|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1441484
日本の通信:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2024~2029年)Japan Telecom - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 日本の通信:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2024~2029年) |
|
出版日: 2024年02月15日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 100 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
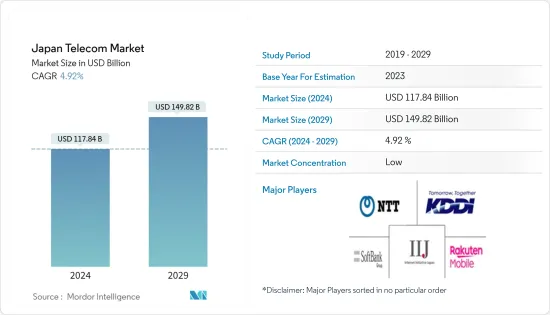
日本通信市場規模は2024年に1,178億4,000万米ドルと推定され、2029年までに1,498億2,000万米ドルに達すると予測されており、予測期間(2024年から2029年)中に4.92%のCAGRで成長します。
日本には、人々が常につながることを可能にする高度に発達したインフラがあります。日本はインターネット普及率が高いことに加えて、スマートフォンの人気の高まりを反映して、かなりのモバイルインターネットユーザーベースを持っています。スマートフォンの普及率は高いもの、今後数年間でさらに多くの個人がスマートフォンを利用すると予想されます。
主なハイライト
- 日本では、モバイル分野の競合促進と利用者の保護を目的として、2019年10月に電気通信事業法が改正されました。それ以来、利用者の負担を軽減するために携帯電話料金を値下げするという議論が行われてきました。総務省は、公正で競争力のある携帯市場の形成による携帯電話料金の引き下げに向けた行動計画を発表しました。 2021年 3月までに、すべてのMNO会社が新しい低価格ブランドと料金体系を導入し、その中には20 GBのデータが含まれるものもありました。
- 6G通信がその可能性を最大限に発揮するには10年かかるかもしれないが、日本はすでに独自の国内ネットワークと技術基盤を確立しつつあります。日本政府は超高速通信の開発促進に数十億米ドルを投資する計画です。日本の機器メーカーNECと富士通、そしてフィンランドの機器メーカーNokiaは、2030年までの6Gサービスの商用開始に向けて、新たなモバイル通信技術の実験を実施する計画を発表しました。
- インターネットのおかげでシステムとプロトコルの進化は続きましたが、モバイルネットワークの発展は、非常に長い間、閉鎖的な文化と独自のテクノロジーによって制約を受けてきました。モバイルネットワークは、さまざまな分野にとって不可欠なインフラストラクチャとなるために、その場で変更や動的なセットアップを提供できなければなりません。 RESTful(Representational State Transfer)アプリケーションプログラミングインターフェイス(API)を統合することで、ソフトバンクはネットワークを調整および変更して消費者のニーズを満たし、より便利なサービスを提供します。
- COVID-19感染症の流行は日本経済に大きな影響を与えました。パンデミック中およびパンデミック後に国家の回復力を高めるためには、デジタル技術の導入が不可欠でした。テクノロジーアプリケーションは、顧客との連絡やデジタルでの事業運営、事業運営の再開、物流のボトルネックを軽減するテクノロジーの導入を支援することで、企業とその従業員がCOVID-19感染症による経済的影響を管理するのに役立ちます。 46兆8,000億円(4,340億米ドル)に相当する日本のデジタル機会のかなりの69%は、企業や従業員がパンデミックが経済に及ぼす影響の管理を支援するテクノロジーから得られていると考えられています。
日本通信市場の動向
5Gの展開
- GSMAの報告書によると、日本は通信事業者が信号機の上に5G基地局を設置することを許可しており、全国的な5G展開が加速しています。小さなセルが配置され、ネットワーク密度が高まると、21のより大容量のユースケースが繁栄する可能性があります。日本の接続普及率は、2021年の153%から2022年には154%に上昇すると予想されています。スマートフォンの普及率は、2021年の71%から2025年には81%に増加すると予測されています。また、日本の加入者数の普及率も、87から87に上昇すると予想されています。 2021年の%から2025年の88%まで。
- iPhone 12と13の価格引き下げと店頭での入手可能性を考慮すると、国内での5G導入の見通しはより有望に思えます。最近、日本政府は、国内の上位3つの携帯電話プロバイダーであるNTTドコモ、KDDI au、ソフトバンク、そして最近参入した楽天モバイルに5G周波数帯を認可しました。今後数年間で、これら日本の通信事業者4社は、基地局、サーバー、光ファイバーなどの資本プロジェクトに140億米ドル以上を投資すると予想されています。 Fitch調査によると、2026年までに5Gが日本の主要な携帯電話技術として4Gを追い越し、2029年までに4G加入者は約4,500万人、5G加入者は1億5,100万人以上になると予想されます。
