
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1851073
貨物フォワーディング:市場シェア分析、産業動向、統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Freight Forwarding - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 貨物フォワーディング:市場シェア分析、産業動向、統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年06月10日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 150 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
貨物輸送市場の2025年の市場規模は5,722億5,000万米ドルで、2030年には7,408億5,000万米ドルに達し、CAGR 5.3%で拡大すると予測されています。
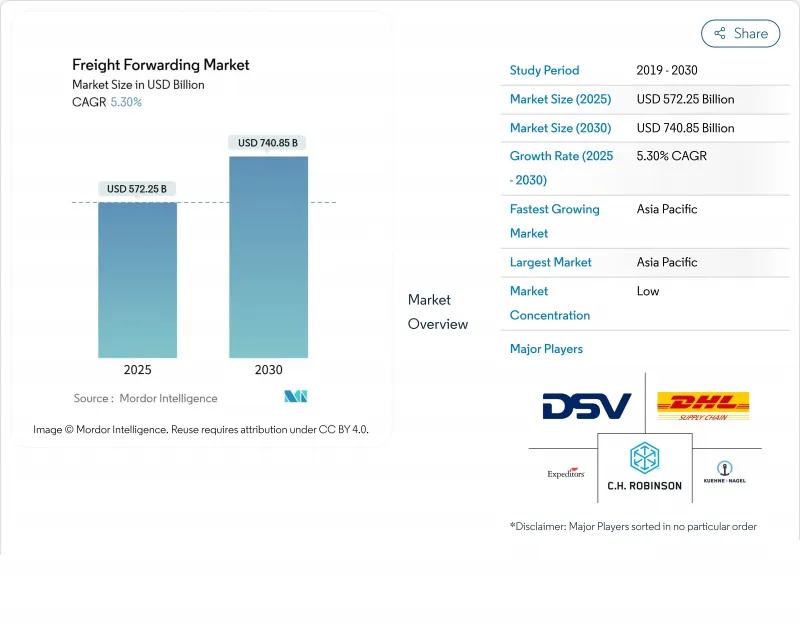
地政学的緊張や度重なるサプライチェーン・ショックにもかかわらず上昇基調が続くのは、デジタル・プラットフォーム、弾力性のある複合一貫輸送ネットワーク、持続的なeコマースの流れが数量を維持しているからです。小包サイズのクロスボーダー貨物に対する需要の高まり、定温輸送能力への着実な投資、ニア・ショアリングに向けた構造的な軸足はすべて、あらゆる主要貿易レーンの貨物量を引き上げています。二次的な効果としては、テクノロジー導入の加速化、リアルタイムの視認性を軸とした新たなプレミアム・サービス層、規模の優位性を追求するフォワーダーによる統合への傾斜などが挙げられます。2025年にDSVがDBシェンカーを159億米ドルで買収したのを筆頭とするM&A活動は、貨物輸送市場における競争上のポジショニングが、いかに規模とデータ密度に支えられているかを物語っています。
世界の貨物輸送市場の動向と洞察
急増する越境eコマース小包量
アジアにおける記録的なオンライン消費は、北米の消費者に向けた小口小包の流れを促進し続けています。フレイト・フォワーダーは、既存の施設を小包の仕分けハブに再利用し、通関の事前手続きを統合し、購入時の摩擦をなくすために予測的な関税計算ツールを重ねています。現在では、単純なコストよりもサービス・スピードがルーティングの決定を左右するようになり、輸送会社は太平洋横断エクスプレス・レーンの週1便の運航を拡大しています。同位体の小包レベルの可視性やブランド返品などの付加価値機能は、既存事業者が純粋な小包インテグレーターに対抗してシェアを守るのに役立っています。
ニアショアリング主導の製造シフト
メキシコ、ポーランド、トルコの近接製造業は、貨物量を長距離海上輸送からより短距離の複合一貫輸送にシフトさせています。米国ーメキシコ間の国境を越えたトラック輸送需要は2024年に2桁の伸びを示し、合理化された国境通関ソフトウェアと保税内陸港への投資を刺激します。通関に精通したフォワーダーは複雑な関税制度を収益化し、鉄道とトラックの統合ソリューションは海上輸送の代替手段と比較してドア・ツー・ドアの所要時間を35%短縮します。
港湾の混雑とコンテナの不均衡
バース待ちの行列の長期化、機器不足、そして予測不可能な運航スケジュールにより、輸送時間のばらつきが増大している。主要なアジアの港における平均滞留時間は2023年と比較して2倍以上に増加しており、機器の再配置には現在、複数の主要航路で18日間の追加日数がかかっています。フォワーダーは何週間も前からコンテナ・スロットを事前予約し、優先ゲート・ウィンドウを交渉し、渋滞するハブを迂回するために補助フィーダーをチャーターしています。アジアー欧州航路のスポット運賃は2025年初頭に255%も急騰し、荷送人は調達先を見直すか、コスト高騰を吸収する必要に迫られています。
セグメント分析
海上貨物は、大洋を横断する大口貨物のTEU当たりの輸送コストが最も低いため、2024年の貨物輸送市場シェアは62%を維持した。同セグメントは、スロット・コストを低く抑える大型船の配備、自動化されたターミナル、拡大したメインライン・フィーダー・ネットワークの恩恵を受けています。その規模の大きさにもかかわらず、海上輸送サービスは隘路に直面し、スケジュールの完全性が損なわれると、荷送人は鉄道や航空便を追加する動機付けとなります。そのため、フォワーダーが海上、鉄道、道路をバンドルして、アジアー欧州航路のリードタイムを2~4日短縮する複合輸送ソリューションのCAGRは6.4%を記録しました。ユーラシア大陸の回廊における鉄道輸送量は2024年に10.7%増加し、引き続きルーティング・リスクの分散を図っています。航空フォワーディングは、タイムクリティカルな製薬、エレクトロニクス、ファッションのドロップを依然として支配しており、そのキャパシティは、腹いっぱいのネットワークが再建されるにつれて回復しています。陸上フォワーディングは、地域配送とラストワンマイルのフルフィルメントを確保するが、燃料サーチャージとドライバー不足がライン輸送料金を高騰させるため、依然としてコストに敏感です。モードを問わないルーティングを編成するフォワーダーは、すべての貨物輸送市場地域で、より高いウォレットシェアとより深い顧客囲い込みを享受しています。
