|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1591427
体外雌雄鑑別技術市場規模・予測、世界・地域シェア、動向、成長機会分析レポート:技術別、エンドユーザー別、地域別Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Size and Forecast, Global and Regional Share, Trend, and Growth Opportunity Analysis Report Coverage: By Technique, End User, and Geography |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 体外雌雄鑑別技術市場規模・予測、世界・地域シェア、動向、成長機会分析レポート:技術別、エンドユーザー別、地域別 |
|
出版日: 2024年10月31日
発行: The Insight Partners
ページ情報: 英文 97 Pages
納期: 即納可能
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
体外雌雄鑑別技術の市場規模は、2023年の5,400万米ドルから2031年には1億584万米ドルに達すると予測されています。同市場は2023年から2031年にかけてCAGR 8.8%を記録すると予測されています。
動物福祉に対する倫理的実践の重視の高まりが卵生交配技術を後押し
コペンハーゲン大学が2024年3月に発表した論文によると、世界の鶏卵産業は、卵を産めず高品質の肉を提供できないことを理由に、毎年約70億日齢のオスのヒナを殺しています。この活動により、動物福祉や養鶏業界が雄のヒナを淘汰することの倫理的意味合いに対する懸念が高まっています。体外雌雄鑑別技術は、雄雛の淘汰に関連する倫理的課題を解決する可能性を秘めています。体外雌雄鑑別技術により、生産者は孵化前のヒナの雌雄を判別することができます。従って、雄のヒナを識別し、生まれる前に排除することができ、淘汰の必要性を防ぐことができます。従って、雌雄判別の導入により、養鶏業者は、倫理基準や動物福祉方針に沿った経営を行うことができるようになります。Hendrix Genetics BVやInnovate Animal Agといった企業が、卵胎内性交渉技術の研究開発に携わっています。卵生性交渉技術を使用する卵生産企業は、消費者や擁護団体から好意的に見られ、ブランド評価を高めています。このアプローチの転換は、倫理的な製品を求める消費者の需要に応えるだけでなく、動物福祉のパイオニアとしての地位を確立することにもつながります。体外雌雄鑑別技術は、養鶏における無駄を減らし資源効率を向上させることで持続可能性に貢献し、責任ある近代的な農法の重要な要素となっています。したがって、動物福祉と淘汰の倫理的意味合いに対する懸念の高まりが、体外雌雄鑑別技術に対する需要を後押ししています。
しかし、体外雌雄鑑別に伴う高コストと複雑さが、体外雌雄鑑別技術市場の成長を妨げています。体外雌雄鑑別技術に関連する高額な費用は、多くの養鶏事業においてその採用を不利なものにしています。小規模農場では、体外雌雄鑑別技術を導入し、これらの手順を実行するための高度な機械を取得するコストが高いと感じることが多いです。中小の養鶏業者の多くは収益性の低い水準で経営しているため、体外雌雄鑑別技術の高額な初期費用を正当化することが難しいです。この経済的障壁は、生産者がより安価で旧式の卵生産方法に依存し続ける可能性があるため、これらの技術の受容率が低いことと関連しています。特に酵素結合免疫吸着分析法(ELISA)やラジオイムノアッセイ法(RIA)などを用いた卵の雌雄鑑別試験や分析にかかる費用が高いことも、生産者がこれらの技術に投資することを躊躇させる要因となっています。これらの経費は、生産者が投資額[投資利益率(ROI)]を回収できるかどうか、あるいはこの技術が最近スケールアップされたばかりであるため、農業部門におけるこの技術の実行可能性が不明であるため、体外雌雄鑑別に資金を投入することを思いとどまらせる可能性があります。孵化させた雛の多くは、まだ消費者市場向けの卵を産んでいないです。さらに、非常に複雑な体外雌雄鑑別技術には、ヒナの性別判定における顕著なエラー率や孵化率への悪影響の可能性が伴う。
