
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1644812
アジア太平洋の決済-市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Asia-Pacific Payments - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| アジア太平洋の決済-市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年01月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 120 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
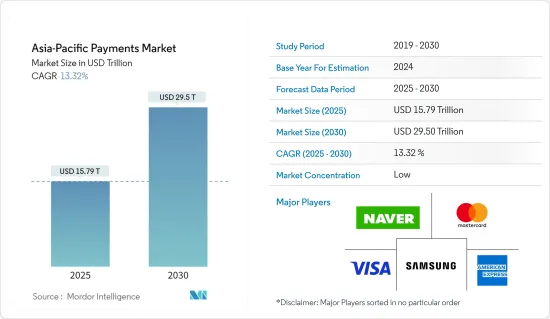
アジア太平洋の決済市場規模は2025年に15兆7,900億米ドルと推定され、予測期間中(2025~2030年)のCAGRは13.32%で、2030年には29兆5,000億米ドルに達すると予測されます。
主要ハイライト
- アジア太平洋では、消費者の非接触決済や電子決済への移行が進んでいます。消費者の現金離れは続いています。この変化の主要理由は、同地域で決済技術が驚異的なスピードで進化していることです。
- アジア太平洋のような新興・開発地域では、モバイル決済は、取引の容易さ、スマートフォンの普及、技術の金融包摂機能により、驚異的な成長を遂げています。
- スマートフォンとインターネットの普及に伴い、モバイルウォレットの普及は年々加速しています。中国とインドは現在、世界のスマートフォン人口の50%以上を占めており、電子財布の利用が主流となっています。電子財布は決済処理に利便性と安全性を提供し、現在、決済変革の最前線にあります。さらに、アジア太平洋の決済環境の特徴は、政府がキャッシュレス決済を奨励する施策を積極的に推進していることです。
- しかし、決済サービスを提供する携帯電話アプリケーションにとって、データプライバシーは依然として大きな課題です。各社は継続的に、よりシンプルで安全な顧客ID認証方法を開発し、施策の安全性と信頼性を高めようとしています。一部の企業は、運転免許証のような公的書類を統合してユーザーを確認し、不正なアカウントを回避することを期待しています。このような対策は、モバイル決済の強化に役立ちます。
- *COVID-19の流行中、アジア太平洋ではデジタル決済が加速しました。パンデミック期間中は、物理的または非接触型のカードやデジタルウォレットが最も一般的な決済手段であったが、一部の国ではパンデミック期間中も現金が主要な決済手段でした。さらに、COVID-19後のデジタル化された世界に不可欠なモバイル決済へのシームレスな移行を図るため、アジア諸国は規制の枠組みを強化し、デジタルIDの利用を可能にするなど、デジタルネットワークやインフラへの投資を進める構えを見せています。
アジア太平洋の決済市場の動向
オンライン販売セグメントが高い成長を示す
- アジア全域のモバイル決済の状況は、デジタル変革により変化しています。また、スマートフォンの技術開発がeコマース決済や外出先での資金移動を可能にし、世界市場の成長を後押ししています。中国を拠点とするTencentのようなモバイル決済プラットフォームは急成長を遂げています。Tencentはタイなど他のアジア諸国にも進出しており、サービスのローカライズを支援する主要パートナーを探しています。
- 最も一般的な決済手段は店頭でのQRコードの掲示で、現地の小規模店舗でもモバイル決済に対応しています。中国やインドがこの形態の決済をリードしてきたように、日本のような国も、2025年にキャッシュレス取引を120兆円(900億米ドル)に倍増させるという政府の目標により、QRコードベースの決済を促進する取り組みを徐々に導入しています。
- デジタル決済手段に対する消費者の嗜好は、非接触型決済手段の利用が増加していることを示しています。例えば、今年、決済サービスを提供するワールドラインは、日本に本社を置くカシオと提携し、日本でのカード決済とキャッシュレス・ショッピングを可能にしました。このサービスを日本で提供することで、日本のより伝統的小売環境を変える努力を支援します。また、地域の決済ソリューション・サプライヤーであるVescaは、主に中小企業の小売業者からなる日本の大規模市場に注力することになります。
