
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1687092
衛星製造・打上げロケット:市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025~2030年)Satellite Manufacturing and Launch Vehicle - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 衛星製造・打上げロケット:市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 291 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
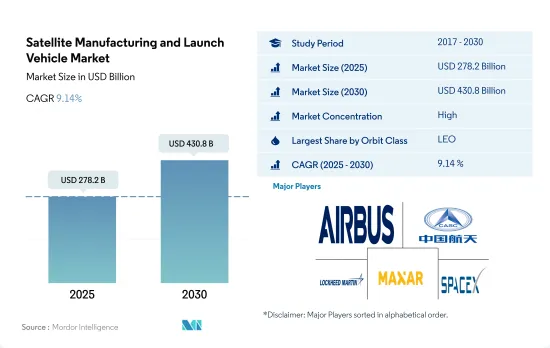
衛星製造・打上げロケット市場規模・推定は、2025年に2,782億米ドル、2030年には4,308億米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間(2025~2030年)のCAGRは9.14%で成長します。
LEO衛星セグメントが市場をリードする見込み
- 衛星や宇宙船は通常、地球を周回する多くの特別な軌道の1つに配置されます。低軌道(LEO)、静止軌道(GEO)、中軌道(MEO)という3種類の軌道のうち、地球に近いLEOが最も広く選ばれているようです。
- 気象衛星や通信衛星の多くは、地上から最も遠い地球高軌道をとる傾向があります。地球中周回軌道の衛星には、特定の地域をモニタリングするために設計された航法衛星や特殊衛星が含まれます。NASAの地球観測システムを含むほとんどの科学衛星は、地球低軌道にあります。
- 衛星製造・打上げロケットの用途はそれぞれ異なります。2017~2022年にかけて、MEO軌道で打ち上げられた56機の衛星のうち、ほとんどがナビゲーション/全地球測位目的で製造されました。GEO軌道に投入された133機の衛星のほとんどは、通信と地球観測の目的で配備されました。同時期に製造・打ち上げられた4,025機以上のLEO衛星は、世界中の様々な国によって所有されていました。
- 電子情報、地球科学/気象学、レーザーイメージング、光学イメージング、気象学などのセグメントで衛星の利用が増加していることから、予測期間中に衛星の開発需要が高まると予想されています。
通信、ナビゲーション、地球観測などの衛星サービスへの需要の高まりが市場成長を後押し
- 世界の衛星製造・打上げロケット市場はダイナミックで急速に発展しており、現代社会において重要な役割を果たしています。この産業を牽引しているのは、衛星を利用したサービスに対する需要の高まりや、官民双方にとっての宇宙へのアクセスの利便性の向上など、さまざまな要因です。その結果、この産業は近年著しい成長を遂げており、新規参入企業や既存企業がその能力を拡大しています。主要な衛星メーカーには、Airbus Defence and Space、Boeing、Lockheed Martin、Thales Alenia Spaceなどがあります。
- 衛星を軌道に運ぶための打ち上げロケットも、この産業の重要なコンポーネントです。これらのロケットには、キューブサットを打ち上げるために設計された小型のものから、複数の衛星を一度に軌道に運ぶことができる大型のものまです。主要なロケット企業には、SpaceX、United Launch Alliance、Arianespace、Roscosmosなどがあります。
- また、小型衛星メーカーやロケット会社など、革新的な技術やビジネスモデルを活用して従来の宇宙産業を破壊しようとする新たな参入企業も出現しています。例えば、ロケット・ラボやヴァージン・オービットのような企業は、小型ロケットを利用して、小型衛星事業者に費用対効果の高い宇宙へのアクセスを提供しています。
- 全体として、世界の衛星製造・打上げロケット市場は、衛星を利用したサービスに対する需要が増加し続け、宇宙へのアクセスが拡大するにつれて、継続的な成長と革新の態勢を整えています。この産業は、通信やナビゲーションから環境モニタリングや科学研究に至るまで、現代社会の未来を形作る上で重要な役割を果たし続けると考えられます。
世界の衛星製造・打上げロケット市場の動向
世界のロケット市場における需要の高まりと競合
- 北米は宇宙開発のパイオニアであり、長年にわたり多くの宇宙ミッションを成功させてきました。SpaceXは、先進的な再使用型ロケットと宇宙船を製造・打ち上げている主要航空宇宙企業です。同社は現在、Falcon-9、Falcon Heavy、Starshipなどの打ち上げロケットを有し、同地域における打ち上げサービスの主要プロバイダーとなっています。2017~2022年にかけて、スペースXのロケットは約2,744基の衛星を軌道に打ち上げました。
- 欧州では、ArianeGroupなどの企業が、アリアンロケットの再使用可能な第1段を含むAriane Nextロケットを開発しています。ロシアのロスコスモスもまた、ロケット開発・配備の長い歴史を持つ、この産業における重要な参入企業です。同社はソユーズロケットとプロトンロケットの開発を担当し、さまざまな衛星を宇宙に打ち上げてきました。2017~2022年にかけて、ソユーズロケットは世界の様々な衛星事業者のために約611個の衛星を宇宙に打ち上げました。
