|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1623613
製造市場の未来:デジタルファクトリー、マイクロファクトリー、ギガファクトリー、テクノロジー、デザイン、サイバーセキュリティ - 地域別(2030年までの予測)Future of Manufacturing Market by Digital Factory, Micro Factory, Giga Factory, Technology, Design, Cybersecurity - Global Forecast to 2030 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 製造市場の未来:デジタルファクトリー、マイクロファクトリー、ギガファクトリー、テクノロジー、デザイン、サイバーセキュリティ - 地域別(2030年までの予測) |
|
出版日: 2024年12月13日
発行: MarketsandMarkets
ページ情報: 英文 110 Pages
納期: 即納可能
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
コボットは、より柔軟で効率的な、人間中心の生産環境を可能にするため、製造業の様相を変えつつあります。
産業用ロボットとは異なり、コボットは人間のオペレーターと一緒に安全に作業できるように設計されており、反復的な作業や肉体的に負荷のかかる作業を支援します。このコラボレーションにより、作業者はイノベーションを推進する、より複雑な作業に集中できるようになり、生産性が向上します。コボットはプログラミングと再構成が便利で、多品種少量生産産業に最適であるため、小規模な製造業者がコボットで自動化に着手できるようにすることで、自動化の障壁を下げることができます。コボットには優れたセンサーが搭載されており、事故の際に動きを止めたり遅くしたりしても安全であるため、より調和のとれた作業空間が実現します。人間の創造性とロボットの精度の融合であるコボットを導入することで、製造業はより機敏になり、変化する世界の需要に対応するため、より弾力的で応答性の高い製造風景が形成されるとみられています。
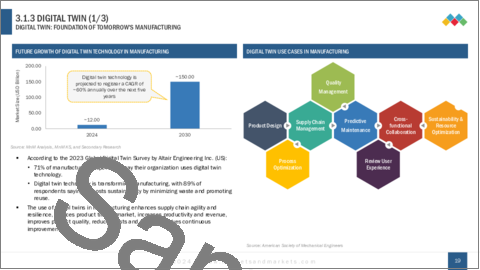
デジタルツインテクノロジーは、生産性の向上と持続可能な開発に焦点を当てた製造システムの革新により、製造業の変革に重要な役割を果たしています。 Altair Engineeringが実施した製造業を対象とした最新の世界デジタルツインサーベイによると、製造業の71%がデジタルツイン技術のコンセプトを活用し、業務変革の効果を理解していることが明らかになっています。テクノロジーの活用は、サプライチェーンの効率を高め、製品を市場に投入するまでの時間を短縮し、資源の浪費や社会的責任をリスクにさらすことなく品質を高めることに浸透しています。例えば、Boeingは製品の設計とテストにデジタルツインを適用し、さらに製品のメンテナンスにも適用することで、組み立て時間とメンテナンスコストを削減し、エラーの発生確率を改善しています。BMWはデジタルツインテクノロジーを使って、自動車の性能と安全性を統合的に再現し、開発し、最適化しています。米国は半導体製造のデジタル・ツインに資金を投入し、英国は国家デジタル・ツイン・センターを設立するなど、政府もデジタル・ツインを採用しています。BMWとDassault Systemes、LG Innotek、NVIDIAの組み合わせは、工場フロアのスマート化とデジタルトランスフォーメーションを推進するために、デジタルツインを他の産業にも応用しようとしています。
IoTとエッジコンピューティングは、生産者が常に機器の状態や使用状況、潜在的な問題を追跡・分析できるようにすることで、製造業の状況を急速に変えつつある革新的なソリューションです。このようなリアルタイムのデータ収集は、予後診断と予防保全の基礎となり、設備全体のダウンタイムを大幅に減らし、機械の耐久性を長くします。調査によると、スマートコンポーネントをソリューションとして使用することで、エネルギー効率と製造全般の効率を高めながら、機器の故障を70%、メンテナンス費用を25%削減することができます。例えば、イタリアのセメント会社Armal S.p.A.は、IoTを通じて機械のエネルギー支出を追跡することで、エネルギーコストを40%削減することに成功しました。例えば、Hersheyは、製造用のIoTセンサーによって、14,000ガロンのバッチあたりのキャンディ・サイズが1%小さくなるごとに、50万米ドルのコスト削減を実現しました。これらのイノベーションは、スマートで最適化された製造環境への道を世界的に開いています。
当レポートでは、世界の製造市場について調査し、主要な技術と動向、地域別情勢、2030年以降の見通しなどをまとめています。
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第2章 製造業の進化
第3章 製造業の未来を形作る主要な技術と動向
- デジタルファクトリー
- 製造業におけるAI
- IoTとエッジコンピューティング
- 付加製造
- デジタルツイン
- クラウド製造と分散型製造
- AR/VR
- 量子コンピューティング
- ブロックチェーン
- 接続性(5Gおよび6G)
- マイクロファクトリー
- ギガファクトリー
- 協働ロボット(コボット)
第4章 製造業の未来:特徴の定義
第5章 2030年の世界の製造業の情勢
- 北米
- 欧州
- アジア太平洋
- インド
- その他の地域
第6章 主な課題とリスク
- スマートファクトリーにおけるサイバーセキュリティの脅威
- 技術革新への対応における課題
第7章 結論:2030年以降の製造業のビジョン
List of Tables
_
List of Figures
_
Cobots are changing the face of manufacturing as they allow more flexible, efficient, and human-centric production environments. Unlike industrial robots, cobots are designed to safely work alongside human operators, helping with repetitive or physically demanding tasks. This collaboration boosts productivity by allowing workers to focus on more complex tasks that drive innovation. Since programming and reconfiguration are convenient for cobots and perfect for high-mix and low-volume industries, they lower the barriers of automation by letting smaller manufacturers take off on automation with them. They have superior sensors, making it safe to stop or slow movement for accidents, thus making for a more harmonious working space. Manufacturing will be more agile as they implement cobots, a blend of human creativity and robotic precision, to shape a more resilient and responsive manufacturing landscape to meet the changing global demands.