- eコマースやO2O市場の台頭により、近年、モバイル決済を導入するシナリオは数多く生まれています。WorldPayによると、アジア太平洋の2024年のeコマース決済において、デジタル/モバイルウォレットが60.2%を占め、クレジットカード(16.1%)がそれに続くと予想されています。一方、モバイル決済は、この地域でオンデマンドの小額決済サービスが登場した当初、摩擦を減らし、簡単に導入できるようにする上で極めて重要でした。こうしたセグメントの急速な開発が、モバイル決済の利用拡大をさらに後押ししています。
- さらに、小売業におけるeコマースセグメントでは、消費者がeコマースサイトを通じて食品や衣料品などの必需品を注文するため、需要が急増しています。越境EC企業を対象とした昨年の調査によると、フィリピンではPayPalがデジタル決済プラットフォームの主流で、74%の企業が利用していました。
- RBIによると、インドにおける決済のデジタル化の度合いを示すために昨年1月に発表されたデジタル決済指数(DPI)は、3月の270.59に対し、同年9月の指数は304.06となりました。これは、インド全土におけるデジタル決済の急速な普及と深化を示しています。
マレーシアが市場の主要シェアを占める見込み
- 決済システムは国の経済インフラに不可欠な要素です。マレーシア中央銀行傘下の決済子会社であるPayments Network Malaysia Sdn Bhd(PayNet)は、マレーシアの広範なバリュー決済システムであるRENTASを運営しています。その破綻はシステム危機の引き金となり、金融システムに衝撃を与える可能性があります。RENTASの効果的な運用により、取引は安全かつ迅速に完了し、経済パフォーマンスを高めることができます。マレーシア中央銀行によると、マレーシアにおける昨年の電子マネー、オンラインバンキング、FPX、モバイルインターネットを含むデジタル決済手段全体の取引額は79億マレーシアリンギット(17億1,000万米ドル)でした。総取引額は前年より19億マレーシア・リンギット増加しました。
- 安全で効果的な決済システムは、マレーシア中央銀行の金融施策遂行をより簡素化し、その目標を達成するために市場ベースの手段をより多く利用できるようにすると同時に、金融システムと経済の有効性を向上させるため、金融の安定を促進するために不可欠です。その重要性に鑑み、同行の主要な基盤のひとつは、信頼性が高く、効率的で、安全な決済システムの推進です。
- さらにCOVID-19は、マレーシアにおけるデジタル決済の需要を大幅に押し上げる結果となりました。マレーシアは近年、有利な施策、イノベーション、成長する銀行セクターのおかげで、金融包摂において大幅な進歩を遂げています。最近では、今年4月にマレーシア銀行(BNM)がデジタルバンクのライセンス申請5件に成功したと発表し、マレーシアの財務大臣がこれを承認しました。この発表を受けて、申請者は業務準備を行うことになり、BNMは業務開始前に監査を通じてこれを検証します。BNMは、金融セクターBlueprint 2022-2026に概説されている5つの戦略的推進事項を通じて、金融・フィンテック部門や主要利害関係者との協力を継続し、全国とすべての社会層における金融サービスへのアクセスを継続的に改善することが期待されています。
- マレーシアがキャッシュレス社会に近づき、デジタル決済がより広く利用されるようになるにつれ、市場プロバイダーは、店舗や商店が将来の商取引に対応し、顧客の期待に応えられるよう、決済オプションを改善しています。しかし、中小企業は依然として現金取引に大きく依存しています。また、キャッシュレス化は特定の小規模事業者にとっては困難であり、露天商はデジタル通貨を保管するための設備取得の支援を必要としています。
