|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1693495
東南アジアの野菜種子:市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025~2030年)Southeast Asia Vegetable Seed - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 東南アジアの野菜種子:市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 341 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
東南アジアの野菜種子市場規模は、2025年に5億5,910万米ドルと推定され、2030年には7億830万米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間(2025~2030年)のCAGRは4.84%で成長すると予測されます。
高収量・耐病性品種への需要が予測期間中に増加すると予測される
- ハイブリッド品種と開放受粉品種、ハイブリッド派生品種が、この地域における2つの主要技術です。ハイブリッド種子は、金額ベースで2022年に75.2%のシェアを占め、野菜種子市場を独占しました。
- ハイブリッド種子のシェアが高いのは、生産性が高く、適応性が広く、生物学的と生物学的ストレスに対する耐性が高いためです。例えば、ナス科の作物では、ハイブリッドは従来の品種よりも50%も収量が多いです。ハイブリッドの幅広い適応性は、主に環境の変動に対する高い緩衝能力によるものです。
- 2022年には、インドネシアとミャンマーが、金額ベースで同地域の開放受粉品種市場全体の約46.0%を占めました。露地受粉品種は肥料や農薬などの投入資材が少なくて済み、低所得農業従事者にとって安価で購入しやすいため、同地域の市場を押し上げています。
- 同様に、東南アジアでは、2022年の露地受粉品種とハイブリッド派生品種の市場シェアは金額ベースで24.8%でした。シェアが低いのは、主に高収量で耐病性のハイブリッドが好まれるためと考えられます。
- この地域では遺伝子組み換えハイブリッド野菜種子の商業栽培を承認している国はないため、すべての作物は遺伝子組み換えでないハイブリッドです。ハイブリッド種子セグメントは、高収量、耐病性、早熟などの利点により、予測期間中にCAGR 5.0%を記録し、この地域で最も急成長するセグメントと予想されます。
- したがって、食品需要の増加と業務用ハイブリッド品種の導入に伴い、ハイブリッド育種技術が予測期間中に市場を独占すると予想されます。
2022年の東南アジア野菜種子市場はインドネシアが独占
- 東南アジアでは、野菜種子市場は2022年に4億8,350万米ドルと評価されました。インドネシア、ベトナム、ミャンマーがこの地域の野菜種子市場に大きく貢献しています。2022年には、これらの国々は合わせて地域市場の49.7%を占めています。これらの国の野菜栽培面積は最も多く、2022年には470万ヘクタール、すなわちこの地域の野菜総栽培面積の53.7%を占めます。
- インドネシアが野菜種子市場を独占し、2022年には同地域で最も高いシェアとなる33.4%を占めたが、これは主に商業種子の大規模な採用と野菜栽培の増加によるものです。同国の野菜作付面積はこの地域で最大で、2022年には200万ヘクタール、すなわちこの地域の野菜作付面積の23.4%を占めます。
- ベトナムとミャンマーは、この地域の野菜種子市場の他の主要貢献国です。2022年、これらの国の野菜種子市場はそれぞれ6,470万米ドル、5,550万米ドルと評価されました。作付面積の増加、保護栽培法の採用、野菜消費の利点に関する認識がこれらの国の種子市場の成長につながりました。
- フィリピンとタイの野菜種子市場は、2022年にはそれぞれ5,380万米ドル、4,500万米ドルと評価されました。これらの国の地方政府は、財政援助を提供することで地元の農業従事者に野菜栽培を奨励する検査的プロジェクトを開始しました。
- したがって、政府の施策、生産量と人口の増加、生野菜の健康上の利点に関する意識の高まり、加工産業からの需要などの要因が、予測期間中にこの地域の野菜種子市場を押し上げると予想されます。
東南アジアの野菜種子市場動向
東南アジアでの野菜栽培は根菜類と球根類が主流です。
- 東南アジアは野菜栽培に適した気候と農学的条件を備えています。その結果、2022年には870万ヘクタールが野菜栽培に充てられ、東南アジアの総栽培面積の10.7%を占めました。根菜類と球根類は東南アジアで最大のセグメントであり、2022年の野菜栽培面積の51.2%を占め、440万ヘクタールでした。これは、これらの作物がこの地域に見られる土壌タイプに適しているためです。これらの作物は生産コストが比較的低く、莫大な量の投入なしに栽培できるため、この地域の農業従事者に好まれています。
- 唐辛子は、東南アジアにおける栽培面積の面で支配的な野菜であり、2022年には同地域の野菜栽培全体の7.1%を占めました。東南アジアでは、インドネシアが主要な唐辛子生産国で、2022年の地域全体の栽培面積の52.2%を占め、32万4,700haでした。最も高いシェアは、加工産業による需要と、同国における唐辛子栽培の先進的メカニズムの採用によるものです。東南アジアで栽培されている他の主要野菜作物は、トマト、ジャガイモ・キャベツ、キュウリです。2017~2022年にかけて、東南アジアのトマト栽培面積はトマトの価格上昇と消費者需要の増加により6.8%増加しました。
- インドネシアは野菜の栽培面積に関してこの地域最大の国であり、2022年にはこの地域の野菜面積の23.5%を占めています。国内外市場からの需要増加により農業従事者が野菜にシフトしたため、面積が増加しています。そのため、先進的なメカニズムの採用が、同地域の野菜作付面積の伸びを牽引すると予想されます。
