
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1910870
日本のコールドチェーン物流:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年)Japan Cold Chain Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 日本のコールドチェーン物流:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年) |
|
出版日: 2026年01月12日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 150 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
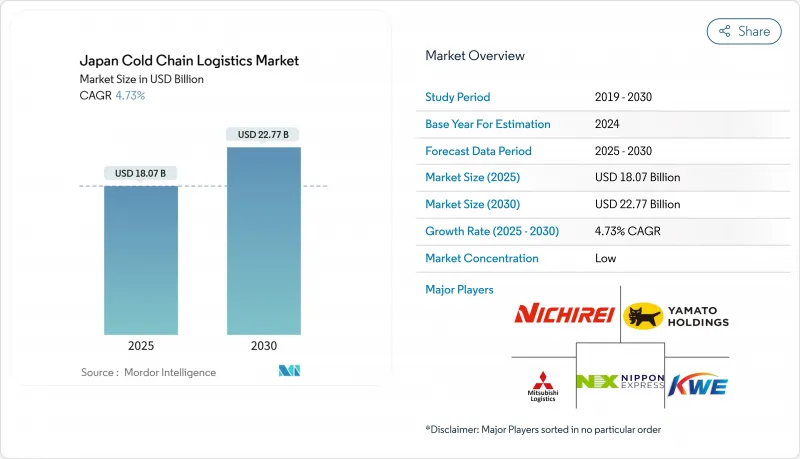
2026年の日本のコールドチェーン物流市場規模は189億2,000万米ドルと推定され、2025年の180億7,000万米ドルから成長し、2031年には237億8,000万米ドルに達すると予測されています。
2026~2031年にかけての年間平均成長率(CAGR)は4.68%となる見込みです。
短期的には、温度管理が必要なEC食品配送、超精密医薬品流通、記録的な水産物輸出が相まって需要の波を形成し、施設の更新、車両の電動化、デジタル可視化プラットフォームの導入を加速させています。小売業者はマイクロフルフィルメントセンターを複数ゾーン対応のハブに転換し、急増する当日配送注文に対応する一方、バイオ医薬品メーカーは高価値在庫を保護するため、2~8℃の冗長な保管容量を確保しています。長期的な成長は、超低温設備の継続的な稼働を確保する政府資金によるワクチン備蓄や、海上冷凍輸送ルートを活性化する地域包括的経済連携(RCEP)の貿易拡大からも恩恵を受けます。これに対応し、主要物流事業者は合併、自動化導入、代替燃料車両の検査運用を推進し、利益率向上と炭素排出リスク低減を図ります。
日本のコールドチェーン物流市場の動向と洞察
温度管理が必要なEC食品配送
オンライン食料品購入の急速な普及により、施設の規模と立地条件が再定義されています。楽天マートは現在、東京と関西で1日7万件の冷蔵・冷凍注文を処理しており、商品搬送ロボットと3ゾーン保管モジュールを備えたマイクロフルフィルメントセンターがこれを支えています。コンビニチェーンも同様のモデルを採用:セブンイレブンの7NOWサービスは2万店舗を通じた全国展開を計画し、零下ロッカーと断熱トートバッグに依存する高密度ラストマイルネットワークを構築中です。小売業者は郊外の高齢者向け移動販売車も導入し、配送車を移動式冷蔵室として活用しています。こうした変化は、小規模な増強が可能な機敏なサードパーティー事業者にとって有利に働きます。一方、既存倉庫所有者は注文量の減少に伴う利益率維持のため、高層倉庫の自動化に投資しています。その結果、消費者の近接性がパレット処理精度と同等に重視されるエコシステムが形成されています。
バイオ医薬品・細胞遺伝子治療パイプライン(2~8℃)
日本のバイオ医薬品産業では、GLP-1サプライチェーン監査で明らかになった480億米ドル規模の温度逸脱損失を抑制するため、精密物流の拡大を進めています。4℃で安定性を維持する新型mRNA製剤は-80℃保管への依存度を大幅に低減し、新規施設では二温度帯戦略が推進されています。つくばメディカルロジスティクスセンター第2期は、15~25℃・2~8℃・~20℃の分離ゾーンと三重冗長電源を備え、PMDAの検証基準を満たすための資本集約性を示しています。小規模な運送業者はこのような複雑な設備の資金調達に苦慮しており、検証済みのデータロガー、24時間365日のモニタリング体制、GDP準拠の標準業務手順書(SOP)を有する企業への契約アウトソーシングが加速しています。茨城県と埼玉県周辺への地理的集中が需給の不均衡を生み、九州や北海道における地域配送センター(DC)プロジェクトを促進しています。
冷蔵トラックの免許保有ドライバー不足
運転手数は、年齢中央値が50歳を超え、時間外労働制限により年間労働時間が制限される中で減少を続けています。冷蔵システムを扱うには高度資格が求められるため、常温輸送業者よりもコールドチェーン事業者の影響が大きくなっています。日本通運は、DC間の自律走行による中間輸送ルートの検査運用にGatik AIへ投資することでこの課題に取り組んでいます。政府支援による東京~大阪間のパイロット事業では、2027年までのプラトーニング(車列走行)の認証取得を目指しています。自律走行が普及するまでの間、事業者は長距離輸送量を鉄道やRORO船にシフトし、貴重なドライバーを複雑なラストマイル配送に集中させています。地方路線では、賃金優遇策で新規免許取得者を確保できなければ、サービス空白が生じ、全国的なカバー率低下につながるリスクがあります。
