
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1911402
マレーシア決済市場:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年)Malaysia Payments - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| マレーシア決済市場:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年) |
|
出版日: 2026年01月12日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 100 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
マレーシアの決済市場規模は、2026年には2,917億9,000万米ドルと推定されており、2025年の2,625億米ドルから成長が見込まれます。
2031年までの予測では4,949億米ドルに達し、2026年から2031年にかけてCAGR11.15%で拡大すると見込まれています。
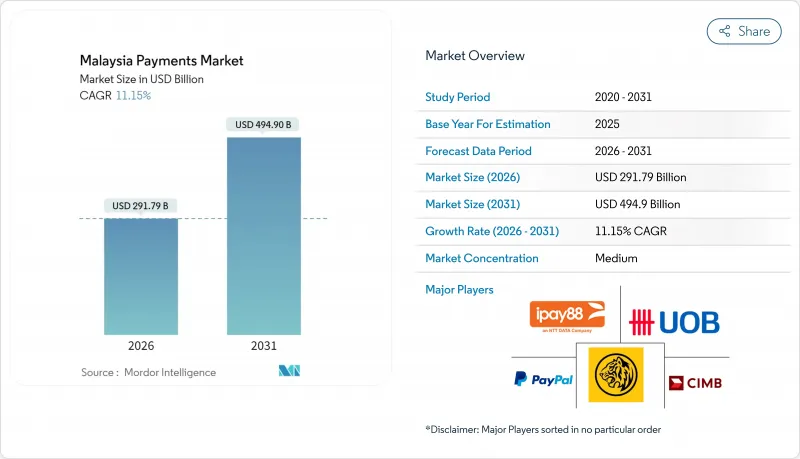
この上昇傾向は、政府の相互運用可能なQR戦略、即時送金を支えるリアルタイム決済ネットワーク、地方の小規模事業者向け積極的なキャッシュレス化インセンティブに支えられています。継続的な電子商取引の拡大、都市部における電子財布の88%普及率、イスラム系フィンテック提案の台頭が相まって、デジタル取引量を二桁成長軌道に維持する好循環を生み出しています。既に主要スーパーアプリに組み込まれた口座間送金(A2A)システムは、夜間支払いを求めるマレーシアのギグワーカー層から新たな利用者を獲得。一方、国境を越えた決済経路は、共有QRインフラを通じて観光客の支出を流入させています。既存カード決済システムは高額オンライン購入で依然重要ですが、その最大の成長要因は、クランバレーの大型スーパーに普及した非接触型POS端末で利用可能なトークン化された認証情報にあります。QR詐欺の手口が高度化する中、サイバーセキュリティは引き続き資本支出の優先事項ですが、国家詐欺対策ポータルによる連携対応により、銀行アプリにおける認証の脆弱性が解消されつつあります。
マレーシア決済市場の動向と洞察
政府主導のQRコードと非接触型カードの相互運用性推進
DuitNowの全国QR標準は現在、Alipay対応加盟店8,000万店をカバーし、インドネシア、シンガポール、タイ、カンボジアとの相互接続が稼働中です。マレーシア中央銀行は加盟店向けQR表示の統一を義務付け、端末の煩雑さを軽減し、零細企業の導入コストを削減しています。2025年5月までに、ペラ州とケランタン州の地方市場露店でも非接触決済が利用可能となり、NFC端末向け補助金の効果を反映しています。中国人民銀行が1回あたりの決済上限を5,000米ドルに引き上げたことで、国境を越えた取引限度額が大幅に増加し、Touch 'n Goユーザーは海外旅行のピーク時に高額購入が可能となりました。加盟店は単一統合により取引を自動的に最安経路に自動ルーティングできるため、利益率の向上と現金取引が主流の地域におけるデジタル化の加速が図られています。
電子商取引の急速な拡大とモバイルショッピングの普及
ソーシャルコマースのライブ販売や送料無料キャンペーンにより、マレーシアのオンライン小売GMVは急増し、より多くのカート決済がプリペイド式電子財布へ誘導されました。ShopeePayおよびTouch 'n GoがGoogle Payの自動入力レイヤーに直接組み込まれたことで、手動でのカード入力が不要となり、飲食業や薬局などの加盟店におけるモバイル決済のコンバージョン率が向上しました。2024年の電子財布普及率88%は転換点を示しており、現在では任意支出においてデジタル決済がデフォルトとなっています。ECプラットフォームは食料品やオンデマンドサービスへ拡大しており、GrabによるJaya Grocer買収がその好例です。これにより高頻度購入の鮮度重視食品が同社のウォレット基盤に組み込まれました。この変化は「今すぐ購入、後払い(BNPL)」の普及も加速させており、BigPay Laterが認可オンライン貸金業者として参入。従来クレジットカード利用が困難だった新社会人層に分割払いオプションを提供しています。
中小企業と地方消費者における現金志向の持続
中小企業の77%は基本的なデジタル成熟度に留まっており、QRコード導入の障壁としてMDR手数料や不安定な携帯電話通信網を挙げています。サバ州とサラワク州では、農産物市場(パサール・タニ)のベンダーが依然として現金決済を主流とする背景には、電子財布の毎日決済処理よりも現金管理が簡便である点が挙げられます。分散した決済処理により、少額取引の加盟店手数料は2%以上を維持しており、農産物の薄利をさらに圧迫し、現金利用への依存を強めています。政府のバウチャー制度は祝祭期に利用率を向上させましたが、補助金が終了すると多くの屋台店主が現金決済に戻ります。その結果、二つの並行システムが存続し、都市部以外におけるマレーシア決済市場の浸透曲線を鈍化させています。
セグメント分析
