
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1692507
英国の地域暖房- 市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)UK District Heating - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 英国の地域暖房- 市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 90 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
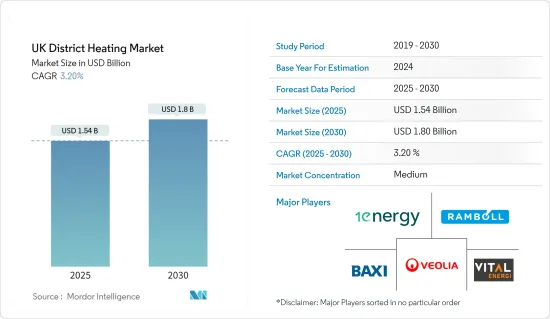
英国の地域暖房市場規模は2025年に15億4,000万米ドルと推定され、予測期間(2025年~2030年)のCAGRは3.2%で、2030年には18億米ドルに達すると予測されています。
主なハイライト
- 持続可能な開発シナリオ(SDS)に対応するため、地域暖房、ヒートポンプ、再生可能エネルギーや水素を利用した暖房などのクリーンな暖房技術が地域暖房ネットワークの売上を伸ばし、市場需要にプラスの影響を与えると予想されます。
- エネルギー効率の高い暖房ソリューションに対する需要の高まりが、新技術の採用を後押ししています。英国政府の調査によると、英国では2030年までに熱需要の14~20%、2050年までに43%が熱ネットワークによって満たされると予想されています。英国で消費されるエネルギーの約半分は熱として利用されています。商業、家庭、公共部門が最終エネルギー消費の3分の2を占めています。熱は主に、住宅/家庭用および商業用建物の給湯と暖房に使用されます。
- 第5世代は、既存の第4世代地域暖房システムに代わる新しいシステムとして登場しつつあります。第5世代の地域冷暖房システムは、双方向で分散化された、地上に近い温度ネットワークであり、冷熱貯蔵と温熱還流の直接交換を利用して熱需要を完全に均衡させるものです。
- 国内で熱ネットワークを拡大するための政府主導の取り組みもいくつかあり、調査対象市場の成長に有利な見通しを生み出しています。例えば、2022年後半に英国政府は、イングランドとウェールズ全域の熱ネットワークを支援することを目的とした政府の熱ネットワーク投資プロジェクト(HNIP)3億2,000万ポンド(3億9,900万米ドル)から得た1,910万ポンド(2,380万米ドル)の資金を発表しました。
- しかし、地域暖房システムは、市場の代替品と比較して資本集約的です。DHCシステムは、トレンチのネットワークと、ポンプとシステムの継続的なメンテナンスを必要とします。こうした要因がDHCシステムの需要を妨げています。
- さらに、地域暖房用の配水管を、そのような機能を計画されていない既存の都市や建物に設置するのは困難でコストがかかるため、設置プロセスが複雑化し、調査対象市場の成長にとって引き続き大きな課題となっています。
英国の地域暖房市場動向
都市化と工業化の進展が市場を牽引
- 英国を含む世界各地の急速な都市化が需要を押し上げ、集中冷暖房のための再生可能エネルギー源への転換を後押ししています。これは、CO2排出量の削減、効率の向上、都市部のエネルギー需要の増加、費用対効果の高い温度制御の実現に役立ちます。例えば、英国では都市化に伴い、北部地域での集中システムの利用が急速に増加しています。
- 世界銀行によると、英国の都市化率は2022年には84.39%に達します。これは、過去10年間でほぼ3ポイント増加したことになります。緩やかではあるが、増加傾向は一貫して前向きで、市場の成長に大きな影響を与えています。
- 寒冷な気象条件が顕著であることを考慮すると、英国はDHCソリューションの世界需要の中で突出したシェアを占めており、配電網の大部分はこの地域の都市部に位置しています。この地域では、20世紀後半に大規模な熱供給インフラが開発されました。これらは現在も、都市部における暖房や給湯のための主要なエネルギー供給手段となっています。
- 地域エネルギーシステムは、このような環境から恩恵を受け、それを支えるものであり、本来、都市景観に適したものです。この技術は、環境条件や労働人口のニーズとの相乗効果により、都市の人口動態に適しています。都市中心部の成長は、地域ネットワークの構築を促進します。イングランド、ロンドン、ウェールズ、ノッティンガムなどがその代表例です。特定の開発規模を必要とすることに加え、熱ネットワークの資本コストが高いため、エンドユーザーの数を最大化するために、エネルギーサービスを可能な限り狭いスペースで提供することが求められます。したがって、密集した都市開発は、分散型熱供給に非常に適しています。
住宅・家庭用セグメントが大きな市場シェアを占める