セグメント分析
2025年時点で、日本のコールドチェーン物流市場における冷蔵倉庫の収益シェアは41.30%を占めており、食品・医薬品産業における在庫バッファ戦略の定着を反映しています。マルチ温度管理施設では、シャトルクレーンや可動式ラックを導入し、敷地面積を拡大せずにSKUの増加に対応しています。LOGI FLAG TECH越谷i.ビルは、民間事業者が太陽光パネルと自然冷媒を導入し、光熱費を抑制しながら-25℃の設定温度を達成する事例を示しています。柔軟な条件を求める中小企業にとって公共倉庫は依然として魅力的ですが、高付加価値医薬品シェアの拡大に伴い、大規模荷主はGDP準拠を保証する専用自社施設へ移行しつつあります。
付加価値サービスは、販売拠点近傍でのキット化・再ラベル貼付・後処理需要の高まりを受け、2031年まで年率4.72%の成長が見込まれます。事業者側は品質保証ラボや簡易組立ゾーンを統合し、パレット保管を収益源へ転換することで、処理量の鈍化を相殺しています。冷蔵輸送は安定した需要を維持しており、鴻池運輸はイオングループの都市部配送向けに航続距離120キロの電気トラックを導入しています。モーダルシフトも拡大:栗林海運が仙台~大阪間の冷凍麺輸送ルートでトラック輸送100%からRORO船へ転換した結果、CO2排出量を74%削減するとともに、港湾間輸送時間を3時間に短縮しました。航空貨物も臨床検査や緊急リコール向けのニッチ市場を維持していますが、JR貨物による冷蔵コンテナの追加導入により、温度管理された鉄道輸送にシェアを譲りつつあります。
その他の特典
- エクセル形態の市場予測(ME)シート
- アナリストサポート(3ヶ月間)
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 温度管理が必要な電子商取引による食料品配送の拡大
- 2~8℃の物流を必要とするバイオ医薬品と細胞・遺伝子治療パイプラインの拡大
- 政府補助によるワクチン備蓄施策
- RCEPによる関税引き下げを背景とした水産物輸出の急増
- 自動化とIoTによるパレット単位の取扱コスト削減
- 水素燃料冷凍トラックの検査導入によるディーゼル依存度低減
- 市場抑制要因
- 高齢化が進む労働力の中で、ライセンシングされた冷凍トラック運転手の不足
- 都市部の不動産価格高騰が新たな冷蔵倉庫建設を制限
- 夏季ピーク時の超低温冷凍庫における電力系統不安定リスク
- フロン類の段階的廃止に関する厳格な規制により、改修設備投資が増加しています
- バリュー/サプライチェーン分析
- 規制情勢
- 技術の展望
- ポーターのファイブフォース
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
- 排出基準とESG目標の影響
- 地政学とパンデミックの影響
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- サービスタイプ別
- 冷蔵保管
- 公共倉庫
- プライベート倉庫
- 冷蔵輸送
- 道路
- 鉄道
- 海路
- 航空便
- 付加価値サービス
- 冷蔵保管
- 温度タイプ別
- 冷蔵(0~5℃)
- 冷凍(-18~0℃)
- 常温
- 超低温冷凍(約20℃以下)
- 用途別
- 果物・野菜
- 肉類・家禽類
- 魚介類
- 乳製品・冷凍デザート
- ベーカリー・菓子類
- レディトゥイートミール
- 医薬品・生物製剤
- ワクチンと臨床検査用材料
- 化学品・特殊材料
- その他
- 地域別(国内)
- 関東
- 関西
- 中部
- 九州・沖縄
- 北海道・東北地方
- その他の中東・アフリカ
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 戦略的動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- Nippon Express
- Yamato Holdings
- Nichirei Logistics Group
- Mitsubishi Logistics
- Kintetsu World Express
- Itochu Logistics
- Sagawa Express
- Konoike Transport Co., Ltd
- K-Line Logistics
- DHL Supply Chain
- Kuehne+Nagel
- CEVA Logistics
- Mitsui-Soko Group
- SENKO Co., Ltd.
- Suzuyo & Co.
- SF Express
- Yusen Logistics(NYK Lineの一部門)
- MOL Logistics
- Matsuoka Co., Ltd.
- YOKOREI Co., Ltd