- 地元報道によると、日本の通信事業者であるNTTドコモは、競合他社も同様に5Gの全国展開のスピードを速める計画だといいます。同記事は、NTTドコモが2024年3月までに日本の人口の80%という当初の目標を上回る90%にサービスを提供する計画であると主張しています。2022年9月、NTTドコモは世界初の商用5Gスタンドアロン(SA)ネットワークを保有していると主張しました。これにより、スマートフォンは、5G NRデュアル接続として知られるミッドバンド(サブ 6 GHz)周波数とミリ波周波数を同時に使用できるようになります。この発表はワイヤレス技術会社クアルコムと共同で行われ、同社は同社のSnapdragon 8 Gen 1プラットフォームを搭載したスマートフォンが新しいネットワークのフルスピードを活用できることをアピールしたいと考えていました。
- 日本の顧客は、Samsung、Sony、Sharp、富士通、Googleのハイエンドスマートフォンを含む幅広いミリ波デバイスと、この技術に対するキャリアの大きな勢いを利用できます。下位ティアを含む他のOEM各社も、今後数カ月以内に日本にミリ波スマートフォンを導入すると予想されています。
- 2022年 5月、ソフトバンク株式会社は、日本全国でMECサーバーの展開を開始し、関東エリアで5G MEC(マルチアクセスエッジコンピューティング)サイトを立ち上げることを宣言しました。「SoftBank 5G MEC」は、5G SA(5G Stand Alone)商用サービスを利用し、低遅延、高品質(低ジッター)、安全性の高いサービス体験を提供します。ソフトバンクは、さまざまなビジネスのデジタルトランスフォーメーション(DX)を推進し、デジタルツイン※2を実現することで、 Beyond 5Gの将来におけるデジタルプラットフォームプロバイダーとして社会課題に応え、業界の発展を図ることが期待されています。
デジタルトランスフォーメーションへの取り組み
- デジタルトランスフォーメーションは、COVID-19危機によって最も目に見えて加速された動向(DX)の1つです。この突然の変化は、ビジネスや組織の運営を改善し、人々の生活に幅広いプラスの影響を与える可能性があります。国際電気通信連合(ITU)の調査によると、2020年に世界中の大都市圏でインターネットにアクセスできる人は76%だったのに対し、地方では39%でした。日本は、人間と持続可能性の両方を重視した「新しい資本主義の形」を創造するという高い目標を掲げ、DXを成長と分配の好循環に向けた取り組みの重要な要素として位置付けています。
- 地方の民間企業はすぐに収益性を達成するのが難しいかもしれませんが、地方自治体や省庁と協力することで斬新なアイデアを実現できる可能性があります。さらに、デジタル化は日本においてはもちろん、地方においても新しいことではありません。総務省の地域IoT推進研究所プロジェクトは、2016年の開始以来、日本全国105地域の研究所を表彰し、最も優れた新しいIoTソリューションや企業を表彰し、地域のプロジェクトやベンチャーの繁栄と離陸を支援するメンターを派遣してきました。
- 日本の大企業は、他の組織のテクノロジー、コンセプト、資産、リソースを活用してイノベーションを促進するために、オープンイノベーションカンファレンスやビジネスコンテストを主催しています。日本ではオープンイノベーションは諸外国に比べてまだ普及していませんが、日本の大手企業ではオープンイノベーションが一般的になり、成長しつつあります。ここ数年、さまざまな分野でオープンイノベーションの取り組みやビジネスコンテストが数多く開催されてきました。例えば、通信分野におけるNTTDataオープンイノベーション。
- 伊那市は2020年8月に、月額利用料を支払う住民向けに全国初となるドローンを使った買い物サービス「支えあい買い物サービス」を導入しました。このサービスはケーブルTVを通じて提供され、通信会社KDDI株式会社と協力して開発されました。顧客はテレビのリモコンを使用して注文し、ケーブル料金を支払うことができます。この地域は山間地のため標準テレビ放送の電波が届きにくいため、市が各家庭にケーブルテレビを提供した結果、ケーブルテレビの普及率はほぼ100%となっています。
- 地方の民間企業はすぐに収益性を達成するのが難しいかもしれませんが、地方自治体や省庁と協力することで斬新なアイデアが実現できる可能性があります。さらに、デジタル化は日本においては、たとえ地方であっても新しいものではありません。経済産業省(METI)の報告書によると、総務省の地域IoT推進研究所プロジェクトは、2016年の開始以来、日本全国105地域の研究所を表彰し、最も優れた新しいIoTソリューションや優れたソリューションを表彰してきました。企業に指導者を派遣し、地域のプロジェクトやベンチャーの繁栄と発展を支援します。
日本通信業界の概要
日本の通信市場は本質的に非常に細分化されています。市場の主要企業としては、日本電信電話株式会社、KDDI株式会社、ソフトバンクグループ株式会社、楽天モバイル株式会社、インターネットイニシアティブ株式会社などが挙げられます。この市場には、他のインターネットサービスプロバイダー(ISP)、MVNO、固定電話会社もホストしています。日本の通信会社の中には、国際的に非常に競争力があり、世界の通信分野で強い地位を築いているところもあります。
- 2022年 1月、NTTコミュニケーションズ株式会社(NTT Com)は、スマートデータプラットフォーム上で、統合運用(SDPF)を備えたエッジコンピューティングソリューションである「SDPF Edge」の即時開始を発表しました。主に製造部門にサービスを提供する新しいSDPFエッジサービスの助けを借りて、企業は大量の生産データを処理して品質管理を維持し、より迅速かつ安価に選択を行うことができます。
