
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1693931
アジア太平洋の衛星バス:市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Asia-Pacific Satellite Bus - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| アジア太平洋の衛星バス:市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 169 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
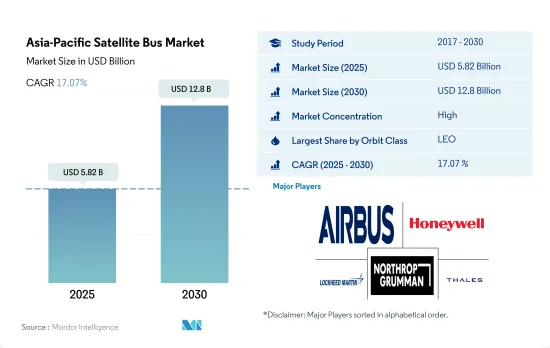
アジア太平洋の衛星バス市場規模は、2025年には58億2,000万米ドルと推定され、2030年には128億米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間中(2025~2030年)のCAGRは17.07%で成長する見込みです。
LEOに打ち上げられる衛星が市場需要を牽引
- アジア太平洋では、幅広い衛星軌道に対応する衛星バスの需要が大幅に増加しています。この需要の原動力となっているのは、衛星を利用した通信、ナビゲーション、リモートセンシングサービスのニーズの高まりです。地球観測衛星は、幅広い用途でますます普及しています。LEO衛星の需要は特に中国で強く、SpacetyやChang Guang Satellite Technologyといった企業がLEOミッション用の衛星バスを提供しています。中国はこの地域で、Gaofenシリーズ衛星の打ち上げを積極的に行っています。2017~2022年の間に、およそ379機の衛星がLEOに打ち上げられました。
- GEO衛星は、テレビやインターネットなどの通信・放送サービスにとって特に重要です。GEO衛星の需要は特にインドで強く、ISROやAntrix Corporation Ltdといった企業が通信ミッション用の先進的衛星バスを開発しています。中国もGEO衛星に多額の投資を行っており、通信衛星のZhongxingシリーズを打ち上げています。2017~2022年にかけて、約66機の衛星がGEOに打ち上げられました。
- GPSやガリレオなどのMEO衛星は、世界ナビゲーションや測位サービスにとってますます重要になっています。日本はMEO航法衛星「みちびき」シリーズの打ち上げでアジア太平洋をリードしてきました。中国も北斗航法システムの打ち上げでMEO衛星に投資しています。2017~2022年にかけて、約24機の衛星がMEOに打ち上げられました。市場全体は、2023~2029年の間に20.72%成長すると予想されます。
アジア太平洋の衛星バス市場動向
同地域では、より優れた燃料と運用効率を使用する傾向が見られる
- 近年、民間/政府、商業、軍事セグメントからの衛星需要の増加が見られます。中国、インド、日本のような国々は、衛星バス製造のセグメントで十分な能力を持っています。しかし、より小型の衛星を製造する方向へのシフトが進むとともに、衛星バスの製造拠点は世界のさまざまな国に拡大すると予想されます。衛星の質量は、衛星の打ち上げに大きな影響を与えます。衛星が重ければ重いほど、宇宙への打ち上げに必要な燃料とエネルギーが増えるからです。
- 2019年、タレスアレニア・スペースはインドネシアのコンソーシアムPSN向けに強力な通信衛星の設計と組み立てをインドネシアから受注しました。打ち上げは2022年末に予定されていました。この衛星は、完全電動プラットフォーム「スペースバス・ネオ」をベースとします。衛星が重くなると、宇宙に打ち上げるために大きなロケットと多くの燃料が必要になるため、打ち上げコストが上昇し、使用できるロケットタイプも限られます。
- 質量による主要分類タイプは、1,000kgを超える大型衛星です。2017~2022年にかけて、約75機以上の大型衛星が打ち上げられ、アジア太平洋の組織が所有しています。中型衛星は500~1,000kgの質量を持っています。打ち上げられた65以上の衛星がアジア太平洋の組織によって運用されました。同様に、500kg以下の衛星は小型衛星とみなされ、アジア太平洋では約200以上の小型衛星が打ち上げられています。
各宇宙機関の宇宙開発費の増加は、衛星産業にプラスの影響を与えると予想されます。
- 共同でサービスを提供する小型衛星のコンステレーションやネットワークの開発は、新たな動向です。これらのコンステレーションは、多くの場合、数十から数百の小型衛星で構成され、ミッション目標を達成するために相互に通信します。分散型衛星ネットワークは、従来の大型衛星に比べて、カバレッジ、冗長性、柔軟性が向上します。軍事と民生の二重目的での商業衛星プラットフォームの利用拡大が市場を押し上げています。衛星通信は5Gインフラに不可欠な要素になると考えられています。衛星輸送導管は、シームレスな接続性を提供するために、全体的な通信マップに統合されつつあります。その結果、都市部や農村部で衛星サービスを拡大する新たな機会が生まれます。
- アジア太平洋における宇宙関連活動の増加を考慮し、衛星メーカーは急速に台頭する市場の潜在力を利用するため、衛星製造能力を強化しています。アジア太平洋で堅牢な宇宙インフラを持つ著名な国は、中国、インド、日本、韓国です。中国国家宇宙局(CNSA)は、国家民間宇宙インフラと地上施設の強化を含む、2021~2025年の宇宙探査優先事項を発表しました。この計画の一環として、中国政府は衛星インターネット用の1万3,000衛星コンステレーション開発のために中国衛星ネットワークグループを設立しました。
アジア太平洋の衛星バス産業概要
アジア太平洋の衛星バス市場はかなり統合されており、上位5社で71%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は、Airbus SE、Honeywell International Inc.、Lockheed Martin Corporation、Northrop Grumman Corporation、Thalesです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主要調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の小型化