マルチモーダルサービスの貨物輸送市場規模は、2030年までにCAGR 6.4%で拡大すると予測されています。統合されたコントロール・タワー・プラットフォーム、統一された見積もりエンジン、ブロック・トレイン・チャーターにより、オペレーションの俊敏性とマージン維持が強化されます。純粋な海上輸送や航空輸送のスペシャリストは現在、インターモーダル鉄道事業者と提携し、顧客が事業者を変更するのを防いでいます。通関の引き渡しをデジタル化し、コンテナ設備を自動割り当てし、単一のダッシュボードで到着通知をリリースする技術が中心的な役割を果たしています。市場リーダーの報告によると、エンド・ツー・エンドの複合一貫輸送契約は、顧客維持率を22%向上させ、貨物輸送市場におけるオーケストレーションされたサービスバンドルの粘着性を浮き彫りにしています。
大企業は2024年の貨物輸送市場規模の70%を占め、5万TEU以上の年間入札量を活用して、指数連動型の海上・航空契約を締結しています。彼らの調達部門は、統一されたグローバルKPIと炭素会計を要求しており、フォワーダーはオペレーション・データの上に分析レイヤーを構築するよう促しています。小規模な輸出業者はこれまで交渉力に欠けていたが、現在ではデジタル・マーケットプレースが中小企業の需要を集約し、日々のスポット買付で輸送会社にオークションを行い、運賃支出を12%削減しています。このダイナミックな動きにより、貨物フォワーディング市場の中小企業のCAGRは6.6%に達します。運賃プラットフォームは、中小企業のキャッシュフロー・サイクルに合わせ、即時の見積もり、マイルストーン・アラート、統合された貿易金融モジュールを提供します。
初心者の荷送人は貨物の申告を誤り、罰金を科される可能性があるため、中小企業の参加はコンプライアンスニーズも鋭くします。デジタルの書類作成ウィザードは、制限品目にフラグを付け、標準的な書式を事前に入力することで、税関での保留を19%削減します。フォワーダーは、保険、関税還付申告、電子インボイシングをサブスクリプション層にバンドルすることで、収益を多様化しています。大手産業界の顧客は、重量級のプロジェクト貨物や工場移転の仕事を依然として独占しているが、eコマースの補充品やニッチな完成品を出荷する中小企業によって、さらなる成長の勢いがあります。したがって、貨物輸送市場は、資源に制約のある輸出企業からの需要が加速するにつれて、徐々にバランスの取れた顧客ポートフォリオを示すようになると思われます。
地域分析
アジア太平洋地域は2024年の収益シェア36%で貨物輸送市場をリードし、2030年までのCAGRは7.8%で拡大します。ベトナム、インドネシア、インドへの製造業の多角化が、ブランドによる調達リスクヘッジとして地域別販売量を急増させる。上海、深セン、シンガポールの主要港は、トラックのターンアラウンド時間を短縮する自動クレーンやスマートゲート技術に多額の投資を行っているが、バース利用率は依然として過去最高水準に近いです。DPワールドは、アジア太平洋の港湾が2027年までに合計で年間20万TEUを取り扱うようになると予想しており、この地域がグローバル・サプライ・チェーンにおいて重要な役割を担っていることを裏付けています。
北米は貨物輸送市場において第2位にランクされており、米国の旺盛な消費者需要と、2024年に米国とメキシコの国境を越えた輸送量を10%押し上げるニアショアリングの進行によって支えられています。テキサス州とアリゾナ州にまたがるダブルスタック回廊への鉄道投資により、長距離トラックからインターモーダルへのモーダルシフトが加速し、ドライバーのキャパシティボトルネックが緩和されます。バンクーバーとプリンスルパートにあるカナダのゲートウェイは、混雑する米国西海岸のターミナルからアジア貨物を引き離すため、鉄道搭載能力を拡大します。
欧州のネットワークは、ドライバー不足、厳しい排ガス規制、パッチワーク的な国境規制など、複合的な課題に直面しています。しかし、付加価値サービス、特に製薬とハイテク機械に対する需要が持続しているため、収益は維持されています。ロッテルダム、ハンブルグ、アントワープの主要ハブは、Fit-for-55の目標に準拠するため、税関をデジタル化し、陸上電源ソリューションを導入しています。南米は、2027年に完成すればメルコスール域内の輸送コストを最大40%削減できるカプリコーンBI海上回廊を背景に急成長します。中東はジェベル・アリ港とキング・アブドラ港を拡張し、東西貿易の架け橋となります。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- アジア発北米向け越境eコマース貨物量の急増