- 家庭用暖房は、英国における全排出量の14%近くを占めており(Institute for Governmentによる)、二酸化炭素削減目標を達成するという政府の目標に沿って、早急に取り組む必要があります。地域暖房は、英国全土の家庭に低炭素の熱を供給するための効果的なソリューションです。現在、英国で地域暖房ネットワークに接続されている住宅は全体の2%強に過ぎないが(Energy Saving Trustによる)、今後数十年の間に国がネット・ゼロに移行するのに伴い、さらに多くの住宅がオンライン化されると予想されています。
- 現在、英国に設置されている地域暖房システムのほとんどは、ガスで発電する熱電併給システム(CHP)を使用しています。CHPは通常、団地や集合住宅では1台が効率的で、各戸にガスボイラーを設置するよりもメンテナンスが少なくて済みます。英国政府の気候変動委員会(CCC)は、2050年までに家庭用暖房の約12%が地域暖房によって供給されると予測しています。
- 英国には17,000を超える熱供給ネットワークがあり、約50万人が熱供給ネットワークに接続しています。ヒート・ネットワークは、都市部の密集地では特に魅力的な選択肢として認識されています。熱供給網は、住宅管理コストを削減しながら燃料貧困に対処する効果的な方法です。
- ヒートネットワークの規模は様々で、道路を掘り返したり、住宅を建て替えたりするような急激な変更を加えることなく、より安価で低炭素な熱源を時間をかけて追加していくことができます。したがって、住宅セクターの二酸化炭素排出量を削減するための努力の高まりが、研究市場の成長を支えることになります。例えば、英国ビジネス・エネルギー・産業戦略省(Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy)などによると、英国の住宅不動産セクターからの二酸化炭素排出量は、2040年までに6,800万トンに達すると予測されています。
- さらに、2025年に英国で導入が予定されている「フューチャー・ホームズ・スタンダード」では、新築住宅から排出される二酸化炭素量を、現在の基準で建てられた住宅よりも約75~80%削減することが求められています。電力網の脱炭素化と暖房の電化の恩恵を受けるためには、住宅は改修工事不要の「ゼロ・カーボン・レディ」でなければならないです。新築住宅では化石燃料による暖房が禁止される可能性があり、ヒートネットワークなどの低炭素暖房技術へのシフトが予想されます。
英国の地域暖房産業の概要
英国の地域暖房市場は、Vital Energi、1 Energy Group Limited、Baxi Heating UK、Ramboll UK Limited、Veolia Environnement SAといった大手企業が存在し、競争は中程度です。市場の企業は、製品提供を強化し、持続可能な競争優位性を獲得するために、提携や買収などの戦略を採用しています。
2023年5月、英国政府はイングランド全土の7つの最先端ヒートネットワーク・プロジェクトに政府資金を授与しました。その中には、英国初の地下から熱を引き込むシステムも含まれており、約4,000世帯に低コストの暖房を提供できる可能性があります。政府によると、特定されたプロジェクトは、政府のグリーン・ヒート・ネットワーク基金から9,100万英ポンド(1億1,360万米ドル)の分配を受ける。
2023年4月、電力会社ピナクル・パワーはDIFキャピタル・パートナーズと、英国全土で10億ポンド(12億5,000万米ドル)相当の低炭素熱ネットワークを構築・展開する契約を結びました。両社の新たなパートナーシップにより、「町や都市規模の熱ネットワーク」の展開が加速され、英国全土のいくつかの家庭や建物の脱炭素化に貢献する可能性が高いです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリスト・サポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場洞察
- 市場概要
- 技術分析
- マクロ経済シナリオが市場に与える影響
- 業界の魅力度-ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 消費者の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
- 代替品の脅威
- 業界サプライチェーン分析
- 政府の取り組みとプログラム
- 地域暖房契約/ライブ入札
第5章 市場力学
- 市場促進要因
- エネルギー効率が高く、費用対効果の高い暖房システムへの需要の高まり
- 都市化と工業化の進展
- 市場の課題
- 高いインフラコスト
第6章 市場セグメンテーション
- エンドユーザー別
- 住宅/家庭用
- 非家庭用
- ヒートネットワークのエネルギーミックスの現状と今後の動向
- セクター別、顧客別ヒートネットワーク接続数
- 蓄熱の利用と将来の可能性
- 地域に基づく熱ネットワークの密度
- 熱ネットワークに対する消費者の意識
- 熱ネットワークの機会
第7章 競合情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Vital Energi Utilities Ltd.