- 衛星質量
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- オーストラリア
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- ニュージーランド
- シンガポール
- 韓国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 用途
- 通信
- 地球観測
- ナビゲーション
- 宇宙観測
- その他
- 衛星質量
- 10~100kg
- 100~500kg
- 500~1,000kg
- 10kg以下
- 1,000kg以上
- 軌道クラス
- GEO
- LEO
- MEO
- エンドユーザー
- 商業
- 軍事・政府
- その他
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Airbus SE
- Ball Corporation
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Indian Space Research Organisation(ISRO)
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Nano Avionics
- NEC
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Thales
第7章 CEOへの主要戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要な洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
目次
Product Code: 50001242
The Asia-Pacific Satellite Bus Market size is estimated at 5.82 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 12.8 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 17.07% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Satellites that are being launched into LEO is driving the market demand
- The Asia-Pacific region has seen a significant increase in the demand for satellite buses to accommodate a wide range of satellite orbits. This demand has been driven by the growing need for satellite-based communication, navigation, and remote sensing services. Earth observation satellites have become increasingly popular for a wide range of applications. The demand for LEO satellites has been particularly strong in China, where companies such as Spacety and Chang Guang Satellite Technology Co. Ltd. offer satellite buses for LEO missions. China has been active in this region with the launch of the Gaofen series satellites. Between 2017 and 2022, approximately 379 satellites were launched into LEO.
- GEO satellites are particularly important for communication and broadcasting services, such as television and the Internet. The demand for GEO satellites has been particularly strong in India, where companies such as ISRO and Antrix Corporation Ltd have been developing advanced satellite buses for communication missions. China has also been investing heavily in GEO satellites, with the launch of the Zhongxing series of communication satellites. Between 2017 and 2022, approximately 66 satellites were launched into GEO.
- MEO satellites, such as GPS and Galileo, have become increasingly important for global navigation and positioning services. Japan has been a leader in Asia-Pacific, with the launch of the Michibiki series of MEO navigation satellites. China has also been investing in MEO satellites with the launch of the Beidou navigation system. Between 2017 and 2022, approximately 24 satellites were launched into MEO. The overall market is expected to grow by 20.72% during 2023-2029.