- アジア太平洋では、CASCは、世界で最も信頼性の高いロケットの1つとなった長征ロケットシリーズを含む、さまざまなロケットの開発と配備を担当しています。2017~2022年にかけて、CASCの長征ロケットは世界の様々な衛星事業者のために約372基の衛星を宇宙に打ち上げました。2017~2022年にかけて、JAXAはH-IIAロケットとH-IIBロケットを使って、世界の衛星事業者のために約25基の衛星を宇宙に打ち上げました。インドの宇宙プログラムも最近の動向で著しい成長を遂げており、ISROは同国のロケット開発で重要な役割を果たしています。2017~2022年にかけて、ISROのロケットは世界の様々な衛星事業者のために約171個の衛星を宇宙に打ち上げました。
世界の衛星製造市場における投資機会の増加
- 北米では、宇宙計画のための政府支出が2021年に過去最高の約1,030億円に達しました。この地域は、世界最大の宇宙機関であるNASAの存在により、宇宙イノベーションと研究の震源地となっています。2022年、米国政府は宇宙プログラムに約620億米ドルを費やし、世界で最も宇宙開発費を投じる国となっています。2023年度の大統領予算要求概要では、2022年度から2027年度にかけて、NASAは138億米ドルを受け取る見込みです。
- 2022年11月、ESAは、2023~2025年にかけて約185億ユーロの予算を支援するよう22カ国に通知したと発表しました。ドイツ、フランス、イタリアが主要貢献国です。39億米ドルをかけて開発され、2020年7月に打ち上げられる予定だったこのプロジェクトは、相次ぐ延期に見舞われています。2022年11月、フランス、ドイツ、イタリアの3カ国政府は、欧州の宇宙への独立系アクセスを確保しつつ、欧州のロケット競合を強化するため、「欧州におけるロケット開発の将来」に関する協定に署名したと発表しました。
- 2023年2月、インド政府は、ISROが様々な宇宙関連活動のために20億米ドルを受領する見込みであることを発表しました。また、944億1,000万インドルピーが打ち上げ活動とロケット、エンジン、衛星などの研究開発費に割り当てられました。2021年3月、日本は宇宙関連活動に41億4,000万米ドルを支出したと発表しました。2023年3月、韓国は次世代キャリアロケットKSLV-2の開発に約1億1,360万米ドルが割り当てられたと発表しました。
衛星製造・打上げロケット産業概要
衛星製造・打上げロケット市場はかなり統合されており、上位5社で89.17%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は、 Airbus SE、China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)、Lockheed Martin Corporation、Maxar Technologies Inc.、Space Exploration Technologies Corp.などです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主要調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の小型化
- 衛星質量
- ロケットの所有者
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- 世界
- オーストラリア
- ブラジル
- カナダ
- 中国
- フランス
- ドイツ
- インド
- イラン
- 日本
- ニュージーランド
- ロシア
- シンガポール
- 韓国
- アラブ首長国連邦
- 英国
- 米国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 用途
- 通信
- 地球観測
- ナビゲーション
- 宇宙観測
- その他
- 衛星質量
- 10~100kg
- 100~500kg
- 500~1,000kg
- 10kg以下
- 1,000kg以上
- 軌道クラス
- GEO
- LEO
- MEO
- ロケット
- 大型
- 小型
- 中型
- エンドユーザー
- 商業
- 軍事・政府
- その他
- 衛星サブシステム
- 推進ハードウェアと推進剤
- 衛星バスとサブシステム
- ソーラーアレイ&パワーハードウェア
- 構造、ハーネス、メカニズム
- 推進技術
- 電気
- ガスベース
- 液体燃料
- 地域
- アジア太平洋
- 国別
- オーストラリア
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- ニュージーランド
- シンガポール
- 韓国
- 欧州
- 国別
- フランス
- ドイツ
- ロシア
- 英国
- 北米
- 国別
- カナダ
- 米国
- その他
- 国別
- ブラジル
- イラン
- サウジアラビア
- アラブ首長国連邦
- その他
- アジア太平洋
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略的動き
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル.
