|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1308678
電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システム市場の2030年までの予測- タイプ別、コンポーネント別、電源別、車両タイプ別、充電方式別、設置別、流通チャネル別、地域別の世界分析Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Forecasts to 2030 - Global Analysis By Type, Component, Power Supply, Vehicle Type, Charging Method, Installation, Distribution Channel and By Geography |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システム市場の2030年までの予測- タイプ別、コンポーネント別、電源別、車両タイプ別、充電方式別、設置別、流通チャネル別、地域別の世界分析 |
|
出版日: 2023年07月01日
発行: Stratistics Market Research Consulting
ページ情報: 英文 175+ Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
Stratistics MRCによると、世界の電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システム市場は2023年に4,978万米ドルを占め、予測期間に44.5%のCAGRで成長し、2030年には6億5,489万米ドルに達すると予測されています。
電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システムは、電線やケーブルを使用せずに電源から消費機器へエネルギーを伝送するものです。電気自動車の電源と充電は、信頼性が高く実用的で安全な技術によって可能になります。物理的なコネクターやコードをなくすことで、効果的で手頃な価格で安全な、従来の充電方法以上の利点を提供します。ワイヤレスEV充電システムは、商業化の可能性が高い有望な技術です。このアプローチは、世界中の大手自動車メーカーによってテストされています。
国際クリーン交通評議会(ICCT)の2021年報告書によると、米国内の電気自動車産業は、2010年の1000台から、2018年から2020年にかけて31万5000台以上に増加しています。
市場力学:
促進要因
燃料の代替としてのエネルギー効率の高いソースの増加
ディーゼルやガソリンを製造するために採掘・加工される原油は、自動車の主な点火源となっています。過去30年間で、石油価格は劇的に上昇し、低・中流階級の顧客にとっては移動コストが高くなっています。原油価格の上昇により、人々はエネルギー効率の高い選択肢を選ぶようになり、1マイルあたりの総コストが下がっています。このため、燃料自動車に比べて電気自動車の需要が高まると予想されます。その結果、車両充電システムの市場成長は加速すると予想されます。
抑制要因
効率の低下
従来の電力伝送と比較すると、ワイヤレス充電技術における電力損失は約7~12%多いです。ワイヤレス充電器は、電磁誘導や磁気共鳴を利用して一定の距離を伝送することしかできないです。特に地上高の高いLCVやSUVの場合、メーカーはこの距離制限の結果として大きなハードルを抱えています。送信機から受信機までの距離と電力効率の比は反比例します。そのため、効率と安全性に関する懸念が、この業界の生産者にとっての障壁となっています。
機会:
高まる政府のインセンティブ
多くの国々で、ワイヤレス充電の進歩は現在、電気自動車に対する政府の補助金や援助によって支えられています。一般の人々は、自動車の充電を待つ必要がないため、長時間働くことができます。この生産時間の増加は、国のGDP成長にも貢献します。完全な自律走行、充電ステーション不要、大都市圏ではスペースを必要としないバッテリーパックの小型化などは、すべてワイヤレス充電システムの利点です。こうした要素が市場の需要を押し上げています。
脅威
高価な技術統合
パワー・コントロール・ユニット(PCU)を使用した電力伝送のために、電気自動車のワイヤレス充電技術には送信コイルと受信コイルが必要です。家庭用に設置されるアフターマーケットのワイヤレス充電システムの総コストは2,500~3,000米ドルです。ワイヤレス充電技術が車両に搭載されると、電気自動車のコストは上昇します。その結果、ワイヤレス電気自動車充電のコストが上昇します。したがって、ワイヤレス充電技術への切り替えにかかる高いコストは、経済情勢と範囲による規模の経済に付随する重大な市場制限であると結論づけることができます。
COVID-19の影響:
COVID-19危機は、EVの生産を制限した各国の封鎖により、世界の自動車部品および自動車製造業を減速させました。これはEV充電インフラの必要性に大きな影響を与えました。広範なロックダウンと政府の制限により、電気自動車充電インフラ建設への大規模投資は保留されています。このため、世界中のEV供給設備メーカーの大半が影響を受けています。
予測期間中、プラグイン・ハイブリッド電気自動車分野が最大になると予想される:
プラグインハイブリッド電気自動車セグメントは、有利な成長を遂げると推定されます。プラグインハイブリッド電気自動車(PHEV)は、電気モーターを駆動するためにバッテリーを使用します。PHEVは、充電装置と回生ブレーキを使ってバッテリーを充電する能力があります。PHEVは、充電装置と回生ブレーキを使ってバッテリーを充電することができます。燃料価格が安い、温室効果ガスの排出が少ない、燃費が良いなどの利点があり、このセグメントの成長を後押ししています。
誘導電力伝達セグメントは、予測期間中に最も高いCAGRが見込まれる:
誘導電力伝送セグメントは、予測期間中に最も速いCAGR成長を示すと予測されています。誘導電力伝送は、機械的または電気的な接触を必要とせずに電力とデジタルデータの伝送を可能にする技術です。このため、高速で完全な耐摩耗性を必要とするモバイル電化システムのメーカーにとっては、設計の選択肢が広がります。比較的長い距離(数メートル)でも作動し、効率が高く(最大95%)、エネルギー損失が減少します。前述の要因が、このセグメントの拡大を促進しています。
