
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1693918
欧州の軍事衛星- 市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Europe Military Satellite - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 欧州の軍事衛星- 市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 139 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
概要
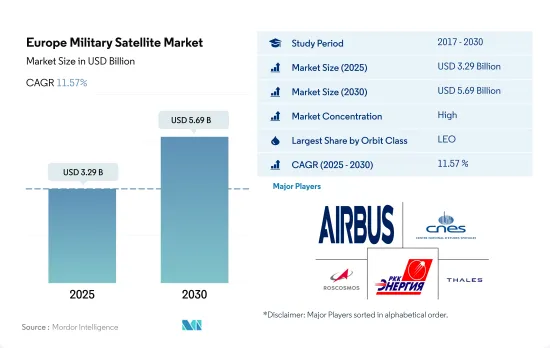
欧州の軍事衛星市場規模は2025年に32億9,000万米ドルと推定・予測され、2030年には56億9,000万米ドルに達し、予測期間(2025~2030年)のCAGRは11.57%で成長すると予測されています。
LEO衛星が市場の成長を牽引し、2029年には84%という大きなシェアを占める
- 軍事作戦を支援するため、安全で弾力性のある通信システムの必要性が高まっています。欧州諸国は、強化された暗号化機能とサイバー脅威からの保護を提供する軍事衛星システムに投資しています。これらのシステムは、指揮統制、情報収集、軍事力間の調整のための信頼性の高い安全な通信チャネルを確保します。
- 打ち上げ時、衛星や宇宙船は通常、地球を周回するいくつかの特別な軌道の1つに配置されます。地球周回軌道には、静止軌道(GEO)、中軌道、低軌道の3種類があります。多くの気象衛星や通信衛星は、地表から最も遠い地球高軌道にある傾向があります。中軌道衛星には、特定の地域をモニタリングするために設計された航法衛星や特殊衛星が含まれます。これらの衛星を含め、ほとんどの科学衛星は地球低軌道にあります。
- この地域で製造・打ち上げられる衛星は用途が異なります。例えば、2017~2022年にかけて、MEOで製造・打ち上げられた16機の衛星のうち、ほとんどがナビゲーション/全地球測位目的で製造されたものです。同様に、GEOの14機の衛星のうち、ほとんどが通信と地球観測の目的で配備されました。欧州の組織は、過去に製造・打ち上げられた約500機以上のLEO衛星を所有していました。
- 電子諜報、地球科学/気象学、レーザーイメージング、電子諜報、光学イメージング、気象学などのセグメントで衛星の利用が拡大していることから、予測期間中、欧州の衛星打ち上げロケット市場では宇宙センサの需要が高まると予想されています。2023~2029年の間に、市場は104%急増すると予想されます。
欧州の軍事衛星市場の動向
欧州における衛星小型化需要の高まりが市場を後押し
- 小型衛星は、先進的ミッション能力を生み出すために、計算、小型化された電子機器、包装の進歩を活用しています。超小型衛星は他のミッションと宇宙空間を共有できるため、打ち上げコストを大幅に削減できます。
- 欧州からの需要は、主にドイツ、フランス、ロシア、英国が牽引しており、これらの国は毎年最も多くの小型衛星を製造しています。この地域からの打ち上げは過去3年間で減少しているもの、この地域の産業には大きな可能性が眠っています。新興企業や超小型衛星開発プロジェクトへの継続的な投資も、この地域市場の収益成長を後押しすると期待されています。この点に関して、2017~2022年にかけて、この地域の様々な参入企業によって50機以上の超小型衛星が軌道に投入されました。
- 企業は、増大する需要に対応するため、これらの衛星を大規模に生産するコスト効率の良いアプローチに注力しています。このアプローチには、開発と設計検証の段階で、低コストの工業用定格受動素子を使用することが含まれます。電子部品と電子システムの小型化と商業化が市場参入企業を牽引し、その結果、現在の市場シナリオを活用し、強化することを目指す新たな市場参入企業が出現しています。2021年8月、フランスはBRO衛星をLEOに打ち上げました。これらの超小型衛星は、世界中の船舶の位置を特定し、識別することができ、海上オペレーターに追跡サービスを提供し、治安部隊を支援します。同国は2025年までに20~25機の超小型衛星のフリートを構築する計画です。
投資機会の急増が欧州の軍事衛星市場を押し上げると予想される
- 欧州諸国は、宇宙セグメントにおける様々な投資の重要性を認識しています。世界の宇宙産業で競合を維持するために、地球観測、衛星航法、接続性、宇宙研究、技術革新などのセグメントへの支出を増やしています。この点に関して、2022年11月、ESAは、地球観測における欧州のリードを維持し、航法サービスを拡大し、米国との探査におけるパートナーであり続けるために、今後3年間で宇宙資金を25%増額することを提案したと発表しました。ESAは、2023~2025年にかけて185億ユーロの予算を支持するよう22カ国に要請しています。2022年9月、フランス政府は、過去3年間で約25%増となる90億米ドル以上を宇宙活動に充てる計画を発表しました。2022年11月、ドイツは、地球観測に約6億6,900万ユーロ、通信に約3億6,500万ユーロ、技術プログラムに5,000万ユーロ、宇宙状況認識と宇宙セキュリティに1億5,500万ユーロ、宇宙輸送と運用に3億6,800万ユーロなど、約23億7,000万ユーロが割り当てられると発表しました。
- 英国政府は、軍事の衛星通信能力の75億米ドルのアップグレードを計画しています。2020年7月、英国国防省(MoD)はAirbus Defence and Spaceに6億3,000万米ドルの契約を発注し、2025年までに運用を開始する予定の新世代宇宙船の導入に先立ち、軍事能力を強化するための応急措置として、新たな通信衛星の建設に着手しました。この契約では、AirbusのEurostar Neo宇宙船をベースとした完全国産衛星となります。
欧州の軍事衛星産業概要
欧州の軍事衛星市場はかなり統合されており、上位5社が100%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は、Airbus SE、Centre National D'etudes Spatiales(CNES)、ROSCOSMOS、RSC Energia、Thalesです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主要調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の小型化
