|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1694052
電気自動車(EV)バッテリー技術の世界市場:サプライチェーン分析(2025年~2035年)Global Electric Vehicle (EV) Battery Technology Market and Supply Chain Analysis, 2025-2035 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 電気自動車(EV)バッテリー技術の世界市場:サプライチェーン分析(2025年~2035年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月28日
発行: M14 Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 47 Pages
納期: 即納可能
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
電気自動車(EV)は世界をより環境に優しい明日へと導いており、そのバッテリーはこの革命の心臓部です。需要急増に伴い、次の10年は技術、市場、競合の激変が予想されます。
EV業界は、今後5~10年の間に大きな飛躍を遂げる準備を整えています。販売台数は急増し、2030年には世界の新車販売台数の20~30%をEVが占める可能性があり、2020年の4%から急上昇すると予想されています。このブームは、バッテリーのコスト削減、広大な充電ネットワーク、化石燃料自動車にブレーキをかける政府の政策にかかっています。バッテリーのエネルギー密度は倍増し、航続距離は500マイルを超える可能性があります。EU諸国などは、2035年の内燃機関廃止を目指しており、EVの普及に拍車をかけています。
現在、リチウムイオンバッテリーは、ニッケル・マンガン・コバルト(NMC)が長い航続距離を実現し、リチウム鉄リン酸塩(LFP)がコストを削減し、安全性を高めるなど、その頂点に君臨しています。
リチウムイオンのバリエーション:リチウムニッケルマンガンコバルト酸化物を使用するNMCバッテリーは高エネルギー密度で一般的である一方、LFPバッテリーは2023年の容量別世界市場シェアで41%を占め、より安価で持続可能です。<>LFPの採用は、エネルギー密度は低いもの、より低コストであることが要因です。
新興技術:2023年にBYDやCATLなどの企業が量産を発表したナトリウムイオンバッテリーは、都市型EVや据置型蓄バッテリーに適しており、コストを20%削減できる可能性があります。<>トヨタとQuantumScapeが開拓した固体バッテリーは、より高いエネルギー密度と安全性を約束するが、まだ実用化されていないです。
イノベーションデュアルイオンバッテリー(DIB)やバイポーラLFPバッテリーが登場し、急速充電と高電圧を実現しているが、サイクル寿命には課題が残る。
ソリッドステートバッテリーは、EVの航続距離を600マイル以上に伸ばす可能性がありますが、コストが高いため、リチウムイオンがあと10年はハンドルを握ることになります。
中国:CATL(2024年の世界シェア37.9%)やBYD(同17.2%)のような生産コストの低い企業が牽引。生産コストの安いLFPバッテリーが主流で、2023年にはEV販売の3分の2がこのケミストリーを使用しています。
北米:米国はTeslaやフォードとSKオンなどの提携に牽引され、2021年以降2100億米ドルの投資を集めています。ただし、生産コストは中国より20%高いです。
欧州:高いコスト(中国より50%高い)とサプライチェーンの弱さという課題に直面しており、Northvoltの倒産はその難しさを浮き彫りにしています。2030年までに35~40カ所のギガファクトリー建設を目指しています。
アジア太平洋:インドや韓国のような新興市場が成長しており、インドでは2023年のEV登録台数が前年比70%増となり、FAME IIのような制度に支えられています。
EV用バッテリー市場は地政学的なチェス盤です。中国は世界生産の70%以上を占め、CATLやBYDのような大手が規模と補助金によって力を発揮しています。日本と韓国がこれに続き、PanasonicとLG ChemがTeslaやヒュンダイのようなブランドに電力を供給しています。欧州は追いつこうと躍起になっており、独自のサプライチェーンを構築するために欧州バッテリー・アライアンスに資金を投入しています。北米は、Teslaのネバダ・ギガファクトリーを筆頭に、アジアへの依存を減らすために国内生産を強化しています。
各地域の生産能力のスナップショット
| タイプ | メリット | デメリット | 採用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| NMC | 高エネルギー密度(~250Wh/kg) | 高価(コバルト依存) | 減少傾向(Tesla、GMが段階的に廃止) |
| LFP | 安価、長寿命、コバルトフリー | エネルギー密度が低い(~180Wh/kg) | 優勢(Tesla、BYD、フォード) |
| ソリッドステート | 超高エネルギー密度(~500Wh/kg) | まだ実用化されていない | トヨタ、QuantumScape 2026-2030年目標 |
| 地域 | 現在の容量(GWh) | 2030年予測(GWh) | 2035年予測(GWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| アジア | 500 | 1500 | 3000 |