- 国内での決済需要の高まりに対応するための提携やパートナーシップの拡大が、市場成長率に寄与する主要要因となっています。例えば、今年9月、WorldlineブランドのIngenicoとGHL Systems Bhdの完全子会社であるPaysys(M)Sdn Bhdは、マレーシアの決済市場に対応するため、両社の商業能力を統合すると発表しました。Ingenicoはこの取引の一環として、マレーシアの顧客と事業資産の一部をGHLに売却する可能性が高いです。この新しいオペレーティング・モデルの開発により、IngenicoはPaysysの市場に対する深い理解を活用し、Ingenicoの幅広い決済ソリューションを提供することで、マレーシアでの地位を強化し、より多くの顧客との新たな機会を開拓し、新たな決済体験を記載しています。
アジア太平洋の決済産業概要
アジア太平洋の決済市場は競争が激しく、同地域の重要な参入企業が様々なエンドユーザー向けアプリケーションのeコマース市場で新たなソリューションを開拓しています。各社はまた、地域ビジネスを成長させ、同国のeコマースプラットフォームを提供するために投資や提携も行っています。Visa、Mastercard、Samsung Pay、American Express、Naver Corporationといった一部の市場参入企業は、未開拓の市場空間を横断的に移動することで市場での存在感を高めています。
2022年6月、Samsung PayはSamsungペ PayとSamsung Payを組み合わせたSamsung Walletを発表しました。このウォレットは、パスワードを安全に保存し、暗号通貨のようなデジタル資産をモニタリングすることができます。さらに、Samsung・ウォレットには運転免許証や学生証を保管する機能も含まれていました。
2022年3月、Mastercard、DBS Bank、Pine Labsは提携し、パインラボとのMastercard Installation Paymentsを開始しました。この新プログラムにより、DBS/POSBクレジットカード会員は、会計時にDBS/POSBを提示し、後払い識別カードを使用するだけで、加盟店で無利息の分割払いができるようになります。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場洞察
- 市場概要
- 産業の利害関係者分析
- 産業の魅力-ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手/消費者の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
- この地域における決済環境の進化
- COVID-19が市場に与える影響の評価
- アジア太平洋における決済詐欺の増加と決済市場への影響分析
第5章 市場力学
- 市場促進要因
- eコマースの高普及とMコマースの採用増加
- 市場のデジタル化を促す主要小売企業と政府による支援プログラム
- アジア太平洋諸国におけるBuy Now Pay Laterの採用拡大
- 市場課題
- 標準的な立法施策の欠如(特に国境を越えた取引の場合)
- 市場機会
- 新規参入企業によるイノベーションが普及を促進
- デジタル決済産業における主要規制と基準
- 主要事例と使用事例の分析
- アジア太平洋の決済産業に関する主要な人口動向とパターンの分析(人口、インターネット普及率、銀行普及率/非銀行人口、年齢・所得などを網羅)
- アジア太平洋における顧客満足度重視の高まりと世界の動向の融合に関する分析
- アジア太平洋における現金離れと非接触決済の台頭の分析
第6章 市場セグメンテーション
- 決済モード別
- オフライン(POS)
- カード決済(デビットカード、クレジットカード、銀行融資プリペイドカードを含む)
- デジタルウォレット(モバイルウォレットを含む)
- 現金
- その他の決済方法
- オンライン販売(eコマース)
- カード決済(デビットカード、クレジットカード、銀行融資プリペイドカードを含む)
- デジタルウォレット(モバイルウォレットを含む)
- その他の決済方法(代金引換、銀行振込、後払い決済を含む)
- オフライン(POS)
- エンドユーザー産業別
- 小売
- エンターテインメント
- 医療
- ホスピタリティ
- その他
- 国別
- 中国
- インド
- 韓国
- 台湾
- シンガポール
- フィリピン
- マレーシア
- インドネシア
- ベトナム
- オーストラリア
- 日本
第7章 競合情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Matercard Inc.