- 衛星質量
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- フランス
- ドイツ
- ロシア
- 英国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 衛星質量
- 10-100kg
- 100-500kg
- 500-1,000kg
- 10kg以下
- 1,000kg以上
- 軌道クラス
- ジオ
- LEO
- MEO
- 衛星サブシステム
- 推進ハードウェアと推進剤
- 衛星バスとサブシステム
- 太陽電池アレイと電源ハードウェア
- 構造、ハーネス、機構
- 用途
- 通信
- 地球観測
- ナビゲーション
- 宇宙観測
- その他
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Airbus SE
- Centre National D'etudes Spatiales(CNES)
- GomSpaceApS
- ROSCOSMOS
- RSC Energia
- Thales
第7章 CEOへの主要戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要な洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
目次
Product Code: 50000972
The Europe Military Satellite Market size is estimated at 3.29 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 5.69 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 11.57% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

LEO satellites are driving the market's growth and occupies a significant share of 84% in 2029
- There is a growing need for secure and resilient communication systems to support military operations. European countries are investing in military satellite systems that offer enhanced encryption capabilities and protection against cyber threats. These systems ensure reliable and secure communication channels for command and control, intelligence gathering, and coordination among military forces.
- At launch, a satellite or spacecraft is usually placed in one of several special orbits around the Earth, or it can be launched during interplanetary travel. There are three types of Earth orbits, namely, geostationary orbit (GEO), medium Earth orbit, and low Earth orbit. Many weather and communications satellites tend to have high Earth orbits farthest from the surface. Medium Earth orbit satellites include navigational and specialized satellites that are designed to monitor a specific area. Most science satellites, including those, are in low Earth orbit.
- The different satellites manufactured and launched in this region have different applications. For instance, during 2017-2022, out of the 16 satellites manufactured and launched in MEO, most were built for navigation/global positioning purposes. Similarly, out of the 14 satellites in GEO, most were deployed for communication and Earth observation purposes. European organizations owned around 500+ LEO satellites that were manufactured and launched during the historical period.
- The growing use of satellites in areas such as electronic intelligence, Earth science/meteorology, laser imaging, electronic intelligence, optical imaging, and meteorology is expected to drive demand for space sensors in the European satellite launch vehicle market during the forecast period. During 2023-2029, the market is expected to surge by 104%.
