
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1906877
マレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス:市場シェア分析、業界動向、統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年)Malaysia Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| マレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス:市場シェア分析、業界動向、統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年) |
|
出版日: 2026年01月12日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 419 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
マレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場は、2025年の297億米ドルから2026年には312億3,000万米ドルへ成長し、2026年から2031年にかけてCAGR5.14%で推移し、2031年までに401億1,000万米ドルに達すると予測されております。
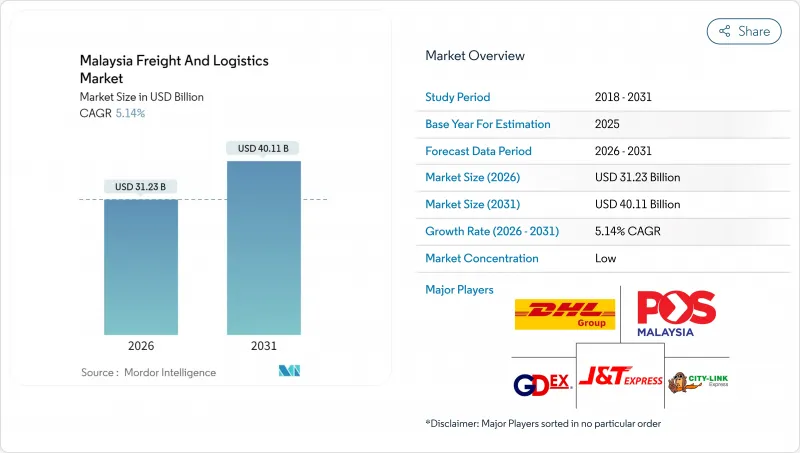
クラン港が世界第10位のコンテナ取扱量を誇る港湾へと成長したこと、鉄道・高速道路プロジェクトへの政府による大規模な資金投入、そして持続的な電子商取引の勢いが相まって、マレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場全体において、サプライチェーンネットワークの再構築、倉庫自動化の優先順位付け、運送会社との提携関係の見直しが進んでいます。2024年の外国直接投資額は3,785億リンギット(823億米ドル)に達し、20万7,000人の雇用を創出するとともに、越境フォワーディング、付加価値型流通、専門製造物流への需要を拡大しています。消費者の即日配送への嗜好はラストマイルネットワークの高度化を加速させており、一方、対象を絞ったディーゼル補助金や簡素化された通関窓口といった規制上の動きは、コスト圧力と国境での摩擦を緩和しています。世界のキャリア各社は、航空貨物輸送量、海上貨物割当、温度管理輸送能力を確保するため現地との連携を強化しており、マレーシアのASEANおよび広域アジア太平洋貿易ネットワークにおけるハブとしての役割を確固たるものにしております。
マレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場の動向と展望
爆発的なB2C電子商取引の増加がラストマイル革新を牽引
即日配送は標準的な期待となり、主要プラットフォームでは注文の95%が24時間以内に発送されています。インターネットユーザーの64.8%が無料配送を好む傾向から、マレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場では自動仕分けシステム、マイクロフルフィルメントセンター、データ駆動型ルート計画の導入が迫られています。MR DIYなどの小売業者はロボットシステム導入後、効率性を200%向上させ、自動化が競争優位性の基盤となっていることを実証しました。UPSとNinja Vanの提携のようなパートナーシップは、世界のエクスプレス製品を52の小売店舗に拡大し、輸出業者に貨物スペースへのより広範なアクセスとデジタル追跡を提供。これは地域貿易における中小企業の参加増加と合致しています。これらの累積的な影響は、輸送能力の回復力とサービスの多様性を高め、マレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場の短期的な成長軌道を支えています。
FDI主導の製造業生産急増が産業物流を変革
2024年に承認された過去最高の3,785億リンギット(823億米ドル)の投資は、半導体製造工場、先進自動車部品、再生可能エネルギー装置へ資金を誘導しています。半導体投資は、静電気放電(ESD)対応包装、安全なロボット技術、保税倉庫通関レーンへの需要を喚起しています。MKS Instrumentsなどの精密機器メーカーは、「スーパーセンター」を建設中です。これには、原材料の入庫フローの同期化と高頻度の出荷が求められます。ジョホール・シンガポール特別経済区内の越境税制優遇措置により、100件のプロジェクトと2万人の熟練職が創出され、マレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場における新たな回廊の基盤が築かれる見込みです。ESG基準の強化に伴い、投資家は再生可能エネルギーや鉄道支線に近い複合輸送拠点も優先し、長期的な貨物多様化を推進しています。