- 2022年 2月、KDDIはサムスンおよび富士通とともに、仮想化無線アクセスネットワーク(vRAN)を活用した世界初の5GスタンドアロンオープンRANサイトが神奈川県川崎市でオンラインになると発表しました。 Open RANとvRANにより、これが5G SAの最初の商用展開となりました。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3か月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場洞察
- 市場概要
- 業界エコシステム分析
- 業界の魅力-ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 消費者の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替製品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の激しさ
- 新型コロナウイルス感染症(COVID-19)が業界エコシステムに与える影響
- 国内の規制状況
第5章 市場力学
- 市場促進要因
- 5Gデバイスの普及と市場拡大の加速
- リモートワークの継続
- 市場抑制要因
- 競合に対する懸念
- 接続性に基づいた市場分析(詳細な動向分析を含むカバレッジ)
- 固定ネットワーク
- ブロードバンド(ケーブルモデム、有線ファイバー、有線DSL、固定Wi-Fi)、ADSL/VDSL、FTTP/B、ケーブルモデム、FWA、5G FWAの動向
- ナローバンド
- モバイルネットワーク
- スマートフォンとモバイルの普及
- モバイルブロードバンド
- 2G、3G、4G、5G接続
- スマートホーム、IoT、M2M接続
- 固定ネットワーク
- 通信塔の分析(格子塔、支線塔、モノポール塔、ステルス塔など、さまざまな種類の塔の詳細な傾向分析を含む)
第6章 市場セグメンテーション
- サービス別のセグメンテーション(サービスセグメント全体のユーザーあたりの平均収益、2020年~2027年の期間の各セグメントの市場規模と推定、および詳細な傾向分析を含む範囲)
- 音声サービス
- 有線
- 無線
- データおよびメッセージングサービス(インターネットおよび携帯電話のデータパッケージ、パッケージ割引を含む範囲)
- OTTおよび有料テレビサービス
- 音声サービス
第7章 競合情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation
- KDDI Corporation
- SoftBank Group Corp.
- Rakuten Mobile, Inc.
- Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- JSAT Corporation
- TOKAI Communications Corporation
- Wowow Inc.
- Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- Z Holdings Corporation
第8章 投資分析
第9章 市場機会と将来の動向
The Japan Telecom Market size is estimated at USD 117.84 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 149.82 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 4.92% during the forecast period (2024-2029).

Japan has a highly developed infrastructure that allows its people to be constantly connected. Along with having a high internet penetration rate, Japan has a sizable mobile internet user base, which reflects the rising popularity of smartphones. Though the smartphone adoption rate is strong, more individuals are anticipated to utilize smartphones in the years to come.
Key Highlights
- In Japan, the Telecommunications Business Law was changed in October 2019 to encourage competition in the mobile sector and safeguard users. Since then, there have been conversations about reducing mobile phone fees to lessen the load on users. The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications unveiled an action plan to lower mobile phone costs by creating a fair and competitive mobile market. By March 2021, all MNO companies introduced new, less-priced brands and pricing schemes, some of which included 20 GB of data.