Europe Military Satellite Market Trends
The rising demand for satellite miniaturization in Europe is boosting the market
- Miniature satellites leverage advances in computation, miniaturized electronics, and packaging to produce sophisticated mission capabilities. As the microsatellites can share the ride to space with other missions, they considerably reduce launch costs.
- The demand from Europe is primarily driven by Germany, France, Russia, and the United Kingdom, which manufacture the largest number of small satellites annually. Though the launches from the region have decreased over the last three years, a huge potential lies in the region's industry. The ongoing investments in the startups and the nano and microsatellite development projects are also expected to boost the revenue growth of the regional market. On this note, from 2017 to 2022, more than 50 nano and microsatellites were placed into orbit by various players in the region.
- Companies are focusing on cost-effective approaches to produce these satellites on a large scale to meet the growing demand. The approach involves the use of low-cost industrial-rated passives at the development and design validation stages. The miniaturization and commercialization of electronic components and systems have driven market participation, resulting in the emergence of new market players that aim to capitalize on and enhance the current market scenario. In August 2021, France launched the BRO satellite into LEO. These nanosatellites can locate and identify ships worldwide, providing tracking services for maritime operators and helping security forces. The country plans to build a fleet of 20-25 nanosatellites by 2025.
The surge in investment opportunities is expected to boost the Europe military satellite market
- European countries are recognizing the importance of various investments in the space domain. They are increasing their spending in areas such as Earth observation, satellite navigation, connectivity, space research, and innovation to stay competitive in the global space industry. On this note, in November 2022, ESA announced that it had proposed a 25% boost in space funding over the next three years designed to maintain Europe's lead in Earth observation, expand navigation services, and remain a partner in exploration with the United States. The ESA is requesting its 22 nations to back a budget of EUR 18.5 billion for 2023-2025. In September 2022, the French government announced that it was planning to allocate more than USD 9 billion to space activities, an increase of about 25% over the past three years. In November 2022, Germany announced that about EUR 2.37 billion were allocated, including about EUR 669 million for Earth observation, about EUR 365 million for telecommunications, EUR 50 million for technology programs, EUR 155 million for space situational awareness and space security, and EUR 368 million for space transport and operations.
- The UK government has planned a USD 7.5 billion upgradation of the satellite telecommunication capabilities of the armed forces. In July 2020, the UK Ministry of Defence (MoD) awarded a USD 630 million contract to Airbus Defence and Space for constructing a new telecommunications satellite as a stopgap to bolster military capabilities ahead of the introduction of a new generation of spacecraft that is scheduled to start entering service by 2025. Under the terms of the contract, the fully indigenous satellite will be based on Airbus' Eurostar Neo spacecraft.
Europe Military Satellite Industry Overview
The Europe Military Satellite Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 100%. The major players in this market are Airbus SE, Centre National D'etudes Spatiales (CNES), ROSCOSMOS, RSC Energia and Thales (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Miniaturization
- 4.2 Satellite Mass
- 4.3 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.4.1 France
- 4.4.2 Germany
- 4.4.3 Russia
- 4.4.4 United Kingdom
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Satellite Mass
- 5.1.1 10-100kg
- 5.1.2 100-500kg
- 5.1.3 500-1000kg
- 5.1.4 Below 10 Kg
- 5.1.5 above 1000kg
- 5.2 Orbit Class
- 5.2.1 GEO
- 5.2.2 LEO
- 5.2.3 MEO
- 5.3 Satellite Subsystem
- 5.3.1 Propulsion Hardware and Propellant
- 5.3.2 Satellite Bus & Subsystems
- 5.3.3 Solar Array & Power Hardware
- 5.3.4 Structures, Harness & Mechanisms
- 5.4 Application
- 5.4.1 Communication
- 5.4.2 Earth Observation
- 5.4.3 Navigation
- 5.4.4 Space Observation
- 5.4.5 Others
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 Centre National D'etudes Spatiales (CNES)
- 6.4.3 GomSpaceApS
- 6.4.4 ROSCOSMOS
- 6.4.5 RSC Energia
- 6.4.6 Thales
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