インフラ投資にもかかわらず港湾混雑が容量を制約
クラン港における船舶平均待機時間1.3~1.46日と、90%を超えるヤード稼働率は、スケジュール信頼性を損なう要因です。2025年2月に導入されたマレーシア海事シングルウィンドウにより、書類処理サイクルは5日から数時間へ短縮されましたが、物理的な埠頭拡張は短期的なTEU成長に追いつかない見込みです。ウェストポート・ホールディングスの数十年にわたる拡張計画は、総処理能力を現在の限界を大きく超える水準に押し上げることを目指していますが、紅海経由の迂回航路の増加により、すでに到着便の集中やヤードの容量超過が深刻化しています。世界の海運会社がコンテナを再配分する中、マレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場は短期的な用船料の急騰や在庫の不均衡に直面しており、処理量増加による利益率の向上を損なう懸念があります。
セグメント分析
2025年時点で製造業はマレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場の38.98%を占め、ペナン州の4,310億リンギット(937億米ドル)規模の輸出エンジンとセランゴール州の電子機器クラスターがこれを支えています。多国籍企業は保税トラック輸送ルート、ESD対応倉庫、貨物護送サービスを求めており、これがサービス差別化を促進しています。電気自動車部品や再生可能エネルギー設備の成長は、特大コンテナの取り扱いと特殊なリギングを必要とするマレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場規模をさらに拡大します。卸売・小売業は絶対額では小規模ながら、可処分所得の増加とデジタル決済の普及に伴い、2026年から2031年にかけてCAGR5.46%で拡大する見込みです。99スピードマートなどのスーパーマーケットチェーンは店舗数を倍増させる計画であり、消費の集中地域に近接した多温度帯クロスドックやマイクロフルフィルメントセンターが求められています。
農業・漁業・林業分野では、中東需要市場への進出に認証済みハラール対応のコールドチェーンが不可欠であり、アルゴリズム駆動型の温度追跡プラットフォームの商業的価値が高まっています。建設物流はRTSリンクやペナン空港拡張といった大型プロジェクトに直結し、重量物用クレーン、夜間護送車列、ジャストインタイム方式の資材供給調整が求められます。石油・ガス・鉱業は依然として景気循環の影響を受けますが、ISOタンクコンテナ、船体洗浄サービス、パイプライン保守部品に対する安定した需要が持続しており、商品価格の変動の中でもマレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス業界の基盤を支えています。
2025年、貨物輸送はマレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場収益の55.62%を占め、根強い製造業輸出と地域流通の流れを反映しています。宅配便・エクスプレス・小包ソリューションに関連するマレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場規模は、e小売業者が当日配送をマルチモーダル輸送業者に委託する動きを受け、2026年から2031年にかけてCAGR5.86%でより急速に拡大しています。UPSとNinja Vanがクランバレー地域に拡大した拠点など、自動化ハブでは住所確認ソフトウェアとIoTタグを活用し、配達失敗率を削減しています。オンライン注文がトラック積載量を埋める中、事業者はデポに傾斜トレイ仕分け機を導入し、クアラルンプール近郊の渋滞地点を回避するため電気バンを配備しています。また、16の貿易協定により越境通関手数料が抑制され、表示基準が統一されたことで、中小企業の海外バイヤーへのアクセスが容易になりました。小包密度の継続的な上昇は航空機貨物室提供業者との交渉力を強化しますが、生産性向上が実現するより早くディーゼル補助金が段階的に削減される場合、利益率の圧縮リスクが残ります。