- ニアショアリングを中心とした製造業のシフトがメキシコー米国間の道路貨物需要を牽引
- 国際小包フルフィルメントを要求するD2C(Direct-to-Consumer)ブランドの普及
- 温度管理された医薬品出荷を支えるリーファーの能力拡大
- オンデマンドの食料品とミールキット・サービスがコールドチェーンと当日輸送量を増加させる
- リアルタイムの可視性に対する消費者の期待が、小売業者をテクノロジーに強いフォワーダーへと向かわせる
- 市場抑制要因
- 港湾の混雑とコンテナの不均衡が輸送の不確実性を高める
- 世界のドライバー不足が北米と欧州の道路貨物運賃を押し上げる
- 加速するファッションの回帰サイクルがフォワーダーにコストとマージンのプレッシャーを与える
- バリュー/サプライチェーン分析
- 業界の規制と政策
- 市場の技術開拓
- ポーターのファイブフォース
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
- 地政学的イベントが市場に与える影響
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- 輸送手段別
- 海路貨物フォワーディング
- FCL
- LCL
- 道路貨物フォワーディング
- FCL
- LCL
- 航空貨物フォワーディング
- 鉄道貨物フォワーディング
- マルチモーダルとインターモーダル輸送
- 海路貨物フォワーディング
- 企業規模別
- 中小企業
- 大企業
- フォワーダーモデル別
- 従来のアセット・ライト・フォワーダー
- デジタルファースト/オンライン貨物プラットフォーム
- その他
- エンドユーザー業界別
- 工業および製造業
- 小売とeコマース
- ヘルスケアと医薬品
- 石油・ガス・エネルギー
- 飲食品
- 自動車
- 化学
- その他のエンドユーザー
- 地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 南米
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
- チリ
- その他南米
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- スペイン
- イタリア
- オランダ
- ロシア
- その他欧州地域
- アジア太平洋地域
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- 韓国
- シンガポール
- ベトナム
- インドネシア
- オーストラリア
- その他アジア太平洋地域
- 中東
- アラブ首長国連邦
- サウジアラビア
- トルコ
- イスラエル
- その他中東
- アフリカ
- 南アフリカ
- エジプト
- ナイジェリア
- ケニア
- その他アフリカ
- 北米
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 戦略的動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- Kuehne+Nagel International AG
- DHL Global Forwarding
- DSV A/S(DSV Panorama)
- C.H. Robinson Worldwide Inc.
- Expeditors International of Washington Inc.
- Bollore Logistics
- Nippon Express Co. Ltd.
- CEVA Logistics(SCX)
- GEODIS SA
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics SE
- Dachser SE
- Kerry Logistics Network Ltd.
- Yusen Logistics Co. Ltd.
- Agility Logistics
- Maersk Logistics and Services(incl. Damco)
- FedEx Logistics
- UPS Supply Chain Solutions
- Sinotrans Ltd.
- XPO Logistics
- Uber Freight LLC
- Lineage Logistics
- Kintetsu World Express
- LX Pantos
- CIMC Wetrans Logistics
- Toll Group