最大のシェアを占める地域
電気自動車メーカーによるハイエンド技術製品の採用により、予測期間中、アジア太平洋地域が最大の市場シェアを占めると予測されます。アジア太平洋地域、特に中国と日本では電気自動車の数が急速に増加しています。さらに、この地域の環境意識の高まりが、環境に優しく燃費の良いワイヤレス充電技術を使用する電気自動車(EV)の販売を後押ししています。この地域のEV充電器市場は、電気自動車を充電するためのインフラを構築するためのいくつかの政府イニシアチブの結果、上昇することも予想されます。
CAGRが最も高い地域:
欧州は、バッテリー式電気自動車の販売台数が増加していることから、予測期間中のCAGRが最も高くなると予測されます。この地域の主要OEMは、BMW、アウディ、メルセデスなど、自社の自動車にワイヤレス充電を組み込む取り組みを行っています。さらに、電気自動車向けワイヤレス充電の実行可能性を評価するための欧州政府の施策とEV販売の増加が、市場の拡大を促進すると予想されます。
主な発展:
2023年6月、トヨタはバッテリーEVの野心的な計画の一環として、全固体電池の製造計画を発表しました。次世代バッテリーEVは、加速、旋回、停止を中心とした「ドライビングフィール」のカスタマイズも可能にします。
2023年6月、テスラはGMおよびフォードとの提携を発表し、EV充電アクセスセットを拡大しました。この提携は、テスラとその充電技術に対する大きな支持を示すものであり、北米車の充電方式の標準化に一歩近づいた。
2022年1月、株式会社東芝は、高エネルギーと高出力を同時に実現する革新的な20Ah-HPのリチウムイオン二次電池セルを発売し、SCiB(TM)製品の提供を拡大しました。
2020年6月、ボッシュは電気自動車(EV) 促進要因に欧州全域の15万カ所以上の充電ポイントへのアクセスを提供する新しいモバイルアプリを発表しました。Charge My EV」アプリは個人・法人を問わず利用可能で、ユーザーは明確な費用の内訳を確認しながら充電ポイントを探し、料金を支払うことができます。
レポート内容
- 地域および国レベルの市場シェア評価
- 新規参入企業への戦略的提言
- 2021年、2022年、2023年、2026年、2030年の市場データをカバー
- 市場動向(促進要因・制約要因・機会・脅威・課題・投資機会・推奨事項)
- 市場推定に基づく主要ビジネスセグメントにおける戦略的提言
- 主要な共通トレンドをマッピングした競合情勢
- 詳細な戦略、財務、最近の動向を含む企業プロファイル
- 最新の技術的進歩をマッピングしたサプライチェーン動向
無料カスタマイズサービス:
本レポートをご購読のお客様には、以下のいずれかの無料カスタマイズオプションをご提供いたします:
- 企業プロファイル
- 追加市場プレイヤーの包括的プロファイリング(3社まで)
- 主要企業のSWOT分析(3社まで)
- 地域セグメンテーション
- 顧客の関心に応じた主要国の市場推計・予測・CAGR(注:フィージビリティチェックによる)
- 競合ベンチマーキング
- 製品ポートフォリオ、地理的プレゼンス、戦略的提携に基づく主要企業のベンチマーキング
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第2章 序文
- 概要
- ステークホルダー
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
- データマイニング
- データ分析
- データ検証
- 調査アプローチ
- 調査ソース
第3章 市場動向分析
- 促進要因
- 抑制要因
- 機会
- 脅威
- 新興市場
- 新型コロナウイルス感染症(COVID-19)の影響
第4章 ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
第5章 世界の電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システム市場:タイプ別
- 動的
- 静的
第6章 世界の電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システム市場:コンポーネント別
- 車両用パッド
- 電源制御ユニット(PCU)
- ベースパッド
- バッテリー管理システム(BMS)
- その他のコンポーネント
第7章 世界の電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システム市場:電源別
- 3~7.7kW
- 7.7~11KW
- 11~20KW
- 20~50KW
- 50KW以上
第8章 世界の電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システム市場:車両タイプ別
- バッテリー電気自動車
- プラグインハイブリッド電気自動車
- 商用電気自動車
第9章 世界の電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システム市場:充電方式別
- 磁気ギアワイヤレス電力伝送(MGWPT)
- 容量性ワイヤレス給電(CWPT)
- 共振誘導電力伝送(RIPT)
- 誘導電力伝送(IPT)
- その他の充電方法
第10章 世界の電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システム市場:設置別
- 商業
- 家
第11章 世界の電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システム市場:流通チャネル別
- OEM
- アフターマーケット
第12章 世界の電気自動車ワイヤレス充電システム市場:地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- イタリア
- フランス
- スペイン
- その他欧州
- アジア太平洋地域
- 日本
- 中国
- インド
- オーストラリア
- ニュージーランド
- 韓国
- その他アジア太平洋地域
- 南米
- アルゼンチン
- ブラジル
- チリ
- その他南米
- 中東とアフリカ
- サウジアラビア
- アラブ首長国連邦
- カタール
- 南アフリカ
- その他中東とアフリカ
第13章 主な発展
- 契約、パートナーシップ、コラボレーション、合弁事業
- 買収と合併
- 新製品の発売
- 事業拡大
- その他の主要戦略
第14章 企業プロファイル