- Visa Inc
- American Express Company
- Samsung(Samsung Pay)
- Naver Corporation(Naver Pay)
- PayCo(NHN Corp.)
- kakaopay Corp.
- JCB Co., Ltd.
- Toss Financial Services Private Limited
- Smile Pay
- Paypal Holdings Inc.
- Google Pay(Alphabet Inc.)
- Ipay88(m)Sdn. Bhd
- Samsung Pay(Samsung Electronics Co.ltd)
- Grab Pay(grab Holdings Limited)
- Huawei Pay(Huawei Technologies Co. Limited)
第8章 投資分析
第9章 市場機会と今後の動向
The Asia-Pacific Payments Market size is estimated at USD 15.79 trillion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 29.50 trillion by 2030, at a CAGR of 13.32% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- In Asia-Pacific, consumers are increasingly moving to contactless and electronic payments. They continue to move away from using cash. The main reason for this change is the incredible speed at which payment technology is evolving in the region.
- In emerging and developing regions such as the Asia Pacific, mobile payments have grown tremendously due to the ease of transactions, the widespread use of smartphones, and the financial inclusion capabilities of technology.
- With the spread of smartphones and the Internet, the adoption of mobile wallets has been accelerating over the years. China and India now make up more than 50% of the world's smartphone population, making e-Wallet use the mainstream. They provide convenience and security for payment processing and are currently at the forefront of payment changes. Additionally, the unique characteristics of the payment environment in the Asia-Pacific region are that the government is actively pursuing policies that encourage cashless payments.
- However, data privacy remains a big challenge for mobile phone applications providing payment services. Companies continuously attempt to create simpler and safer methods of authenticating their clients' identities, increasing their policies' safety and dependability. Some companies look forward to integrating official papers like driver's licenses to verify users and avoid fraudulent accounts. Such measures help to strengthen mobile payments.
- *During the COVID-19 pandemic, digital payments accelerated in the Asia-Pacific region. Physical or contactless cards and digital wallets were the most common payment methods during the pandemic, but in some countries, during the Covid-19 pandemic cash remained the primary payment method. Further, to seamlessly transition to mobile payments, which may be an integral part of the more digital post-COVID-19 world, the Asian economies are poised to strengthen their regulatory frameworks and invest in digital networks and infrastructure, such as those enabling the usage of digital IDs.
APAC Payments Market Trends
Online sales segment to show higher growth
- The mobile payment landscape across Asia is changing due to digital transformation. Also, the technological developments in the smartphone have enabled e-commerce payments and on-the-go fund transfers, fueling the global market growth. Mobile payment platforms like Tencent, based in China, have grown rapidly. Tencent also expanded in other Asian countries, like Thailand, and it is searching for major partners to help it localize its services.
- The most common payment medium is projecting QR codes at the shop, wherein small-scale local shops also accept mobile payments. As China and India have been leading in this form of payment, countries like Japan are slowly introducing initiatives to promote QR code-based payments due to the government's aim to double cashless transactions to JPY 120 trillion (90 Billion USD) in 2025.
- The consumer preference toward digital payment methods indicates the increasing use of contactless payment modes. For instance, in the current year, Worldline, a provider of payment services, teamed up with Casio, a business with its headquarters in Japan, to enable card payments and cashless shopping in Japan. Offering this service in Japan will support efforts to change that country's more traditional retail environment. This will also involve Vesca, a regional payment solution supplier, focusing on a large Japanese market primarily of small business retailers.
- The rise of e-commerce and the O2O market has created many scenarios for people to adopt mobile payments in recent years. According to WorldPay, digital/mobile wallet is expected to occupy 60.2% of e-commerce payments in 2024 in Asia-Pacific, followed by credit card (16.1%). On the other hand, mobile payment was crucial in reducing friction and making on-demand, small-ticket services easily adoptable when they first emerged in the region. Rapid developments in these sectors, in turn, further drive the uptake in mobile payment usage.