- 1Energy Group Limited
- Baxi Heating UK
- Ramboll UK Limited
- Veolia Environnement SA
- Sweco UK(AWECO AB)
- Vanttenfall(Vattenfall AB)
- Equans Services Limited
- E.ON PLC
第8章 投資分析
第9章 市場の将来
The UK District Heating Market size is estimated at USD 1.54 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 1.80 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 3.2% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- To meet the Sustainable Development Scenario (SDS), clean heating technologies, such as district heating, heat pumps, and renewable and hydrogen-based heating, are expected to increase the sales of district heating networks, positively influencing market demand.
- The rising demand for energy-efficient heating solutions is pushing for the adoption of new technologies. As per the UK government's research, 14-20 percent of the heat demand in the United Kingdom is expected to be met by heat networks by 2030 and 43 percent by 2050. Around half of the energy consumed in the United Kingdom is used as heat. The commercial, domestic, and public sectors accounted for two-thirds of the final energy consumption. Heat is primarily used for water and space heating in residential/domestic and commercial buildings.
- The fifth generation is emerging as a new system to replace the existing fourth-generation district heating system. 5th generation district heating & cooling systems are bi-directional, decentralized, close-to-ground temperature networks that use the direct exchange of cold and warm thermal storage and return flows to balance the thermal demand in full measure.
- Several government-led initiatives to expand the heat networks in the country also create a favorable outlook for the growth of the studied market. For instance, in late 2022, the UK Government announced GBP19.1 million (USD 23.8 million) funding that came from the government's GBP320 million (USD 399 million) Heat Networks Investment Project (HNIP), aimed at supporting heat networks across England and Wales.
- However, district heating systems are more capital-intensive as compared to alternatives in the market. The DHC system requires a network of trenches and continuous maintenance of pumps and systems. These factors hinder the demand for DHC systems.
- Furthermore, it becomes difficult and costly to install distribution pipes for district heating in pre-existing cities/buildings that were not planned for such features, thereby adding complexity to the installation process, which continues to remain among the major challenging factors for the growth of the studied market.
UK District Heating Market Trends
Rising Urbanization and Industrialization to Drive the Market
- Rapid urbanization across the world, including in the UK, is driving the demand and pushing the switch to renewable energy sources for centralized heating & cooling, which can help reduce CO2 emissions, improve efficiency, increase urban energy needs, and provide cost-effective temperature control. For instance, driven by urbanization, the United Kingdom has rapidly increased its use of centralized systems in its northern regions.
- In the United Kingdom, urbanization amounted to 84.39% in 2022, as per the World Bank. This presents almost a three percentage point increase over the past decade. Though slow, the upward trend has been consistently positive, significantly influencing the market growth.
- Considering the prominence of cold weather conditions, the UK commands a prominent share of the global demand for DHC solutions, and a major share of the distribution network is situated in urban areas in the region. Large heat distribution infrastructures were developed during the second half of the 20th century in the region. These remain the principal ways to provide energy for space and water heating in urban areas.
- District energy systems benefit from and support this environment and are inherently appropriate to urban landscapes. The technology's synergy with the environmental conditions and the working population's needs are well suited for urban demographics. The growth of urban centers facilitates the construction of district networks. England, London, Wales, and Nottingham are some of the best examples in the market. In addition to requiring a particular scale of development, the high capital costs of heat networks demand energy services be delivered in the tightest space possible to maximize the number of end users. Thus, dense urban developments are highly suitable for distributed heat provision.
