
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1690108
アジア太平洋地域の小型衛星:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Asia-Pacific Small Satellite - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| アジア太平洋地域の小型衛星:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 158 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
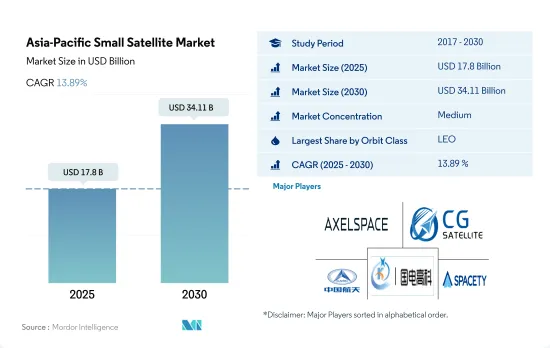
アジア太平洋の小型衛星の市場規模は2025年に178億米ドルと推定され、2030年には341億1,000万米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間中(2025-2030年)のCAGRは13.89%で成長する見込みです。
LEOに打ち上げられる衛星が市場需要を牽引
- 近年、この地域では小型衛星の需要が急速に高まっており、費用対効果が高く汎用性の高い宇宙船の利点を活用しようとする企業や政府が増えています。
- LEO衛星は、アジア太平洋地域で打ち上げられる小型衛星の中で最も人気のあるタイプの一つです。それらは、リモートセンシング、地球観測、通信を含む様々な用途に使用されています。同地域では、2017年から2022年にかけて、約240機の衛星がLEOに打ち上げられ、そのうち128機が地球観測用、次いで67機が技術開発用、24機が通信用、12機が宇宙科学用でした。
- MEO衛星もアジア太平洋地域で人気を集めている小型衛星です。これらの衛星は、世界ナビゲーション、通信、リモートセンシングの用途に使用されています。MEO衛星は、LEO衛星よりもカバー範囲が広く、広帯域の通信サービスを提供できるなど、いくつかの利点があります。
- アジア太平洋地域で打ち上げられるもう1つの衛星は、GEO衛星です。これらの衛星は、通信や気象観測の用途に使用されます。GEO衛星の主な利点の1つは、地球に対して一定の位置に留まることができることで、テレビ放送やインターネット接続など、継続的なカバレッジを必要とするアプリケーションに最適です。2017年から2022年にかけて、監視用に1機の衛星がGEOに打ち上げられました。これらの進歩により、2023~2029年の間にこのセグメントの成長率は182%増加すると予測されています。
アジア太平洋小型衛星市場動向
燃料効率と運用効率の向上に関する動向が成長の主な原動力になると予想される
- 最近の衛星は小型化しています。小型衛星は、従来の衛星の数分の一のコストで、従来の衛星が行うことのほとんどすべてを行うという事実が、小型衛星コンステレーションの構築、打ち上げ、運用をますます実行可能なものにしました。それに応じて、小型衛星への依存度も飛躍的に高まっています。
- 小型衛星は通常、開発サイクルが短く、開発チームも小規模で、打ち上げコストもはるかに低いです。革命的な技術の進歩は、エレクトロニクスの小型化を促進し、スマート材料の発明を後押しし、衛星バスのサイズと質量をメーカーが時間をかけて削減しました。
- 衛星の質量は、衛星の打ち上げに大きな影響を与えます。これは、衛星が重くなればなるほど、衛星を宇宙に打ち上げるために必要な燃料とエネルギーが増えるからです。人工衛星を打ち上げるには、時速約2万8000kmという超高速まで加速して地球周回軌道に投入する必要があります。
- 衛星が重ければ重いほど、宇宙へ打ち上げるにはより大きなロケットとより多くの燃料が必要になり、打ち上げコストが高くなり、使用できるロケットの種類も限られます。同様に、500kg未満の衛星は小型衛星とみなされ、この地域では約200以上の小型衛星が打ち上げられました。全体として、衛星の質量は打ち上げに大きく影響し、重い衛星を打ち上げるにはより多くのエネルギーと燃料を必要とするため、コストが上昇し、利用可能な打ち上げオプションが制限される可能性があります。アジア太平洋地域で運用されている衛星の数は、商業・軍事宇宙分野の需要増加により、2023~2029年に急増すると予測されています。
各宇宙機関の宇宙開発費の増加は、アジア太平洋地域の小型衛星市場にプラスの影響を与えると予想されます。
- アジア太平洋地域の小型衛星市場は、技術の進歩、投資の増加、小型衛星サービスの需要拡大により、近年急速に成長しています。超小型・超小型衛星は、従来の衛星よりも小型でコスト効率が高いため、幅広い組織が利用しやすいです。
- 中国、インド、日本は、完全なエンド・ツー・エンドの宇宙開発能力を有し、宇宙インフラ、宇宙技術衛星製造、ロケット、宇宙港を完備しています。その他の地域の国々は、それぞれの宇宙計画を遂行するために国際協力に頼らざるを得ないが、これは今後数年である程度変わると予想されます。しかし、この地域の多くの国々は、最新の機敏な戦略の一環として、固有の宇宙能力を開発しています。2022年6月、韓国はヌリ・ロケットを打ち上げて6基の衛星を軌道に乗せ、完全国産ペイロードの打ち上げに成功した世界で7番目の国となりました。
- 2022年、日本の予算案によると、日本の宇宙予算は14億米ドル以上でした。これには、H3ロケットの開発、技術試験衛星9号、情報収集衛星計画など、11の省庁の宇宙活動への投資が含まれています。
- アジア太平洋地域における宇宙関連活動の増加を考慮し、衛星メーカーは、急速に台頭する市場の潜在力を利用するため、衛星製造能力を強化しています。強固な宇宙インフラを有するアジア太平洋の代表的な国は、中国、インド、日本、韓国です。中国国家宇宙局(CNSA)は、国家民間宇宙インフラを強化することを含む、2021年から2025年における宇宙探査の優先事項を発表しました。
アジア太平洋地域の小型衛星産業の概要
アジア太平洋地域の小型衛星市場は適度に統合されており、上位5社で61.64%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は以下の通りです。Axelspace Corporation, Chang Guang Satellite Technology, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC), Guodian Gaoke and Spacety Aerospace Co.(sorted alphabetically).
