|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1429267
風力タービンブレードリサイクル市場:現状分析と予測(2023年~2030年)Wind Turbine Blade Recycling Market: Current Analysis and Forecast (2023-2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 風力タービンブレードリサイクル市場:現状分析と予測(2023年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2024年01月30日
発行: UnivDatos Market Insights Pvt Ltd
ページ情報: 英文 148 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
これらのリサイクル素材は、建設、自動車、さらには航空宇宙など、さまざまな産業で用途を見つけることができます。例えばガラス繊維は、建設プロジェクトで使用される複合材料の製造に再利用できます。炭素繊維は、自動車分野の軽量部品の製造に利用できます。風力タービンのブレードをリサイクルすることで、貴重な資源が節約され、原材料を採取する必要性が減る。
風力タービンブレードリサイクル市場はまだ発展途上であり、いくつかの課題に直面しています。廃止されたブレードから排出される廃棄物の規模が拡大しているため、効率的なリサイクル技術とインフラの開発が必要です。さらに、リサイクルのコストは輸送や処理技術などの要因によって異なるため、リサイクルの経済性も考慮しなければならないです。
ブレードの素材によって、風力タービンブレードリサイクル市場は炭素繊維とガラス繊維に二分されます。ガラス繊維セグメントは、予測される数年間において大きな需要に応えることが期待されます。ガラス繊維は、炭素繊維に比べて比較的低コストであるため、風力タービンブレードの伝統的な選択肢となっています。また、耐久性に優れ、リサイクルプロセスも広く確立されています。これらの要因から、ガラス繊維ブレードの市場シェアが大きくなっています。
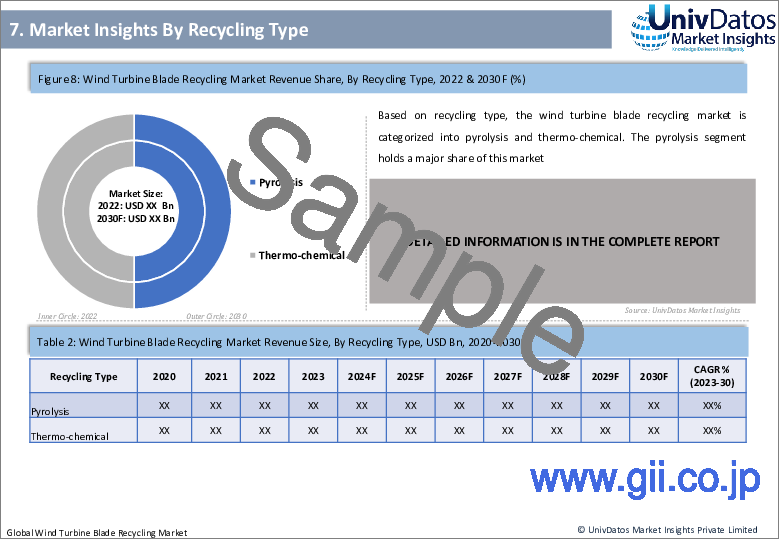
リサイクルの種類によって、風力タービンブレードリサイクル市場は熱分解と熱化学に分類されます。この市場では熱分解分野が大きなシェアを占めています。熱分解は炭素繊維のような貴重な製品別を生産する能力で知られており、一方、熱化学プロセスはより高いエネルギー回収率をもたらす可能性を秘めています。
風力タービンブレードリサイクル業界の市場導入に関する理解を深めるため、市場は北米(米国、カナダ、その他北米地域)、欧州(ドイツ、英国、フランス、スペイン、その他欧州地域)、アジア太平洋地域(中国、日本、インド、オーストラリア、その他アジア太平洋地域)、その他の地域における世界の存在に基づいて分析されています。アジア太平洋地域は、風力タービンブレードリサイクル市場において重要な需要を担っています。風力タービン設備の増加により、使用済みタービン部品、特にブレードの適切な管理の必要性が高まっています。アジア太平洋地域はこの需要を認識し、風力タービンブレードリサイクルの持続可能なソリューションの開発に積極的に取り組んでいます。さらに、風力エネルギー分野における循環型経済を強化するための取り組みも行われています。これは、新しい風力タービンブレードの製造にリサイクル材料の使用を促進することで、原材料への依存を減らし、廃棄物の発生を最小限に抑えるというものです。
目次
第1章 市場イントロダクション
- 市場の定義
- 主な目標
- ステークホルダー
- 制限事項
第2章 調査手法または前提条件
- 調査プロセス
- 調査手法
- 回答者プロファイル
第3章 市場要約
第4章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第5章 風力タービンブレードリサイクル市場収益 、2020-2030年
第6章 ブレード材料別の市場洞察
- カーボンファイバー
- グラスファイバー
第7章 リサイクルタイプ別の市場洞察
- 熱分解
- 熱化学
第8章 地域別の市場洞察
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- その他北米地域
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- スペイン
- その他欧州地域
- アジア太平洋
- 中国
- 日本
- インド
- オーストラリア
- その他アジア太平洋地域
- 世界のその他の地域
第9章 風力タービンブレードリサイクル市場力学
- 市場促進要因
- 市場の課題
- 影響分析
第10章 風力タービンブレードリサイクル市場機会
第11章 風力タービンブレードリサイクル市場動向
第12章 需要側と供給側の分析
- 需要側分析
- 供給側分析
第13章 バリューチェーン分析
第14章 競合シナリオ
- 競合情勢
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
第15章 企業プロファイル
- Siemens AG
- Acconia S.A
- Vestas Wind Systems
- Gamesa Corporacion Technologica
- EnBW
- Nordex SE
- MFG Wind
- Enercon Gmbh
- Hitachi Power Solutions
- Sinoma Wind Power Blade Co. Ltd
第16章 免責事項
The wind turbine blade recycling market refers to the industry that deals with the recycling and disposal of wind turbine blades. As wind energy becomes more popular as a renewable energy source, the number of decommissioned or damaged wind turbine blades is increasing. Proper recycling of these blades is crucial to minimize their environmental impact. Due to factors such as complex composition and dimensions, wind turbine blades cannot be easily disposed of in traditional waste management systems. This has led to the emergence of the wind turbine blade recycling market, which aims to address the challenge of recycling this large structure.
