
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1693929
アジア太平洋の軍事衛星- 市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Asia-Pacific Military Satellite - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| アジア太平洋の軍事衛星- 市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 143 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
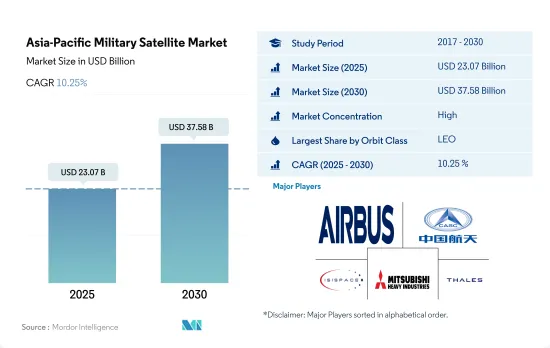
アジア太平洋の軍事衛星市場規模は、2025年に230億7,000万米ドルと推定され、2030年には375億8,000万米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間中(2025~2030年)のCAGRは10.25%で成長する見込みです。
2029年にはLEO衛星が84%の主要シェアを占め、需要を牽引
- アジア太平洋では、地球低軌道(LEO)、地球中軌道(MEO)、静止地球軌道(GEO)など、幅広い衛星軌道に対応する軍事衛星の需要が大幅に増加しています。この需要は、衛星を利用した通信、航法、リモートセンシングサービスのニーズの高まりに後押しされています。
- LEO衛星は、地球観測、気象予報、通信など幅広い用途でますます普及しています。LEO衛星の需要は特に中国で強く、SpacetyやChang Guang Satellite Technologyといった企業がLEOミッション用の衛星バスを提供しています。中国は、「高芬」シリーズの衛星を打ち上げるなど、この地域で積極的に活動しています。
- MEO衛星は、GPSやガリレオのような世界ナビゲーションや測位サービスにとってますます重要になってきています。この地域では、中国がBeiDouナビゲーションシステムの打ち上げでこのセグメントをリードしてきました。
- GEO衛星は、テレビやインターネットなどの通信・放送サービスにとって特に重要です。GEO衛星の需要は特にインドで強く、ISROやAntrix Corporation Ltdなどの企業が通信ミッション用の先進的な衛星バスを開発しています。中国もGEO衛星に多額の投資を行っており、通信衛星の中興シリーズを打ち上げています。
アジア太平洋の軍事衛星市場の動向
世界の衛星小型化需要の高まり
- 小型衛星は、計算、電子機器の小型化、包装の進歩を活用して、先進的ミッション能力を生み出します。超小型衛星は他のミッションと宇宙空間を共有することができ、打ち上げコストの大幅な削減を実現します。アジア太平洋の需要は、主に中国、日本、韓国、インドが牽引しており、毎年最も多くの小型衛星を製造しています。同国からの打ち上げは過去3年間で減少しているもの、同国の産業には大きな可能性が眠っており、新興諸国や超小型衛星開発プロジェクトへの継続的な投資が同地域の収益成長を後押しすると期待されています。2017~2022年の間に、この地域の様々な参入企業によって50機以上の超小型・超小型衛星が軌道に投入されました。
- 例えば、2021年11月、中国は西昌衛星発射センターから新しいリモートセンシング衛星Yaogan-35Aの宇宙への打ち上げに成功しました。Yaogan-35Aは情報・モニタリング・偵察(ISR)衛星です。Yaogan-35Aシリーズの衛星は、中国科学院(CAS)の小型衛星センターによって製造されています。これらの衛星は信号または電子情報(SIGINT/ELINT)収集システムであり、船舶からの無線放射を収集し、位置を特定するもので、中国の海洋領域認識任務の一部であると推測されています。
世界の衛星製造市場における投資機会
- アジア太平洋における宇宙関連活動の増加を考慮し、衛星メーカーは急速に台頭しつつある市場の潜在力を利用するため、衛星製造能力を強化しています。堅牢な宇宙インフラを持つアジア太平洋の著名な国は、中国、インド、日本、韓国です。中国国家宇宙局(CNSA)は、国家民間宇宙インフラと地上施設の強化を含む、2021~2025年の宇宙探査優先事項を発表しました。この計画の一環として、中国政府は衛星インターネット用の1万3,000衛星コンステレーション開発のために中国衛星ネットワークグループを設立しました。
- 2022年、日本の予算案によると、日本の宇宙予算は14億米ドルを超え、その中には、H3ロケット、技術検査衛星9号、国の情報収集衛星(IGS)計画の開発など、11の省庁の宇宙活動への投資が含まれています。インドは第三者打上げサービスの世界的リーダーとなっており、新しい打上げプラットフォームの研究開発プログラムもいくつか進行中です。22年度のインドの宇宙開発予算案は18億3,000万米ドルでした。
- 韓国の宇宙計画は、他国がコア技術の移転に消極的なため、進展が遅れています。2022年、科学情報通信省は、人工衛星、ロケット、その他の重要な宇宙機器の製造のために6億1,900万米ドルの宇宙予算を発表しました。多くの東南アジア諸国が宇宙技術への投資を開始しています。2021年3月現在、インドネシア政府は、2023年の打ち上げに向け、官民連携(PPP)スキームを利用した超高スループット衛星(SATRIA)の製造を継続するため、5億4,500万米ドルを確保しました。
アジア太平洋の軍事衛星産業概要
アジア太平洋の軍事衛星市場はかなり統合されており、上位5社で95%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は、Airbus SE、China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)、Innovative Solutions in Space BV、Mitsubishi Heavy Industries、Thalesです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主要調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の小型化
