
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1693930
アジア太平洋の衛星姿勢・軌道制御システム- 市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Asia-Pacific Satellite Attitude and Orbit Control System - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| アジア太平洋の衛星姿勢・軌道制御システム- 市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 159 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
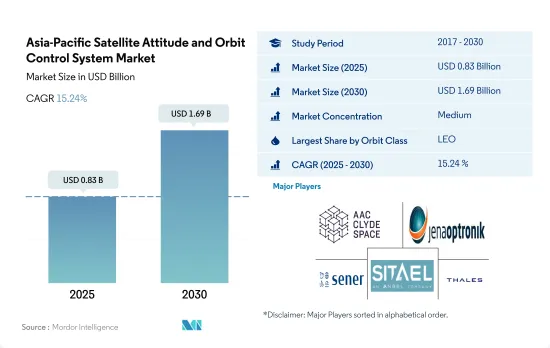
アジア太平洋の衛星姿勢・軌道制御システム市場規模は、2025年に8億3,000万米ドルと推定され、2030年には16億9,000万米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間中(2025~2030年)のCAGRは15.24%で成長する見込みです。
LEOに打ち上げられる衛星が市場需要を牽引
- 衛星AOCSは、異なる軌道にある衛星の安定性と精度を維持する上で重要な役割を果たしています。LEO衛星の需要は、宇宙技術の進歩や世界の接続性のニーズの高まりによって、近年急速に伸びています。AOCSはLEO衛星の安定性と精度を維持する上で重要な役割を担っており、特に高速で周回する衛星は大気抵抗や日射など様々な外力を受けています。その結果、アジア太平洋ではLEO衛星用AOCSの需要が高まっており、中国、日本、インド、韓国が宇宙基盤技術に多額の投資を行っています。2017~2022年にかけて、約379機の衛星がLEOに打ち上げられました。
- GEO衛星はより高い高度を周回し、主に放送と通信に使用されます。高速インターネットやデジタル通信の需要が高まっているため、アジア太平洋ではGEO衛星の需要が高まっています。2017~2022年の間に、約66機の衛星がGEOに打ち上げられました。
- アジア太平洋はまた、航空、海事、防衛を含むいくつかの産業で正確で信頼できるナビゲーションシステムへの要求が高まっているため、MEO衛星の需要も上昇しました。その結果、同地域ではMEO衛星用AOCSの需要が増加しており、中国、日本、韓国はナビゲーション測位システムにかなりの支出を行っています。2017~2022年にかけて、約24機の衛星がMEOに打ち上げられました。市場全体は2023~2029年にかけて18.42%の成長が見込まれています。
アジア太平洋の衛星姿勢・軌道制御システム市場動向
同地域では、衛星の質量に関する燃料効率と運用効率を向上させる傾向が見られました。
- 衛星の質量は衛星の打ち上げに大きな影響を与えます。衛星が重ければ重いほど、宇宙に打ち上げるために必要な燃料とエネルギーが増えるからです。衛星を打ち上げるには、時速約2万8,000キロという超高速まで加速し、地球の周回軌道に乗せる必要があります。この速度を達成するために必要なエネルギー量は、衛星の質量に比例します。
- その結果、衛星が重ければ重いほど、宇宙へ打ち上げるにはより大きなロケットとより多くの燃料が必要になります。その結果、打ち上げコストが上昇し、使用できるロケットタイプも制限されることになります。質量による主要分類タイプは、1,000kgを超える大型衛星です。2017~2022年にかけて、約75機以上の大型衛星が打ち上げられ、北米の組織が所有しています。中型衛星は、500~1,000kgの質量を持っています。アジア太平洋の組織は65機以上の衛星を打ち上げて運用しました。同様に、500kg以下の衛星は小型衛星と呼ばれ、この地域では約200機以上の小型衛星が打ち上げられています。
- 全体的に、衛星の質量は打ち上げに大きく影響し、重い衛星を打ち上げるにはより多くのエネルギーと燃料を必要とするため、コストが増加し、利用可能な打ち上げオプションが制限される可能性があります。アジア太平洋で運用されている衛星の数は、商業と軍事宇宙部門からの需要の増加により、2023~2029年にかけて急増すると予測されています。
さまざまな宇宙機関の宇宙開発費の増加は、市場にプラスの影響を与えると予想されます。
- AOCSは、あらゆるミッションモードで3軸の安定した地球指向姿勢を制御し、宇宙船の速度と軌道位置を測定します。アジア太平洋における宇宙関連活動の増加を考慮し、衛星メーカーは急速に台頭する市場の潜在力を利用するため、衛星生産能力を強化しています。強力な宇宙インフラを持つ著名なアジア太平洋諸国は、中国、インド、日本、韓国です。
- 中国国家宇宙局(CNSA)は、国家民間宇宙インフラと地上施設の強化を含む、2021~2025年の宇宙探査の優先事項を発表しました。この計画の一環として、中国政府は中国衛星ネットワークグループを設立し、衛星インターネット用の13,000衛星コンステレーションを開発しました。
- アジア太平洋では、中国、インド、日本だけが、完全なエンド・ツー・エンドの宇宙能力を有し、宇宙技術(通信衛星、地球観測衛星(EO)、航法衛星)、衛星製造、ロケット、宇宙港などの宇宙インフラを完備しています。この地域の他の国々は、それぞれの宇宙計画を遂行するために国際協力に頼らざるを得ないです。これは今後数年間である程度変化すると予想されるが、この地域の多くの国々は、最新の機敏な戦略の一環として、固有の宇宙能力を開発しています。2022年6月、韓国はヌリ・ロケットを打ち上げ、6基の衛星を軌道に乗せた。これにより韓国は、1トンを超える重量のペイロードを航空ロケットに載せて打ち上げることに成功した世界で7番目の国となりました。
アジア太平洋の衛星姿勢・軌道制御システム産業概要
アジア太平洋の衛星姿勢・軌道制御システム市場は、上位5社で55%を占め、適度に統合されています。この市場の主要企業は、AAC Clyde Space、Jena-Optronik、SENER Group、Sitael S.p.A.、Thalesです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主要調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の小型化
