|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1803889
自律システム向けイメージングレーダーの特許情勢の分析(2025年)Imaging Radar for Autonomous Systems Patent Landscape Analysis 2025 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 自律システム向けイメージングレーダーの特許情勢の分析(2025年) |
|
出版日: 2025年09月03日
発行: KnowMade
ページ情報: 英文 PDF>150 slides, Excel File >10,600 Patent Families
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
高解像度自律性の中核的な促進要因、イメージングレーダー
イメージングレーダーは、基本的な範囲と速度の測定しかできない従来のレーダーの限界を克服するために設計された、次世代のレーダーセンシング技術です。範囲、速度、方位角、仰角を同時に取得することで、イメージングレーダーは高解像度の3D/4D認識を実現します。これらの高密度なレーダー点群により、物体の分類、フリースペースの検出、マッピング、シーンの再構築などの先進の認識機能が可能になります。悪天候、低照度、複雑な操作環境下での堅牢性により、イメージングレーダーは安全で信頼性の高い自律システムの基礎となりつつあります。その展開は、ADAS、L2-L4自動運転、ロボタクシープラットフォームなどの陸上モビリティから、空中ドローン、海洋船舶、ロボティクス、宇宙、防衛用途にまで及びます。特許活動の急速な加速は、この勢いを反映しています。世界中で10,600を超える特許ファミリー(発明)に分類された2万2,200件を超える特許出願が確認されており、その中にはイメージングレーダー領域との関連性が高い2,800件を超えるコア特許ファミリーが含まれています。この強力な知的財産(IP)の力学は、イメージングレーダーが補完的なセンサーから第一の認識モダリティへと移行しつつあり、自律性の未来を形成し、先進のセンシングにおいてもっとも競争力のあるIP戦場の1つを牽引していることを示しています。
世界のIP動向と戦略的企業
イメージングレーダーの特許情勢は、かつてない加速を経験しています。2015年~2024年、イメージングレーダー特許ファミリーの公開件数は145件から1,790件へと1,100%超増加し、CAGRは32%で、爆発的なイノベーションの時代を迎えています。この急増は、4Dイメージングレーダー、AIによる認識、マルチセンサーフュージョンへの技術的移行を反映しています。米国と中国がこの分野を席巻しており、合わせて世界の出願件数の過半を占めている一方、欧州はBosch、ZF、ValeoなどのTier-1サプライヤーを通じて強力な地位を維持しています。Intel-Mobileye、Bosch、General Motors、Alphabet - Waymo、Huawei-Yinwang、Magnaなどの既存企業は、レーダーハードウェア、認識ソフトウェア、センサーフュージョンにまたがる多様な特許ポートフォリオを保有しています。同時に、Arbe Robotics、Uhnder、Aptiv、Metawaveなどの専門イノベーターは、4Dレーダーチップセット、点群処理、リアルタイム環境認識で的を絞ったポートフォリオを構築しています。Xidian University、UESTC、BUAA、AIRCASをはじめとする学術機関は、波形、アンテナ設計、ビームフォーミングにおける基礎的な技術革新を形成し続けています。産業界のリーダー、スタートアップ、研究機関のこの複雑な相互作用は、先進のセンシングにおけるもっとも競争力のあるIP領域の1つを定義しています。
用途と技術層にわたるIPイノベーション
イメージングレーダーの特許は、陸上、航空、海上、宇宙、ロボティクス、防衛の6つの主な応用領域に分類されています。さらに、特許情勢は、波形設計やシステムプラットフォームから校正、認識、センサーフュージョンに至るまで11の主な実現技術を包含する5つの技術層に構造化されています。当社の分析によれば、陸上モビリティは、ADAS、レベル2~レベル4の自律性、ロボットタクシーの展開により、もっとも活発で技術的に進んだ分野です。UAVナビゲーション、海上センシング、防衛用途などの他の領域も拡大しています。技術スタック全体では、技術革新はFMCWやMIMO信号処理からAIで強化された認識やマルチセンサーフュージョンへと広がり、次世代の自律性におけるイメージングレーダーの中心的役割を強く示しています。
当レポートでは、世界の自律システム向けイメージングレーダー産業について調査分析し、1万600件を超える特許のExcelデータベースに加え、世界の特許動向の解説や、主要企業のIPプロファイルなどを提供しています。
当レポートで取り上げる企業(抜粋)
|
|
など。
目次
イントロダクション
エグゼクティブサマリー
特許情勢の概要
- IP力学
- 特許公開の推移:国別
- 主な特許権者(特許ファミリー数、特許出願数、コア発明数別。類型別、法的地位別、国内/グローバルIP戦略別などに分類)
- IP企業のタイムライン
- 特許権者のIPリーダーシップ
- 主要企業の特許の地理的範囲
- 付与された特許ポートフォリオの影響力の大きい特許権者
- IPエコシステム
- サブブランドと内部部門
- ジョイントベンチャー - IP共同所有モデル
- 買収関連企業
- 主な共同所有IP
特許のセグメンテーション
- セグメントの定義
- 特許のセグメンテーション - 用途
- セグメンテーションの概要(特許ファミリー数、アクティブな特許権者数、主な特許権者、IP新規参入者、その他)
- 各セグメント(陸上、航空、ロボティクス、宇宙、海上、防衛)について
- 特許ポートフォリオの概要(IP力学、地理的範囲など)
- 特許権者のIPリーダーシップ
- 注目すべき特許
- 陸上用途の主な特許権者のランキング
- 特許のセグメンテーション - 技術
- セグメンテーションの概要(特許ファミリー数、アクティブな特許権者数、主な特許権者、IP新規参入者など)
- 各セグメント(11の技術で構成される5つの技術層)について
- イメージングレーダーの各技術の導入
- 特許ポートフォリオの概要(IP力学、地理的範囲など)
- 注目すべき特許
- 4Dイメージングレーダーの特許権者のIPリーダーシップ