| 欧州 | 50 | 400 | 800 |
| 北米 | 100 | 300 | 600 |
バッテリーメーカーの競合は激しいです。
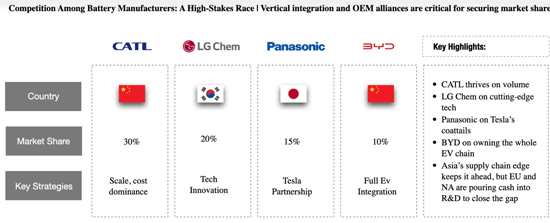
CATLは数量で、LG Chemは最先端技術で、PanasonicはTeslaの尻尾で、そしてBYDはEVチェーン全体を所有することで成功を収めています。アジアはサプライチェーンで優位に立つが、北米と欧州はその差を縮めるべく研究開発に資金を投入しています。
中国がリードし、CATLとBYDが独占、統合されたサプライチェーンと低コストの恩恵を受けています。2024年におけるCATLの339.3GWhの設置は、そのリードを強調するものです。
LG Energy Solutionのような北米企業やNorthvoltのような欧州企業は、欧州のコスト高(中国より50%高い)やサプライチェーンの弱点という課題に直面しています。2024年のNorthvoltの破産は、こうした困難を浮き彫りにしています。
Tesla、BYD、伝統的なOEM(GM、Volkswagen)のような企業は、価格、革新性、サプライチェーン・コントロールで競争しています。Teslaの市場シェアは競争により2019年の17%から2022年には13%に低下しました。Teslaのギガファクトリーのような業種は、コスト優位性をもたらします。
アジア企業、特に中国企業は、ニッチ市場(手頃な価格の小型車など)や政府補助金を通じてスペースを確保し、欧州市場を破壊します。彼らは、オンライン販売やコミュニティ形成戦略を活用しています。
電気自動車(EV)市場では、既存の自動車メーカーと新興参入企業が激しい競争を繰り広げています。Tesla、Volkswagen、General Motors (GM)といった業界大手は、自らの地位を強化するために積極的な戦略を推進しています。Teslaはバッテリー生産を垂直統合して自給率を高め、VolkswagenはNorthvoltと協力して信頼性の高いバッテリー供給を確保し、GMは大衆市場向けEVの開発に注力して顧客層を広げています。
同時に、電気トラックに特化したRivianや、高級EVセグメントをターゲットとするLucid Motorsといった新規参入企業も、革新的な設計と先進技術を活用して市場シェアを獲得し、市場に参入しています。この競合情勢における成功の重要な決定要因は、バッテリーの安定的かつ十分な供給を確保できるかどうかです。
Rivianのような新規参入企業は、既存の自動車メーカーを混乱させる可能性がありますが、それは供給不足の世界でバッテリーを確保した場合に限られます。
EV用バッテリー市場は、電動化が定着するにつれて需要が急増し、指数関数的な成長を遂げようとしています。現在はアジアがリードしていますが、欧州と北米は投資と技術革新によってその差を縮めつつあります。価格変動と競合が課題となっていますが、革新と適応に取り組む企業にはチャンスがあふれています。ティア1サプライヤーとバッテリーメーカーにとって、進むべき道は明確です。明日のEVに電力を供給するために、技術に投資し、サプライチェーンを確保し、持続可能性を受け入れることです。
当レポートでは、世界の電気自動車(EV)バッテリー技術市場について調査し、市場の概要とともに技術動向、市場の見通しと予測、課題、競合情勢、および市場に参入する企業のプロファイルなどをまとめています。
目次
調査範囲
調査手法
バッテリー技術の動向とダイナミクス
- 原材料不足とリサイクルが2030年までにギャップを埋める
- 中国の優位性によりLFPバッテリーが世界市場に溢れる
- 米国とEU別中国製バッテリーへの新たな関税の可能性、国内製造業の活性化
- ギガファクトリー建設が増加- Tesla、GM、フォードが先頭に立つ
- AI駆動型バッテリー管理システム(BMS)
- バッテリー交換ネットワークが普及
- バッテリー・アズ・ア・サービス(BAAS)モデル
市場の見通しと予測
- 世界のEV車販売予測- 車種別・地域別内訳
- 地域別EVバッテリー生産統計
- ギガファクトリーの容量- 計画と運用
- EVバッテリー市場の規模と予測、2025年~2035年
- EVバッテリーの設置容量、2024年のGWH、2025年、2035年までの予測
- EVバッテリー市場規模- 技術タイプ別内訳、2025年~2035年
- リチウムイオン-LFPとNMC
- 新興技術- 固体およびナトリウムイオン
- EVバッテリー市場規模- 地域別内訳、2025年~2035年
- 北米市場、2025年~2035年
- 欧州市場、2025年~2035年
- 中国市場、2025年~2035年
- アジア太平洋(中国を除く)市場、2025年~2035年
主な市場の課題
- 地政学的緊張(中国と西側の分離)
- 原材料価格の変動
- ソリッドステート遅延
- 補助金政策の変更
競合評価
- 競合のベンチマーク
- 市場シェア分析
- トップバッテリーメーカー
- OEM社内製造バッテリーと外注バッテリー
- ギガファクトリーの合弁事業
- スタートアップとOEMパートナーシップ
- 業界を超えたコラボレーション
企業プロファイル
- esla
- Byd
- CaTL
- LG Energy Solution
- Panasonic
- SK On
- Northvolt
- Samsung SDI
- QuantumScape