"Digital Twins are Driving the Future of Manufacturing by Enhancing Efficiency and Innovation"
Digital twin technology plays a vital role in the transformation of the manufacturing by innovating its manufacturing systems towards increased productivity and a focused orientation to sustainable development. The latest survey of the manufacturers conducted by Altair Engineering on the Global Digital Twin Survey revealed that 71% of the manufacturers are using the concept of digital twin technology with an understanding of the effect of transforming their operations. The use of technology is prevalent in increasing supply chain efficiency, decreasing the time to introduce products in the market, and enhancing their quality without risking the waste of resources and social responsibility. For instance, Boeing applies digital twins in product design and testing, in addition to its application in product maintenance, to lower assembly time and maintenance costs and improve the probability of errors. BMW uses digital twin technology to replicate, develop, and optimize the instantiation of cars with respect to their integrated performance and safety. They are also being adopted by governments, with the US putting money towards a semiconductor manufacturing digital twin and the United Kingdom creating a national digital twin center. A BMW- Dassault Systemes, LG Innotek, and NVIDIA combination is taking digital twins into other industries to make its industrial application more fatal to smartening factory floors and driving digital transformation.
"Transforming Manufacturing with IoT and Edge Computing Innovations"
IoT and edge computing are innovative solutions that are rapidly changing the landscape of the manufacturing by allowing producers always to track and analyze the status of the equipment and its usage as well as potential problems. Such real-time data collection is the basis of prognostics and preventative maintenance, vastly decreasing overall equipment downtime and lengthening the machines' durability. Based on research, using smart components as a solution can help companies decrease equipment failures by 70% and maintenance expenses by 25% while enhancing energy efficiency and all-around manufacturing effectiveness. For example, the Italian cement company Armal S.p.A., through IoT, managed to cut energy costs by 40 percent by tracking the energy spending of the machinery. For instance, Hershey realized cost savings of USD 0.5 million for every 1% decrease in candy size per 14,000-gallon batch through IoT sensors for production. These innovations are paving the way for smart and optimized manufacturing environments globally.
