
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1631638
アジア太平洋地域の風力タービン用ローターブレード:市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Asia Pacific Wind Turbine Rotor Blade - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| アジア太平洋地域の風力タービン用ローターブレード:市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年01月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 110 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
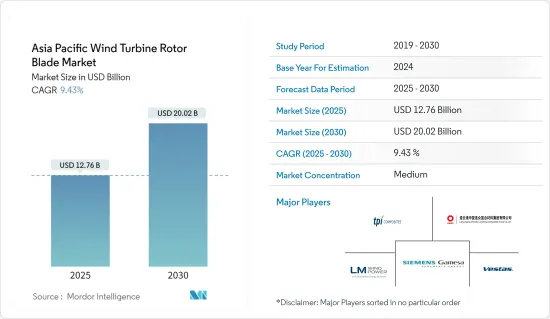
アジア太平洋地域の風力タービン用ローターブレード市場規模は2025年に127億6,000万米ドルと推定・予測され、予測期間中(2025~2030年)のCAGRは9.43%で、2030年には200億2,000万米ドルに達すると予測されます。
中期的には、風力発電コストの低下や風力発電分野への投資の増加といった要因が、予測期間中にアジア太平洋地域の風力タービン用ローターブレード市場を牽引すると予想されます。
一方、それに伴う輸送コストの高騰や、太陽光発電、水力発電などの代替クリーン電源のコスト競合といった要因は、予測期間中の市場成長を阻害する可能性を秘めています。
とはいえ、風力発電業界では費用対効果の高いソリューションが求められており、高効率の製品は業界の力学を変える可能性を秘めています。古いタービンが交換された例もあるが、これは破損が原因ではなく、より効率的なブレードが市場に出回ったためです。したがって、技術開拓は風力タービン用ローターブレード市場にとって間もなく好機となります。
予測期間中、中国はアジア太平洋地域の風力タービン用ローターブレード市場を独占すると予想されます。
アジア太平洋地域の風力タービン用ローターブレード市場動向
陸上セグメントが市場を独占
- 陸上風力発電技術は、設置されたメガワット容量あたりの発電量を最大化し、風速の低いより多くの場所をカバーするために、過去5年間で進化してきました。これに加え、近年では風力タービンの大型化が進み、ハブの高さが高く、直径が広く、風力タービンのブレードが大きくなっています。
- Global Wind Energy Council(GWEC)によると、アジア太平洋陸上風力発電市場は2022年に3,697万kWを追加し、世界の陸上風力発電設備全体の53.72%を占める。
- 中国やインドなどいくつかの主要国での投資拡大が、予測期間中の市場需要を牽引すると予想されます。中国とインドは、世界で最も急速に経済成長を遂げている国のひとつであり、そのため国内の電力消費量も大きな伸びを記録しています。
- 2021年11月のCOP26で、インド首相は、インドが2030年までに排出強度を45%以上削減し、2005年以下のレベルにする計画であることを発表し、2030年までに非化石燃料のエネルギー容量を500GW、2030年までにエネルギーミックスの50%を自然エネルギーにすると発表しました。
- 2022年1月現在、非化石燃料は発電容量全体の38.5%を占めています。風力は現在、このうち10.2%を占めています。2030年の気候変動対策の一環として、新・再生可能エネルギー省(MNRE)は140GWの風力発電容量が必要と見積もっています。
- 2022年10月、石炭省傘下の公営企業(PSU)であるNLC India Ltd.は、新・再生可能エネルギー省(MNRE)傘下の研究開発機関である国立風力エネルギー研究所(NIWE)と、インドにおける陸上風力発電プロジェクトの開発に関する戦略的協力協定を締結しました。
- インドは、2022年時点で世界第4位の陸上風力発電設備容量を保有しています。これらのプロジェクトは、主に国の北部、南部、西部に広がっています。IRENAによると、インドの総設備風力発電容量は4,193万kWで、2021年の4,006万kWに比べ4.64%増加しました。
- さらに、国際エネルギー機関(International Energy Agency)によると、平準化エネルギーコスト(LCOE)と世界加重平均総CAPEXは、2016年の76.1米ドル/MWhと1730.5米ドル/MWhから、2021年には48.2米ドル/MWhと1396.3米ドル/MWhに減少する見込みです。さらに、LCOEと平均加重 CAPEXは予測期間中に減少し、2025年にはそれぞれ44.6 USD/MWh、1338.2 USD/MWhになると予想されます。
- 陸上大型風力タービン用ローターブレード市場は、クリーンなエネルギー源による高いエネルギー需要と相まって、LCOEの低下とCAPEXの削減により、予測期間中に成長すると予想されます。
市場を独占する中国
- 中国は世界最大のエネルギー消費国であり、再生可能エネルギー市場でもあります。同国は、主に化石燃料火力発電所の排出ガスによる大気汚染に悩まされてきたため、全体の排出量を削減しながら増大するエネルギー需要を満たすため、再生可能エネルギー能力の拡大に注力してきました。