特許権者のIPプロファイル
- General Motors、Intel - Mobileye、Bosch、Huawei -Yinwang、Magna、Alphabet - Waymo
- 各企業について
- 特許ポートフォリオの概要(IP力学、セグメント、法的ステータス、地理的範囲、引用、特許ファミリー拡張比率、その他)
- 注目すべき特許
- 注目すべき出願中の特許
- 各企業について
特許訴訟
付録
KnowMadeのプレゼンテーション
The global IP battlefield is heating up: who are the key players, and which technologies will shape the future of imaging radar for autonomous mobility?
Key features:
- PDF >150 slides
- Excel database containing all patents analyzed in the report (>10,600 patent families), including patent segmentations and hyperlinks to an updated online database.
- Global patenting trends, including time evolution of patent publications, countries of patent filings, etc.
- Main patent assignees and IP newcomers in the different segments.
- Key players' IP position and the relative strength of their patent portfolio.
- IP ecosystems including sub-brands, JV with shared IP ownership, main co-owned IP, etc.
- Patents categorized by 6 application domains (terrestrial, aerial, robotics, space, marine, defense) and 5 technology layers comprising 11 techniques (FMCW, MIMO, Beamforming, 4D imaging radar, SAR, ISAR, calibration, point cloud, SLAM, tracking, AI and sensor fusion), with a focus on terrestrial applications and 4D imaging radar.
- IP profile of key players (patent portfolio overview, technical coverage, geographical coverage, notable granted and pending patents, etc.)
Imaging Radar A Core Driver of High-Resolution Autonomy
Imaging radar represents the next generation of radar sensing technologies, designed to overcome the limitations of conventional radars that provide only basic range and velocity measurements. By simultaneously capturing range, velocity, azimuth and elevation, imaging radar produces high-resolution 3D/4D perception. These dense radar point clouds enable advanced perception functions including object classification, free space detection, mapping and scene reconstruction. Thanks to its robustness in adverse weather, low light and complex operating environments, imaging radar is becoming a cornerstone for safe and reliable autonomous systems. Its deployment spans terrestrial mobility such as ADAS, L2-L4 autonomous driving and robotaxi platforms, as well as aerial drones, marine vessels, robotics, space, and defense applications. The rapid acceleration of patenting activity reflects this momentum. More than 22,200 patent applications grouped into over 10,600 patent families (inventions) have been identified worldwide, including more than 2,800 core patent families that demonstrate a high degree of relevance to the imaging radar domain. This strong intellectual property (IP) dynamic demonstrates that imaging radar is transitioning from a complementary sensor to a primary perception modality, shaping the future of autonomy and driving one of the most competitive IP battlefields in advanced sensing.