"North America is revolutionizing its manufacturing sector by embracing advanced technologies"
The manufacturing industry in North America is experiencing a special dynamic shift, predicting continued production dominance through the year 2030. The US, Canada, and Mexico are now focusing on manufacturing with innovative technologies and using sustainable resources to construct factories. Major improvements are noted in using various smart technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and digital twins. US Departments of Defense and Energy are funding AI projects that involve research into semiconductor material and improving the application of digital twins in manufacturing. On the other hand, Canada has been funding projects promoting new types of jobs - accelerating the industrial development of the manufacturing sector and promoting a more diverse population in the region's work market. These efforts are critical in building the strength of the region's manufacturing base and its sustainable and innovative future industry.
Research Coverage:
This report examines the future of manufacturing and considers what could happen in terms of advancing automation, smart factory capability, industrial hubs, and more sustainable manufacturing practices. Such an analysis would provide a forward-looking outlook for industry participants navigating the evolving landscape marked by technological innovation and environmental responsibility.
Report Scope
This report insightfully analyzes the transformation trends that will transform manufacturing beyond recognition. Major focus areas are integrating cognitive and immersive technologies, smart and sustainable factories, interconnected manufacturing hubs, innovative approaches toward operational efficiency, revenue diversification, improved production capabilities, and how manufacturing will support the circular economy. Such insights are invaluable for manufacturers, investors, technology providers, and policy-makers seeking to secure competitive advantage while keeping their strategies aligned with future developments in the industry.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
2 EVOLUTION OF MANUFACTURING
- 2.1 HISTORICAL CONTEXT: FROM INDUSTRY 1.0 TO 5.0
- 2.2 KEY DRIVERS SHAPING FUTURE OF MANUFACTURING
3 KEY TECHNOLOGIES AND TRENDS SHAPING FUTURE OF MANUFACTURING
- 3.1 DIGITAL FACTORY
- 3.1.1 AI IN MANUFACTURING
- 3.1.2 IOT AND EDGE COMPUTING
- 3.1.3 ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
- 3.1.4 DIGITAL TWIN
- 3.1.5 CLOUD MANUFACTURING AND DECENTRALIZED MANUFACTURING
- 3.1.6 AR/VR
- 3.1.7 QUANTUM COMPUTING
- 3.1.8 BLOCKCHAIN
- 3.1.9 CONNECTIVITY (5G & 6G)
- 3.2 MICROFACTORIES
- 3.3 GIGAFACTORIES
- 3.4 COLLABORATIVE ROBOTS (COBOTS)
4 FUTURE OF MANUFACTURING: DEFINING CHARACTERISTICS
- 4.1 DATA-DRIVEN DECISION-MAKING
- 4.2 INTEROPERABILITY AND SYSTEM INTEGRATION
- 4.3 CYBERSECURITY AND RESILIENCE IN SMART FACTORIES
- 4.4 FOCUS ON SUSTAINABILITY
5 GLOBAL LANDSCAPE OF MANUFACTURING IN 2030
- 5.1 NORTH AMERICA
- 5.2 EUROPE
- 5.3 ASIA PACIFIC
- 5.3.1 INDIA
- 5.3.1.1 Emerging Markets in India
- 5.3.1.1.1 Semiconductor
- 5.3.1.1.2 Gigafactories
- 5.3.1.1.3 Defense and Aviation
- 5.3.1.1.4 Data Centers
- 5.3.1.1 Emerging Markets in India
- 5.3.1 INDIA
- 5.4 REST OF THE WORLD
6 KEY CHALLENGES AND RISKS
- 6.1 CYBERSECURITY THREATS IN SMART FACTORIES
- 6.2 CHALLENGES OF MANAGING TECHNOLOGICAL DISRUPTIONS