2025年時点でデジタルウォレットはマレーシア決済市場シェアの35.10%を占め、総取引額の921億4,000万米ドルに相当します。ウォレット市場規模はスマートフォン普及率の上昇と歩調を合わせ、CAGR11.15%で拡大すると予測されます。DuitNow即時決済基盤を活用したA2A決済は12.02%のCAGRで最速成長を記録し、150万人のギグワーカーへの給与支払いをほぼ即時決済サイクルに組み込みました。チャージバック保護のため高額航空券・電子機器分野ではカード決済が根強いもの、非接触型MyDebitカードの継続的発行により、公共交通機関の小口運賃支払いがトークンから移行しつつあります。代金引換の重要性は低下傾向にあります。地方物流ネットワークが宅配ロッカーQR決済を導入したことで、配達員の現金管理負担が軽減されたためです。BNPL(後払い決済)の取扱高は、ベースは小さいもの、BigPay Laterがオンライン貸金業免許を取得した2024年に40%増加。これは、ウォレット決済フローに組み込まれた分割払いクレジットに対し、規制当局が容認姿勢を示していることを示唆しています。
第二世代ウォレットは、クローズドループ型ロイヤルティプログラム、Alipay+による海外ローミング、マイクロ投資モジュールを組み込み、ユーザーを単一のスーパーアプリ内に留めます。GrabPayとPayPalのAPI提携は、PayNetのインターチェンジ上限下で現地MDR経済性を維持しつつ、世界のマーケットプレースへの決済受け入れを拡大します。競合上の差別化は現在、不正利用率のパフォーマンスとギグ労働者への支払い遅延に焦点が移っており、従来型銀行は預金フローを維持するため、高速決済「オーバーレイサービス」に投資しています。A2Aプロバイダーは、加盟店がQRコードステッカーを回避し、消費者向け銀行アプリに直接請求書をポップアップ表示できる「Request-to-Pay」機能を推進しており、これはウォレット基盤の次なる波によるカニバリゼーションを示唆しています。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- アナリストサポート(3ヶ月間)
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 電子商取引の急速な拡大とモバイルショッピングの普及
- 政府による相互運用可能なQRコード決済(DuitNow)および非接触型カードの導入推進
- 非接触型カードの普及率とNFC端末の導入状況
- イスラム系フィンテックの台頭とシャリーア準拠決済ソリューションの提案
- ASEAN域内電子財布相互運用性イニシアチブ
- リアルタイム決済システムによるギグエコノミー向け即時支払い
- 市場抑制要因
- 中小企業および地方消費者における持続的な現金選好
- 増加する不正行為とサイバーセキュリティ懸念による信頼低下
- 分散したアクワイアリング市場により、小規模加盟店向けMDRは高水準を維持しております
- 移民労働者および外国人労働者向け電子本人確認(e-KYC)の障壁
- 業界バリューチェーン分析
- 規制情勢
- テクノロジーの展望
- マクロ経済要因の影響
- 業界利害関係者分析
- マレーシアにおける決済環境の進化
- キャッシュレス導入を推進する主要動向
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
- 主要な規制と基準
- 主要な事例研究と使用事例
- 人口統計学的要因が決済手段の選好に与える影響
- 顧客体験と世界の動向の収束
- 現金代替と非接触決済の勢い
- 投資分析
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- 支払い方法別
- 販売時点情報管理(POS)
- デビットカード決済
- クレジットカード決済
- 口座間決済(A2A)
- デジタルウォレット
- 現金
- その他の販売時点決済方法
- オンライン販売
- デビットカード決済
- クレジットカード決済
- 口座間決済(A2A)
- デジタルウォレット
- 代金引換
- その他のオンライン販売決済方法
- 販売時点情報管理(POS)
- エンドユーザー業界別
- 小売り
- エンターテインメント
- ホスピタリティ
- ヘルスケア
- 運輸・物流
- その他のエンドユーザー産業
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 戦略的展開と提携関係
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- Malayan Banking Berhad(Maybank)
- CIMB Group Holdings Berhad
- Touch'n Go Digital Sdn Bhd
- PayPal Holdings, Inc.
- Visa Inc.
- Mastercard Incorporated
- UnionPay International Co., Ltd.
- Payments Network Malaysia Sdn Bhd(PayNet)
- Ipay88(m)Sdn Bhd
- Boost Holdings Sdn Bhd
- Razer Merchant Services Sdn Bhd
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.(Huawei Pay)
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.(Samsung Pay)
- Stripe, Inc.
- BigPay Later Sdn Bhd
- Pine Labs Private Ltd.(FavePay)
- Ant Group Co., Ltd.(Alipay)
- United Overseas Bank(Malaysia)Bhd
- Bank Islam Malaysia Berhad