- Toshiba Corporation
- Tesla
- Robert Bosch GmbH
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- ZTE Corporation
- Momentum Dynamis Corporation
- Nission
- TGOOD Global Ltd
- HELLA GmbH & Co
- Qualcomm Inc
- Coninental AG
- DAIHEN Corporation
- BMW
- Lumen Pty Ltd
- WiTricity Corporation
- HEVO Inc
- ElectReon Wireless Ltd
- Mojo Mobility Inc
- Plugless Power LLC
- Wave LLC
List of Tables
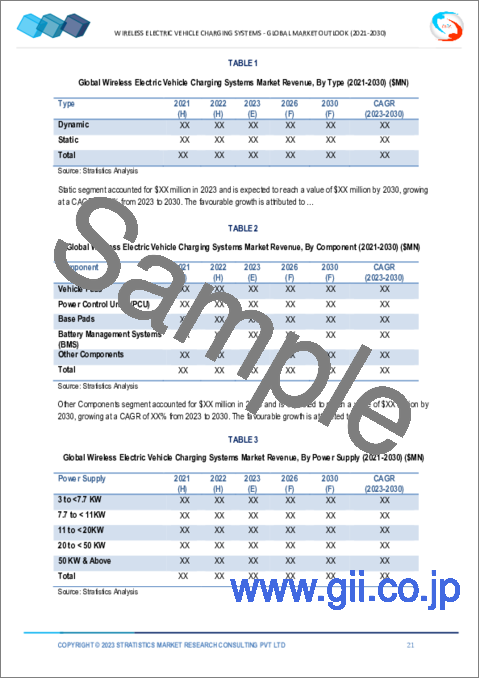
- Table 1 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Region (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 2 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Type (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 3 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Dynamic (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 4 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Static (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 5 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Component (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 6 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Vehicle Pads (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 7 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Power Control Units (PCU) (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 8 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Base Pads (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 9 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Battery Management Systems (BMS) (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 10 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Other Components (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 11 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Power Supply (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 12 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By 3 to <7.7 KW (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 13 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By 7.7 to < 11KW (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 14 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By 11 to < 20KW (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 15 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By 20 to < 50 KW (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 16 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By 50 KW & Above (2021-2030) ($MN)
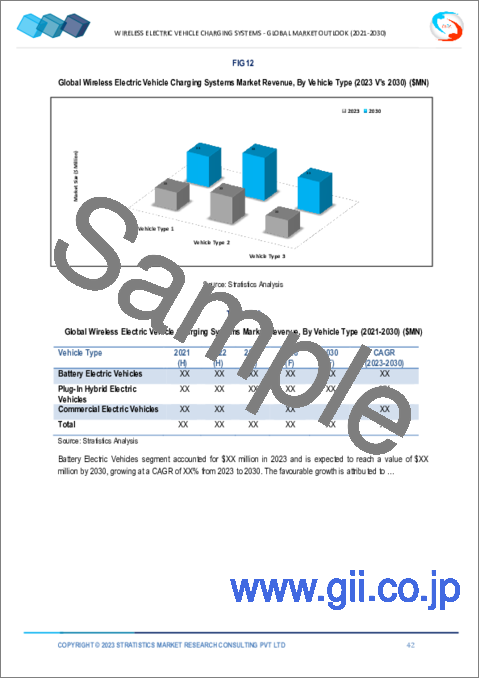