These recycled materials can find applications in various industries, such as construction, automotive, and even aerospace. Fiberglass, for instance, can be repurposed for manufacturing composite materials used in construction projects. Carbon fiber can be utilized in the production of lightweight components for the automotive sector. By recycling wind turbine blades, valuable resources are conserved, reducing the need for raw materials extraction.
The wind turbine blade recycling market is still evolving and faces some challenges. The scale of the growing waste stream from decommissioned blades requires the development of efficient recycling technologies and infrastructure. Additionally, the economic viability of recycling must be considered, as the costs of recycling can vary depending on factors such as transportation and processing techniques.
Based on the blade material, the wind turbine blade recycling market is bifurcated into carbon fiber and glass fiber. The glass fiber segment is expected to cater to significant demand in the projected years. Glass fiber has been a traditional choice for wind turbine blades due to its relatively lower cost compared to carbon fiber. It also offers good durability and has widely established recycling processes. These factors have contributed to glass fiber blades having a larger market share.
Based on recycling type, the wind turbine blade recycling market is categorized into pyrolysis and thermo-chemical. The pyrolysis segment holds a major share of this market. Pyrolysis is known for its ability to produce valuable by-products such as carbon fibers, while thermo-chemical processes have the potential to yield higher energy recovery rates.
For a better understanding of the market adoption of the wind turbine blade recycling industry, the market is analyzed based on its worldwide presence in countries such as North America (U.S., Canada, and the Rest of North America), Europe (Germany, U.K., France, Spain, Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, India, Australia, Rest of Asia-Pacific), Rest of World. Asia Pacific is indeed catering to a significant demand in the wind turbine blade recycling market. The growth of wind turbine installations has led to an increasing need for proper management of end-of-life turbine components, particularly the blades. The Asia Pacific region has recognized this demand and is actively working on developing sustainable solutions for wind turbine blade recycling. In addition, efforts are being made to enhance the circular economy in the wind energy sector. This involves promoting the use of recycled materials in the manufacturing of new wind turbine blades, thereby reducing the reliance on raw materials and minimizing waste generation.
Some of the major players operating in the market include Siemens AG, Acconia S.A, Vestas Wind Systems, Gamesa Corporacion Technologica, EnBW, Nordex SE, MFG Wind, Enercon Gmbh, Hitachi Power Solutions, and Sinoma Wind Power Blade Co. Ltd.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 MARKET INTRODUCTION
- 1.1. Market Definitions
- 1.2. Main Objective
- 1.3. Stakeholders
- 1.4. Limitation
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY OR ASSUMPTION
- 2.1. Research Process of the Wind Turbine Blade Recycling Market
- 2.2. Research Methodology of the Wind Turbine Blade Recycling Market
- 2.3. Respondent Profile
3 MARKET SYNOPSIS
4 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
5 WIND TURBINE BLADE RECYCLING MARKET REVENUE (USD BN), 2020-2030F
6 MARKET INSIGHTS BY BLADE MATERIAL
- 6.1. Carbon Fiber
- 6.2. Glass Fiber
7 MARKET INSIGHTS BY RECYCLING TYPE
- 7.1. Pyrolysis
- 7.2. Thermo-chemical
8 MARKET INSIGHTS BY REGION
- 8.1. North America
- 8.1.1. U.S.
- 8.1.2. Canada
- 8.1.3. Rest of North America
- 8.2. Europe
- 8.2.1. Germany
- 8.2.2. U.K.
- 8.2.3. France
- 8.2.4. Spain
- 8.2.5. Rest of Europe
- 8.3. Asia-Pacific
- 8.3.1. China
- 8.3.2. Japan
- 8.3.3. India
- 8.3.4. Australia
- 8.3.5. Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 8.4. Rest of World
9 WIND TURBINE BLADE RECYCLING MARKET DYNAMICS
- 9.1. Market Drivers
- 9.2. Market Challenges
- 9.3. Impact Analysis
10 WIND TURBINE BLADE RECYCLING MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
11 WIND TURBINE BLADE RECYCLING MARKET TRENDS
12 DEMAND AND SUPPLY-SIDE ANALYSIS
- 12.1. Demand Side Analysis
- 12.2. Supply Side Analysis
13 VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
14 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
- 14.1. Competitive Landscape
- 14.1.1. Porters Fiver Forces Analysis
15 COMPANY PROFILED
- 15.1. Siemens AG
- 15.2. Acconia S.A
- 15.3. Vestas Wind Systems
- 15.4. Gamesa Corporacion Technologica
- 15.5. EnBW
- 15.6. Nordex SE
- 15.7. MFG Wind
- 15.8. Enercon Gmbh
- 15.9. Hitachi Power Solutions
- 15.10. Sinoma Wind Power Blade Co. Ltd