- 第14次5カ年計画(2021~2025年)の一環として、同国は2025年までに国内電力消費の33%を、水力以外の再生可能エネルギーの18%を供給することを目指しています。同国は、再生可能エネルギー発電を2030年までに3,300TWhまで増加させることを目標としています。
- 中国は、最新の国家決定貢献(NDC)において、パリ協定における約束の一環として、2030年までに排出量のピークを達成し、カーボンニュートラルを達成することを約束しています。エネルギー目標に関しては、GDP当たりのCO2排出量を2005年比で65%以上削減し、風力と太陽光の合計設置容量を1,200GWに増やすことを目標としています。
- CarbonBriefによると、同国における再生可能エネルギー産業の急速な成長に基づき、風力+太陽光発電の導入量1,200GWという目標は、2030年の期限を大幅に前倒しして達成されると推定されています。このような風力エネルギー設備容量の急速な伸びは、環境問題への取り組みによって生まれた需要の高まりによるもので、予測期間中、国内エネルギー消費の増加が風力エネルギー市場を牽引すると予想されます。
- 中国の各省は、国家目標の一部として、再生可能エネルギー・プロジェクトの個別目標を設定しています。最大の目標は、広大な砂漠地帯の存在を活用するため、北西部の内モンゴル自治区と甘粛省が設定しています。この2つの省は、2022年5月現在の設備容量74GWに加え、2025年までに累積190GWの風力・太陽光発電プロジェクトを追加する計画です。これらの省に続いて、陝西省、河北省、山東省が2021年から2025年にかけて190GWの太陽光発電と風力発電の新設を計画しています。
- GWECによると、2022年、中国の総風力発電設備容量は前年比11.5%増加しました。風力発電の総設備容量は約365.44GWでした。
- 中国の沿岸地方は、新たな洋上風力発電の開発に力を入れています。広東省は2025年までに1,800万kWの洋上風力発電設備の設置を目指しており、福建省、浙江省、江蘇省はそれぞれ2025年までに1,330万kW、600万kW、900万kWの洋上風力発電プロジェクトの設置を目指しています。
- 山東省は、2030年までに3,500万kWの洋上風力発電容量を追加する一方、2025年までに1,000万kWのプロジェクトの建設を開始し、5,000万kWを送電網に追加することを目標としています。島嶼部の海南省は、国家エネルギー局(NEA)から2025年までに1,230万kWの洋上風力発電の建設を許可されています。
- さらに2022年12月には、中国の風力タービンメーカーMingyang Smart Energyが、2021年に発表したローター直径242mの16MWモデルの高架バージョンであるMySE 16-260洋上風力タービン用に、世界最長の台風対策洋上風力タービンブレードを製造しました。
- このように、国有企業からの投資の増加と風力発電における有利な政府政策が、予測期間中の中国風力タービン用ローターブレード市場の成長を促進すると予想されます。
アジア太平洋地域の風力タービン用ローターブレード産業概要
アジア太平洋地域の風力タービン用ローターブレード市場は、適度に断片化されています。同市場の主要企業には、Lianyungang Zhongfu Lianzhong Composites Group、TPI Composites Inc.、LM Wind Power(a GE Renewable Energy Business)、Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy S.A.、Vestas Wind Systems A/Sなどがあります。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査範囲
- 市場の定義
- 調査の前提
第2章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第3章 調査手法
第4章 市場概要
- イントロダクション
- 2029年までの市場規模および需要予測(単位:米ドル)
- 最近の動向と開発
- 政府の規制と政策
- 市場力学
- 促進要因
- 風力エネルギーのコスト低下
- 風力発電プロジェクトへの投資の増加
- 抑制要因
- 代替クリーン電源の採用増加
- 促進要因
- サプライチェーン分析
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 消費者の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 展開場所別
- オンショア
- オフショア
- ブレード材料別
- 炭素繊維
- ガラス繊維
- その他のブレード材料
- 地域別
- 中国
- インド
- 韓国
- 日本
- マレーシア
- タイ
- インドネシア
- ベトナム
- その他アジア太平洋地域
第6章 競合情勢
- M&A、合弁事業、提携、協定
- 主要企業の戦略
- Companies Profiles
- TPI Composites Inc.