- Table 17 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Vehicle Type (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 18 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Battery Electric Vehicles (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 19 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 20 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Commercial Electric Vehicles (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 21 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Charging Method (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 22 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Magnetic Gear Wireless Power Transfer (MGWPT) (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 23 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Capacitive Wireless Power Transfer (CWPT) (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 24 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Resonant Inductive Power Transfer (RIPT) (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 25 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Inductive Power Transfer (IPT) (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 26 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Other Charging Methods (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 27 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Installation (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 28 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Commercial (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 29 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Home (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 30 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Distribution Channel (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 31 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By OEMs (2021-2030) ($MN)
- Table 32 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market Outlook, By Aftermarket (2021-2030) ($MN)
Note: Tables for North America, Europe, APAC, South America, and Middle East & Africa Regions are also represented in the same manner as above.
According to Stratistics MRC, the Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market is accounted for $49.78 million in 2023 and is expected to reach $654.89 million by 2030 growing at a CAGR of 44.5% during the forecast period. Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems are based on the transmission of energy from a power source to a consuming device without wires or cables. Electric vehicle power and charging is made possible by a dependable, practical, and secure technology. By doing away with physical connectors and cords, it offers benefits over conventional charging methods that are effective, affordable, and safe. Wireless EV charging systems are a promising technology with a high commercialisation potential. The approach has been tested by major automobile manufacturers all around the world.
According to the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) 2021 report, the electrical automobile industry within the U.S. has increased from 1000's automobiles sold in 2010 to more than 315,000 automobiles sold from 2018 to 2020.