Global IP Trends and Strategic Players
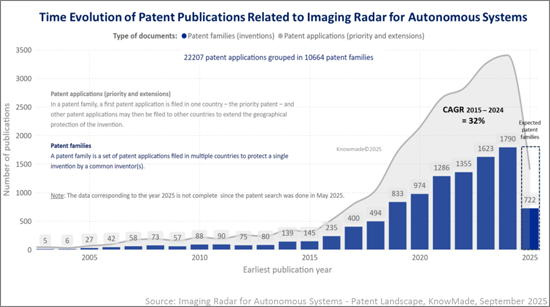
The patent landscape for imaging radar has experienced an unprecedented acceleration. From 2015 to 2024, imaging radar patent family publications grew from 145 to 1,790, an increase of over 1100% and a CAGR of 32% marking a period of explosive innovation. This surge reflects the technological transition toward 4D imaging radar, AI-driven perception and multi-sensor fusion. The United States and China dominate the field, together accounting for more than half of global filings, while Europe maintains a strong position through Tier-1 suppliers such as Bosch, ZF and Valeo. Established players including Intel-Mobileye, Bosch, General Motors, Alphabet - Waymo, Huawei-Yinwang and Magna hold diversified patent portfolios that span radar hardware, perception software and sensor fusion. At the same time, specialized innovators such as Arbe Robotics, Uhnder, Aptiv and Metawave are building targeted portfolios in 4D radar chipsets, point cloud processing and real-time environmental perception. Academic institutions, notably Xidian University, UESTC, BUAA and AIRCAS, continue to shape foundational innovation in waveforms, antenna design and beamforming. This complex interplay of industrial leaders, startups and research institutes defines one of the most competitive IP domains in advanced sensing.
IP Innovation Across Applications and Technical Layers
Imaging radar patents are classified into six main application domains: terrestrial, aerial, marine, space, robotics and defense. The patent landscape has been further structured into five technology layers encompassing 11 key enabling techniques, ranging from waveform design and system platforms to calibration, perception and sensor fusion. Our analysis indicates that terrestrial mobility is the most active and technically advanced area, driven by ADAS, Level 2 to Level 4 autonomy and robotaxi deployment. Other domains such as UAV navigation, maritime sensing and defense applications are also expanding. Across the technology stack, innovation spans from FMCW and MIMO signal processing to AI-enhanced perception and multi-sensor fusion, highlighting the central role of imaging radar in next generation autonomy.

A Competitive and Rapidly Evolving IP Landscape
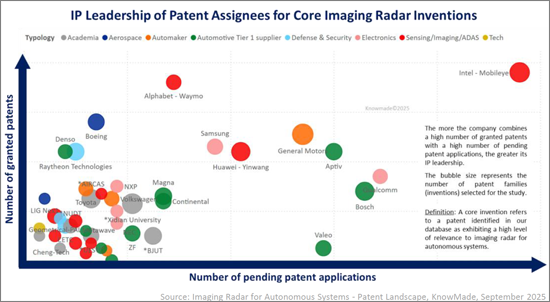
The imaging radar IP landscape is highly dynamic. Established OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers maintain strong positions, but new entrants are rapidly reshaping the field, with radar startups and ADAS suppliers particularly active. IP leadership now depends not only on the size of a portfolio but also on enforceability, geographic reach and technological impact. Companies such as GM, Intel-Mobileye, Bosch and Huawei-Yinwang combine extensive portfolios with a high volume of patent applications, while patent assignees like Arbe Robotics and Uhnder have demonstrated high IP strength and influence per patent.