Asia-Pacific Satellite Bus Market Trends
The trend of using better fuel and operational efficiency has been witnessed in the region
- Increased demand for satellites from the civil/government, commercial, and military segments has been witnessed in recent years. Countries like China, India, and Japan have adequate capabilities in the area of satellite bus manufacturing. However, along with the growing shift toward manufacturing smaller satellites, the manufacturing base of satellite buses is expected to expand to various countries across the world. The mass of a satellite has a significant impact on the launch of the satellite. This is because the heavier the satellite, the more fuel and energy are required to launch it into space.
- In 2019, Thales Alenia Space was selected by Indonesia to design and assemble a powerful telecommunication satellite for the Indonesian consortium PSN. The launch was scheduled for the end of 2022. The satellite will be based on the full electric platform Spacebus Neo. A heavier satellite requires a larger rocket and more fuel to launch it into space, thus increasing the cost of the launch and limiting the types of launch vehicles that can be used.
- The primary classification types according to mass are large satellites that are more than 1,000 kg. During 2017-2022, around 75+ large satellites launched were owned by Asia-Pacific organizations. A medium-sized satellite has a mass between 500 and 1000 kg. More than 65+ satellites launched were operated by Asia-Pacific organizations. Similarly, satellites weighing less than 500 kg are considered small satellites, and around 200+ small satellites were launched in the region.
The increasing space expenditures of different space agencies are expected to positively impact the satellite industry
- The development of constellations or networks of small satellites working together to provide a collective service is an emerging trend. These constellations often consist of dozens or even hundreds of small satellites that communicate with each other to achieve mission goals. Distributed satellite networks provide improved coverage, redundancy, and flexibility compared to traditional large satellites. The growing utilization of commercial satellite platforms for dual (military and civil) purposes has boosted the market. Satellite communications are envisioned to be an essential part of the 5G infrastructure. The satellite transport conduit is being integrated into the overall communication map to provide seamless connectivity. This will result in new opportunities for extending satellite services in urban and rural areas.
- Considering the increase in space-related activities in Asia-Pacific, satellite manufacturers are enhancing their satellite production capabilities to tap into the rapidly emerging market potentials. The prominent countries in Asia-Pacific that pose a robust space infrastructure are China, India, Japan, and South Korea. China National Space Administration (CNSA) announced space exploration priorities for the 2021-2025 period, including enhancing national civil space infrastructure and ground facilities. As a part of this plan, the Chinese government established China Satellite Network Group Co. Ltd for the development of a 13,000-satellite constellation for satellite internet.
Asia-Pacific Satellite Bus Industry Overview
The Asia-Pacific Satellite Bus Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 71%. The major players in this market are Airbus SE, Honeywell International Inc., Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation and Thales (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Miniaturization
- 4.2 Satellite Mass
- 4.3 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.4.1 Australia
- 4.4.2 China
- 4.4.3 India
- 4.4.4 Japan
- 4.4.5 New Zealand
- 4.4.6 Singapore
- 4.4.7 South Korea
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Application
- 5.1.1 Communication
- 5.1.2 Earth Observation
- 5.1.3 Navigation
- 5.1.4 Space Observation
- 5.1.5 Others
- 5.2 Satellite Mass
- 5.2.1 10-100kg
- 5.2.2 100-500kg
- 5.2.3 500-1000kg
- 5.2.4 Below 10 Kg
- 5.2.5 above 1000kg
- 5.3 Orbit Class
- 5.3.1 GEO
- 5.3.2 LEO
- 5.3.3 MEO
- 5.4 End User
- 5.4.1 Commercial
- 5.4.2 Military & Government
- 5.4.3 Other
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 Ball Corporation
- 6.4.3 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.4 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- 6.4.5 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.6 Nano Avionics
- 6.4.7 NEC
- 6.4.8 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.9 Thales
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