- Further, the e-commerce sector in retail businesses is witnessing a spike in demand as consumers order essential items such as food and clothes, among others, through e-commerce websites, where most consumers prefer the digital mode of payment. According to a survey of cross-border e-commerce enterprises last year, PayPal was the dominant digital payment platform in the Philippines, with 74% of the enterprises using it.
- According to RBI, the digital payments index (DPI), launched in January of last year to indicate the extent of digitization of payments in India, the index for September of the same year stood at 304.06 against 270.59 in March. This shows the rapid adoption and deepening of digital payments across the country.
Malaysia is Expected to hold Major Market Share of the Market
- Payment systems are an essential component of a country's economic infrastructure. The Bank Negara Malaysia-owned Payments Network Malaysia Sdn Bhd (PayNet), a payment subsidiary, operates Malaysia's extensive value payment system, RENTAS, which permits the transfer and settlement of high-value interbank payments and securities. Its failure could trigger a systemic crisis and send shockwaves through the financial system. With RENTAS's effective operation, transactions may be completed securely and promptly, boosting economic performance. According to Bank Negara Malaysia, the overall transaction value for digital payment methods in Malaysia last year, including e-money, online banking, FPX, and mobile internet, was RM 7.9 Billion (1.71 Billion USD). Total transaction value increased by 1.9 billion Malaysian ringgit over the previous year.
- Payment systems that are secure and effective are essential for promoting financial stability as they make it simpler for Bank Negara Malaysia to carry out its monetary policy by allowing it to use more market-based instruments to accomplish its goals while also improving the effectiveness of the financial system and the economy. Given its significance, one of the bank's primary foundations is promoting a reliable, efficient, and secure payment system.
- Furthermore, COVID-19 resulted in a significant boost in demand for digital payments in the country. Malaysia has achieved substantial progress in financial inclusion in recent years, owing to favorable policies, innovation, and a growing banking sector. Recently, in April of the current year, Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM) announced five successful applications for digital bank licenses, which Malaysia's Minister approved Finance. The applicants will undergo operational preparedness following this announcement, which BNM will verify through an audit before commencing operations. BNM is expected to continue collaborating with the financial and fintech sectors and key stakeholders through the five strategic thrusts outlined in the Financial Sector Blueprint 2022-2026 to continuously improve access to financial services nationwide and among all societal segments.
- As Malaysia moves closer to becoming a cashless society and digital payments become more widely used, market providers are improving their payment options to help shops and merchants position themselves for the future of commerce and meet customer expectations. However, small businesses continue to rely heavily on cash transactions. Getting cashless will also be difficult for certain small businesses, and street vendors need help acquiring the equipment to keep their digital currency.
- The growing collaborations and partnerships to meet the growing demand for payments in the country are the key factors contributing to the market growth rate. For instance, in September of the year, Ingenico, a Worldline Brand, and Paysys(M) Sdn Bhd, a wholly owned subsidiary of GHL Systems Bhd, announced merging their commercial competencies to address the Malaysian payment market. Ingenico will likely sell some of its client and business assets to GHL in Malaysia as part of this deal. By developing this new operating model, Ingenico will strengthen its position in Malaysia by utilizing Paysys' in-depth understanding of the market and bringing Ingenico's wide array of payment solutions to open new opportunities with more clients and unlock new payment experiences.
APAC Payments Industry Overview
The Asia-Pacific payments market is highly competitive as crucial players in the region are developing new solutions in the e-commerce market for various end-user applications. Companies also invest and form partnerships to grow their regional businesses and provide the country's e-commerce platform. Some market players, such as Visa, Mastercard, Samsung Pay, American Express, and Naver Corporation, are increasing their market presence by moving across the untapped market space.
In June 2022, Samsung Pay introduced the Samsung Wallet by combining Samsung Pay and Samsung Pass. This wallet could securely save passwords and monitor digital assets like cryptocurrencies. Moreover, the Samsung Wallet included features to store driving licenses and student IDs.