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主な調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の質量
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- オーストラリア
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- ニュージーランド
- シンガポール
- 韓国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 用途
- 通信
- 地球観測
- ナビゲーション
- 宇宙観測
- その他
- 軌道クラス
- GEO
- LEO
- MEO
- エンドユーザー
- 商業
- 軍事・政府
- その他
- 推進技術
- 電気式
- ガス
- 液体燃料
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略的動き
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル.
- Axelspace Corporation
- Chang Guang Satellite Technology Co. Ltd
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)
- Guodian Gaoke
- MinoSpace Technology
- Spacety Aerospace Co.
- Zhuhai Orbita Control Engineering
第7章 CEOへの主な戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
The Asia-Pacific Small Satellite Market size is estimated at 17.8 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 34.11 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 13.89% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Satellites that are being launched into LEO is driving the market demand
- In recent years, demand for small satellites in the region has been rising rapidly, with more and more businesses and governments seeking to leverage the benefits of the cost-effective and versatile spacecraft.
- LEO satellites are one of the most popular types of small satellites launched in the Asia-Pacific region. They are used for various applications, including remote sensing, Earth observation, and communication. In the region, during 2017-2022, around 240 satellites were launched into LEO, of which 128 satellites were launched for Earth observation, followed by 67 satellites for technology development, 24 for communication, and 12 for space science.
- The MEO satellite is another small satellite gaining popularity in the Asia-Pacific region. These satellites are used for global navigation, communication, and remote sensing applications. MEO satellites offer several advantages over LEO satellites, including broader coverage and the ability to provide high-bandwidth communication services.
- The other type of satellites being launched into space in the Asia-Pacific region are GEO satellites. These satellites are used for communication and weather monitoring applications. One of the main advantages of GEO satellites is their ability to remain in a fixed position relative to the Earth, making them ideal for applications requiring continuous coverage, including television broadcasting and internet connectivity. During 2017-2022, one satellite was launched into GEO for surveillance. These advancements are projected to increase this segment's growth rate by 182% during 2023-2029.