技術ベースの洞察
体外雌雄鑑別技術市場は、技術に基づき、非侵襲的イメージング、遺伝子編集、揮発性分析、雌雄逆転、液体ベースの分析に区分されます。非侵襲的イメージングセグメントは2023年に市場で最大のシェアを占め、2024-2031年に最も高いCAGRを記録すると予測されています。非侵襲的イメージング技術は、ハイパースペクトルイメージング、磁気共鳴イメージング(MRI)、ラマン分光法、蛍光分光法などの高度な技術を採用しています。これらの方法は、卵の殻を傷つけることなく、卵の中の胚を検査して性別を判定することを可能にします。様々な鶏卵生産者が、高品質の卵を生産し、従来の雌雄判定法に伴う倫理的懸念を軽減するために、非侵襲的イメージング技術を採用し、開発しています。Hendrix Genetics社の産卵鶏孵化場に導入されているOrbem社のGenus Focusシステムや、AAT社のCheggyテクノロジーは、卵性判定技術市場で利用可能な非侵襲的技術の数例です。Orbem社のイメージングと分類技術は、Vencomatic Groupの自動化装置と組み合わされ、孵化12日目のニワトリ胚の信頼性の高い、非侵襲的なリアルタイムの性別判定を可能にしています。フランスのヘンドリックス・ジェネティクス孵化場の設備は、日齢のヒナの孵化中に1日あたり~25万個の卵を分析することができます。
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
第2章 エグゼクティブサマリー
- 主要な洞察
第3章 調査手法
- 2次調査
- 1次調査
- 仮説の策定
- マクロ経済要因分析
- 基礎数値の作成
- データの三角測量
- 国レベルのデータ
第4章 体外雌雄鑑別技術の市場情勢
- PEST分析
第5章 体外雌雄鑑別技術市場:主要市場力学
- 体外雌雄鑑別技術市場- 主要市場力学
- 市場促進要因
- 動物福祉のための倫理的慣行の重視の高まり
- 体外雌雄鑑別の商業化への注目の高まり
- 市場抑制要因
- 体外雌雄鑑別に伴う高コストと複雑さ
- 市場機会
- 新たな地域セグメントでの市場拡大
- 今後の動向
- 効率的で正確かつ倫理的な診療を支援する技術の進歩
第6章 体外雌雄鑑別技術市場-世界市場分析
- 体外雌雄鑑別技術市場の収益、2021年~2031年
第7章 体外雌雄鑑別技術市場分析-技術別
- 非侵襲的イメージング
- 遺伝子編集
- 揮発性分析
- 性転換
- 液体ベース分析
第8章 体外雌雄鑑別技術市場の分析-エンドユーザー別
- 孵化場
- 養鶏場
第9章 体外雌雄鑑別技術市場-地域別分析
- 米国体外雌雄鑑別技術市場:2031年までの収益と予測
- ドイツ体外雌雄鑑別技術市場:2031年までの収益と予測
- フランス体外雌雄鑑別技術市場:2031年の収益と予測
- イタリア体外雌雄鑑別技術市場:2031年の収益と予測
- スペイン体外雌雄鑑別技術市場:2031年の収益と予測
- その他欧州体外雌雄鑑別技術市場:2031年の収益と予測
- イスラエル体外雌雄鑑別技術市場:2031年の収益と予測
- 世界のその他の地域体外雌雄鑑別技術市場:2031年の収益と予測
第10章 体外雌雄鑑別技術市場:業界情勢
- 体外雌雄鑑別技術市場の成長戦略
- 有機的成長戦略
- 無機的成長戦略
第11章 企業プロファイル
- Orbem GmbH
- In Ovo BV
- Respeggt Group
- Omegga GmbH
- eggXYt
- SOOS Technology Ltd.