- It might take a decade for 6G telecommunications to reach its full potential, but Japan is already establishing its own domestic network and technology foundation. The Japanese government plans to invest billions of dollars in promoting the development of ultra-high-speed communication. Japanese equipment manufacturers NEC and Fujitsu, as well as Finnish equipment manufacturer Nokia, announced plans to conduct experimental trials of new mobile communications technologies for the targeted commercial launch of 6G services by 2030.
- Though system and protocol evolution continued due to the Internet, the development of mobile networks was constrained by closed cultures and proprietary technologies for a very long time. Mobile networks must be able to offer modification and dynamic set up on the spot to be essential infrastructure for many different sectors. By integrating RESTful (Representational State Transfer) application programming interfaces (APIs), SoftBank tailors and modifies its network to meet the needs of consumers and offer more convenient services.
- The COVID-19 outbreak significantly impacted the Japanese economy. The adoption of digital technology was essential for the nation to become more resilient during and after the pandemic. Technology applications can help businesses and their employees manage the financial effects of COVID-19 by assisting them in contacting clients and conducting business digitally, restarting business operations, and implementing technologies that reduce logistical bottlenecks. A sizable 69% of Japan's digital opportunity, valued at JPY 46.8 trillion (USD 434 billion), was thought to be sourced from technology that assists companies and employees in managing the effects of the pandemic on the economy.
Japan Telecom Market Trends
5G Rollouts
- According to a GSMA report, Japan allows operators to mount 5G base stations atop traffic signals, accelerating 5G deployments nationwide. 21 higher-capacity use cases can flourish when tiny cells are put into place, and network density is raised. The connection penetration in Japan is expected to rise from 153% in 2021 to 154% in 2022. The projected increase in smartphone adoption rate is from 71% in 2021 to 81% in 2025. Subscriber penetration in Japan is also expected to rise from 87% in 2021 to 88% in 2025.
- Given the price reductions and the availability of the iPhone 12 and 13 in stores, the prospects for 5G adoption in the nation seem more promising. Recently, the Japanese government granted the 5G spectrum to the country's top three mobile providers, NTT Docomo, KDDI au, Softbank, and a recent entrant, Rakuten Mobile. Over the following years, these four Japanese carriers are anticipated to invest more than USD 14 billion in capital projects, including base stations, servers, and fiber optics. According to Fitch Research, by 2026, 5G will overtake 4G as the primary cellular technology in Japan, and by 2029 there will be around 45 million 4G subscribers and more than 151 million 5G subscribers.
- According to the local press, Japanese carrier, NTT Docomo, plans to quicken the speed of its 5G rollout nationwide while competitors do the same. The same article claims that NTT Docomo plans to provide coverage to 90% of the Japanese population, up from its earlier target of 80%, by March 2024. In September 2022 NTT Docomo claimed to have the world's first commercial 5G Standalone (SA) network that enables smartphones to simultaneously use mid-band (sub-6 GHz) and mmWave frequencies, known as 5G NR Dual Connectivity. The announcement was made with wireless technology company Qualcomm, which was keen to showcase that smartphones powered by its Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 platform can exploit the full speed of the new network.
- Japanese customers have access to a wide range of mmWave devices, including high-end smartphones from Samsung, Sony, Sharp, Fujitsu, and Google, and significant carrier momentum for the technology. Other OEMs, including those from lower tiers, are expected to introduce mmWave smartphones in Japan in the coming months.
- In May 2022, SoftBank Corp. declared beginning the statewide deployment of MEC servers in Japan and launching a 5G MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) site in the Kanto area. Using 5G SA (5G Stand Alone) commercial services, SoftBank 5G MEC offers low-latency, high-quality (low-jitter), and highly secure service experience. By encouraging the digital transformation (DX) of various businesses and achieving Digital Twin*2, SoftBank is expected to address societal concerns and advance the industry as a digital platform provider in the Beyond 5G future.
Digital Transformation Initiatives
- Digital transformation is one of the trends that the COVID-19 crisis has most visibly hastened (DX). This abrupt change can improve business and organization operations and have a wide range of positive effects on people's lives. In metropolitan regions throughout the world, 76% of people had internet access in 2020, compared to 39% in rural areas, according to research by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). With the lofty objective of creating a "New Form of Capitalism" that would be both people- and sustainability-focused, Japan has positioned DX as a key component of its initiatives for a virtuous cycle of growth and distribution.
- Private businesses in rural locations may find it difficult to reach profitability quickly, but collaboration with regional authorities and ministries may be able to make novel ideas workable. Additionally, digitalization is nothing new in Japan, not even in rural regions. Since its inception in 2016, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication's Local IoT Acceleration Laboratories project has recognized labs in 105 areas around Japan, awarded the finest new IoT solutions and enterprises, and sent mentors to help regional projects and ventures flourish and take off.