- Solid Power
- Nio
- ChargePoint
- ABB
- StoreDot
- Freyr Battery
- ACC (Automotive Cells Co.)
- Farasis Energy
- Envision AESC
- Microvast
- Romeo Power
- ProLogium
- Nexeon
- Ample
- SparkCharge
- Electrify America
- Ionity
- Our Next Energy (ONE)
利害関係者(OEM、サプライヤー、投資家)への推奨事項
付録
二次情報のリスト
調査会社について
Lithium-ion (LFP and NMC) and Emerging Battery Technology (Solid-state and Sodium-ion) Market Sizing, Regional breakdown, Regulatory Policies, Battery-as-a-Service Model (BaaS), Gigafactories, Trends & Dynamic, Supply Chain Analysis, Competition.
Key Highlights:
This comprehensive study examines the -
- Strategic Implications and Actionable Insights on EV Battery Technology for Automotive Players
- Battery technology trends, supply chain risks, and future outlook.
- Raw material price spikes and supply chain distribution
- China's market dominance and potential new tariffs impacting the growth of EV Battery industry
- Gigafactory constructions, battery swapping networks, and Batter-as0a Service model (BaaS)
- EV Battery Market Sizing and forecasting, 2025-2035
- Market breakdown by Technology- LPF, NMC, Solid-state, and Sodium-Ion
- Research & Development Analysis
- Partnership between OEMs and Start-ups, Cross-Industry Partnerships
- Market Analysis from perspective of OEMs, Battery Manufacturers, and Investors
Exhaustive Coverage:
- Global EV Car Sales Forecast - Breakdown by Vehicle Type and Region
- EV Battery Production Statistics, by Region
- Gigafactory Capacity- Planned Vs Operational
- EV Battery Market Sizing and Forecast, 2025-2035
- EV Batteries Installed Capacity, GWh in 2024, Estimated in 0225, Forecasted to 2035
- EV Batteries Market Breakdown- By Technology Type , 2025-2035
- Lithium-ion including LFP AND NMC
- Emerging Tech including Solid-State and Sodium-ion
- EV Batteries Market Size- Regional Breakdown, 2025-2035
- North America Market, 2025-2035
- Europe Market, 2025-2035
- China Market, 2025-2035
- Asia-Pacific (except China) Market, 2025-2035
- Key Market Challenges
- Geopolitical Tensions (China-West Decoupling)
- Raw Material Price Volatility
- Solid-Sate Delays
- Changing Subsidy policies
- Competition Assessment
- Competitor Benchmarking
- Market Share Analysis
- Top Battery Makers
- OEM In-housed Vs Outsourced
- Joint Ventures for Gigafactories
- Start-up and OEM partnerships
- Cross-industry collaborations
- Company Profiles
WHAT SHOULD YOU LOOK AT ?
