|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1377259
LNG船市場- 世界の産業規模、シェア、動向、機会、予測、2018年~2028年LNG Carrier Market - Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, 2018-2028 Segmented By Containment Type, By Storage Capacity, By Propulsion Type, By End User Industry, By Region, By Competition |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| LNG船市場- 世界の産業規模、シェア、動向、機会、予測、2018年~2028年 |
|
出版日: 2023年10月03日
発行: TechSci Research
ページ情報: 英文 190 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
LNG船の世界市場規模は2022年に100億8,000万米ドルとなり、2028年までのCAGRは6.19%で、予測期間中に力強い成長が予測されています。
LNG船市場とは、液化天然ガス(LNG)を生産・液化施設から流通ターミナルやエンドユーザーまで輸送する世界の産業を指します。LNGは世界のエネルギー貿易に不可欠な要素であり、LNG運搬船として知られる特殊な船舶は、海上でのLNGの安全かつ効率的な移動を促進する上で極めて重要な役割を果たしています。これらの運搬船は、天然ガスを液化した状態で輸送するための高度な極低温技術を備えており、極低温に冷却することで輸送をコンパクトにすることができます。LNG船市場は、これらの船舶の設計、建造、運用、保守を含む様々な側面を包含しています。市場の主な利害関係者には、LNG生産者、ターミナル・オペレーター、船会社、政府などが含まれます。市場力学は、世界のエネルギー需要のシフト、環境規制の変更、経済動向、地政学的動向などの要因によって影響を受ける。市場は、LNG需要の増加に対応し、環境問題に対処するため、船舶の設計、推進システム、安全対策、環境性能の革新によって継続的に進化しています。
まとめると、LNG船市場は世界のエネルギー情勢において極めて重要な要素であり、世界中の多様なエネルギー需要を支えるLNGの確実かつ効率的な輸送を促進しています。
| 市場概要 | |
|---|---|
| 予測期間 | 2024-2028 |
| 市場規模 | 100億8,000万米ドル |
| 2028年の市場規模 | 145億8,000万米ドル |
| CAGR 2023-2028 | 6.19% |
| 急成長セグメント | 120,000~160,000立方メートル |
| 最大市場 | アジア太平洋 |
市場促進要因
LNGインフラの拡大:
LNGインフラの拡大は、世界のLNG船市場の重要な促進要因です。LNGインフラには、液化プラント、再ガス化ターミナル、貯蔵施設、パイプラインなどが含まれます。LNGインフラの建設や拡張に投資する国が増えるにつれ、これらの施設と国際市場の間でLNGを輸送するLNG船の必要性が高まっています。多くの国が、LNG基地やLNGと天然ガスの両方を扱える基地に投資することで、エネルギー源の多様化を積極的に模索しています。この多様化戦略は、エネルギー安全保障と信頼性を高める。その結果、これらの施設内や施設間のLNGの移動を容易にするLNG運搬船の需要が高まる。
環境への懸念とLNGの役割:
温室効果ガスの排出削減や気候変動対策などの環境問題への懸念から、よりクリーンなエネルギー源へのシフトが世界的に進んでいます。LNGは、石炭や石油のような二酸化炭素排出量の多い化石燃料と比較して、二酸化炭素排出量を削減できる架け橋となる燃料と考えられています。LNGの環境面での利点は、先進経済諸国と新興経済諸国の双方にとって魅力的な選択肢となっています。LNG運搬船は、LNGの輸送を可能にし、環境目標を遵守しながら、これらの市場の増大するエネルギー需要を満たすことができます。
経済成長と工業化:
世界のLNG船市場は、特に新興市場における経済成長と工業化の影響を受けています。各国が急速な工業化と都市化を遂げるにつれ、エネルギー消費量は大幅に増加します。LNG船は、発電、工業プロセス、暖房に使用される天然ガスの供給において重要な役割を果たしています。
特にアジアは、中国やインドを筆頭に著しい経済成長を遂げています。これらの国々では、拡大する経済に燃料を供給し、増加する人口のエネルギー需要を満たすために、LNGに対する需要が高まっています。このような経済成長は、LNG輸送サービスに対する需要の増加につながるため、LNG船市場の主要な促進要因となっています。
LNG船設計の技術的進歩:
技術の進歩により、より効率的で環境に優しいLNG運搬船が開発されています。こうした技術革新には、船舶設計、推進システム、安全機能の改善が含まれます。先進材料とエンジニアリング・ソリューションの採用は、世界のエネルギー輸送市場におけるLNG船の競争力を高めています。最新のLNG船はエネルギー効率が高くなるように設計されており、燃料消費量と排出量が削減されています。さらに、LNGの安全輸送を確保するための安全対策も強化され、事故や環境事故のリスクを最小限に抑えています。こうした技術的進歩は、LNG運搬船をオペレーターにとってより魅力的なものにするだけでなく、市場全体の成長にも貢献しています。
世界のエネルギー安全保障への配慮:
エネルギー安全保障は多くの国にとって重要な関心事であり、天然ガスの供給源を多様化することは、安全保障を強化するための戦略的アプローチです。LNG船は、様々な地域からのLNG輸送を容易にすることで、この戦略において極めて重要な役割を果たしています。単一のエネルギー源や供給元への依存を減らすことで、各国はエネルギー安全保障と回復力を高めることができます。
結論として、世界のLNG船市場は、LNG需要の増加、LNGインフラの拡大、環境への配慮、経済成長と工業化、技術の進歩、世界のエネルギー安全保障への懸念によって牽引されています。これらの要因は、世界規模でのLNG船産業の継続的な成長と活性化に寄与しています。
政府政策が市場を牽引する可能性が高い
環境規制と排出基準:
世界各国の政府政策は、環境保護と温室効果ガス排出量削減にますます重点を置くようになっています。LNG船市場では、こうした政策が船舶の設計、運航、排出に大きな影響を与えます。多くの政府は、LNG船を含む海上輸送に厳しい規制と排出基準を導入しています。これらの基準は、低硫黄燃料のようなよりクリーンな燃料の使用や、排ガス浄化システム(スクラバー)のような高度な排出制御技術の採用を要求することが多いです。各国政府はまた、従来の船舶用燃料に比べて炭素や硫黄の含有量が少ないことから、船舶用燃料としてLNGの採用を奨励しています。LNGを海上燃料として促進するインセンティブ、補助金、規制は、LNGを貨物として輸送し、推進用燃料として使用する可能性のあるLNG運搬船の需要に影響を与える可能性があります。
エネルギー安全保障政策:
エネルギー安全保障は多くの政府にとって最優先事項であり、エネルギーの安定供給確保に関連する政策はLNG船市場に影響を与える可能性があります。一部の国々は、単一の供給元やエネルギー源への依存を減らすため、エネルギー源や供給ルートを多様化する戦略的計画を策定しています。LNG船は、さまざまな地域からのLNG輸入を可能にすることで、こうした戦略において重要な役割を果たしています。各国政府は、エネルギー安全保障を強化するために、LNG船だけでなく、LNG基地や関連インフラの建設・運営にもインセンティブを与えることがあります。こうした政策には、LNGの安定供給を確保するためのLNG輸出国との協定や提携がしばしば含まれます。
貿易・関税政策:
国際貿易と関税に関する政府の政策は、世界のLNG船市場に影響を与える可能性があります。貿易協定、輸出入関税、貿易障壁はLNGの流れ、ひいてはLNG船の需要に影響を与えます。LNGに関する自由貿易協定や特恵貿易条件は、国家間のLNGの移動を促進することにより、LNG船市場を刺激することができます。逆に、LNGに対する貿易制限や関税は、特定の市場でLNGの競争力を低下させることにより、市場の成長を妨げる可能性があります。
安全・セキュリティ規制:
各国政府が課す安全・保安規制は、LNG運搬船の運航や設計に大きな影響を与えます。LNGは極低温の液体であり、その輸送には特殊な安全対策が必要となります。各国政府は、LNG輸送に関連するリスクを軽減するため、LNG運搬船の建造、運航、緊急対応手順に関する厳しい規制を制定することが多いです。これらの規制は、船体設計、格納システム、緊急停止システム、乗組員の訓練などの側面を包含しています。LNG船運航に必要な許認可を得るためには、安全・保安規制の遵守が不可欠です。
インフラ開発政策:
液化プラント、再ガス化ターミナル、貯蔵施設を含むLNGインフラの開発は、政府の政策やインセンティブの影響を受けることが多いです。政府はLNGインフラへの民間部門の投資を促進するため、財政的インセンティブ、税制優遇措置、規制支援を提供することがあります。こうした政策は、LNGサプライチェーンの拡大、ひいてはLNG船需要の拡大に寄与します。整備されたインフラ・ネットワークは、LNGの安定供給と効率的な流通を保証し、LNGをターミナルと新興国市場の間で輸送するLNG船の必要性を促進します。
環境・エネルギー転換政策:
気候変動と闘い、温室効果ガスの排出を削減するための世界の取り組みに伴い、多くの政府がLNGを含むよりクリーンな燃料や技術の使用を促進する政策を実施しています。こうした政策には、排出削減目標、カーボンプライシングメカニズム、再生可能エネルギー奨励策などが含まれることが多いです。各国政府は、より厳しい排出量目標を達成するため、海運業界における過渡的燃料としてLNGの採用を奨励する可能性があります。これは、LNG船への投資や、既存船をLNGで航行できるように改造する船主の決断に影響を与える可能性があります。さらに、LNG電気やLNGと水素のハイブリッド・システムなど、LNG船によりクリーンな推進技術を開発・採用するインセンティブも、こうした政策の一部となり得る。
結論として、政府の政策は世界のLNG船市場に大きな影響を与えます。環境規制、エネルギー安全保障、貿易、安全性、インフラ整備、エネルギー転換に関する政策はすべて、LNG船の需要や業界全体のダイナミクスを形成する上で極めて重要な役割を果たしています。
主な市場課題
LNG需要と供給の不安定性:
世界のLNG船市場は、LNG需給に内在する変動性という持続的な課題に直面しています。この変動は、地政学的緊張、景気変動、各国のエネルギー政策の変更など、様々な要因の結果です。
需要の変動性:
LNGの需要は、天候パターン、経済成長、エネルギー政策などの要因に非常に影響を受けやすいです。例えば、主要輸入地域で特に寒い冬が到来すると、暖房目的のLNG需要が急増する可能性があります。逆に、暖冬であれば需要が減少することもあります。また、景気後退が産業界のエネルギー消費に影響を与え、LNG需要に影響を与えることもあります。
さらに、再生可能エネルギー源の重視やエネルギー発電方法の転換など、エネルギー政策の変化もLNG需要に影響を与える可能性があります。例えば、再生可能エネルギーの利用を奨励または義務化する政府の政策は、LNG需要を減少させる可能性があるため、船会社が市場の変化を予測し、効果的に対応することは困難です。
供給の不安定性:
LNG市場の供給サイドも同様に変動に左右されます。LNGプロジェクト、特に液化ターミナルの開発には資本集約的で時間がかかります。プロジェクトの承認、建設、試運転の遅れは、供給スケジュールを混乱させる可能性があります。さらに、予期せぬ技術的問題や自然災害がLNGの生産や輸出能力に影響を与えることもあります。
地政学的要因も供給変動の一因となります。LNG生産国や地域間の紛争は、LNGサプライチェーンの混乱につながる可能性があります。例えば、中東や南シナ海での緊張は、LNG生産や輸送ルートに影響を与え、LNG船への供給の信頼性に影響を与える可能性があります。
LNG船にとって、このような需給変動に対応することは困難であり、船舶が十分に活用されなかったり、高価な配置転換が必要になったりする可能性があります。LNG船は、短期傭船契約の締結や顧客基盤の多様化など、変化する市場環境に適応するための柔軟な戦略を策定する必要があります。
資本集約と技術の進歩:
世界のLNG船市場が直面するもう一つの重要な課題は、LNG船建造の資本集約度と業界における技術進歩の急速なペースです。
資本集約度:
LNG船の建造と運航は資本集約的な取り組みです。LNG船は、極低温・高圧でLNGを安全に輸送するための極低温タンクや高度な格納システムなど、複雑なインフラを備えた特殊な船です。これらの船舶の建造と維持には多額の費用がかかり、船主やオペレーターはしばしば多額の資金を必要とします。
さらに、LNG運搬船の大型化・高度化という業界の動向は、建造コストを上昇させています。これらの大型船はスケールメリットをもたらすが、同時に多額の先行投資を必要とします。LNG船プロジェクトの資金調達は、特に小規模な事業者や新規参入者にとって困難な場合があります。
技術の進歩:
LNG船市場は、船舶の効率性、安全性、環境性能の向上を目指した急速な技術進歩が特徴です。このような進歩は、排出ガスの削減や船舶の能力向上という点ではプラスであるが、同時に課題でもあります。
船主や運航会社は、競争力を維持し、進化する環境規制を遵守するために、既存の船隊の改造やアップグレードに継続的に投資しなければならないです。このような技術の進歩に対応し続けることは、予算を圧迫し、多大な計画と投資を必要とします。
さらに、LNG電気やLNGと水素のハイブリッドシステムなど、新しい推進技術の導入には多額の設備投資が必要であり、乗組員の訓練やメンテナンスに関する運用上の課題もあります。
結論として、世界のLNG船市場は、需要と供給の変動、船舶建造の資本集約度、急速な技術進歩に関連する課題に直面しています。こうした課題に対し、船会社は柔軟な戦略を採用し、十分な資金を確保し、進化する業界で競争力を維持するために船隊に継続的に投資する必要があります。
セグメント別の洞察
モスタイプの洞察
モス型は2022年に最大の市場シェアを占め、予測期間中もその地位を維持する見込みです。モス型封じ込めシステムは数十年にわたって使用され、その信頼性と安全性を実証してきました。この長年の実績は、LNG船の運航会社、造船会社、投資家に信頼を与えています。モス型格納容器を搭載した多くのLNG船は、安全かつ効率的に運航されており、継続的な使用に貢献しています。小型船への柔軟性モス・タイプのタンクは小型のLNG船に適しています。様々な船型やサイズに対応できるため、様々なLNG輸送ニーズに対応できます。この適応性は、多様な市場の要求に応える上で貴重なものです。堅牢な設計モス型タンクは、過酷な海洋環境に耐える球形貯蔵タンクを採用した堅牢な設計です。球体形状は応力を均等に分散し、構造の完全性と安全性を高めます。この設計上の特徴は、荒波や極端な天候などの厳しい条件下で操業するLNG船にとって特に有益です。モス・タイプ・タンクは効果的な断熱性を提供し、LNG輸送中のボイルオフ・ガス発生率を低減します。この効率は、LNGのロスを最小限に抑え、貨物の出荷量を最大化するために不可欠です。モス型タンクは、他の格納容器システムに比べ、メンテナンスや修理のためのアクセスが比較的容易です。このメンテナンスの容易さは、ダウンタイムや操業中断を減らし、コスト削減と信頼性に貢献します。LNG船は多額の投資を必要とするため、安全性と性能に定評のある技術が優先されます。モス・タイプの格納容器システムは、LNG生産者、ターミナル・オペレーター、投資家を含む多くの利害関係者から信頼を得ています。船舶のサイズや用途によっては、モス・タイプの格納容器システムは、代替システムと比較して費用対効果が高い場合があります。初期建設コストと運用コストは格納容器の選択に影響を与える要因であり、モス・タイプはこの点で競合できます。