CEP(小口配送)分野以外では、倉庫・フォワーディング事業者が従量課金制を導入し、零細企業がパレット単位ではなくコンテナ単位でスペースを借りられるようにしています。温度管理輸送はマレーシアのハラール認証基準に適合し、水産物・菓子・バイオ医薬品などの付加価値型集荷向けにプレミアム輸送ルートを開拓しています。マレーシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場における貨物輸送のシェアは、小口配送や契約物流活動が過大な資本を吸収するため、2031年までにわずかに減少すると予想されます。しかしながら、大型プロジェクト貨物(ソーラーパネル、タービン、製油所用タンクなど)向けの特殊トラック輸送は、引き続きベースライン輸送量を支えます。技術準備状況、規制の明確性、労働力の確保が、既存事業者か新規参入者かのいずれが増分価値を獲得するかを大きく左右するでしょう。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- アナリストによる3ヶ月間のサポート
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 人口統計
- 経済活動別GDP分布
- 経済活動別GDP成長率
- インフレ
- 経済的パフォーマンスとプロファイル
- 電子商取引業界の動向
- 製造業の動向
- 輸送・貯蔵セクターのGDP
- 輸出動向
- 輸入動向
- 燃料価格
- トラック輸送の運営コスト
- トラック輸送車両規模(種類別)
- 主要トラック供給業者
- 物流パフォーマンス
- 輸送モード別シェア
- 海上輸送船隊の積載能力
- 定期船輸送の接続性
- 寄港地とパフォーマンス
- 貨物運賃の動向
- 貨物輸送量の動向
- インフラストラクチャー
- 規制枠組み(道路・鉄道)
- 規制枠組み(海上・航空)
- バリューチェーン及び流通チャネル分析
- 市場促進要因
- 爆発的なB2C電子商取引の取引量
- 外国直接投資主導の製造業生産高の急増
- 政府主導の大型プロジェクト(ECRL、パン・ボルネオ高速道路)
- RCEPによる国境を越えた貿易の流れ
- 認証済みハラール物流への需要増加
- ワクチンおよび生物学的製剤向けコールドチェーンの整備
- 市場抑制要因
- 港湾およびラストマイルの混雑
- 慢性的なトラック運転手不足
- 国内カボタージュ政策による沿岸輸送の制限
- ユーロ6相当の排出規制強化、設備投資の抑制
- 市場における技術革新
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- エンドユーザー産業
- 農業、漁業、林業
- 建設業
- 製造業
- 石油・ガス、鉱業・採石業
- 卸売・小売業
- その他
- ロジスティクス機能
- 宅配便・エクスプレス・小包(CEP)
- 目的地別
- 国内
- 国際
- 目的地別
- 貨物フォワーディング
- 輸送手段別
- 航空
- 海上・内陸水路
- その他
- 輸送手段別
- 貨物輸送
- 輸送手段別
- 航空
- パイプライン
- 鉄道
- 道路
- 海上・内陸水路
- 輸送手段別
- 倉庫・保管
- 温度管理別
- 非温度管理
- 温度管理
- 温度管理別
- その他のサービス
- 宅配便・エクスプレス・小包(CEP)
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 主要な戦略的動き
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- City-Link Express
- CJ Logistics Corporation
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S(Including DB Schenker)
- FedEx
- FM Global Logistics Holdings Bhd
- GDEX Group
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- Hextar Technologies Solutions Bhd
- J&T Express
- Keretapi Tanah Melayu Bhd
- Kuehne+Nagel
- MMC Corporation Bhd
- NYK(Nippon Yusen Kaisha)Line
- POS Malaysia Bhd
- SF Express(KEX-SF)
- SkyNet Worldwide Express, Inc.
- Taipanco Sdn Bhd
- Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings Bhd
- Transocean Holdings Bhd
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
- Xin Hwa Holdings Bhd