THE SHIFTING DYNAMICS OF EV BATTERY INDUSTRY
- RAW MATERIAL SHORTAGE AND RECYCLING BRIDGING THE GAP BY 2023
- CHINA'S DOMINANCE FLOODING GLOBAL MARKET WITH LFP BATTERIES
- POTENTIAL NEW TARIFFS BY US AND EU ON CHINESE BATTERIES BOOMING THE DOMESTIC
- GIGAFACTORY CONSTRUCTIONS ON RISE - TELSA, GM FORD ON LEAD
- AI DRIVEN BATTERY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (BMS)
- BATTERY SWAPPING NETWORKS GAINING TRACTION
- BATTERY AS A SERVICE (BAAS) MODEL
Market Overview
Charging the Future: The Explosive Rise of EV Batteries
Electric vehicles (EVs) are steering the world toward a greener tomorrow, and their batteries are the beating heart of this revolution. With demand skyrocketing, the next decade promises seismic shifts in technology, markets, and competition.
This report unpacks the electrifying future of EV batteries-where we're headed, who's leading the charge, and how manufacturers can stay ahead in this high-voltage race.
The Electric Horizon: Where EVs Are Headed in 10 Years
The EV industry is gearing up for a massive leap over the next 5 to 10 years. Sales are expected to surge, with EVs potentially claiming 20-30% of global new car sales by 2030, a steep climb from 4% in 2020. This boom hinges on shrinking battery costs, sprawling charging networks, and government policies slamming the brakes on fossil-fuel vehicles. Battery energy density could double, pushing ranges beyond 500 miles, while ultra-fast charging slashes wait times to mere minutes. Countries like those in the EU are eyeing 2035 to phase out internal combustion engines, turbocharging EV adoption.
"The EV tipping point is near-by 2030, one in three new cars could be electric, driven by cheaper batteries and a global push to ditch gas guzzlers."
Battery Breakthroughs: Powering Tomorrow's Drives
Today, lithium-ion batteries reign supreme, with Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC) delivering long ranges and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) slashing costs and boosting safety.
Lithium-Ion Variants: NMC batteries, using lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxides, are common for high energy density, while LFP batteries, with 41% global market share by capacity in 2023, are cheaper and more sustainable. <>LFP's adoption is driven by its lower cost, despite lower energy density
Emerging Technologies: Sodium-ion batteries, announced for mass production by companies like BYD and CATL in 2023, could cost 20% less, suitable for urban EVs and stationary storage. Solid-state batteries, pioneered by <>Toyota and QuantumScape, promise higher energy density and safety but are not yet commercial.
Innovations: Dual-ion batteries (DIB) and bipolar LFP batteries are emerging, offering quick charging and higher voltage, though cycle life remains a challenge.
"Solid-state batteries could zap EV ranges past 600 miles, but their high costs mean lithium-ion will hold the wheel for another decade."
The Global Battery Battle: Who's Winning?
Regional leadership in the EV battery market is evident, with distinct roles:
- China: Dominates with over 51% market share in 2022, driven by low production costs and firms like CATL (37.9% global share in 2024) and BYD (17.2%). LFP batteries, cheaper to produce, are prevalent, with two-thirds of EV sales using this chemistry in 2023.
- North America: Growing, with the US attracting $210 billion in investments since 2021, led by Tesla and partnerships like Ford with SK On. However, production costs are 20% higher than in China.