Residential and Domestic Segment Holds Significant Market Share
- Domestic heating accounts for nearly 14 percent of all emissions in the United Kingdom (according to the Institute for Government) and needs to be tackled urgently in line with the government's aim to meet its carbon reduction targets. District heating offers an effective solution for the supply of low-carbon heat to homes across the United Kingdom. While just over 2 percent of residences in the United Kingdom are currently connected to a district heating network (as per Energy Saving Trust), more are expected to come online as the country transitions to net zero over the coming decades.
- Most district heating systems currently installed in the United Kingdom use a gas-powered combined heat and power system (CHP), which generates electricity. A single CHP is usually more efficient in a housing estate or block of flats and requires less maintenance than a gas-powered boiler in every flat or house. The UK government's Committee for Climate Change (CCC) estimates that around 12 percent of domestic heat will be supplied by district heating by 2050.
- There are over 17,000 heat networks in place in the United Kingdom, and around half a million connections to them, most of them being domestic customers (as per Energy Saving Trust). They are perceived as a particularly attractive option in dense urban areas. They are an effective way of dealing with fuel poverty while reducing housing management costs.
- The establishment of heat networks, which can vary widely in size, implies that cheaper, lower-carbon sources of heat generation can be added over time without abrupt changes, such as digging up roads or changing people's homes. Hence, the growing efforts to reduce the carbon footprint of the residential sector will support the studied market's growth. For instance, according to sources like the UK Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy, carbon dioxide emission from the residential real estate sector in the United Kingdom is anticipated to reach 68 million metric tons by 2040.
- Furthermore, the Future Homes Standard, expected to be introduced in the United Kingdom in 2025, requires carbon emissions produced by new homes to be around 75-80 percent lower than those built to current standards. Houses will have to be 'zero carbon ready,' with no retrofit work needed to benefit from the electricity grid's decarbonization and the heating's electrification. Fossil fuel heating may be banned in new houses, with an expected shift toward low-carbon heating technologies, such as heat networks.
UK District Heating Industry Overview
The UK district heating market is moderately competitive, with the presence of major players like Vital Energi, 1 Energy Group Limited, Baxi Heating UK, Ramboll UK Limited, and Veolia Environnement SA. Players in the market are adopting strategies such as partnerships and acquisitions to enhance their product offerings and gain sustainable competitive advantage.
In May 2023, the UK Government awarded government funding to 7 state-of-the-art heat network projects across England, which includes the UK's first system drawing heat from underground, with the potential of providing low-cost heating for nearly 4,000 homes. According to the government, the identified projects will receive a share of GBP 91 million (USD 113.6 million) from the government's Green Heat Network Fund.
In April 2023, Utility company Pinnacle Power entered an agreement with DIF Capital Partners to build and deploy GBP 1 billion (USD 1.25 billion) worth of low-carbon heat networks across the UK. The new partnership between the companies will accelerate the deployment of "town-and-city-scale heat networks" that will likely help to decarbonize several homes and buildings across the country.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Technological Analysis
- 4.3 Impact of Macroeconomic Scenarios on the Market
- 4.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.4.5 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5 Industry Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Government Initiatives and Programs
- 4.7 District Heating Contracts/Live Tenders
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Augmented Demand for Energy-efficient and Cost-effective Heating Systems
- 5.1.2 Rising Urbanization and Industrialization
- 5.2 Market Challenges
- 5.2.1 High Infrastructure Cost
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By End User
- 6.1.1 Residential/Domestic
- 6.1.2 Non-domestic
- 6.2 Current Energy Mix of Heat Networks and Future Trends
- 6.3 Heat Network Connections by Sectors and Customers
- 6.4 Thermal Storage Usage and Future Potential
- 6.5 Heat Networks Density Based on Regions
- 6.6 Consumer Attitudes to Heat Networks
- 6.7 Opportunities for Heat Network
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Vital Energi Utilities Ltd.
- 7.1.2 1Energy Group Limited
- 7.1.3 Baxi Heating UK
- 7.1.4 Ramboll UK Limited
- 7.1.5 Veolia Environnement SA
- 7.1.6 Sweco UK (AWECO AB)
- 7.1.7 Vanttenfall (Vattenfall AB)
- 7.1.8 Equans Services Limited
- 7.1.9 E.ON PLC