- PLANTegg GmbH
- Agri Advanced Technologies GmbH
第12章 付録
List Of Tables
- Table 1. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Segmentation
- Table 2. United States: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by Technique
- Table 3. United States: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by End User
- Table 4. Germany: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by Technique
- Table 5. Germany: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by End User
- Table 6. France: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by Technique
- Table 7. France: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by End User
- Table 8. Italy: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by Technique
- Table 9. Italy: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by End User
- Table 10. Spain: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by Technique
- Table 11. Spain: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by End User
- Table 12. Rest of Europe: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by Technique
- Table 13. Rest of Europe: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by End User
- Table 14. Israel: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by Technique
- Table 15. Israel: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by End User
- Table 16. Rest of World: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by Technique
- Table 17. Rest of World: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand) - by End User
- Table 18. Recent Organic Growth Strategies in Ovo Sexing Technology Market
- Table 19. Recent Inorganic Growth Strategies in the Ovo Sexing Technology Market
List Of Figures
- Figure 1. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Segmentation, by Geography
- Figure 2. PEST Analysis
- Figure 3. Impact Analysis of Drivers and Restraints
- Figure 4. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Revenue (US$ Thousand), 2021-2031
- Figure 5. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Share (%) - by Technique (2023 and 2031)
- Figure 6. Non-invasive Imaging: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 7. Genetic Editing: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 8. Volatile Analysis: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 9. Sex Reversal: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 10. Liquid Based Analysis: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 11. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Share (%) - by End User (2023 and 2031)
- Figure 12. Hatcheries: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 13. Poultry Farms: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 14. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by Region, 2023 and 2031 (%)
- Figure 15. United States: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 16. Germany: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 17. France: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 18. Italy: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 19. Spain: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 20. Rest of Europe: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 21. Israel: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 22. Rest of World: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- Figure 23. Growth Strategies in Ovo Sexing Technology Market
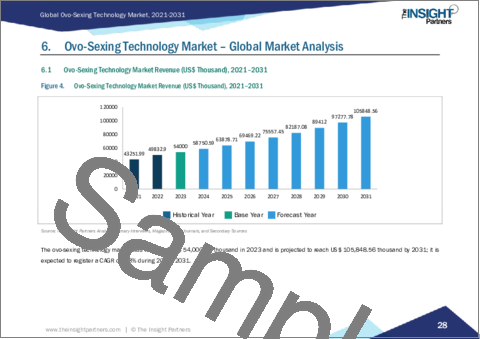
The ovo-sexing technology market size is projected to reach US$ 105.84 million by 2031 from US$ 54.00 million in 2023. The market is expected to register a CAGR of 8.8% during 2023-2031.
Increasing Emphasis on Ethical Practices for Animal Welfare Propels Ovo-Sexing Technology
According to an article published by the University of Copenhagen in March 2024, the global egg industry kills approximately 7 billion-day-old male chicks every year due to their inability to lay eggs and provide high-quality meat. This activity has led to increased concerns about animal welfare and the ethical implications of culling male chicks by the poultry industry. Ovo-sexing technologies have the potential to address ethical challenges associated with male chick culling. Technologies such as in-ovo sexing allow producers to determine the sex of chicks before they hatch; thus, male chicks can be identified and eliminated before they are born, preventing the need for culling. Thus, adopting in-ovo sexing allows poultry producers to align their operations with ethical standards and animal welfare policies, which are increasingly mandated by regulatory bodies in various regions, particularly in Europe. Companies such as Hendrix Genetics BV and Innovate Animal Ag are involved in the research and development of in-ovo sexing technologies. Egg-producing businesses using ovo-sexing technology are viewed favorably by consumers and advocacy groups, enhancing their brand reputation. This shift in approach not only helps manufacturers meet consumer demand for ethical products but also positions them as pioneers of animal welfare. Ovo-sexing technologies contribute to sustainability by reducing waste and improving resource efficiency in poultry farming, making them a critical component of modern, responsible farming practices. Therefore, the growing concerns about animal welfare and the ethical implications of culling drive the demand for in-ovo sexing technologies.