- Europe: Faces challenges with higher costs (50% more than China) and supply chain weaknesses, with Northvolt's bankruptcy highlighting difficulties. Efforts to build local capacity include gigafactory projects, aiming for 35-40 by 2030.
- Asia Pacific: Emerging markets like India and South Korea are growing, with India seeing 70% year-on-year EV registration growth in 2023, supported by schemes like FAME II .
The EV battery market is a geopolitical chessboard. China commands over 70% of global production, with giants like CATL and BYD flexing muscle through scale and subsidies. Japan and South Korea follow, with Panasonic and LG Chem powering brands like Tesla and Hyundai. Europe's scrambling to catch up, pumping funds into the European Battery Alliance to build its own supply chain. North America, led by Tesla's Nevada Gigafactory, is revving up domestic production to cut reliance on Asia.
Here's a snapshot of regional capacities:
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Adoption |
|---|---|---|---|
| NMC | High energy density (~250 Wh/kg) | Expensive (cobalt reliance) | Declining (Tesla, GM phasing out) |
| LFP | Cheap, long lifespan, cobalt-free | Lower energy density (~180 Wh/kg) | Dominating (Tesla, BYD, Ford) |
| Solid-State | Ultra-high energy density (~500 Wh/kg) | Not yet commercialized | Toyota, QuantumScape targeting 2026–2030 |
| Region | Current capacity(GWh) | Projected 2030(GWh) | Projected 2035(GWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | 500 | 1500 | 3000 |
| Europe | 50 | 400 | 800 |
| North America | 100 | 300 | 600 |
Battery Giants Face Off: The Heavyweight Showdown
Competition among battery makers is fierce. Here's how the big players stack up:

CATL thrives on volume, LG Chem on cutting-edge tech, Panasonic on Tesla's coattails, and BYD on owning the whole EV chain. Asia's supply chain edge keeps it ahead, but Europe and North America are pouring cash into R&D to close the gap.
Highlights:
- Leaders: China leads, with CATL and BYD dominating, benefiting from integrated supply chains and lower costs. CATL's 339.3 GWh installations in 2024 underscore its lead.
- Followers: North American firms like LG Energy Solution and European players like Northvolt face challenges, with Europe's higher costs (50% more than China) and supply chain weaknesses. Northvolt's bankruptcy in 2024 highlights these difficulties.
OEM Competition and New Entrants
- OEM Strategies: Companies like Tesla, BYD, and traditional OEMs (GM, Volkswagen) compete on pricing, innovation, and supply chain control. Tesla's market share fell from 17% in 2019 to 13% in 2022 due to competition. Vertical integration, like Tesla's gigafactories, provides cost advantages.
- New Entrants: Asian firms, especially Chinese, find space through niche markets (e.g., affordable small cars) and government subsidies, disrupting Europe's market. They leverage online sales and community-building strategies.
Established automotive manufacturers and emerging players are engaged in intense competition within the electric vehicle (EV) market. Industry leaders such as Tesla, Volkswagen, and General Motors (GM) are pursuing aggressive strategies to strengthen their positions. Tesla is vertically integrating its battery production to enhance self-sufficiency, Volkswagen is collaborating with Northvolt to ensure a reliable battery supply, and GM is focusing on the development of mass-market EVs to broaden its customer base.
Concurrently, new entrants such as Rivian, which specializes in electric trucks, and Lucid Motors, which targets the luxury EV segment, are entering the market by leveraging innovative designs and advanced technology to capture market share. A critical determinant of success in this competitive landscape is the ability to secure a stable and sufficient supply of batteries.
New entrants like Rivian could disrupt the established automakers, but only if they lock down batteries in a supply-starved world.
Final conclusion:
What's Next for EV Batteries?
The EV battery market is set for exponential growth, with demand soaring as electrification takes hold. Asia leads today, but Europe and North America are closing the gap through investment and innovation. Price volatility and competition pose challenges, yet opportunities abound for those who innovate and adapt. For tier-1 suppliers and battery manufacturers, the path forward is clear: invest in technology, secure supply chains, and embrace sustainability to power the EVs of tomorrow.
Key Questions Answered:
- What battery technology shifts (solid-state, sodium-ion) will disrupt the market by 2035, and how should companies prepare?