Market Dynamics:
Driver:
Raising energy-efficient sources as an alternative to fuel
Crude oil, which is extracted and processed to create diesel and gasoline, serves as the main ignition source in automobiles. Over the past three decades, the price of oil has dramatically risen, making travel more expensive for low- and middle-class customers. People are now choosing energy-efficient options as a result of rising oil prices, which lowers the overall cost per mile. This is expected to raise demand for electric vehicles relative to fuel-powered vehicles. As a result, the market growth for vehicle charging systems is expected to pick up speed.
Restraint:
Loss of efficiency
When compared to conventional power transfer, power loss in wireless charging technology is around 7-12% more. A wireless charger can only transmit over a fixed distance using electromagnetic induction and/or magnetic resonance. Manufacturers have a significant hurdle as a result of this range restriction, particularly in the case of LCVs and SUVs with high ground clearance. The ratio of power efficiency to transmitter-to-receiver separation is inversely proportional. Therefore, concerns about efficiency and safety have turned into a barrier for producers in this industry.
Opportunity:
Growing government incentives
In many nations, the advancement of wireless charging is currently supported by government subsidies and assistance for electric vehicles. The general population can work for longer periods of time since they don't have to wait for their vehicle to charge. This increase in productive hours also contributes to a country's GDP growth. Full autonomy, no need for a charging station, and smaller battery packs with less need for space in metropolitan areas are all benefits of wireless charging systems. These elements are boosting market demand.
Threat:
Expensive integration of technology
For power transfer using a power control unit (PCU), the wireless charging technique for electric vehicles needs transmitter and receiver coils. The total cost of an installed aftermarket wireless charging system for a home is between USD 2,500 and 3,000. The cost of the electric vehicle increases when wireless charging technology is included in the vehicle. Consequently, this raises the cost of wireless electric vehicle charging. Therefore, it can be concluded that the high cost of switching to wireless charging technology is a significant market restriction attached to the economic climate and the scope-induced economies of scale.
COVID-19 Impact:
The COVID-19 crisis slow downed the global auto part and vehicle manufacturing industries owing to lockdown in various countries that restricted EV production. It has significantly affected the need for EV charging infrastructure. Due to widespread lockdowns and governmental limitations, major investments in the construction of electric vehicle charging infrastructure have been put on hold. This has affected the majority of EV supply equipment manufacturers worldwide.
The plug-in hybrid electric vehicles segment is expected to be the largest during the forecast period:
The plug-in hybrid electric vehicles segment is estimated to have a lucrative growth. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) use batteries to power an electric motor. PHEVs have the ability to recharge their batteries using charging devices and regenerative braking. Operating expenses and fuel consumption are decreased when some or all of the time the vehicle is powered by the grid. The advantages it offers, such as cheaper fuel prices, fewer greenhouse gas emissions, and fuel economy estimation, are propelling the segment's growth.
The inductive power transfer segment is expected to have the highest CAGR during the forecast period:
The inductive power transfer segment is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR growth during the forecast period. Inductive Power Transfer is a technology that allows for the transmission of power and digital data without the need for mechanical or electrical contact. This opens up a wide range of design options for manufacturers of mobile electrification systems that require quick speeds and complete wear resistance. It operates even at relatively long distances (a few meters), has higher efficiency (up to 95%), and decreases energy losses. The aforementioned factors are promoting the segment's expansion.
Region with largest share:
Asia Pacific is projected to hold the largest market share during the forecast period owing to the adoption of high-end technology products by electric vehicle manufacturers. The number of electric vehicles is rapidly increasing in the Asia-Pacific region, particularly in China and Japan. Additionally, the region's growing environmental consciousness has boosted sales of electric vehicles (EVs) that use environmentally friendly and fuel-efficient wireless charging technology. The market for EV chargers in this region is also anticipated to rise as a result of several government initiatives to build up the infrastructure for charging electric vehicles.
Region with highest CAGR:
Europe is projected to have the highest CAGR over the forecast period, owing to the increasing sales of battery electric vehicles. Major OEMs in this region are working to incorporate wireless charging in their vehicles, including BMW, Audi, and Mercedes. Additionally, it is anticipated that the European government's measures to evaluate the viability of wireless charging for electric vehicles and the increase in EV sales will propel the market's expansion.