- Lianyungang Zhongfu Lianzhong Composites Group Co., Ltd.
- LM Wind Power(a GE Renewable Energy Business)
- Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy S.A.
- Vestas Wind Systems A/S
- Sinoma Technology Wind Power Blade Co., Ltd.
- Suzlon Energy Limited
- Nordex SE
- Enercon GmbH
- 市場ランキング/シェア分析
第7章 市場の可能性と将来の動向
- 新興市場と未開拓市場からの洋上風力エネルギーへの関心の高まり
The Asia Pacific Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Market size is estimated at USD 12.76 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 20.02 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 9.43% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Over the medium term, factors such as the declining cost of wind energy and increasing investments in the wind power sector are expected to drive the wind turbine rotor blade market in the Asia-Pacific region during the forecast period.
On the other hand, factors such as the associated high cost of transportation and cost competitiveness of alternate clean power sources like solar power, hydropower, etc., have the potential to hinder the market growth during the forecast period.
Nevertheless, the wind power industry has been in demand for cost-effective solutions, and a highly efficient product has the potential to change the dynamics of the industry. There were instances where old turbines were replaced, not because of the damage but due to the availability of more efficient blades in the market. Hence, technological developments present themselves as a good opportunity for the wind turbine rotor blade market soon.
China is expected to dominate the wind turbine rotor blade market in the Asia-Pacific region during the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Market Trends
Onshore Segment to Dominate the Market
- The onshore wind energy power generation technology has evolved over the last five years to maximize electricity produced per megawatt capacity installed and to cover more sites with lower wind speeds. Besides this, in recent years, wind turbines have become larger with taller hub heights, broader diameters, and larger wind turbine blades.
- According to the Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), the Asia-Pacific onshore wind market added 36.97 GW in 2022 and contributed 53.72% of the total global onshore wind installations in 2022.
- The growing investments in several major countries, such as China and India, are expected to drive the market demand during the forecast period. China and India are some of the fastest-growing economies in the world, and hence, they have registered significant growth in domestic power consumption.
- During COP26 in November 2021, the Prime Minister of India announced that India plans to reduce emission intensity by 45% or more by 2030, bringing it to levels below those of 2005, and announced 500 GW of non-fossil fuels energy capacity by 2030; 50% renewables in the energy mix by 2030.
- As of January 2022, non-fossil fuels represent 38.5% of overall power generation capacity. Wind currently accounts for 10.2% of this capacity. As part of its 2030 climate commitments, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) estimates 140 GW of wind energy capacity is required.
- In October 2022, the NLC India Ltd., a Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) part of the Ministry of Coal, entered into a strategic collaboration agreement with the National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE), an autonomous Research and Development institution under the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), for the development of onshore wind power projects in India.
- India holds the fourth-largest onshore wind power installed capacity globally as of 2022. These projects are majorly spread in the northern, southern, and western parts of the country. According to IRENA, India's total installed wind capacity was 41.93 GW, witnessing an increase of 4.64% compared to 40.06 GW in 2021.
- Moreover, according to the International Energy Agency, the Levelized cost of energy (LCOE) and global weighted average total CAPEX is likely to decrease from 76.1 USD/MWh and 1730.5 USD/MWh in 2016 to 48.2 USD/MWh and 1396.3 USD/MWh in 2021. In addition, the LCOE and average weighted CAPEX are expected to decrease in the forecast period to 44.6 USD/MWh and 1338.2 USD/MWh, respectively, by 2025.
- The onshore large wind turbine rotor blade market is expected to grow in the forecast period due to declining LCOE and reduced CAPEX, coupled with high energy demand through clean sources.
China to Dominate the Market
- China is the largest energy consumer and renewable energy market globally, and the country is rapidly expanding its renewable energy capacity to satiate its domestic energy demand. As the country has been suffering from air pollution caused primarily by fossil-fuel-fired power plant emissions, it has focused on expanding its renewable energy capacity to meet its growing energy demands while reducing overall emissions.
- As part of its 14th five-year plan (2021-2025), the country aims to supply 33% of national power consumption by 2025 and 18% of non-hydro renewables. The country aims to increase renewable energy generation to 3,300 TWh by 2030.