In addition to individual patent portfolios, the IP ecosystem is shaped by sub-brands, joint ventures with shared IP ownership and co-owned patent families, all of which highlight the strategic role of IP in driving both competition and collaboration.
From Key Players to the Entire IP Landscape
This report provides in-depth insights into the IP strategies of the main actors shaping the imaging radar domain. It includes detailed profiles of General Motors, Intel-Mobileye, Bosch, Huawei-Yinwang, Magna and Alphabet-Waymo, covering portfolio dynamics, notable granted and pending patents, legal status and global coverage. Beyond these key players, the report delivers a comprehensive classification of all identified patent assignees including automakers, Tier-1 suppliers, sensing and ADAS companies, electronics manufacturers, technology firms, academia, and defense and aerospace players. Within each segment, we identify both the established IP leaders and the IP newcomers, providing a clear view of how innovation and competition are distributed across the ecosystem.
For executives, IP professionals and R&D teams, the report delivers a comprehensive overview of a fast-evolving and competitive technology space. By aligning patent intelligence with strategic planning, companies can strengthen their innovation roadmap, secure competitive advantage and position themselves at the forefront of autonomous mobility and advanced sensing.
Useful Excel patent database
This report includes an extensive Excel database with the 10,600+ patent families (inventions) analyzed in this study, including patent information (publication numbers, assignees, dates, title, abstract, etc.), hyperlinks to an updated online database (original documents, legal status, etc.), and structured classification by application segments (terrestrial, aerial, robotics, space, marine, and defense), five technology layers with 11 key technique segments (FMCW, MIMO, beamforming, 4D imaging radar, SAR, ISAR, calibration, point cloud, SLAM, tracking, AI and sensor fusion), as well as the identified core inventions. This database supports advanced multi-criteria searches and provides direct access to updated records, enabling users to benchmark portfolios, monitor competitors, identify potential partners or acquisition targets and evaluate freedom-to-operate constraints.
Companies mentioned in the report (non-exhaustive):
|
|
and more.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
- Context of the report
- Scope and objectives of the report
- Reading guide
- Excel database
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
PATENT LANDSCAPE OVERVIEW
- IP dynamics
- Time evolution of patent publications by countries
- Main patent assignees (according to number of patent families, number of patent applications, number of core inventions; classified by typology, by legal status, by domestic vs. global IP strategies, etc.)
- Timeline of IP players
- IP leadership of patent assignees
- Geographical coverage of main players' patents
- High-impact patent assignees for granted patent portfolios
- IP ecosystems
- Sub-brands and Internal Divisions
- Joint Ventures - Shared IP Ownership Models
- Acquisition-related Companies
- Main co-owned IP
PATENT SEGMENTATION
- Segments definition
- Patent segmentation - applications
- Segmentation overview (number of patent families, number of active patent assignees, main patent assignees, IP newcomers, etc)
- For each segment (terrestrial, aerial, robotics, space, marine, and defense):
- Patent portfolio overview (IP dynamics, geographic coverage, etc.)
- IP leadership of patent assignees
- Notable patents
- Main patent assignees ranking for terrestrial applications
- Patent segmentation - technologies
- Segmentation overview(number of patent families, number of active patent assignees, main patent assignees, IP newcomers, etc)
- For each segment (five technology layers comprising 11 techniques) :
- Introduction of each technology for imaging radar
- Patent portfolio overview (IP dynamics, geographic coverage, etc.)
- Notable patents
- IP leadership of patent assignees for 4D imaging radar
IP PROFILE OF A SELECTION OF PATENT ASSIGNEES
- General Motors, Intel - Mobileye, Bosch, Huawei -Yinwang, Magna and Alphabet - Waymo
- For each player:
- Patent portfolio overview (IP dynamics, segments, legal status, geographic coverage, citations, patent family extension ratio, etc.)
- Notable granted patents
- Notable pending patents
- For each player:
PATENT LITIGATION
ANNEX
- Methodology for patent search, selection and analysis
- Methodology to identify key patents
- Terminology