- 衛星質量
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- オーストラリア
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- ニュージーランド
- シンガポール
- 韓国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 衛星質量
- 10~100kg
- 100~500kg
- 500~1,000kg
- 10kg以下
- 1,000kg以上
- 軌道クラス
- GEO
- LEO
- MEO
- 衛星サブシステム
- 推進ハードウェアと推進剤
- 衛星バスとサブシステム
- 太陽電池アレイと電源ハードウェア
- 構造、ハーネス、機構
- アプリケーション
- 通信
- 地球観測
- ナビゲーション
- 宇宙観測
- その他
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Airbus SE
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)
- Indian Space Research Organisation(ISRO)
- Innovative Solutions in Space BV
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Thales
第7章 CEOへの主要戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要な洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
The Asia-Pacific Military Satellite Market size is estimated at 23.07 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 37.58 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 10.25% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

LEO satellites driving the demand by occupying a major share of 84% in 2029
- Asia-Pacific has seen a significant increase in the demand for military satellites to accommodate a wide range of satellite orbits, including low Earth orbit (LEO), medium Earth orbit (MEO), and geostationary Earth orbit (GEO). This demand has been driven by the growing need for satellite-based communication, navigation, and remote sensing services.
- LEO satellites have become increasingly popular for a wide range of applications, including Earth observation, weather forecasting, and communication. The demand for LEO satellites has been particularly strong in China, where companies such as Spacety and Chang Guang Satellite Technology Co. Ltd offer satellite buses for LEO missions. China has been active in this region with the launch of the Gao Fen series satellites.
- MEO satellites have become increasingly important for global navigation and positioning services such as GPS and Galileo. In the region, China has been a leader in this area with the launch of the BeiDou navigation system.
- GEO satellites are particularly important for communication and broadcasting services, such as television and the Internet. The demand for GEO satellites has been particularly strong in India, where companies such as ISRO and Antrix Corporation Ltd have been developing advanced satellite buses for communication missions. China has also been investing heavily in GEO satellites, with the launch of the Zhongxing series of communication satellites.