However, the high cost and complexity associated with in-ovo sexing hamper the growth of the in-ovo sexing technologies market. High expenses associated with in-ovo sexing technologies render its adoption unfavorable in many poultry businesses. Smaller farms often find the cost of implementing ovo-sexing technology and acquiring sophisticated machinery to perform these procedures high. Many small and medium poultry producers operate at low profitability levels, making it difficult for them to justify the high initial costs of in-ovo sexing technologies. This economic barrier is associated with the low acceptance rates of these technologies, as producers may continue to rely on cheaper and older methods of egg production. The high costs of in-ovo sexing tests and analyses performed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or radioimmunoassay (RIA) methods, among others, also act as a deterrent for producers to invest in these technologies. These expenses may discourage producers from committing funds to in-ovo sexing because they are unsure of recovering their investments [return on investment (ROI)] or the viability of the technology in the agriculture sector, as the technology has been recently scaled up. Many of the in-ovo hatched chicks have not yet produced eggs for consumer markets. In addition, the highly complex in-ovo sexing technologies come with the possibility of a notable error rate in the gender determination of chicks or a negative impact on hatchability, which might adversely affect the acceptance of in-ovo screenings and hamper the growth of the in-ovo sexing technologies market.
Technique-Based Insights
The ovo-sexing technology market, based on technique, is segmented into noninvasive imaging, genetic editing, volatile analysis, sex reversal, and liquid-based analysis. The noninvasive imaging segment held the largest share of the market in 2023, and it is expected to register the highest CAGR during 2024-2031. Noninvasive imaging technology for ovo-sexing of chicks employs advanced techniques such as hyperspectral imaging, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Raman spectroscopy, and fluorescence spectroscopy. These methods enable the examination of the embryo inside an egg to determine its sex without harming the shell. Various egg producers are adopting and developing noninvasive imaging technologies to produce high-quality eggs and reduce the ethical concerns associated with traditional sex determination methods. Orbem's Genus Focus system, which has been implemented in the laying hen hatchery of Hendrix Genetics, and AAT's Cheggy technology are a few examples of noninvasive technologies available in the ovo-sexing technology market. Orbem's imaging and classification technology is combined with Vencomatic Group's automation equipment to enable the reliable, noninvasive, real-time sex determination of chick embryos on day 12 of incubation. The French Hendrix Genetics hatchery's installation can analyze ~250,000 eggs per day during the incubation of day-old chicks.
Table Of Contents
1. Introduction
- 1.1 The Insight Partners Research Report Guidance
- 1.2 Market Segmentation
2. Executive Summary
- 2.1 Key Insights
3. Research Methodology
- 3.1 Secondary Research
- 3.2 Primary Research
- 3.2.1 Hypothesis formulation:
- 3.2.2 Macro-economic factor analysis:
- 3.2.3 Developing base number:
- 3.2.4 Data Triangulation:
- 3.2.5 Country level data:
4. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Landscape
- 4.1 Overview
- 4.2 PEST Analysis
5. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Key Market Dynamics
- 5.1 Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Key Market Dynamics
- 5.2 Market Drivers
- 5.2.1 Increasing Emphasis on Ethical Practices for Animal Welfare
- 5.2.2 Rising Focus on Commercialization of In-Ovo Sexing Methods
- 5.3 Market Restraints
- 5.3.1 High Cost and Complexity Associated with In-Ovo Sexing
- 5.4 Market Opportunities
- 5.4.1 Market Expansion in New Geographic Segments
- 5.5 Future Trends
- 5.5.1 Technological Advancements to Aid Efficient, Accurate, and Ethical Practices
6. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Global Market Analysis
- 6.1 Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Revenue (US$ Thousand), 2021-2031
7. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Analysis - by Technique
- 7.1 Non-invasive Imaging
- 7.1.1 Overview
- 7.1.2 Non-invasive Imaging: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 7.2 Genetic Editing
- 7.2.1 Overview
- 7.2.2 Genetic Editing: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 7.3 Volatile Analysis