120,000~160,000立方メートルのインサイト
120,000~160,000立方メートルのセグメントは2022年に最大の市場シェアを占め、予測期間中に急成長すると予測されます。120,000~160,000立方メートルのLNG船は汎用性が高く、多様なLNG貿易ルートやターミナル構成に適しています。大規模なLNGターミナルにも、より小規模で遠隔地のターミナルにも効率的に対応でき、多様な市場の需要に応える高い柔軟性を提供します。これらの運搬船は、貨物容量と運航効率のバランスをうまくとっています。LNG輸送の単位あたりの建設コストと運航コストにおいて、規模の経済を達成するのに十分な大きさです。同時に、小型船ほど大きさに制限がないため、大量のLNGを輸送することができます。世界中のLNGターミナルの深度制限とインフラ能力は様々です。120,000~160,000立方メートルのLNG船は通常、これらの制限を満たすように設計されているため、大きな制約を受けることなく幅広いターミナルにアクセスすることができます。これらの船は、中程度の量のLNGプロジェクトにコスト効率の良い輸送を提供します。これらの船は、小型船による高い輸送コストと、超大型船による過大になりかねないコストとのバランスをうまく取っています。このため、輸送費の最適化を目指すLNG生産者や消費者にとっては魅力的な存在となっています。多くのLNGターミナル、特に過去に建設されたターミナルは、12万~16万立方メートルのLNG船を収容できるように設計されています。この互換性により、既存のターミナルを大々的に改造する必要性が減り、LNG貿易業務の効率が向上します。歴史的に見ても、LNGプロジェクトと貿易ルートの大半は、このサイズの運搬船に適しています。市場の需要、貿易パターン、プロジェクトの可用性は、多くの場合、船腹容量の選択に影響を与えます。
.
地域別インサイト
アジア太平洋:
アジア太平洋地域は、2022年にLNG船にとって最大の市場となっています。これは、中国をはじめとする同地域の国々におけるLNG需要の拡大によるものです。中国は世界最大のLNG輸入国であり、今後もLNG輸入量の増加が見込まれます。この地域の他の主要市場には、日本、韓国、インド、インドネシアが含まれます。
欧州
2022年のLNG船市場は欧州が第2位でした。輸入石油・ガスへの依存を減らす必要性から、欧州のLNG需要は伸びています。英国は欧州最大のLNG輸入国であり、フランス、スペインがこれに続く。
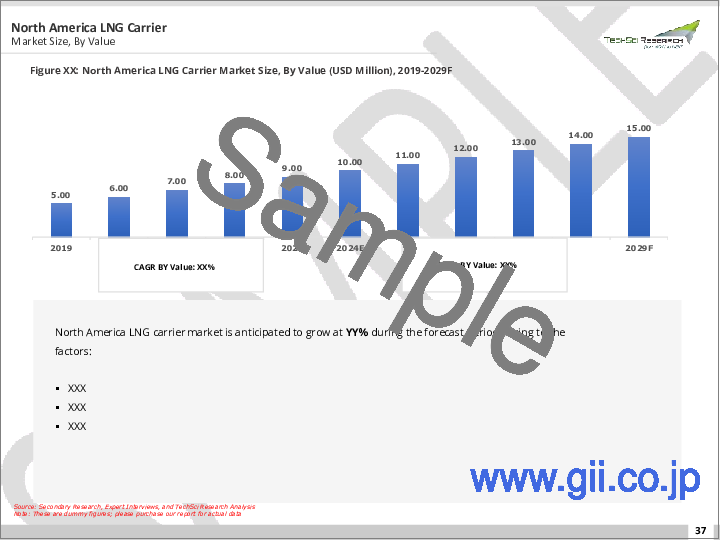
北米:
北米は、2022年にLNG船にとって第3位の市場となっています。北米のLNG需要は、米国とカナダにおける新たなLNG輸出ターミナルの開発によって拡大しています。米国は世界最大のLNG輸出国であり、今後もLNG輸出の増加が見込まれます。
目次
第1章 概要
第2章 主要市場セグメンテーション
第3章 調査手法
第4章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第5章 顧客の声
第6章 世界のLNG船市場展望
- 市場規模・予測
- 金額別
- 市場シェアと予測
- コンテナタイプ別(モスタイプ、メンブレンタイプ)
- 貯蔵容量別(12万立方メートル未満、12~16万立方メートル、16万立方メートル以上)
- 推進タイプ別(蒸気タービン、二重燃料ディーゼルエンジン/三重燃料ディーゼルエンジン(DFDE/TFDE)、低速ディーゼル(SSD)、M型電子制御ガス噴射(ME-GI)、XDF-2ストロークエンジン、蒸気再加熱ステージ)
- エンドユーザー産業別(運輸、防衛、その他)
- 地域別
- 企業別(2022年)
- 市場マップ
第7章 北米のLNG船市場展望
- 市場規模・予測
- 金額別
- 市場シェア・予測
- コンテナタイプ別
- 貯蔵容量別
- 推進力タイプ別
- エンドユーザー産業別
- 国別
- 北米国別分析
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
第8章 欧州のLNG船市場の展望
- 市場規模・予測
- 金額別
- 市場シェア・予測
- コンテナタイプ別
- 貯蔵容量別
- 推進力タイプ別
- エンドユーザー産業別
- 国別
- 欧州国別分析
- ドイツ
- 英国
- イタリア
- フランス
- スペイン
第9章 アジア太平洋のLNG船市場展望
- 市場規模・予測
- 金額別
- 市場シェアと予測
- コンテナタイプ別
- 貯蔵容量別
- 推進力タイプ別
- エンドユーザー産業別
- 国別
- アジア太平洋地域国別分析
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- 韓国
- オーストラリア
第10章 南米のLNG船市場の展望
- 市場規模・予測
- 金額別
- 市場シェア・予測
- コンテナタイプ別
- 貯蔵容量別
- 推進力タイプ別
- エンドユーザー産業別
- 国別
- 南米:国別分析
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
- コロンビア
第11章 中東・アフリカのLNG船市場の展望
- 市場規模・予測
- 金額別
- 市場シェアと予測
- コンテナタイプ別
- 貯蔵容量別
- 推進力タイプ別
- エンドユーザー産業別
- 国別
- MEA:国別分析
- 南アフリカ
- サウジアラビア
- アラブ首長国連邦
- クウェート
- トルコ
第12章 市場力学
第13章 市場動向と発展
第14章 競合情勢
- BW Group
- China Merchants Heavy Industry
- Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering
- Excelerate Energy
- GasLog Partners LP
- Hyundai Heavy Industries Co. Ltd
- K Line LNG Shipping Ltd
- Mitsui O.S.K. Lines Ltd
- Qatar Gas Transport Company Limited
- New Fortress Energy Inc
第15章 戦略的提言
第16章 調査会社について・免責事項
Global LNG Carrier Market has valued at USD 10.08 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to project robust growth in the forecast period with a CAGR of 6.19% through 2028.
The LNG Carrier Market refers to the global industry involved in the transportation of liquefied natural gas (LNG) from production and liquefaction facilities to distribution terminals and end-users. LNG is a vital component of the global energy trade, and specialized vessels known as LNG carriers play a pivotal role in facilitating the safe and efficient movement of LNG across the seas. These carriers are equipped with advanced cryogenic technologies to transport natural gas in its liquefied form, which is achieved by cooling it to