- Large Japanese firms host Open Innovation conferences and business competitions to foster innovation by employing other organizations' technology, concepts, assets, and resources. Open innovation is still not as prevalent in Japan as it is in other countries, but it is becoming more common among major Japanese corporations, and it is growing. Over the past several years, numerous open innovation initiatives and business competitions have been held in various sectors. For example, NTTData Open Innovation for the telecom sector.
- Ina City introduced a "Mutual Support Shopping Service" in August 2020, which is Japan's first drone-delivered shopping service for residents who pay a monthly subscription fee. The service is delivered via cable TV and was developed in collaboration with the telecom company KDDI Corp. Customers can use the TV remote control to place orders and pay their cable bill. As a result of the city providing cable TV to households due to poor signal reception for standard television broadcasts due to the area's mountainous terrain, cable TV has almost 100% penetration.
- Private businesses in rural locations may find it difficult to reach profitability quickly, but collaboration with regional authorities and ministries may make novel ideas workable. Additionally, digitalization is nothing new in Japan, not even in rural areas. As per the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) report, since its inception in 2016, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication's Local IoT Acceleration Laboratories project has recognized labs in 105 regions around Japan, awarded the finest new IoT solutions and enterprises, and sent mentors to help regional projects and ventures flourish and take off.
Japan Telecom Industry Overview
The Japanese telecom market is highly fragmented in nature. Some major players in the market include Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation, KDDI Corporation., SoftBank Group Corp., Rakuten Mobile, Inc, and Internet Initiative Japan, Inc. The market also hosts other Internet service providers (ISPs), MVNOs, and fixed-line service providers. Some Japanese telecommunication companies are very competitive internationally and hold strong ground in the global telecom space.
- In January 2022, on its Smart Data Platform, NTT Communications Corporation (NTT Com) announced the immediate launch of "SDPF Edge," an edge-computing solution with integrated operations (SDPF). With the help of the new SDPF Edge service, which primarily serves the manufacturing sector, companies may process massive volumes of production data to maintain quality control and make choices more quickly and inexpensively.
- In February 2022, KDDI, along with Samsung and Fujitsu, announced the world's first 5G Standalone Open RAN site, powered by a virtualized Radio Access Network (vRAN), will go online in Kawasaki, Kanagawa. With Open RAN and vRAN, this happened to be the first commercial deployment of 5G SA.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Ecosystem Analysis
- 4.3 Industry Attractiveness-Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 4.3.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.3.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.3.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.3.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.3.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.4 Impact of COVID-19 on the Industry Ecosystem
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape in the Country
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 5G Device Penetration and Accelerated Expansion of Market
- 5.1.2 Continuation of Remote Work
- 5.2 Market Restrains
- 5.2.1 Concerns on Competition
- 5.3 Analysis of the Market based on Connectivity (Coverage to include In-depth Trend Analysis)
- 5.3.1 Fixed Network
- 5.3.1.1 Broadband (Cable modem, wireline-fiber, wireline DSL, fixed Wi-Fi ), Trends regarding ADSL/VDSL, FTTP/B, cable modem, FWA, and 5G FWA )
- 5.3.1.2 Narrowband
- 5.3.2 Mobile Network
- 5.3.2.1 Smartphone and Mobile Penetration
- 5.3.2.2 Mobile Broadband
- 5.3.2.3 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G connections
- 5.3.2.4 Smart Home, IoT, and M2M connections
- 5.3.1 Fixed Network
- 5.4 Analysis of Telecom Towers (Coverage to include in-depth trend analysis of various types of towers, like, lattice, guyed, monopole, and stealth towers)
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 Segmentation by Services (Coverage to include Average Revenue Per User for the overall Services segment, Market size and Estimates for each segment for the period of 2020-2027 and in-depth Trend Analysis)
- 6.1.1 Voice Services
- 6.1.1.1 Wired
- 6.1.1.2 Wireless
- 6.1.2 Data and Messaging Services (Coverage to include Internet & Handset Data packages, Package Discounts)
- 6.1.3 OTT and Pay-tv Services
- 6.1.1 Voice Services
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation
- 7.1.2 KDDI Corporation
- 7.1.3 SoftBank Group Corp.
- 7.1.4 Rakuten Mobile, Inc.
- 7.1.5 Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- 7.1.6 JSAT Corporation
- 7.1.7 TOKAI Communications Corporation
- 7.1.8 Wowow Inc.
- 7.1.9 Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- 7.1.10 Z Holdings Corporation