- Airbus SE
- Ariane Group
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)
- Indian Space Research Organisation(ISRO)
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Maxar Technologies Inc.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Sierra Nevada Corporation
- Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- Thales
- The Boeing Company
- United Launch Alliance, LLC.
第7章 CEOへの主要戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
The Satellite Manufacturing and Launch Vehicle Market size is estimated at 278.2 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 430.8 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.14% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The LEO Satellites Segment Is Expected To Lead The Market
- A satellite or a spacecraft is usually placed into one of many special orbits around the Earth, or it can be launched into an interplanetary journey based on its intended application. Out of the three orbit types, namely Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Geostationary Orbit (GEO), and Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), LEO appears to be the most widely chosen because of its close proximity to the Earth.
- Many weather and communication satellites tend to have high Earth orbits, which are farthest from the surface. Satellites in medium Earth orbit include navigational and specialized satellites designed to monitor a specific area. Most science satellites, including NASA's Earth Observation System, are in low Earth orbit.
- The different satellites manufactured and launched have different applications. During 2017-2022, of the 56 satellites launched in the MEO orbit, most were built for Navigation/Global Positioning purposes. Most of the 133 satellites in the GEO orbit were deployed for communication and Earth observation purposes. Over 4,025 LEO satellites manufactured and launched in the same period were owned by various countries across the globe.
- The increasing use of satellites in areas such as electronic intelligence, Earth science/meteorology, laser imaging, optical imaging, and meteorology is expected to drive the demand for the development of satellites during the forecast period.
Growing demand for satellite services such as communications, navigation, and earth observation is aiding the market growth
- The global satellite manufacturing and launch vehicles market is dynamic and rapidly evolving, which plays a critical role in modern society. The industry is driven by a range of factors, including the growing demand for satellite-based services as well as the increasing accessibility of space to both public and private entities. As a result, the industry has seen significant growth in recent years, with new players entering the market and established companies expanding their capabilities. Some of the leading satellite manufacturers include Airbus Defence and Space, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Thales Alenia Space.
- Launch vehicles, which are used to carry satellites into orbit, are also a critical component of the industry. These vehicles range from small rockets designed to launch CubeSats to larger rockets capable of carrying multiple satellites into orbit at once. The leading launch vehicle companies include SpaceX, United Launch Alliance, Arianespace, and Roscosmos.
- The industry is also seeing the emergence of new players, such as small satellite manufacturers and launch vehicle companies, that are leveraging innovative technologies and business models to disrupt the traditional space industry. For example, companies like Rocket Lab and Virgin Orbit use small launch vehicles to provide cost-effective access to space for small satellite operators.
- Overall, the global satellite manufacturing and launch vehicles market is poised for continued growth and innovation as demand for satellite-based services continues to increase and the accessibility of space expands. This industry will continue to play a critical role in shaping the future of modern society, from communication and navigation to environmental monitoring and scientific research.
Global Satellite Manufacturing and Launch Vehicle Market Trends
Growing Demand and Competition in the Global Launch Vehicle Market
- North America has been a pioneer in space exploration, with many successful space missions over the years. SpaceX is a leading aerospace company that manufactures and launches advanced reusable rockets and spacecraft. It is currently the leading provider of launch services in the region, with its launch vehicles including Falcon-9, Falcon Heavy, and Starship. During 2017-2022, SpaceX's rockets launched approximately 2,744 satellites into orbit.
- In Europe, companies such as ArianeGroup are developing the Ariane Next rockets, which involves a reusable first stage for the Ariane rocket. Russia's Roscosmos is another key player in the industry, with a long history of developing and deploying launch vehicles. The company is responsible for the development of the Soyuz and Proton rockets, which have been used to launch a range of satellites into space. During 2017-2022, the Soyuz rocket launched approximately 611 satellites into space for various satellite operators globally.
- In Asia-Pacific, CASC is responsible for the development and deployment of a range of launch vehicles, including the Long March series, which has become one of the most reliable launch vehicles in the world. During 2017-2022, CASC's Long March rocket launched approximately 372 satellites into space for various satellite operators globally. During 2017-2022, JAXA launched approximately 25 satellites into space for satellite operators globally using its H-IIA and H-IIB rockets. India's space program has also seen significant growth in recent years, with the ISRO playing a key role in the development of the country's launch vehicles. During 2017-2022, ISRO's rockets launched approximately 171 satellites into space for various satellite operators globally.
