
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1910869
日本のサードパーティ・ロジスティクス(3PL)市場:シェア分析、業界動向、統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年)Japan Third-Party Logistics (3PL) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 日本のサードパーティ・ロジスティクス(3PL)市場:シェア分析、業界動向、統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年) |
|
出版日: 2026年01月12日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 150 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
2026年の日本のサードパーティ・ロジスティクス市場規模は384億4,000万米ドルと推定され、2025年の373億8,000万米ドルから成長し、2031年には441億9,000万米ドルに達すると予測されています。
2026年から2031年にかけての年間平均成長率(CAGR)は2.83%となる見込みです。
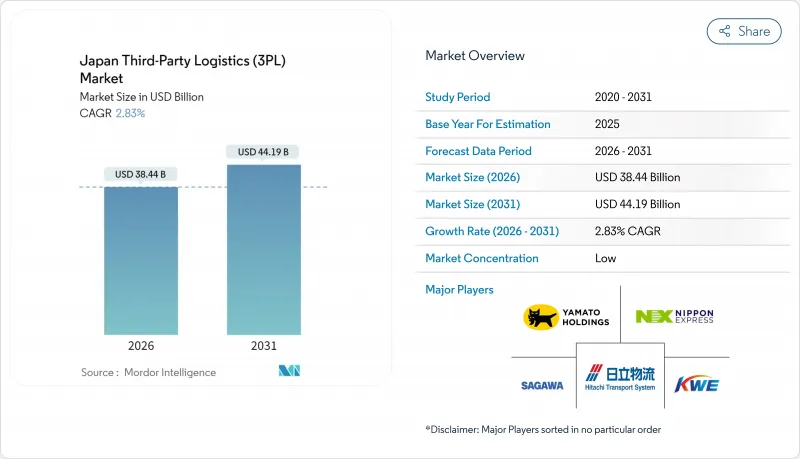
新たな運転手の時間外労働制限、デジタル化推進のための包括的補助金、高まる脱炭素化目標により、全ての物流事業者はネットワーク設計の再考を迫られています。資産集約型事業者は自動化予算と賃料上昇のバランスを取る一方、デジタルプラットフォームを活用する資産軽量型の新規参入企業は自社車両を所有せずに成長を遂げています。小売業者、医療企業、半導体メーカーは全国規模のカバー範囲とリアルタイム可視性を求めており、リードタイムとカーボンフットプリントを削減する統合ソリューションの需要が高まっています。その結果、日本の3PL市場は、深刻な労働力・土地制約下でも貨物の流れを維持するデータ駆動型オーケストレーションへと、単機能輸送から静かに移行しつつあります。
日本のサードパーティ・ロジスティクス(3PL)市場の動向と洞察
即日・翌日配送を前提としたEC文化が小売業者に全国規模の3PLネットワーク構築を迫る
消費者の迅速な配送需要の高まりを受け、小売業者は日本3PL市場に分散型フルフィルメント拠点を展開する3PLパートナーとの連携を迫られています。ヤマト運輸がAmazonの当日配送サービスから撤退した後、丸和運輸などの新興企業が新規事業獲得に向け1万台の新型軽トラック導入を表明し、機敏なプレイヤーにとっての機会を浮き彫りにしました。小売業者は単一拠点在庫モデルから、最終配送距離を短縮しドライバーの労働時間制限下でもサービス水準を維持する複数DC戦略へ移行中です。人口密集都市圏では、3PL事業者が需要急増に対応するためマイクロフルフィルメントセンターを展開し、リアルタイム配車ソフトウェアを統合しています。こうした動きを受け、全国ネットワーク網の整備は、大規模なEC契約を獲得するための必須条件となり、日本3PL市場全体において迅速な対応能力の戦略的重要性が確固たるものとなりました。
全国的なサプライチェーンのデジタル化義務化(グリーン物流法およびオープンAPIイニシアチブ)
日本のグリーン物流法とオープンAPI指令は、国内3PL市場全体でのデジタル導入を加速させています。国土交通省が監督する積荷マッチングプラットフォーム、共通データ規格、カーボン追跡ツールに対し、総額880億円の公的資金が投入されています。共同配送のパイロット事業では、CO2削減量を測定し、取引可能なクレジットに変換できるため、早期導入企業には輸送能力とデータを共有する具体的なインセンティブが生まれています。主要プロバイダーはAPIファーストの輸送管理システムを展開し、中堅事業者はコンソーシアムプラットフォームに参加してデジタル貨物仲介サービスにアクセスしています。中期的には、標準化されたデータフローにより平均トラック積載率が向上し、新たな労働規則による輸送能力の減少を部分的に相殺することが期待されています。
慢性的なトラック運転手不足
新たな時間外労働制限により週当たりの運転時間が削減される一方、配送件数は増加を続けております。5社中4社の運送会社が賃上げ後も運転手の空きポストを抱えております。倉庫内ではロボットがパレットを搬送するため、不足する運転手は道路走行に集中可能となり、スポーツを基盤とした採用活動で若年層の獲得を目指す企業も現れております。創意工夫による対策にもかかわらず、人材不足は成長を阻む最も差し迫った課題であり続けております。
セグメント分析