- 衛星質量
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- オーストラリア
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- ニュージーランド
- シンガポール
- 韓国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 用途
- 通信
- 地球観測
- ナビゲーション
- 宇宙観測
- その他
- 衛星質量
- 10~100kg
- 100~500kg
- 500~1,000kg
- 10kg以下
- 1,000kg以上
- 軌道クラス
- GEO
- LEO
- MEO
- エンドユーザー
- 商業
- 軍事・政府
- その他
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- AAC Clyde Space
- Innovative Solutions in Space BV
- Jena-Optronik
- NewSpace Systems
- SENER Group
- Sitael S.p.A.
- Thales
第7章 CEOへの主要戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要な洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
目次
Product Code: 50001241
The Asia-Pacific Satellite Attitude and Orbit Control System Market size is estimated at 0.83 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 1.69 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 15.24% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Satellites that are being launched into LEO are driving the market demand
- Satellite AOCS plays a critical role in maintaining the stability and precision of satellites in different orbits. The demand for LEO satellites has been growing rapidly in recent years, driven by advances in space technology and the increasing need for global connectivity. AOCS plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and precision of LEO satellites, especially as they orbit at high speeds and are subject to various external forces, including atmospheric drag and solar radiation. As a result, there is a growing demand for AOCS for LEO satellites in the Asia-Pacific region, with China, Japan, India, and South Korea investing heavily in space-based technologies. During 2017-2022, approximately 379 satellites were launched into LEO.
- GEO satellites orbit at higher altitudes and are primarily used for broadcasting and communications. Owing to the growing demand for high-speed internet and digital communication, the demand for GEO satellites has risen in the Asia-Pacific region. During 2017-2022, approximately 66 satellites were launched into GEO.
- The Asia-Pacific region also experienced a rise in demand for MEO satellites, owing to the growing requirement for accurate and dependable navigation systems in several industries, including aviation, maritime, and defence. As a result, the region is seeing an increase in demand for AOCS for MEO satellites, with China, Japan, and South Korea spending considerably on navigation and positioning systems. During 2017-2022, approximately 24 satellites were launched into MEO. The overall market is expected to grow by 18.42% from 2023 to 2029.