キャベツ、カボチャ、カボチャは東南アジアで重要な野菜作物であり、消費者の高い需要に応えるために耐病性品種や品質属性品種への需要が高まっています。
- キャベツは東南アジアで最も重要な野菜作物のひとつです。この地域で栽培されているキャベツタイプには、ベトナムキャベツ、中国キャベツ、バクチョイなどがあります。病害耐性(アルテルナリア葉枯病、しも病、腐敗病)、頭の大きさ、頭の葉の色、頭の形などの品質形質、害虫抵抗性や幅広い適応性などのその他の形質を持つ品種が、広く採用されている主要形質です。さらに、頭の大きさと頭の重さは、1ヘクタール当たりの収量生産性を高めるのに役立つため、大きな需要がある主要形質です。LimagrainやRijk Zwaanなどの企業は、これらの形質を持つキャベツの種子を提供しており、悪天候下でも高品質で栽培できるようにしています。
- カボチャとカボチャは、この地域で広く栽培されている主要なウリ科作物です。形、大きさ、色の良さ、貯蔵期間の長さ、耐病性、特にジェミニン・ウイルスに対する耐性、気候や土壌の違いに対する適応性の広さといった品質特性が人気です。今後、各社がベト病耐性やウイルス抵抗性、均一性、色、風味を備えた新品種を開発するにつれ、耐病性や品質属性形質がより広く利用できるようになることが期待されます。さらに、East-West Seedは、18880 F1やPujitha F1のような、ジェミニンやポティウィルスに抵抗性を持つ品種を作付しています。フィリピンでは、エンザ・ザーデンが2021年にビタリス・オーガニックシードとの提携により新品種を発売しました。
- ウイルスに対する抵抗性、品質特性、高収量を備えた新品種の導入などの要因が、予測期間中の野菜種子市場の成長に寄与すると予想されます。
東南アジアの野菜種子産業概要
東南アジアの野菜種子市場はセグメント化されており、上位5社で21.57%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は、Bayer AG、East-West Seed、Groupe Limagrain、Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV、Syngenta Groupなどです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主要調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 栽培面積
- 野菜
- 最も人気のある品種
- キャベツ、カボチャ、カボチャ
- トマトと唐辛子
- 育種技術
- 野菜
- 規制の枠組み
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 育種技術
- 雑種
- 開放受粉品種とハイブリッド派生品種
- 栽培メカニズム
- 露地栽培
- 保護栽培
- 作物
- アブラナ科
- キャベツ
- ニンジン
- カリフラワー&ブロッコリー
- その他のアブラナ
- ウリ科
- キュウリ・ガーキン
- かぼちゃ・カボチャ
- その他ウリ科
- 根菜・球根
- ニンニク
- タマネギ
- ジャガイモ
- その他の根菜類
- ナス科
- 唐辛子
- ナス科
- トマト
- その他ナス科
- 分類されていない野菜
- アスパラガス
- レタス
- オクラ
- エンドウ豆
- ほうれん草
- その他分類されていない野菜
- アブラナ科
- 生産国
- インドネシア
- ミャンマー
- フィリピン
- タイ
- ベトナム
- その他の東南アジア諸国
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Bejo Zaden BV
- Charoen Pokphand Group(CP Group)
- East-West Seed
- Enza Zaden
- Groupe Limagrain
- Known You Seed Co. LTD
- Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- Syngenta Group
第7章 CEOへの主要戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 世界市場規模とDRO
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表リスト
- 主要な洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
目次
Product Code: 92558
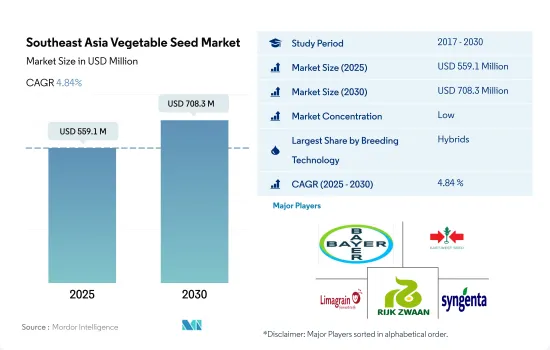
The Southeast Asia Vegetable Seed Market size is estimated at 559.1 million USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 708.3 million USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 4.84% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The demand for high-yielding and disease-resistant varieties is anticipated to increase during the forecast period
- Hybrid and open-pollinated varieties and hybrid derivatives are two major technologies in the region. Hybrid seeds dominated the vegetable seed market by holding a share of 75.2% in 2022 in terms of value.
