州OEM戦略European OEM Strategies for Passenger Car CO2 Emissions Compliance Towards 2030 |
||||||
| 2030年に向けた乗用車のCO2排出量規制に対応する欧州OEM戦略 |
|
出版日: 2022年09月07日
発行: Frost & Sullivan
ページ情報: 英文 78 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
OEMがコンプライアンス遵守のためにゼロエミッション運転に移行する転換期が急速に近づいています。
当レポートでは、2030年に向けた乗用車のCO2排出量規制に対応する欧州OEM戦略について調査し、法規制と市場概要、戦略的必須要件、成長環境と範囲、OEMプロファイルなどの情報を提供しています。
目次
エグゼクティブサマリー
- エグゼクティブサマリー
- 燃費と排出ガスの向上技術
- CO2コンプライアンスへの技術的影響
- 2030年に向けたOEMによるCO2排出量予測
- xEV普及率と比較した実績値vs.目標値
戦略的必須事項
- 成長がますます困難になっている理由
- The Strategic Imperative 8(TM)
- EUと英国のパワートレイン業界に対する上位3つの戦略的必須事項の影響
- 成長パイプラインエンジン(TM)を促進する成長機会
成長環境と範囲 - 欧州パワートレイン業界
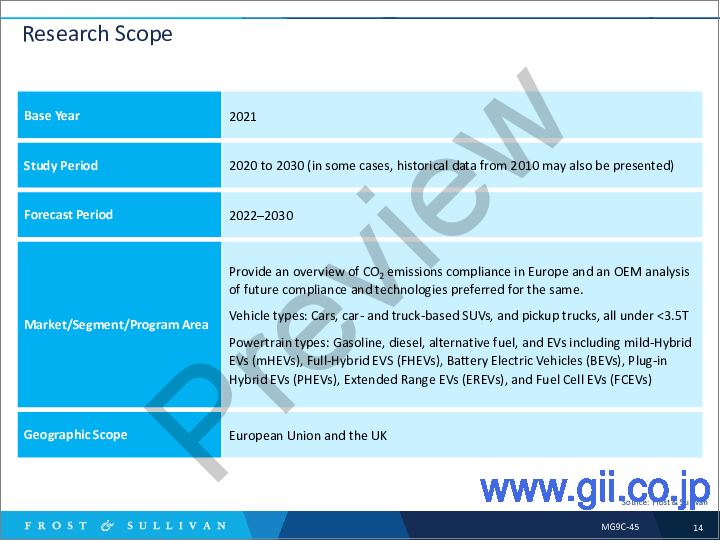
- 調査範囲
- 車両セグメンテーション
- セグメンテーション
法規制と市場概要
- 地域の排出量と試験手法
- 世界の乗用車の企業平均燃費目標
- EUと英国の排出量見通し
- EUと英国の乗用車の平均CO2目標
- 質量ベースのCO2目標:OEMプール別
- 技術ロードマップ:パワートレインの開発動向
CO2推定量と技術の影響
- フリート平均CO2排出量に向けた柔軟性
- フリート平均CO2排出量:OEMプール別
- フリート平均排出量に対するWLTPの影響
- 排出量コンプライアンスのための技術の重要性
- 予測フレームワーク
- 業界平均実績
OEMプロファイル
- BMW Group
- CO2コンプライアンスに対する技術の影響
- Mercedes-Benz Group
- Ford Group
- Honda Group
- Hyundai-Kia Group
- Renault-Nissan Group
- Stellantis Group
- Toyota Group
- Volkswagen Group
- Volvo Group
成長機会ユニバース
- 成長機会1:電動化に向けたOEMとサプライヤーのパートナーシップ
- 成長機会2:xEVによる車両電動化への投資増加
- 成長機会3:低排出ガス化のための燃焼最適化
- 頭字語
- 図表リスト
- 免責事項
The Tipping Point for OEMs to Move to Zero-emissions Driving as a Means for Compliance is Fast Approaching
Industry-wide fleet average CO2 emission targets for 2025 have been set to be 15% lower than 2020 levels, while 2030 levels will be 37.5% lower than 2020 levels. These targets are more stringent and are for cars only (separate targets are set for LCVs).
Once the focus area for emission reduction, developments in IC engines no longer play an integral role in emissions compliance. Though investment in IC engine development is still beneficial, it is not the primary road to compliance. The availability of flexibilities played a critical role in most OEMs' compliance in 2020. However, these flexibilities reduce year-on-year, with only eco-innovations continuing to be active while moving towards ZLEV mandates of 15% from 2025 and 35% from 2030.