Asia-Pacific Satellite Attitude and Orbit Control System Market Trends
The trend for better fuel and operational efficiency with respect to satellite mass was witnessed in the region
- The mass of a satellite has a significant impact on the launch of the satellite. This is because the heavier the satellite, the more fuel and energy are required to launch it into space. Launching a satellite involves accelerating it to a very high speed, typically around 28,000 kilometers per hour, to place it in orbit around the Earth. The amount of energy required to achieve this speed is proportional to the satellite's mass.
- As a result, a heavier satellite requires a larger rocket and more fuel to launch it into space. This, in turn, increases the cost of the launch and can also limit the types of launch vehicles that can be used. The primary classification types according to mass are large satellites that are more than 1,000 kg. During 2017-2022, around 75+ large satellites launched were owned by North American organizations. A medium-sized satellite has a mass between 500 and 1000 kg. Asia-Pacific organizations operated more than 65+ satellites launched. Similarly, satellites that have a group of less than 500 kg are considered small satellites, and around 200+ small satellites were launched in this region.
- Overall, the mass of a satellite significantly impacts its launch, requiring more energy and fuel to launch a heavier satellite, which increases the cost and can limit the launch options available. The number of operating satellites in the Asia-Pacific region is projected to surge during 2023-2029 due to the growing demand from the commercial and military space sectors.
The increasing space expenditures of different space agencies are expected to impact the market positively
- AOCS controls a three-axis stable Earth-pointing attitude in all mission modes and measures spacecraft velocity and orbital position. Considering the increase in space-related activities in the Asia-Pacific region, satellite manufacturers are enhancing their satellite production capabilities to tap into the rapidly emerging market potentials. The prominent Asia-Pacific countries with robust space infrastructure are China, India, Japan, and South Korea.
- China National Space Administration (CNSA) announced space exploration priorities during 2021-2025, including enhancing national civil space infrastructure and ground facilities. As a part of this plan, the Chinese government established China Satellite Network Group Co. Ltd to develop a 13,000-satellite constellation for satellite internet.
- In Asia-Pacific, only China, India, and Japan have full end-to-end space capacity and complete space infrastructure space technology (communication, Earth observation (EO), and navigation satellites), satellite manufacturing, rockets, and spaceports. Other countries in the region must rely on international cooperation to carry out their respective space programs. This is expected to change to some extent in the coming years, although many countries in the region are developing indigenous space capabilities as part of their latest agile strategies. In June 2022, South Korea launched the Nuri rocket, putting six satellites into orbit, making it the seventh country in the world to successfully launch a payload weighing more than one metric ton onto an air launch vehicle.
Asia-Pacific Satellite Attitude and Orbit Control System Industry Overview
The Asia-Pacific Satellite Attitude and Orbit Control System Market is moderately consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 55%. The major players in this market are AAC Clyde Space, Jena-Optronik, SENER Group, Sitael S.p.A. and Thales (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Miniaturization
- 4.2 Satellite Mass
- 4.3 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.4.1 Australia
- 4.4.2 China
- 4.4.3 India
- 4.4.4 Japan
- 4.4.5 New Zealand
- 4.4.6 Singapore
- 4.4.7 South Korea
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Application
- 5.1.1 Communication
- 5.1.2 Earth Observation
- 5.1.3 Navigation
- 5.1.4 Space Observation
- 5.1.5 Others
- 5.2 Satellite Mass
- 5.2.1 10-100kg
- 5.2.2 100-500kg
- 5.2.3 500-1000kg
- 5.2.4 Below 10 Kg
- 5.2.5 above 1000kg
- 5.3 Orbit Class
- 5.3.1 GEO
- 5.3.2 LEO
- 5.3.3 MEO
- 5.4 End User
- 5.4.1 Commercial
- 5.4.2 Military & Government
- 5.4.3 Other
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 AAC Clyde Space
- 6.4.2 Innovative Solutions in Space BV
- 6.4.3 Jena-Optronik
- 6.4.4 NewSpace Systems
- 6.4.5 SENER Group
- 6.4.6 Sitael S.p.A.
- 6.4.7 Thales
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