- In its latest updated Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC), China has committed to reaching peak emissions by 2030 and achieving carbon neutrality as part of its commitments under the Paris Agreement. In terms of energy targets, the country aims to cut C02 emissions per unit of GDP by more than 65% from 2005 levels and increase the total installed wind plus solar capacity to 1,200 GW.
- According to CarbonBrief, based on the rapid growth of the renewable energy industry in the country, it is estimated that China will reach its target of 1,200 GW of wind+solar deployment significantly ahead of its 2030 deadline. Such rapid growth in the installed wind energy capacity is due to the rising demand created due to environmental commitments, and the increasing domestic energy consumption is expected to drive the wind energy market during the forecast period.
- China's provinces have set up individual targets for renewable energy projects as a part of national targets. The largest targets have been set up by the northwestern provinces of Inner Mongolia and Gansu to leverage the presence of large tracts of uninhabited desert lands. These two provinces plan to add a cumulative 190 GW of wind and solar projects by 2025, in addition to the 74 GW of installed capacity as of May 2022. These provinces are followed by Shaanxi, Hebei, and Shandong, which have planned to install 190 GW of new solar and wind capacity additions during 2021-2025.
- According to GWEC, in 2022, the total wind installed capacity increased by 11.5% compared to the previous year in China. The total wind energy installed capacity accounted for about 365.44 GW.
- Coastal provinces in China have been focused on developing new offshore wind capacity. Guangdong aims to install 18 GW of offshore capacity by 2025, while Fujian, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu aim to install 13.3GW, 6GW, and 9GW of offshore wind power projects by 2025, respectively.
- Shandong aims to add 35 GW of offshore wind power capacity by 2030 while starting the construction of 10 GW of projects and adding 5 GW to the grid by 2025. The island province of Hainan has been permitted by the National Energy Administration (NEA) to build 12.3 GW of offshore wind by 2025.
- Further, in December 2022, Chinese wind turbine manufacturer Mingyang Smart Energy produced the World's Longest Anti-Typhoon Offshore Wind Turbine Blade for the MySE 16-260 offshore wind turbine, an elevated version of its 16 MW model, announced in 2021 with a 242-meter rotor diameter.
- Thus, the growing investment from state-owned companies and favorable government policies in wind energy generation are expected to drive the growth of the Chinese wind turbine rotor blade market during the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Industry Overview
The Asia-Pacific wind turbine rotor blade market is moderately fragmented. Some of the major players in the market include Lianyungang Zhongfu Lianzhong Composites Group Co., Ltd., TPI Composites Inc., LM Wind Power (a GE Renewable Energy Business), Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy S.A., and Vestas Wind Systems A/S, among others.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Market Definition
- 1.3 Study Assumptions
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Market Size and Demand Forecast in USD, till 2029
- 4.3 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.4 Government Policies and Regulations
- 4.5 Market Dynamics
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.5.1.1 Declining Cost of Wind Energy
- 4.5.1.2 Increasing Investments in Wind Energy Power Generation Projects
- 4.5.2 Restraints
- 4.5.2.1 Increasing Adoption of Alternate Clean Power Sources
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.6 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes Products and Services
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGEMENTATION
- 5.1 Location of Deployment
- 5.1.1 Onshore
- 5.1.2 Offshore
- 5.2 Blade Material
- 5.2.1 Carbon Fiber
- 5.2.2 Glass Fiber
- 5.2.3 Other Blade Materials
- 5.3 Geography
- 5.3.1 China
- 5.3.2 India
- 5.3.3 South Korea
- 5.3.4 Japan
- 5.3.5 Malaysia
- 5.3.6 Thailand
- 5.3.7 Indonesia
- 5.3.8 Vietnam
- 5.3.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers and Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Collaborations, and Agreements
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Leading Players
- 6.3 Companies Profiles
- 6.3.1 TPI Composites Inc.
- 6.3.2 Lianyungang Zhongfu Lianzhong Composites Group Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.3 LM Wind Power (a GE Renewable Energy Business)
- 6.3.4 Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy S.A.
- 6.3.5 Vestas Wind Systems A/S
- 6.3.6 Sinoma Technology Wind Power Blade Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.7 Suzlon Energy Limited
- 6.3.8 Nordex SE
- 6.3.9 Enercon GmbH
- 6.4 Market Ranking/Share Analysis
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES and FUTURE TRENDS
- 7.1 Increasing Interest in Offshore Wind Energy from Developing and Untapped Markets