Most European and American OEMs have increased the sale of PHEVs and BEVs for compliance but Asian OEMs have been late in adopting electric powertrains due to the strong focus on hybridisation. Electrification is fast becoming the de-facto requirement for compliance. All OEMs accelerating electrification, which is showing a higher return on investment from a compliance perspective and will shortly do so from the revenue perspective as well.
Europe has been at the forefront of engine downsizing, which is evident from the high share of direct-injected, turbocharged gasoline engines. Alternate combustion cycles, Atkinson and Miller, are also expected to find increased adoption, with Atkinson Cycle being adopted by OEMs with full hybrids.
With the adoption of diesel powertrains declining in Europe since the dieselgate scandal, mHEVs and FHEVs have stepped up to meet the demand. In the short term, mHEVs are projected to be the leading xEV type and post the highest growth rates. The primary driver for increased xEV adoption was to meet the targets for 2020. The adoption of xEVs however, varies between OEMs, with BMW, Mercedes-Benz and Volvo prioritising PHEVs, while Kia, Renault-Nissan, and Volkswagen focus more on BEVs. Asian OEMs, meanwhile, focus on hybridisation and overall efficiency improvement. With OEMs meeting the targets for 2020 and 2021, it is now clear that maintaining the xEV ratio will suffice until the next set of targets come into effect.
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
- Executive Summary
- Technology for Improving Fuel Economy and Emissions
- Technology Impact on CO2 Compliance
- Technology Impact on CO2 Compliance (continued)
- CO2 Emission Projection by OEM Towards 2030
- Actual Versus Target Compared to xEV Penetration
Strategic Imperatives
- Why Is It Increasingly Difficult to Grow?
- The Strategic Imperative 8™
- The Impact of the Top 3 Strategic Imperatives on the EU and UK Powertrain Industry
- Growth Opportunities Fuel the Growth Pipeline Engine™
Growth Environment and Scope-European Powertrain Industry
- Research Scope
- Vehicle Segmentation
- Segmentation
Legislative and Market Overview
- Regional Emissions and Testing Procedures
- Global Passenger Car Corporate Average Fuel Economy Targets
- EU and UK-Emissions Outlook
- EU and UK Passenger Car Fleet Average CO2 Targets
- Mass-based CO2 Targets by OEM Pool
- Technology Roadmap: Powertrain Development Trends
CO2 Estimates and Technology Impact
- Flexibilities Towards Fleet Average CO2 Emissions
- Fleet Average CO2 Emissions by OEM Pool
- Impact of WLTP on Fleet Average Emissions
- Importance of Technology for Emissions Compliance
- Frost & Sullivan-Forecasting Framework
- Industry Average Performance
OEM Profiles
- BMW Group
- BMW Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance
- BMW Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance (continued)
- Mercedes-Benz Group
- Mercedes-Benz Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance
- Mercedes-Benz Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance (continued)
- Ford Group
- Ford Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance
- Ford Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance (continued)
- Honda Group
- Honda: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance
- Honda: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance (continued)
- Hyundai-Kia Group
- Hyundai-Kia Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance
- Hyundai-Kia Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance (continued)
- Renault-Nissan Group
- Renault-Nissan Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance
- Renault-Nissan Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance (continued)
- Stellantis Group
- Stellantis: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance
- Stellantis: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance (continued)
- Toyota Group
- Toyota: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance
- Toyota: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance (continued)
- Volkswagen Group
- Volkswagen Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance
- Volkswagen Group: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance (continued)
- Volvo Group
- Volvo: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance
- Volvo: Impact of Technology on CO2 Compliance (continued)
Growth Opportunity Universe
- Growth Opportunity 1: OEM-supplier Partnerships for Electrification
- Growth Opportunity 1: OEM-supplier Partnerships for Electrification (continued)
- Growth Opportunity 2: Increased Investment in Vehicle Electrification Through xEVs
- Growth Opportunity 2: Increased Investment in Vehicle Electrification Through xEVs (continued)
- Growth Opportunity 3: Optimising Combustion for Lowering Emissions
- Growth Opportunity 3: Optimising Combustion for Lowering Emissions (continued)
- Initialisms
- List of Exhibits
- List of Exhibits (continued)
- List of Exhibits (continued)
- Legal Disclaimer