- 7.3.1 Overview
- 7.3.2 Volatile Analysis: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 7.4 Sex Reversal
- 7.4.1 Overview
- 7.4.2 Sex Reversal: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 7.5 Liquid Based Analysis
- 7.5.1 Overview
- 7.5.2 Liquid Based Analysis: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
8. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Analysis - by End User
- 8.1 Hatcheries
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Hatcheries: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 8.2 Poultry Farms
- 8.2.1 Overview
- 8.2.2 Poultry Farms: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
9. Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Geographical Analysis
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.1.1.1 United States: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 9.1.1.1.1 United States: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by Technique
- 9.1.1.1.2 United States: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by End User
- 9.1.1.2 Germany: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 9.1.1.2.1 Germany: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by Technique
- 9.1.1.2.2 Germany: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by End User
- 9.1.1.3 France: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 9.1.1.3.1 France: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by Technique
- 9.1.1.3.2 France: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by End User
- 9.1.1.4 Italy: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 9.1.1.4.1 Italy: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by Technique
- 9.1.1.4.2 Italy: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by End User
- 9.1.1.5 Spain: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 9.1.1.5.1 Spain: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by Technique
- 9.1.1.5.2 Spain: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by End User
- 9.1.1.6 Rest of Europe: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 9.1.1.6.1 Rest of Europe: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by Technique
- 9.1.1.6.2 Rest of Europe: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by End User
- 9.1.1.7 Israel: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 9.1.1.7.1 Israel: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by Technique
- 9.1.1.7.2 Israel: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by End User
- 9.1.1.8 Rest of World: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
- 9.1.1.8.1 Rest of World: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by Technique
- 9.1.1.8.2 Rest of World: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market Breakdown by End User
- 9.1.1.1 United States: Ovo-Sexing Technology Market - Revenue and Forecast to 2031 (US$ Thousand)
10. Ovo Sexing Technology Market - Industry Landscape
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Growth Strategies in Ovo Sexing Technology Market
- 10.3 Organic Growth Strategies
- 10.3.1 Overview
- 10.4 Inorganic Growth Strategies
- 10.4.1 Overview
11. Company Profiles
- 11.1 Orbem GmbH
- 11.1.1 Key Facts
- 11.1.2 Business Description
- 11.1.3 Products and Services
- 11.1.4 Financial Overview
- 11.1.5 SWOT Analysis
- 11.1.6 Key Developments
- 11.2 In Ovo BV
- 11.2.1 Key Facts
- 11.2.2 Business Description
- 11.2.3 Products and Services
- 11.2.4 Financial Overview
- 11.2.5 SWOT Analysis
- 11.2.6 Key Developments
- 11.3 Respeggt Group
- 11.3.1 Key Facts
- 11.3.2 Business Description
- 11.3.3 Products and Services
- 11.3.4 Financial Overview
- 11.3.5 SWOT Analysis
- 11.3.6 Key Developments
- 11.4 Omegga GmbH
- 11.4.1 Key Facts
- 11.4.2 Business Description
- 11.4.3 Products and Services
- 11.4.4 Financial Overview
- 11.4.5 SWOT Analysis
- 11.4.6 Key Developments
- 11.5 eggXYt
- 11.5.1 Key Facts
- 11.5.2 Business Description
- 11.5.3 Products and Services
- 11.5.4 Financial Overview
- 11.5.5 SWOT Analysis
- 11.5.6 Key Developments
- 11.6 SOOS Technology Ltd.
- 11.6.1 Key Facts
- 11.6.2 Business Description
- 11.6.3 Products and Services
- 11.6.4 Financial Overview
- 11.6.5 SWOT Analysis
- 11.6.6 Key Developments
- 11.7 PLANTegg GmbH
- 11.7.1 Key Facts
- 11.7.2 Business Description
- 11.7.3 Products and Services
- 11.7.4 Financial Overview
- 11.7.5 SWOT Analysis
- 11.7.6 Key Developments
- 11.8 Agri Advanced Technologies GmbH
- 11.8.1 Key Facts
- 11.8.2 Business Description
- 11.8.3 Products and Services
- 11.8.4 Financial Overview
- 11.8.5 SWOT Analysis
- 11.8.6 Key Developments
12. Appendix
- 12.1 About The Insight Partners