Asia-Pacific Military Satellite Market Trends
Increasing demand for satellite miniaturization globally
- Miniature satellites leverage advances in computation, miniaturized electronics, and packaging to produce sophisticated mission capabilities. Microsatellites can share the ride to space with other missions and offer a considerable reduction in launch costs. The demand from Asia-Pacific is primarily driven by China, Japan, South Korea, and India, which manufacture the largest number of small satellites each year. Though the launches from the country have decreased over the last three years, a huge potential lies in the country's industry, and the ongoing investments in the startups and the nano and microsatellite development projects are expected to boost the revenue growth of the region. Between 2017 and 2022, more than 50 nano and microsatellites were placed into orbit by various players in the region.
- For instance, in November 2021, China successfully launched a new remote-sensing satellite, Yaogan-35A, into space from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center. Yaogan-35A is an intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) satellite. The Yaogan-35A series of satellites are built by the Small Satellite Centre at the China Academy of Science (CAS). It is speculated that these satellites are signals or electronic intelligence (SIGINT/ELINT) gathering systems that will collect and geolocate radio emissions from ships and are part of the Chinese maritime domain awareness mission.
Investment opportunities in the global satellite manufacturing market
- Considering the increase in space-related activities in Asia-Pacific, satellite manufacturers are enhancing their satellite production capabilities to tap into the rapidly emerging market potential. The prominent countries in Asia-Pacific that pose a robust space infrastructure are China, India, Japan, and South Korea. China National Space Administration (CNSA) announced space exploration priorities for the 2021-2025 period, including enhancing national civil space infrastructure and ground facilities. As a part of this plan, the Chinese government established China Satellite Network Group Co. Ltd for the development of a 13,000-satellite constellation for satellite internet.
- In 2022, according to the draft budget of Japan, the space budget of the country was over USD 1.4 billion, which included investment for space activities of 11 government ministries, such as the development of the H3 rocket, Engineering Test Satellite-9, and the nation's Information Gathering Satellite (IGS) program. India has become a global leader in third-party launch services and has several ongoing R&D programs for new launch platforms. The proposed budget for India's space programs for FY22 was USD 1.83 billion.
- South Korea's space program has seen slow progress as other countries are reluctant to transfer core technologies. In 2022, the Ministry of Science and ICT announced a space budget of USD 619 million for manufacturing satellites, rockets, and other key space equipment. Many Southeast Asian countries have started investing in space technology. As of March 2021, the Indonesian government secured USD 545 million to continue the fabrication of the very high throughput satellite (SATRIA), using a public-private partnership (PPP) scheme, for launch in 2023.
Asia-Pacific Military Satellite Industry Overview
The Asia-Pacific Military Satellite Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 95%. The major players in this market are Airbus SE, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), Innovative Solutions in Space BV, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and Thales (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Miniaturization
- 4.2 Satellite Mass
- 4.3 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.4.1 Australia
- 4.4.2 China
- 4.4.3 India
- 4.4.4 Japan
- 4.4.5 New Zealand
- 4.4.6 Singapore
- 4.4.7 South Korea
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Satellite Mass
- 5.1.1 10-100kg
- 5.1.2 100-500kg
- 5.1.3 500-1000kg
- 5.1.4 Below 10 Kg
- 5.1.5 above 1000kg
- 5.2 Orbit Class
- 5.2.1 GEO
- 5.2.2 LEO
- 5.2.3 MEO
- 5.3 Satellite Subsystem
- 5.3.1 Propulsion Hardware and Propellant
- 5.3.2 Satellite Bus & Subsystems
- 5.3.3 Solar Array & Power Hardware
- 5.3.4 Structures, Harness & Mechanisms
- 5.4 Application
- 5.4.1 Communication
- 5.4.2 Earth Observation
- 5.4.3 Navigation
- 5.4.4 Space Observation
- 5.4.5 Others
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- 6.4.3 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- 6.4.4 Innovative Solutions in Space BV
- 6.4.5 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- 6.4.6 Thales
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