- Which regulatory changes (EU Battery Regulation, IRA sourcing rules) will impact market access and profitability?
- Where should OEMs source critical materials to reduce China dependence while maintaining cost competitiveness?
- How can Tier 1 suppliers maintain relevance as OEMs like Tesla vertically integrate battery production?
- What R&D investments (solid-state, silicon anodes) offer the highest ROI for battery component suppliers?
- Which emerging markets (India's PLI scheme, Poland's recycling hub) present the best growth opportunities?
- How can Tier 2 suppliers protect margins against volatile lithium (300% price spikes) and cobalt prices?
- Which alternative chemistries (sodium-ion, LFP) will reshape raw material demand in next 5-10 years?
- How will recycling innovations (second-life batteries, 30% cost reductions) transform the supply chain?
- What strategic timelines (short/mid/long-term) should different players follow to maintain competitiveness?
Companies Mentioned:
|
|
|
TABLE OF CONTENTS
RESEARCH SCOPE
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
BATTERY TECHNOLOGY TRENDS AND DYNAMIC
- RAW MATERIAL SHORTAGE AND RECYCLING BRIDGING THE GAP BY 2030
- CHINA'S DOMINANCE FLOODING GLOBAL MARKET WITH LFP BATTERIES
- POTENTIAL NEW TARIFFS BY US AND EU ON CHINESE BATTERIES BOOMING THE DOMESTIC MANUFACTURING
- GIGAFACTORY CONSTRUCTIONS ON RISE- TESLA, GM, FORD ON LEAD
- AI DRIVEN BATTERY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (BMS)
- BATTERY SWAPPING NETWORKS GAINING TRACTION
- BATTERY AS A SERVICE (BAAS) MODEL
MARKET OUTLOOK AND FORECAST
- GLOBAL EV CAR SALES FORECAST - BREAKDOWN BY VEHICLE TYPE AND REGION
- EV BATTERY PRODUCTION STATISTICS BY REGION
- GIGAFACTORY CAPACITY- PLANNED VS OPERATIONAL
- EV BATTERY MARKET SIZING AND FORECAST, 2025-2035
- EV BATTERIES INSTALLED CAPACITY, GWH IN 2024, ESTIMATED IN 2025, FORCASTED TO 2035
- EV BATTERIES MARKET SIZE- BREAKDOWN BY TECHNOLOGY TYPE , 2025-2035
- LITHIUM-ION- LFP AND NMC
- EMERGING TECH- SOLID-STATE AND SODIUM-ION
- EV BATTERIES MARKET SIZE- REGIONAL BREAKDOWN, 2025-2035
- NORTH AMERICA MARKET, 2025-2035
- EUROPE MARKET, 2025-2035
- CHINA MARKET, 2025-2035
- ASIA-PACIFIC (EXCEPT CHINA) MARKET, 2025-2035
KEY MARKET CHALLENGES
- GEOPOLITICAL TENSIONS (CHINA-WEST DECOUPLING)
- RAW MATERIAL PRICE VOLATILITY
- SOLID-STATE DELAYS
- CHANGING SUBSIDY POLICIES
COMPETITION ASSESSMENT
- COMPETITOR BENCHMARKING
- MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS
- TOP BATTERY MAKERS
- OEM IN-HOUSED VS OUTSOURCED BATTERIES
- JOINT VENTURES FOR GIGAFACTORIES
- START-UPS AND OEM PARTENRSHIPS
- CROSS INDUSTRY COLLABORATIONS
COMPANY PROFILES
- Tesla
- Byd
- CaTL
- LG Energy Solution
- Panasonic
- SK On
- Northvolt
- Samsung SDI
- QuantumScape
- Solid Power
- Nio
- ChargePoint
- ABB
- StoreDot
- Freyr Battery
- ACC (Automotive Cells Co.)
- Farasis Energy
- Envision AESC
- Microvast
- Romeo Power
- ProLogium
- Nexeon
- Ample
- SparkCharge
- Electrify America
- Ionity
- Our Next Energy (ONE)