- Hybrids have a higher share due to higher productivity, wider adaptability, and a high degree of resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. For instance, in Solanaceae crops, hybrids give 50% more yield than conventional varieties. Hybrids' wider adaptability is mainly due to their high buffering capacity to environmental fluctuations.
- In 2022, Indonesia and Myanmar together accounted for about 46.0% of the total open-pollinated varieties market in the region by value. Open-pollinated varieties require fewer inputs, such as fertilizer and pesticides, and are less expensive and more affordable for low-income farmers, thus boosting the market in the region.
- Similarly, in Southeast Asia, the open-pollinated varieties and hybrid derivatives held a market share of 24.8% by value in 2022. The low share can be mainly due to the preference for high-yielding and disease-resistant hybrids.
- All crops are non-transgenic hybrids, as no countries in the region have approved commercial cultivation of transgenic hybrid vegetable seeds. The hybrid seeds segment is anticipated to be the fastest-growing segment in the region, registering a CAGR of 5.0% during the forecast period, owing to the advantages, such as high yield, disease resistance, and early maturity.
- Therefore, with increasing food demand and the implementation of commercial hybrid varieties, hybrid breeding technology is expected to dominate the market during the forecast period.
Indonesia dominated the Southeast Asian vegetable seed market in 2022
- In Southeast Asia, the vegetable seed market was valued at USD 483.5 million in 2022. Indonesia, Vietnam, and Myanmar are the major contributors to the vegetable seed market in the region. In 2022, these countries together accounted for 49.7% of the regional market. These countries have the highest acreage in terms of vegetable cultivation, accounting for 4.7 million hectares, i.e., 53.7% of the total vegetable acreage in the region in 2022.
- Indonesia dominated the vegetable seed market, accounting for 33.4% of the market in 2022, the highest share in the region, primarily due to its large adoption of commercial seeds and increased vegetable cultivation. The country held the maximum vegetable acreage in the region, recorded at 2.0 million hectares in 2022, i.e., 23.4% of the vegetable acreage in the region.
- Vietnam and Myanmar are the other major contributors to the regional vegetable seed market. In 2022, the vegetable seed market in these countries was valued at USD 64.7 million and USD 55.5 million, respectively. The increased acreage, adoption of protected cultivation methods, and awareness about the benefits of vegetable consumption led to the growth of the seed market in these countries.
- The Philippine and Thai vegetable seed markets were valued at USD 53.8 million and USD 45 million in 2022, respectively. The local governments in these countries initiated pilot projects to encourage the local farmers to cultivate vegetables by providing financial assistance.
- Therefore, factors such as government measures, increasing production and population, growing awareness about the health benefits of raw vegetables, and the demand from processing industries are anticipated to boost the region's vegetable seed market during the forecast period.
Southeast Asia Vegetable Seed Market Trends
Root and bulbs dominate vegetable cultivation in Southeast Asia as they are well-suited to the soil types found in the region
- Southeast Asia has a favorable climate and agronomic conditions for vegetable cultivation. As a result, in 2022, the region dedicated 8.7 million hectares to vegetable cultivation, which accounted for 10.7% of the total cultivation area in Southeast Asia. Roots and bulbs are the largest segment in Southeast Asia, and it accounted for 51.2% of the vegetable area in 2022, with 4.4 million ha. This is because they are well-suited to the soil types found in the region. These crops have a relatively low cost of production and can be grown without huge amounts of inputs, making them the preferred choice by farmers in the region.
- Chili is the dominant vegetable in terms of cultivation area in Southeast Asia, and it accounted for 7.1% of the total vegetable cultivation in the region in 2022. In Southeast Asia, Indonesia was the major chili-producing country, which held a share of 52.2% of the region's overall cultivation area in 2022, with 324.7 thousand ha. The highest share is due to the demand by processing industries and the adoption of advanced mechanisms for chili cultivation in the country. The other major vegetable crops cultivated in Southeast Asia are tomato, potato cabbage, and cucumber. Between 2017 and 2022, Southeast Asia's tomato area increased by 6.8% due to the increase in the prices of tomatoes and higher consumer demand.