Key players in the market
Some of the key players profiled in the Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market include Toshiba Corporation, Tesla, Robert Bosch GmbH, Toyota Motor Corporation, ZTE Corporation, Momentum Dynamis Corporation, Nission, TGOOD Global Ltd, HELLA GmbH & Co, Qualcomm Inc, Coninental AG, DAIHEN Corporation, BMW, Lumen Pty Ltd, WiTricity Corporation, HEVO Inc, ElectReon Wireless Ltd, Mojo Mobility Inc, Plugless Power LLC and Wave LLC.
Key Developments:
In June 2023, Toyota announced plans to make an all-solid-state battery as part of its ambitious plans for battery electric vehicles. The next-generation battery EV will also enable customization of the 'driving feel,' with a focus on acceleration, turning, and stopping.
In June 2023, Tesla announced partnership with GM and Ford to expand EV charging access set. The partnerships represent a major endorsement for Tesla and its charging technology, taking a step closer toward standardizing a charging type for North American vehicles.
In January 2022, Toshiba Corporation expanded its SCiB™ product offering with the launch of an innovative 20Ah-HP rechargeable lithium-ion battery cell that delivers high energy and high power at the same time.
In June 2020, Bosch has launched a new mobile app that gives electric vehicle (EV) drivers access to more than 150,000 charging points across Europe. The Charge My EV app is available to private and business customers and allows users to find and pay for charging with a clear breakdown of costs.
Types Covered:
- Dynamic
- Static
Components Covered:
- Vehicle Pads
- Power Control Units (PCU)
- Base Pads
- Battery Management Systems (BMS)
- Other Components
Power Supplies Covered:
- 3 to <7.7 KW
- 7.7 to < 11KW
- 11to < 20KW
- 20 to < 50 KW
- 50 KW & Above
Vehicle Types Covered:
- Battery Electric Vehicles
- Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles
- Commercial Electric Vehicles
Charging Methods Covered:
- Magnetic Gear Wireless Power Transfer (MGWPT)
- Capacitive Wireless Power Transfer (CWPT)
- Resonant Inductive Power Transfer (RIPT)
- Inductive Power Transfer (IPT)
- Other Charging Methods
Installations Covered:
- Commercial
- Home
Distribution Channels Covered:
- OEMs
- Aftermarket
Regions Covered:
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- UK
- Italy
- France
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Chile
- Rest of South America
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Qatar
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
What our report offers:
- Market share assessments for the regional and country-level segments
- Strategic recommendations for the new entrants
- Covers Market data for the years 2021, 2022, 2023, 2026, and 2030
- Market Trends (Drivers, Constraints, Opportunities, Threats, Challenges, Investment Opportunities, and recommendations)
- Strategic recommendations in key business segments based on the market estimations
- Competitive landscaping mapping the key common trends
- Company profiling with detailed strategies, financials, and recent developments
- Supply chain trends mapping the latest technological advancements
Free Customization Offerings:
All the customers of this report will be entitled to receive one of the following free customization options:
- Company Profiling
- Comprehensive profiling of additional market players (up to 3)
- SWOT Analysis of key players (up to 3)
- Regional Segmentation
- Market estimations, Forecasts and CAGR of any prominent country as per the client's interest (Note: Depends on feasibility check)