extremely low temperatures, making it more compact for shipping. The LNG Carrier Market encompasses various aspects, including the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of these vessels. Key stakeholders in the market include LNG producers, terminal operators, shipping companies, and governments. Market dynamics are influenced by factors such as shifts in global energy demand, changes in environmental regulations, economic trends, and geopolitical developments. The market continuously evolves with innovations in vessel design, propulsion systems, safety measures, and environmental performance to meet the growing demand for LNG and address environmental concerns.
In summary, the LNG Carrier Market is a crucial component of the global energy landscape, facilitating the reliable and efficient transport of LNG to support diverse energy needs worldwide.
| Market Overview | |
|---|---|
| Forecast Period | 2024-2028 |
| Market Size 2022 | USD 10.08 billion |
| Market Size 2028 | USD 14.58 billion |
| CAGR 2023-2028 | 6.19% |
| Fastest Growing Segment | 120,000-160,000 cubic meter |
| Largest Market | Asia-Pacific |
Key Market Drivers
Increasing LNG Demand and Production:
The global LNG Carrier market is being driven by the rising demand for liquefied natural gas (LNG) and the concurrent increase in LNG production. Natural gas, considered a cleaner alternative to coal and oil, is in high demand due to its lower carbon emissions and versatility. As countries aim to reduce their carbon footprints and transition towards more sustainable energy sources, the demand for LNG has surged. LNG carriers play a critical role in transporting this valuable energy resource from exporting countries to importing regions. One of the primary reasons for the growth in LNG production is the abundance of natural gas reserves worldwide. Countries with substantial natural gas reserves have been investing heavily in LNG production facilities, which, in turn, fuels the demand for LNG carriers. These carriers are specially designed to store and transport LNG at extremely low temperatures and high pressures, ensuring the safe and efficient delivery of LNG to its destination.
Expanding LNG Infrastructure:
The expansion of LNG infrastructure is a significant driver of the global LNG Carrier market. LNG infrastructure includes liquefaction plants, regasification terminals, storage facilities, and pipelines. As more countries invest in building or expanding their LNG infrastructure, there is a growing need for LNG carriers to transport LNG between these facilities and international markets. Many nations are actively seeking to diversify their energy sources by investing in LNG terminals and terminals that can handle both LNG and natural gas. This diversification strategy enhances energy security and reliability. Consequently, it boosts the demand for LNG carriers as they facilitate the movement of LNG within and between these facilities.
Environmental Concerns and LNG's Role:
Environmental concerns, including the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change, have led to a global shift towards cleaner energy sources. LNG is viewed as a bridge fuel that can help reduce carbon emissions compared to more carbon-intensive fossil fuels like coal and oil. The environmental benefits of LNG make it an attractive choice for both developed and emerging economies. LNG carriers enable the transportation of LNG to meet the growing energy demands of these markets while adhering to environmental goals.