In March 2022, Mastercard, DBS Bank, and Pine Labs partnered to launch Mastercard Installation Payments with Pine Labs. This new program allows DBS/POSB credit cardholders to pay interest-free installments with merchants by simply presenting the DBS / POSB and using a later pay identifier card at checkout.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Stakeholder Analysis
- 4.3 Industry Attractiveness- Porter's Five Forces Analysis'
- 4.3.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.3.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.3.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.3.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.3.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.4 Evolution of the payments landscape in the region
- 4.5 Assessment of Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
- 4.6 Analysis of Growing Payment Fraud in Asia-Pacific and its Impact on the Payments Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 High Proliferation of E-commerce and Rising Adoption of M-commerce
- 5.1.2 Enablement Programs by Key Retailers and Government Encouraging Digitization of the Market
- 5.1.3 Growing Adoption of Buy Now Pay Later in Asia-Pacific Countries
- 5.2 Market Challenges
- 5.2.1 Lack of a Standard Legislative Policy Remains, Especially in the Case of Cross-border Transactions
- 5.3 Market Opportunities
- 5.3.1 New Entrants to Drive Innovation Leading to Higher Adoption
- 5.4 Key Regulations and Standards in the Digital Payments Industry
- 5.5 Analysis of Major Case Studies and Use-cases
- 5.6 Analysis of Key Demographic Trends and Patterns Related to Payments Industry in the Asia Pacific (Coverage to include Population, Internet Penetration, Banking Penetration/Unbanking Population, Age & Income etc.)
- 5.7 Analysis of the Increasing Emphasis on Customer Satisfaction and Convergence of Global Trends in the Asia Pacific
- 5.8 Analysis of Cash Displacement and Rise of Contactless Payment Modes in the Asia-Pacific
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Mode of Payment
- 6.1.1 Offline (Point of Sale)
- 6.1.1.1 Card Payments (includes debit cards, credit cards, and bank financing prepaid cards)
- 6.1.1.2 Digital Wallets (includes mobile wallets)
- 6.1.1.3 Cash
- 6.1.1.4 Other Modes of Payment
- 6.1.2 Online Sale (E-commerce)
- 6.1.2.1 Card Payments (includes debit cards, credit cards, and bank financing prepaid cards)
- 6.1.2.2 Digital Wallets (includes mobile wallets)
- 6.1.2.3 Other Modes of Payment (Includes cash on delivery, bank transfer, and buy now pay later)
- 6.1.1 Offline (Point of Sale)
- 6.2 By End-user Industry
- 6.2.1 Retail
- 6.2.2 Entertainment
- 6.2.3 Healthcare
- 6.2.4 Hospitality
- 6.2.5 Other End-user Industries
- 6.3 By Country
- 6.3.1 China
- 6.3.2 India
- 6.3.3 South Korea
- 6.3.4 Taiwan
- 6.3.5 Singapore
- 6.3.6 Philippines
- 6.3.7 Malaysia
- 6.3.8 Indonesia
- 6.3.9 Vietnam
- 6.3.10 Australia
- 6.3.11 Japan
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Matercard Inc.
- 7.1.2 Visa Inc
- 7.1.3 American Express Company
- 7.1.4 Samsung (Samsung Pay)
- 7.1.5 Naver Corporation (Naver Pay)
- 7.1.6 PayCo (NHN Corp.)
- 7.1.7 kakaopay Corp.
- 7.1.8 JCB Co., Ltd.
- 7.1.9 Toss Financial Services Private Limited
- 7.1.10 Smile Pay
- 7.1.11 Paypal Holdings Inc.
- 7.1.12 Google Pay (Alphabet Inc.)
- 7.1.13 Ipay88 (m) Sdn. Bhd
- 7.1.14 Samsung Pay (Samsung Electronics Co.ltd)
- 7.1.15 Grab Pay (grab Holdings Limited)
- 7.1.16 Huawei Pay (Huawei Technologies Co. Limited