- Competitive Benchmarking
- Benchmarking of key players based on product portfolio, geographical presence, and strategic alliances
Table of Contents
1 Executive Summary
2 Preface
- 2.1 Abstract
- 2.2 Stake Holders
- 2.3 Research Scope
- 2.4 Research Methodology
- 2.4.1 Data Mining
- 2.4.2 Data Analysis
- 2.4.3 Data Validation
- 2.4.4 Research Approach
- 2.5 Research Sources
- 2.5.1 Primary Research Sources
- 2.5.2 Secondary Research Sources
- 2.5.3 Assumptions
3 Market Trend Analysis
- 3.1 Introduction
- 3.2 Drivers
- 3.3 Restraints
- 3.4 Opportunities
- 3.5 Threats
- 3.6 Emerging Markets
- 3.7 Impact of Covid-19
4 Porters Five Force Analysis
- 4.1 Bargaining power of suppliers
- 4.2 Bargaining power of buyers
- 4.3 Threat of substitutes
- 4.4 Threat of new entrants
- 4.5 Competitive rivalry
5 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market, By Type
- 5.1 Introduction
- 5.2 Dynamic
- 5.3 Static
6 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market, By Component
- 6.1 Introduction
- 6.2 Vehicle Pads
- 6.3 Power Control Units (PCU)
- 6.4 Base Pads
- 6.5 Battery Management Systems (BMS)
- 6.6 Other Components
7 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market, By Power Supply
- 7.1 Introduction
- 7.2 3 to <7.7 KW
- 7.3 7.7 to < 11KW
- 7.4 11 to < 20KW
- 7.5 20 to < 50 KW
- 7.6 50 KW & Above
8 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market, By Vehicle Type
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.2 Battery Electric Vehicles
- 8.3 Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles
- 8.4 Commercial Electric Vehicles
9 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market, By Charging Method
- 9.1 Introduction
- 9.2 Magnetic Gear Wireless Power Transfer (MGWPT)
- 9.3 Capacitive Wireless Power Transfer (CWPT)
- 9.4 Resonant Inductive Power Transfer (RIPT)
- 9.5 Inductive Power Transfer (IPT)
- 9.6 Other Charging Methods
10 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market, By Installation
- 10.1 Introduction
- 10.2 Commercial
- 10.3 Home
11 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market, By Distribution Channel
- 11.1 Introduction
- 11.2 OEMs
- 11.3 Aftermarket
12 Global Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Systems Market, By Geography
- 12.1 Introduction
- 12.2 North America
- 12.2.1 US
- 12.2.2 Canada
- 12.2.3 Mexico
- 12.3 Europe
- 12.3.1 Germany
- 12.3.2 UK
- 12.3.3 Italy
- 12.3.4 France
- 12.3.5 Spain
- 12.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 12.4 Asia Pacific
- 12.4.1 Japan
- 12.4.2 China
- 12.4.3 India
- 12.4.4 Australia
- 12.4.5 New Zealand
- 12.4.6 South Korea
- 12.4.7 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 12.5 South America
- 12.5.1 Argentina
- 12.5.2 Brazil
- 12.5.3 Chile
- 12.5.4 Rest of South America
- 12.6 Middle East & Africa
- 12.6.1 Saudi Arabia
- 12.6.2 UAE
- 12.6.3 Qatar
- 12.6.4 South Africa
- 12.6.5 Rest of Middle East & Africa
13 Key Developments
- 13.1 Agreements, Partnerships, Collaborations and Joint Ventures
- 13.2 Acquisitions & Mergers
- 13.3 New Product Launch
- 13.4 Expansions
- 13.5 Other Key Strategies
14 Company Profiling
- 14.1 Toshiba Corporation
- 14.2 Tesla
- 14.3 Robert Bosch GmbH
- 14.4 Toyota Motor Corporation
- 14.5 ZTE Corporation
- 14.6 Momentum Dynamis Corporation
- 14.7 Nission
- 14.8 TGOOD Global Ltd
- 14.9 HELLA GmbH & Co
- 14.10 Qualcomm Inc
- 14.11 Coninental AG
- 14.12 DAIHEN Corporation
- 14.13 BMW
- 14.14 Lumen Pty Ltd
- 14.15 WiTricity Corporation
- 14.16 HEVO Inc
- 14.17 ElectReon Wireless Ltd
- 14.18 Mojo Mobility Inc
- 14.19 Plugless Power LLC
- 14.20 Wave LLC