保管・仕分けスペースは現在、最も収益成長が速い分野であり、CAGR4.35%で拡大しています。需要はオムニチャネル小売業者やワクチン流通業者から発生しており、温度管理区画、自動シャトル、品目単位のスキャン機能を備えた施設が求められています。国内輸送管理は依然として最大の取扱量を占めますが、運転時間規制と燃料価格の変動が成長を抑制しています。輸送とスマート倉庫管理を融合したプロバイダーは、より高い顧客シェアと長期契約を獲得しています。
商品搬送ロボット、メザニン式ピッキングモジュール、音声指示型受入ステーションへの投資が活発化しております。日本通運は自律走行カートを導入したユニバーサルデザイン倉庫を開設し、従業員が付加価値業務に集中できる環境を整えました。こうした設備投資により、事業者は人手不足を克服し、平方メートルあたりの稼働率向上を通じて地域賃料の抑制を実現しております。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- アナリストサポート(3ヶ月間)
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 当日・翌日配送を特徴とするEコマース文化が小売業者を全国規模の3PLネットワーク構築へと導いております
- 国内サプライチェーンのデジタル化義務(グリーン物流法およびオープンAPIイニシアチブ)
- カーボンニュートラルへの取り組みと排出量取引パイロット事業が、グリーン3PLへのモーダルシフトを推進
- サプライチェーンのレジリエンス補助金と中国プラスワン戦略によるリショアリングが国内工場物流需要を促進
- 高齢化する消費者層温度管理が可能な3PLネットワークを必要とする宅配食料品・医療品チャネルの拡大
- 5GおよびIoTの導入により、リアルタイム可視性への期待が高まり、技術集約型のサードパーティロジスティクス(3PL)への投資が促進されています。
- 市場抑制要因
- 慢性的なトラック運転手不足と労働力の高齢化
- 倉庫用地の不足と賃料上昇
- 過当競争状態にあるラストマイル小口配送市場は、利益率を圧迫し、イノベーション投資を阻害しております。
- 中堅製造業における社内物流への文化的嗜好
- バリュー/サプライチェーン分析
- 主要な政府規制と施策
- 技術動向と自動化
- 倉庫市場の一般的な動向
- CEP、ラストマイル配送、コールドチェーン分野からの需要
- 電子商取引ビジネスに関する洞察
- 地政学的イベントが市場に与える影響
- ポーターのファイブフォース
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手・消費者の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- サービス別
- 国内輸送管理
- 道路
- 鉄道
- 航空
- 内陸水路
- 国際輸送管理
- 航空
- 海上輸送
- その他
- 付加価値型倉庫・流通サービス(VAWD)
- 国内輸送管理
- エンドユーザー産業別
- 自動車
- エネルギー・公益事業
- 製造業
- ライフサイエンス・ヘルスケア
- テクノロジー・エレクトロニクス
- 小売・Eコマース
- 消費財・日用品
- 食品・飲料
- その他
- 物流モデル別
- 資産軽量型(管理ベース)
- 資産集約型(自社車両・倉庫所有)
- ハイブリッド
- 地域別(日本)
- 関東
- 関西
- 中部
- 九州・沖縄
- 中国
- 四国
- 北海道
- 東北
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 戦略的動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- Nippon Express Co., Ltd.
- Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Kintetsu World Express, Inc.
- SG Holdings Co., Ltd.
- LOGISTEED, Ltd.
- NYK Line(Including Yusen Logistics)
- Mitsui-Soko Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Sankyu Inc.
- Nichirei Corporation
- Marubeni Logistics Corporation
- Kokusai Express Co., Ltd.
- Toyotsu Logistics Service Co., Ltd.
- Senko Group Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Japan Post Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Sumitomo Corporation
- Meitetsu Group
- DHL Group
- SBS Holdings, Inc.
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Samsung SDS