Economic Growth and Industrialization:
The global LNG Carrier market is influenced by economic growth and industrialization, particularly in emerging markets. As countries experience rapid industrialization and urbanization, their energy consumption increases significantly. LNG carriers play a vital role in supplying natural gas, which is used for electricity generation, industrial processes, and heating.
Asia, in particular, has witnessed substantial economic growth, with countries like China and India leading the way. These nations have a growing appetite for LNG to fuel their expanding economies and meet the energy needs of their growing populations. This economic growth is a major driver of the LNG Carrier market, as it translates into higher demand for LNG transport services.
Technological Advancements in LNG Carrier Design:
Advancements in technology have led to the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly LNG carriers. These innovations include improved ship designs, propulsion systems, and safety features. The adoption of advanced materials and engineering solutions has enhanced the competitiveness of LNG carriers in the global energy transport market. Modern LNG carriers are designed to be more energy-efficient, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Additionally, safety measures have been enhanced to ensure the secure transportation of LNG, minimizing the risk of accidents and environmental incidents. These technological advancements not only make LNG carriers more attractive to operators but also contribute to the overall growth of the market.
Global Energy Security Considerations:
Energy security is a critical concern for many countries, and diversifying the sources of natural gas supply is a strategic approach to enhancing it. LNG carriers play a pivotal role in this strategy by facilitating the transportation of LNG from various regions. By reducing dependence on a single energy source or supplier, countries can enhance their energy security and resilience.
In conclusion, the global LNG Carrier market is driven by the growing demand for LNG, expanding LNG infrastructure, environmental considerations, economic growth and industrialization, technological advancements, and global energy security concerns. These drivers collectively contribute to the continued growth and vitality of the LNG Carrier industry on a global scale.
Government Policies are Likely to Propel the Market
Environmental Regulations and Emission Standards:
Government policies around the world are increasingly focused on environmental protection and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. In the context of the LNG Carrier Market, these policies have a significant impact on vessel design, operation, and emissions. Many governments have implemented stringent regulations and emission standards for maritime transportation, including LNG carriers. These standards often require the use of cleaner fuels, such as low-sulfur fuels, and the adoption of advanced emission control technologies like exhaust gas cleaning systems (scrubbers). Governments also encourage the adoption of LNG as a marine fuel due to its lower carbon and sulfur content compared to traditional marine fuels. Incentives, subsidies, and regulations promoting LNG as a maritime fuel can influence the demand for LNG carriers equipped to transport LNG as cargo and potentially use it as fuel for propulsion.
Energy Security Policies:
Energy security is a top priority for many governments, and policies related to ensuring a stable energy supply can impact the LNG Carrier Market. Some countries have developed strategic plans to diversify their energy sources and supply routes to reduce dependence on a single supplier or energy source. LNG carriers play a crucial role in these strategies by enabling the importation of LNG from various regions. Governments may incentivize the construction and operation of LNG terminals and associated infrastructure, as well as LNG carriers, to enhance energy security. These policies often involve agreements and partnerships with LNG-exporting countries to secure a stable supply of LNG.
Trade and Tariff Policies:
Government policies related to international trade and tariffs can influence the global LNG Carrier Market. Trade agreements, import/export tariffs, and trade barriers impact the flow of LNG and, consequently, the demand for LNG carriers. Free trade agreements and preferential trade terms for LNG can stimulate the LNG Carrier Market by facilitating the movement of LNG between countries. Conversely, trade restrictions or tariffs on LNG can hinder the market's growth by making LNG less competitive in certain markets.
Safety and Security Regulations:
Safety and security regulations imposed by governments have a substantial impact on LNG carriers' operation and design. LNG is a cryogenic liquid, and its transportation requires specialized safety measures. Governments often enact strict regulations regarding LNG carrier construction, operation, and emergency response procedures to mitigate risks associated with LNG transportation. These regulations encompass aspects such as hull design, containment systems, emergency shutdown systems, and crew training. Compliance with safety and security regulations is essential for obtaining the necessary permits and approvals for LNG carrier operations.
Infrastructure Development Policies:
The development of LNG infrastructure, including liquefaction plants, regasification terminals, and storage facilities, is often influenced by government policies and incentives. Governments may provide financial incentives, tax breaks, or regulatory support to encourage private sector investment in LNG infrastructure. These policies are instrumental in expanding the LNG supply chain and, consequently, the demand for LNG carriers. A well-developed infrastructure network ensures a consistent supply of LNG and efficient distribution, driving the need for LNG carriers to transport LNG between terminals and international markets.
Environmental and Energy Transition Policies:
In line with global efforts to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, many governments are implementing policies that promote the use of cleaner fuels and technologies, including LNG. These policies often include emissions reduction targets, carbon pricing mechanisms, and renewable energy incentives. Governments may encourage the adoption of LNG as a transitional fuel in the shipping industry to meet stricter emissions targets. This can influence shipowners' decisions to invest in LNG carriers and retrofit existing vessels to run on LNG. Additionally, incentives to develop and adopt cleaner propulsion technologies for LNG carriers, such as LNG-electric or LNG-hydrogen hybrid systems, can be part of these policies.
In conclusion, government policies significantly impact the global LNG Carrier Market. Policies related to environmental regulations, energy security, trade, safety, infrastructure development, and the energy transition all play a pivotal role in shaping the demand for LNG carriers and the overall dynamics of the industry.
Key Market Challenges
Volatility in LNG Demand and Supply:
The global LNG Carrier Market faces a persistent challenge driven by the inherent volatility in both LNG demand and supply. This volatility is a result of various factors, including geopolitical tensions, economic fluctuations, and changes in energy policies across countries.
Demand Volatility:
The demand for LNG can be highly sensitive to factors such as weather patterns, economic growth, and energy policies. For instance, a particularly cold winter in a major importing region can lead to a sudden surge in LNG demand for heating purposes. Conversely, a mild winter can result in reduced demand. Economic downturns can also impact industrial energy consumption, affecting LNG demand.
Moreover, changes in energy policies, such as increased emphasis on renewable energy sources or shifts in energy generation methods, can influence the demand for LNG. Government policies to incentivize or mandate the use of renewables, for example, can reduce LNG demand, making it challenging for carriers to predict and respond to market shifts effectively.
Supply Volatility:
The supply side of the LNG market is equally subject to volatility. The development of LNG projects, particularly liquefaction terminals, is capital-intensive and time-consuming. Delays in project approvals, construction, or commissioning can disrupt supply timelines. Additionally, unexpected technical issues or natural disasters can impact LNG production and export capabilities.
Geopolitical factors also contribute to supply volatility. Disputes among LNG-producing countries or regions can lead to disruptions in LNG supply chains. For example, tensions in the Middle East or the South China Sea have the potential to affect LNG production and shipping routes, affecting the reliability of supply for LNG carriers.
Navigating these demand and supply fluctuations is challenging for LNG carriers and can lead to underutilization of vessels or the need for expensive repositioning. Carriers must develop flexible strategies to adapt to changing market conditions, such as entering into shorter-term charter agreements or diversifying their customer base.
Capital Intensity and Technological Advancements:
Another significant challenge facing the global LNG Carrier Market is the capital intensity of LNG carrier construction and the rapid pace of technological advancements in the industry.
Capital Intensity:
Building and operating LNG carriers is a capital-intensive endeavor. LNG carriers are specialized vessels with complex infrastructure, including cryogenic tanks and sophisticated containment systems to transport LNG safely at extremely low temperatures and high pressures. The cost of constructing and maintaining these vessels is substantial, and owners and operators often require substantial financial resources.
Furthermore, the industry trend toward larger and more advanced LNG carriers has increased construction costs. These larger vessels offer economies of scale, but they also require substantial upfront investments. Securing financing for LNG carrier projects can be challenging, particularly for smaller operators or new entrants to the market.
Technological Advancements:
The LNG Carrier Market is characterized by rapid technological advancements aimed at improving vessel efficiency, safety, and environmental performance. While these advancements are positive in terms of reducing emissions and enhancing vessel capabilities, they also present challenges.
Owners and operators must continuously invest in retrofitting or upgrading existing fleets to remain competitive and comply with evolving environmental regulations. Keeping pace with these technological advancements can strain budgets and require significant planning and investment.
Additionally, the introduction of new propulsion technologies, such as LNG-electric or LNG-hydrogen hybrid systems, necessitates substantial capital expenditures and presents operational challenges related to crew training and maintenance.
In conclusion, the global LNG Carrier Market faces challenges related to demand and supply volatility, as well as the capital intensity of vessel construction and rapid technological advancements. These challenges require carriers to adopt flexible strategies, secure adequate financing, and continually invest in their fleets to remain competitive in an evolving industry.
Segmental Insights
Moss Type Insights
The Moss Type segment had the largest market share in 2022 & expected to maintain it in the forecast period. Moss Type containment systems have been in use for several decades and have demonstrated their reliability and safety. This long and successful track record instills confidence among LNG carriers' operators, shipbuilders, and investors. Many LNG carriers equipped with Moss Type containment systems have operated safely and effectively, contributing to their continued use. Flexibility for Smaller Vessels: Moss Type tanks are well-suited for smaller LNG carriers. They can be adapted to fit various vessel sizes and configurations, making them a versatile choice for a range of LNG transport needs. This adaptability is valuable in meeting diverse market demands. Robust Design: Moss Type tanks have a robust design with spherical storage tanks that can withstand the harsh marine environment. The spherical shape evenly distributes the stress, enhancing structural integrity and safety. This design feature is particularly beneficial for LNG carriers operating in challenging conditions, such as in rough seas or extreme weather. Moss Type tanks provide effective thermal insulation, which helps reduce boil-off gas rates during LNG transport. This efficiency is essential for minimizing LNG losses and maximizing cargo delivery. Moss Type tanks are relatively easier to access for maintenance and repairs compared to some other containment systems. This ease of maintenance can reduce downtime and operational disruptions, contributing to cost savings and reliability. LNG carriers are substantial investments, and operators often prioritize proven technologies with a strong reputation for safety and performance. Moss Type containment systems have earned the trust of many industry stakeholders, including LNG producers, terminal operators, and investors. For certain vessel sizes and applications, Moss Type containment systems may be cost-effective compared to alternative systems. The initial construction and operational costs are factors that influence the choice of containment system, and Moss Type can be competitive in this regard.
120,000-160,000 cubic meter Insights
The 120,000-160,000 cubic meter segment had the largest market share in 2022 and is projected to experience rapid growth during the forecast period. LNG carriers in the 120,000-160,000 cubic meter range are versatile and well-suited to a wide variety of LNG trade routes and terminal configurations. They can efficiently serve both large-scale LNG terminals and smaller, more remote terminals, offering a high degree of flexibility in meeting diverse market demands. These carriers strike a balance between cargo capacity and operational efficiency. They are large enough to achieve economies of scale in terms of construction costs and operational costs per unit of LNG transported. At the same time, they are not as size-restricted as smaller carriers, allowing them to carry substantial LNG volumes. LNG terminals worldwide have varying depth restrictions and infrastructure capabilities. LNG carriers in the 120,000-160,000 cubic meter range are typically designed to meet these limitations, making them capable of accessing a broad range of terminals without significant constraints. These carriers offer cost-effective transportation for LNG projects with moderate volumes. They strike a balance between the higher transportation costs associated with smaller carriers and the potentially excessive costs of very large carriers. This makes them attractive for LNG producers and consumers looking to optimize their transportation expenses. Many LNG terminals, particularly those built in the past, were designed to accommodate LNG carriers in the 120,000-160,000 cubic meter range. This compatibility reduces the need for extensive modifications to existing terminals and enhances the efficiency of LNG trade operations. Historically, the majority of LNG projects and trade routes have been well-suited to carriers in this size range. Market demand, trade patterns, and the availability of projects often influence the choice of carrier capacity.
.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific:
The Asia Pacific region was the largest market for LNG carriers in 2022. This is due to the growing demand for LNG in China and other countries in the region. China is the largest importer of LNG in the world, and it is expected to continue to grow its LNG imports in the coming years. Other major markets in the region include Japan, South Korea, India, and Indonesia.
Europe:
Europe was the second-largest market for LNG carriers in 2022. The demand for LNG in Europe is growing, driven by the need to reduce reliance on imported oil and gas. The United Kingdom is the largest importer of LNG in Europe, followed by France and Spain.
North America:
North America was the third-largest market for LNG carriers in 2022. The demand for LNG in North America is growing, driven by the development of new LNG export terminals in the United States and Canada. The United States is the largest exporter of LNG in the world, and it is expected to continue to grow its LNG exports in the coming years.
Key Market Players
BW Group
China Merchants Heavy Industry
Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering
Excelerate Energy
GasLog Partners LP
Hyundai Heavy Industries Co. Ltd
K Line LNG Shipping Ltd
Mitsui O.S.K. Lines Ltd
Qatar Gas Transport Company Limited
New Fortress Energy Inc
Report Scope:
In this report, the Global LNG Carrier Market has been segmented into the following categories, in addition to the industry trends which have also been detailed below:
LNG Carrier Market, By Containment Type:
- Moss Type
- Membrane Type
LNG Carrier Market, By Storage Capacity:
- Under 120,000 cubic meter,
- 120,000-160,000 cubic meter
- Above 160,000 cubic meter
LNG Carrier Market, By Propulsion Type:
- Steam Turbines,
- Dual Fuel Diesel Engine/Tri-Fuel Diesel Engine (DFDE/TFDE),
- Slow-Speed Diesel (SSD),
- M-type Electronically Controlled Gas Injection (ME-GI),
- XDF- Two Stroke Engine
- Steam Re-heat and Stage
LNG Carrier Market, By End User Industry:
- Transport,
- Defense
- Others
LNG Carrier Market, By Region:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Germany
- Spain
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia
- South Korea
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Kuwait
- Turkey
Competitive Landscape
- Company Profiles: Detailed analysis of the major companies present in the Global LNG Carrier Market.
Available Customizations:
- Global LNG Carrier market report with the given market data, Tech Sci Research offers customizations according to a company's specific needs. The following customization options are available for the report:
Company Information
- Detailed analysis and profiling of additional market players (up to five).
Table of Contents
1. Product Overview
- 1.1. Market Definition
- 1.2. Scope of the Market
- 1.2.1. Markets Covered
- 1.2.2. Years Considered for Study
2. Key Market Segmentations
3. Research Methodology
- 3.1. Objective of the Study
- 3.2. Baseline Methodology
- 3.3. Formulation of the Scope
- 3.4. Assumptions and Limitations
- 3.5. Sources of Research
- 3.5.1. Secondary Research
- 3.5.2. Primary Research
- 3.6. Approach for the Market Study
- 3.6.1. The Bottom-Up Approach
- 3.6.2. The Top-Down Approach
- 3.7. Methodology Followed for Calculation of Market Size & Market Shares
- 3.8. Forecasting Methodology
- 3.8.1. Data Triangulation & Validation
4. Executive Summary
5. Voice of Customer
6. Global LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 6.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 6.1.1. By Value
- 6.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 6.2.1. By Containment Type (Moss Type and Membrane Type)
- 6.2.2. By Storage Capacity (Under 120,000 cubic meter, 120,000-160,000 cubic meter and Above 160,000 cubic meter)
- 6.2.3. By Propulsion Type (Steam Turbines, Dual Fuel Diesel Engine/Tri-Fuel Diesel Engine (DFDE/TFDE), Slow-Speed Diesel (SSD), M-type Electronically Controlled Gas Injection (ME-GI), XDF- Two Stroke Engine and Steam Re-heat and Stage)
- 6.2.4. By End User Industry (Transport, Defense and Others)
- 6.2.5. By Region
- 6.2.6. By Company (2022)
- 6.3. Market Map
7. North America LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 7.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 7.1.1. By Value
- 7.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 7.2.1. By Containment Type
- 7.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 7.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 7.2.4. By End User Industry
- 7.2.5. By Country
- 7.3. North America: Country Analysis
- 7.3.1. United States LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 7.3.1.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 7.3.1.1.1. By Value
- 7.3.1.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 7.3.1.2.1. By Containment Type
- 7.3.1.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 7.3.1.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 7.3.1.2.4. By End User Industry
- 7.3.1.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 7.3.2. Canada LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 7.3.2.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 7.3.2.1.1. By Value
- 7.3.2.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 7.3.2.2.1. By Containment Type
- 7.3.2.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 7.3.2.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 7.3.2.2.4. By End User Industry
- 7.3.2.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 7.3.3. Mexico LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 7.3.3.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 7.3.3.1.1. By Value
- 7.3.3.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 7.3.3.2.1. By Containment Type
- 7.3.3.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 7.3.3.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 7.3.3.2.4. By End User Industry
- 7.3.3.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 7.3.1. United States LNG Carrier Market Outlook
8. Europe LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 8.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 8.1.1. By Value
- 8.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 8.2.1. By Containment Type
- 8.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 8.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 8.2.4. By End User Industry
- 8.2.5. By Country
- 8.3. Europe: Country Analysis
- 8.3.1. Germany LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 8.3.1.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 8.3.1.1.1. By Value
- 8.3.1.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 8.3.1.2.1. By Containment Type
- 8.3.1.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 8.3.1.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 8.3.1.2.4. By End User Industry
- 8.3.1.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 8.3.2. United Kingdom LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 8.3.2.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 8.3.2.1.1. By Value
- 8.3.2.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 8.3.2.2.1. By Containment Type
- 8.3.2.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 8.3.2.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 8.3.2.2.4. By End User Industry
- 8.3.2.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 8.3.3. Italy LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 8.3.3.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 8.3.3.1.1. By Value
- 8.3.3.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 8.3.3.2.1. By Containment Type
- 8.3.3.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 8.3.3.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 8.3.3.2.4. By End User Industry
- 8.3.3.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 8.3.4. France LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 8.3.4.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 8.3.4.1.1. By Value
- 8.3.4.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 8.3.4.2.1. By Containment Type
- 8.3.4.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 8.3.4.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 8.3.4.2.4. By End User Industry
- 8.3.4.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 8.3.5. Spain LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 8.3.5.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 8.3.5.1.1. By Value
- 8.3.5.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 8.3.5.2.1. By Containment Type
- 8.3.5.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 8.3.5.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 8.3.5.2.4. By End User Industry
- 8.3.5.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 8.3.1. Germany LNG Carrier Market Outlook
9. Asia-Pacific LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 9.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 9.1.1. By Value
- 9.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 9.2.1. By Containment Type
- 9.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 9.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 9.2.4. By End User Industry
- 9.2.5. By Country
- 9.3. Asia-Pacific: Country Analysis
- 9.3.1. China LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 9.3.1.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 9.3.1.1.1. By Value
- 9.3.1.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 9.3.1.2.1. By Containment Type
- 9.3.1.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 9.3.1.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 9.3.1.2.4. By End User Industry