- Indonesia is the largest country in the region with respect to the area under cultivation of vegetables, and it accounted for 23.5% of the region's vegetable area in 2022. The area was increasing as the farmers shifted toward vegetables due to the increase in the demand from the domestic and international markets. Therefore, the adoption of advanced mechanisms is expected to drive the growth of vegetable acreage in the region.
Cabbage, pumpkin and squash are vital vegetable crops in Southeast Asia, with a rising demand for disease resistant and quality attributes varieties to meet the higher consumer demand
- Cabbage is one of the most important vegetable crops in Southeast Asia. Different types of cabbages grown in the region are Vietnamese cabbages, Chinese cabbages, and Bak Choy. Varieties with disease tolerance (Alternaria leaf blight, wilts, and rots), quality traits such as the size of the head, the color of head leaves, the shape of the head, and other traits such as pest resistance and wider adaptability are the major traits widely adopted. Additionally, the size of heads and head weight are the major traits that have a significant demand, as they help in increasing yield productivity per hectare. Companies such as Limagrain and Rijk Zwaan are providing cabbage seeds with these traits to grow in adverse weather conditions with high quality.
- Pumpkin and squash are the major cucurbits widely grown in the region. The popular traits of the crop are quality attributes such as good shape, size, and color, longer storage life, disease resistance, especially against the geminin virus, and wider adaptability to different climatic and soil types. It is expected that in the future, disease resistance and quality attribute traits will be more widely available as companies develop new varieties with mildew tolerance and virus resistance, as well as uniformity, color, and flavor. Moreover, East-West Seed has varieties, such as 18880 F1 and Pujitha F1, which provide resistance to geminin and potyvirus in the crop. In the Philippines, Enza Zaden launched new seed varieties through a partnership with Vitalis Organic Seeds in 2021.
- Factors such as the introduction of new seed varieties with higher resistance to viruses, quality attributes, and high yield are expected to help in the growth of the vegetable seed market during the forecast period.
Southeast Asia Vegetable Seed Industry Overview
The Southeast Asia Vegetable Seed Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 21.57%. The major players in this market are Bayer AG, East-West Seed, Groupe Limagrain, Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV and Syngenta Group (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Area Under Cultivation
- 4.1.1 Vegetables
- 4.2 Most Popular Traits
- 4.2.1 Cabbage, Pumpkin & Squash
- 4.2.2 Tomato & Chilli
- 4.3 Breeding Techniques
- 4.3.1 Vegetables
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Breeding Technology
- 5.1.1 Hybrids
- 5.1.2 Open Pollinated Varieties & Hybrid Derivatives
- 5.2 Cultivation Mechanism
- 5.2.1 Open Field
- 5.2.2 Protected Cultivation
- 5.3 Crop Family
- 5.3.1 Brassicas
- 5.3.1.1 Cabbage
- 5.3.1.2 Carrot
- 5.3.1.3 Cauliflower & Broccoli
- 5.3.1.4 Other Brassicas
- 5.3.2 Cucurbits
- 5.3.2.1 Cucumber & Gherkin
- 5.3.2.2 Pumpkin & Squash
- 5.3.2.3 Other Cucurbits
- 5.3.3 Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.3.1 Garlic
- 5.3.3.2 Onion
- 5.3.3.3 Potato
- 5.3.3.4 Other Roots & Bulbs
- 5.3.4 Solanaceae
- 5.3.4.1 Chilli
- 5.3.4.2 Eggplant
- 5.3.4.3 Tomato
- 5.3.4.4 Other Solanaceae
- 5.3.5 Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.5.1 Asparagus
- 5.3.5.2 Lettuce
- 5.3.5.3 Okra
- 5.3.5.4 Peas
- 5.3.5.5 Spinach
- 5.3.5.6 Other Unclassified Vegetables
- 5.3.1 Brassicas
- 5.4 Country
- 5.4.1 Indonesia
- 5.4.2 Myanmar
- 5.4.3 Philippines
- 5.4.4 Thailand
- 5.4.5 Vietnam
- 5.4.6 Rest of SouthEast Asia
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 BASF SE
- 6.4.2 Bayer AG
- 6.4.3 Bejo Zaden BV
- 6.4.4 Charoen Pokphand Group (CP Group)
- 6.4.5 East-West Seed
- 6.4.6 Enza Zaden
- 6.4.7 Groupe Limagrain
- 6.4.8 Known You Seed Co. LTD
- 6.4.9 Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel BV
- 6.4.10 Syngenta Group
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SEEDS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Global Market Size and DROs
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms