
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1907302
インドネシアの貨物およびロジスティクス:市場シェア分析、業界動向、統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年)Indonesia Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| インドネシアの貨物およびロジスティクス:市場シェア分析、業界動向、統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年) |
|
出版日: 2026年01月12日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 472 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
インドネシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場規模は、2026年に1,393億5,000万米ドルと推定されております。
これは2025年の1,312億米ドルから成長した数値であり、2031年には1,883億8,000万米ドルに達すると予測されております。2026年から2031年にかけての年間平均成長率(CAGR)は6.21%と予測されております。
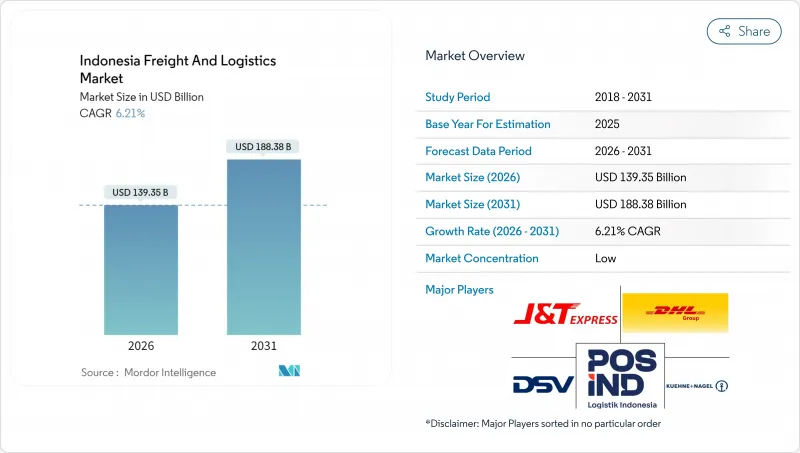
同国の電子商取引の急成長、2,700キロメートルに及ぶ新たな有料道路の整備、輸出向け製造業生産高の増加が相まって成長を加速させております。一方、インフラメガプロジェクトにより、ジャワ島以外の地域への地理的カバー範囲が拡大しております。国家物流エコシステム(NLE)などのデジタルプラットフォームへの投資は、通関時間の短縮と管理コストの削減を実現し、インドネシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場に構造的な効率性向上をもたらしております。同時に、コールドチェーン施設の拡充、航空貨物輸送能力の増強、マルチモーダルネットワークのアップグレードにより、事業者はサービス差別化を図る道が開かれます。競合環境は、データ駆動型のルート最適化とリアルタイム可視化ツールを用いて、深刻な都市部の渋滞、変動する燃料価格、重複する規制を乗り切れる技術力のあるプロバイダーに有利に働きます。
インドネシア貨物およびロジスティクス市場の動向と洞察
Eコマースの急成長と小口貨物量の急増
急速なデジタル化により、オンライン小売取引は2025年までに年率15%で増加し、前例のない小口小包の流通量をラストマイルネットワークに流入させています。J&TエクスプレスやJNEなどのCEP(小口配送)専門企業は、自動化されたハブや集荷拠点のエコシステムを拡大し、この流れを効率的に処理しています。ジャワ島の密集した都市圏が発注の主流を占めていますが、デジタル決済の普及に伴い、地方都市でも二桁の流通量増加が見られます。ジャカルタの都市部では道路の混雑により平均配送速度が時速10~15kmに制限され、1個あたりのコストが増大。これにより事業者各社はマイクロフルフィルメント、二輪車配送網、AIを活用したルート計画への移行を推進しています。詳細な住所データベースと動的ルート設定を保有する事業者はコスト面で優位性を発揮する一方、従来の貨物輸送業者は消費者向け配送に対応するため、大量貨物処理プロセスの改造に奔走しています。
インフラメガプロジェクト(有料道路・港湾・空港)
国家戦略プロジェクト計画により4,000億米ドルが道路・港湾・空港に投入され、ジャワ島の産業拠点間の輸送時間が最大40%短縮されました。2700kmを超える新規有料道路が内陸工場と主要港湾を接続し、INAPORTNET港湾デジタル化により通関滞留時間が短縮されています。マカッサル港が主要ハブに昇格したことで新たな東部輸出回廊が形成され、ジャワ島の混雑緩和に寄与しています。接続性の向上により、貨物輸送業者はマルチモーダル輸送ルートを再設計でき、在庫バッファーを削減し、水産地域へのコールドチェーン拡大を促進します。支援となる内陸鉄道支線や工業団地の稼働に伴い、効果は徐々に蓄積されますが、早期導入企業は既に、改善された幹線輸送の信頼性に基づき倉庫の配置を再最適化しています。
深刻な都市部渋滞とラストマイルのボトルネック
ジャカルタのピーク時平均速度は時速10~15キロに留まり、配送コストの50%に達するラストマイル料金を押し上げています。CEP事業者は夜間配送、マイクロデポ、バイク便を導入して渋滞回避を図っていますが、これらの対策は労務管理の複雑化を招いています。温度管理が必要な商品は、渋滞で停車中に腐敗するリスクがあり、荷主は保証時間付きプレミアムサービスを選択せざるを得ません。奇数・偶数ナンバープレート規制などの政府対策は、スケジュール調整が困難な商用トラックにとってわずかな緩和策に過ぎません。Eコマース小包量が増加する中、都市物流ゾーニングや路上外荷役規制が進化しない限り、渋滞コストはさらに深刻化すると予想されます。
セグメント分析
2025年、製造業は自動車、電子機器、繊維産業を牽引役として、インドネシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場需要の28.45%を占めました。輸出志向の高さから、保税物流センターや港湾・空港へのジャストインタイム配送が求められています。一方、卸売・小売業は中産階級の消費拡大に伴い、2026年から2031年にかけてCAGR6.64%で拡大し、物流企業は複数拠点型流通ネットワークの構築を迫られています。農林水産業は商品輸出に連動した安定した取扱量を維持する一方、建設物流はインフラ投資拡大に伴い増加傾向にあります。
卸売・小売業の顧客は全国配送において即日または翌日配達を要求する傾向が強まっており、地域配送センターと堅牢な幹線輸送網の必要性が高まっています。製造業の荷主は循環型経済目標を採用し、返品やリサイクルのためのリバースロジスティクスフローを追加しているため、インドネシアの貨物およびロジスティクス業界におけるサービスポートフォリオはさらに多様化しています。
2025年時点で、貨物輸送はインドネシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場に58.95%のシェアを占めました。CEP(宅配便)は規模こそ小さいもの、B2C出荷の増加を背景に2026年から2031年にかけてCAGR7.12%を記録し、成長速度において他の機能を追い越しています。フォワーディング業務は、特に工業団地と輸出港を結ぶ海陸複合輸送チェーンにおいて、マルチモーダル調整に不可欠な役割を果たし続けています。倉庫保管サービスは、オムニチャネル対応を支える在庫管理サービスモデルの普及に伴い、収益を着実に拡大しています。通関業務やサプライチェーンコンサルティングなどのその他サービスは、規制の複雑化と貿易のデジタル化から恩恵を受けています。
CEP(宅配便)の急成長は、年間15%のEC取引増加に起因し、高密度配送ネットワークと高い仕分け処理能力が求められています。自動化ハブは1個あたりの配送コストを削減し、当日配達を可能にします。貨物輸送事業者は宅配ロッカーへの投資や配車サービスとの連携により競争力を維持。一方、倉庫事業者は小包流通向けにクロスドックエリアを改修し、インドネシアの貨物およびロジスティクス市場における機能統合が進んでいます。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- アナリストによる3ヶ月間のサポート
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 人口統計
- 経済活動別GDP分布
- 経済活動別GDP成長率
- インフレ
- 経済パフォーマンスと概要
- 電子商取引業界の動向
- 製造業の動向
- 輸送・保管セクターのGDP
- 輸出動向
- 輸入動向
- 燃料価格
- トラック輸送の運営コスト
- トラック輸送車両規模(種類別)
- 主要トラック供給業者
- 物流パフォーマンス
- 輸送モード別シェア
- 海上輸送船隊の積載能力
- 定期船輸送の接続性
- 寄港地とパフォーマンス
- 貨物運賃の動向
- 貨物輸送量の動向
- インフラ
- 規制の枠組み(道路・鉄道)
- 規制の枠組み(海上・航空)
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
- 市場促進要因
- 電子商取引の急成長と小包取扱量の急増
- インフラメガプロジェクト(有料道路、港湾、空港)
- 製造業・輸出の回復(自動車、電子機器、繊維製品)
- 国内消費の増加と中産階級の支出拡大
- 国家物流エコシステム(NLE)デジタルプラットフォームの導入
- 養殖業および水産物輸出によるコールドチェーン需要
- 市場抑制要因
- 深刻な都市部の渋滞とラストマイルのボトルネック
- 規制の断片化とライセンスの重複
- 燃料価格の変動性が高め
- 物流技術人材の不足
- 市場における技術革新
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- エンドユーザー産業
- 農業、漁業、林業
- 建設業
- 製造業
- 石油・ガス、鉱業・採石業
- 卸売・小売業
- その他
- ロジスティクス機能
- 宅配便・エクスプレス・小包(CEP)
- 目的地別
- 国内
- 国際
- 目的地別
- 貨物フォワーディング
- 輸送手段別
- 航空
- 海上・内陸水路
- その他
- 輸送手段別
- 貨物輸送
- 輸送手段別
- 航空
- パイプライン
- 鉄道
- 道路
- 海上・内陸水路
- 輸送手段別
- 倉庫保管
- 温度管理別
- 非温度管理
- 温度管理
- 温度管理別
- その他のサービス
- 宅配便・エクスプレス・小包(CEP)
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 主要な戦略的動きs
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S(Including DB Schenker)
- Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
- FedEx
- J&T Express
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Linfox Pty Ltd.
- LOGWIN
- Ninja Van(Including Ninja Express)
- NYK(Nippon Yusen Kaisha)Line
- Pancaran Group
- PT ABM Investama TBK(including CKB Logistics)
- PT Bina Sinar Amity(BSA Logistics Indonesia)
- PT Cardig International
- PT Citrabati Logistik International
- PT Dunia Express Transindo
- PT Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir(JNE Express)
- PT Kamadjaja Logistics
- PT Lautan Luas TBK
- PT Pandu Siwi Group(Pandu Logistics)
- PT Perusahaan Perdagangan Indonesia(including BGR Indonesia)
- PT Pos Indonesia(Persero)
- PT Repex Wahana(RPX)
- PT Samudera Indonesia Tangguh
- PT Satria Antaran Prima TBK(SAPX Express)
- PT Siba Surya
- PT Soechi Lines Tbk
- Puninar Logistics
- SF Express(KEX-SF)
- Sinotrans, Ltd.
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)