Asia-Pacific Small Satellite Market Trends
The trends for better fuel and operational efficiency are expected to be major drivers of growth
- Satellites are getting smaller nowadays. The fact that the small-sized satellite does almost everything that a conventional satellite does at a fraction of the cost of the conventional satellite made the building, launching, and operation of the small satellite constellations increasingly viable. Correspondingly, our reliance on them has been growing exponentially.
- Small satellites typically have shorter development cycles, smaller development teams, and cost much less for launch. Revolutionary technological advancements facilitated the miniaturization of electronics, which pushed the invention of smart materials, reducing the satellite bus size and mass over time for manufacturers.
- The mass of a satellite has a significant impact on the launch of the satellite, and this is because the heavier the satellite, the more fuel and energy are required to launch it into space. Launching a satellite involves accelerating it to a very high speed, typically around 28,000 km per hour, to place it in orbit around the Earth.
- A heavier satellite requires a larger rocket and more fuel to launch it into space, which increases the cost of the launch and limits the types of launch vehicles that can be used. Similarly, satellites with less than 500 kg are considered small satellites, and around 200+ small satellites were launched in this region. Overall, the mass of a satellite significantly impacts its launch, requiring more energy and fuel to launch a heavier satellite, which increases the cost and can limit the launch options available. The number of operating satellites in the Asia-Pacific region is projected to surge during 2023-2029 due to growing demand in the commercial and military space sector.
Increasing space expenditures of different space agencies are expected to impact the Asia-Pacific small satellite market positively
- The Asia-Pacific small satellite market has grown rapidly in recent years, owing to technological advancements, increased investment, and growing demand for small satellite services. Nano and microsatellites are smaller and more cost-effective than traditional satellites, making them more accessible to a broader range of organizations
- China, India, and Japan have complete end-to-end space capacity and complete space infrastructure, space technology satellite manufacturing, rockets, and spaceports. Other regions' countries must rely on international cooperation to carry out their respective space programs, which is expected to change to some extent in the coming years. However, many countries in the region are developing indigenous space capabilities as part of their latest agile strategies. In June 2022, South Korea launched the Nuri rocket, putting six satellites into orbit, making it the seventh country in the world to successfully launch a wholly indigenous payload.
- In 2022, according to the draft budget of Japan, the space budget of the country was over USD 1.4 billion. It included investment in space activities of 11 government ministries, such as the development of the H3 rocket, Engineering Test Satellite-9, and the country's Information Gathering Satellite program.
- Considering the increase in space-related activities in the Asia-Pacific region, satellite manufacturers are enhancing their satellite production capabilities to tap into the rapidly emerging market potentials. The prominent Asia-Pacific countries that possess robust space infrastructure are China, India, Japan, and South Korea. China National Space Administration (CNSA) announced space exploration priorities during 2021-2025, including enhancing national civil space infrastructure.
Asia-Pacific Small Satellite Industry Overview
The Asia-Pacific Small Satellite Market is moderately consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 61.64%. The major players in this market are Axelspace Corporation, Chang Guang Satellite Technology Co. Ltd, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), Guodian Gaoke and Spacety Aerospace Co. (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Mass
- 4.2 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.3 Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.1 Australia
- 4.3.2 China
- 4.3.3 India
- 4.3.4 Japan
- 4.3.5 New Zealand
- 4.3.6 Singapore
- 4.3.7 South Korea
- 4.4 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Application
- 5.1.1 Communication
- 5.1.2 Earth Observation
- 5.1.3 Navigation
- 5.1.4 Space Observation
- 5.1.5 Others
- 5.2 Orbit Class
- 5.2.1 GEO
- 5.2.2 LEO
- 5.2.3 MEO
- 5.3 End User
- 5.3.1 Commercial
- 5.3.2 Military & Government
- 5.3.3 Other
- 5.4 Propulsion Tech
- 5.4.1 Electric
- 5.4.2 Gas based
- 5.4.3 Liquid Fuel
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Axelspace Corporation
- 6.4.2 Chang Guang Satellite Technology Co. Ltd
- 6.4.3 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- 6.4.4 Guodian Gaoke
- 6.4.5 MinoSpace Technology
- 6.4.6 Spacety Aerospace Co.
- 6.4.7 Zhuhai Orbita Control Engineering
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