- 9.3.1.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 9.3.2. India LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 9.3.2.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 9.3.2.1.1. By Value
- 9.3.2.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 9.3.2.2.1. By Containment Type
- 9.3.2.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 9.3.2.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 9.3.2.2.4. By End User Industry
- 9.3.2.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 9.3.3. Japan LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 9.3.3.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 9.3.3.1.1. By Value
- 9.3.3.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 9.3.3.2.1. By Containment Type
- 9.3.3.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 9.3.3.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 9.3.3.2.4. By End User Industry
- 9.3.3.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 9.3.4. South Korea LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 9.3.4.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 9.3.4.1.1. By Value
- 9.3.4.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 9.3.4.2.1. By Containment Type
- 9.3.4.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 9.3.4.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 9.3.4.2.4. By End User Industry
- 9.3.4.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 9.3.5. Australia LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 9.3.5.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 9.3.5.1.1. By Value
- 9.3.5.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 9.3.5.2.1. By Containment Type
- 9.3.5.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 9.3.5.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 9.3.5.2.4. By End User Industry
- 9.3.5.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 9.3.1. China LNG Carrier Market Outlook
10. South America LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 10.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 10.1.1. By Value
- 10.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 10.2.1. By Containment Type
- 10.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 10.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 10.2.4. By End User Industry
- 10.2.5. By Country
- 10.3. South America: Country Analysis
- 10.3.1. Brazil LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 10.3.1.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 10.3.1.1.1. By Value
- 10.3.1.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 10.3.1.2.1. By Containment Type
- 10.3.1.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 10.3.1.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 10.3.1.2.4. By End User Industry
- 10.3.1.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 10.3.2. Argentina LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 10.3.2.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 10.3.2.1.1. By Value
- 10.3.2.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 10.3.2.2.1. By Containment Type
- 10.3.2.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 10.3.2.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 10.3.2.2.4. By End User Industry
- 10.3.2.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 10.3.3. Colombia LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 10.3.3.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 10.3.3.1.1. By Value
- 10.3.3.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 10.3.3.2.1. By Containment Type
- 10.3.3.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 10.3.3.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 10.3.3.2.4. By End User Industry
- 10.3.3.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 10.3.1. Brazil LNG Carrier Market Outlook
11. Middle East and Africa LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 11.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 11.1.1. By Value
- 11.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 11.2.1. By Containment Type
- 11.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 11.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 11.2.4. By End User Industry
- 11.2.5. By Country
- 11.3. MEA: Country Analysis
- 11.3.1. South Africa LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 11.3.1.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 11.3.1.1.1. By Value
- 11.3.1.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 11.3.1.2.1. By Containment Type
- 11.3.1.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 11.3.1.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 11.3.1.2.4. By End User Industry
- 11.3.1.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 11.3.2. Saudi Arabia LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 11.3.2.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 11.3.2.1.1. By Value
- 11.3.2.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 11.3.2.2.1. By Containment Type
- 11.3.2.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 11.3.2.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 11.3.2.2.4. By End User Industry
- 11.3.2.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 11.3.3. UAE LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 11.3.3.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 11.3.3.1.1. By Value
- 11.3.3.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 11.3.3.2.1. By Containment Type
- 11.3.3.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 11.3.3.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 11.3.3.2.4. By End User Industry
- 11.3.3.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 11.3.4. Kuwait LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 11.3.4.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 11.3.4.1.1. By Value
- 11.3.4.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 11.3.4.2.1. By Containment Type
- 11.3.4.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 11.3.4.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 11.3.4.2.4. By End User Industry
- 11.3.4.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 11.3.5. Turkey LNG Carrier Market Outlook
- 11.3.5.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 11.3.5.1.1. By Value
- 11.3.5.2. Market Share & Forecast
- 11.3.5.2.1. By Containment Type
- 11.3.5.2.2. By Storage Capacity
- 11.3.5.2.3. By Propulsion Type
- 11.3.5.2.4. By End User Industry
- 11.3.5.1. Market Size & Forecast
- 11.3.1. South Africa LNG Carrier Market Outlook
12. Market Dynamics
13. Market Trends & Developments
14. Competitive Landscape
- 14.1. BW Group
- 14.1.1. Business Overview
- 14.1.2. Key Revenue and Financials
- 14.1.3. Recent Developments
- 14.1.4. Key Personnel/Key Contact Person
- 14.1.5. Key Product/Services Offered
- 14.2. China Merchants Heavy Industry
- 14.2.1. Business Overview
- 14.2.2. Key Revenue and Financials
- 14.2.3. Recent Developments
- 14.2.4. Key Personnel/Key Contact Person
- 14.2.5. Key Product/Services Offered
- 14.3. Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering
- 14.3.1. Business Overview
- 14.3.2. Key Revenue and Financials
- 14.3.3. Recent Developments
- 14.3.4. Key Personnel/Key Contact Person
- 14.3.5. Key Product/Services Offered
- 14.4. Excelerate Energy
- 14.4.1. Business Overview
- 14.4.2. Key Revenue and Financials
- 14.4.3. Recent Developments
- 14.4.4. Key Personnel/Key Contact Person
- 14.4.5. Key Product/Services Offered
- 14.5. GasLog Partners LP
- 14.5.1. Business Overview
- 14.5.2. Key Revenue and Financials
- 14.5.3. Recent Developments
- 14.5.4. Key Personnel/Key Contact Person
- 14.5.5. Key Product/Services Offered
- 14.6. Hyundai Heavy Industries Co. Ltd
- 14.6.1. Business Overview
- 14.6.2. Key Revenue and Financials
- 14.6.3. Recent Developments
- 14.6.4. Key Personnel/Key Contact Person
- 14.6.5. Key Product/Services Offered
- 14.7. K Line LNG Shipping Ltd
- 14.7.1. Business Overview
- 14.7.2. Key Revenue and Financials
- 14.7.3. Recent Developments
- 14.7.4. Key Personnel/Key Contact Person
- 14.7.5. Key Product/Services Offered
- 14.8. Mitsui O.S.K. Lines Ltd
- 14.8.1. Business Overview
- 14.8.2. Key Revenue and Financials
- 14.8.3. Recent Developments
- 14.8.4. Key Personnel/Key Contact Person
- 14.8.5. Key Product/Services Offered
- 14.9. Qatar Gas Transport Company Limited
- 14.9.1. Business Overview
- 14.9.2. Key Revenue and Financials
- 14.9.3. Recent Developments
- 14.9.4. Key Personnel/Key Contact Person
- 14.9.5. Key Product/Services Offered
- 14.10. New Fortress Energy Inc
- 14.10.1. Business Overview
- 14.10.2. Key Revenue and Financials
- 14.10.3. Recent Developments
- 14.10.4. Key Personnel/Key Contact Person
- 14.10.5. Key Product/Services Offered