Increasing Investment Opportunities in the Global Satellite Manufacturing Market
- In North America, government expenditure for space programs hit a record of approximately 103 billion in 2021. The region is the epicenter of space innovation and research, with the presence of the world's biggest space agency, NASA. In 2022, the US government spent nearly USD 62 billion on its space programs, making it the highest spender on space in the world. In terms of funds allocated for launch vehicle development, under the FY 2023 president's budget request summary from FY 2022 to FY 2027, NASA is expected to receive USD 13.8 billion.
- In November 2022, ESA announced that it notified its 22 nations to back a budget of some EUR 18.5 billion for 2023-2025. Germany, France, and Italy are the major contributors. Developed at a cost of under USD 3.9 billion and set for an inaugural launch in July 2020, the project has been hit by a series of delays. In November 2022, the governments of France, Germany, and Italy announced that they signed an agreement on "the future of launcher exploitation in Europe" to enhance the competitiveness of European vehicles while ensuring independent European access to space.
- In February 2023, the Indian government announced that ISRO was expected to receive USD 2 billion for various space-related activities while INR 9,441 crore was allocated for launch activity and R&D on rockets, engines, satellites, etc., under the outlay on major schemes. In March 2021, Japan announced that it had spent USD 4.14 billion on space-related activities. In March 2023, South Korea announced that approximately USD 113.6 million was allotted to develop a next-generation carrier rocket, the KSLV-2.
Satellite Manufacturing and Launch Vehicle Industry Overview
The Satellite Manufacturing and Launch Vehicle Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 89.17%. The major players in this market are Airbus SE, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), Lockheed Martin Corporation, Maxar Technologies Inc. and Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Miniaturization
- 4.2 Satellite Mass
- 4.3 Owner Of Launch Vehicle
- 4.4 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.5 Regulatory Framework
- 4.5.1 Global
- 4.5.2 Australia
- 4.5.3 Brazil
- 4.5.4 Canada
- 4.5.5 China
- 4.5.6 France
- 4.5.7 Germany
- 4.5.8 India
- 4.5.9 Iran
- 4.5.10 Japan
- 4.5.11 New Zealand
- 4.5.12 Russia
- 4.5.13 Singapore
- 4.5.14 South Korea
- 4.5.15 United Arab Emirates
- 4.5.16 United Kingdom
- 4.5.17 United States
- 4.6 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Application
- 5.1.1 Communication
- 5.1.2 Earth Observation
- 5.1.3 Navigation
- 5.1.4 Space Observation
- 5.1.5 Others
- 5.2 Satellite Mass
- 5.2.1 10-100kg
- 5.2.2 100-500kg
- 5.2.3 500-1000kg
- 5.2.4 Below 10 Kg
- 5.2.5 above 1000kg
- 5.3 Orbit Class
- 5.3.1 GEO
- 5.3.2 LEO
- 5.3.3 MEO
- 5.4 Launch Vehicle Mtow
- 5.4.1 Heavy
- 5.4.2 Light
- 5.4.3 Medium
- 5.5 End User
- 5.5.1 Commercial
- 5.5.2 Military & Government
- 5.5.3 Other
- 5.6 Satellite Subsystem
- 5.6.1 Propulsion Hardware and Propellant
- 5.6.2 Satellite Bus & Subsystems
- 5.6.3 Solar Array & Power Hardware
- 5.6.4 Structures, Harness & Mechanisms
- 5.7 Propulsion Tech
- 5.7.1 Electric
- 5.7.2 Gas based
- 5.7.3 Liquid Fuel
- 5.8 Region
- 5.8.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.8.1.1 By Country
- 5.8.1.1.1 Australia
- 5.8.1.1.2 China
- 5.8.1.1.3 India
- 5.8.1.1.4 Japan
- 5.8.1.1.5 New Zealand
- 5.8.1.1.6 Singapore
- 5.8.1.1.7 South Korea
- 5.8.2 Europe
- 5.8.2.1 By Country
- 5.8.2.1.1 France
- 5.8.2.1.2 Germany
- 5.8.2.1.3 Russia
- 5.8.2.1.4 United Kingdom
- 5.8.3 North America
- 5.8.3.1 By Country
- 5.8.3.1.1 Canada
- 5.8.3.1.2 United States
- 5.8.4 Rest of World
- 5.8.4.1 By Country
- 5.8.4.1.1 Brazil
- 5.8.4.1.2 Iran
- 5.8.4.1.3 Saudi Arabia
- 5.8.4.1.4 United Arab Emirates
- 5.8.4.1.5 Rest of World
- 5.8.1 Asia-Pacific
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Airbus SE
- 6.4.2 Ariane Group
- 6.4.3 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- 6.4.4 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- 6.4.5 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.6 Maxar Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.7 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- 6.4.8 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.9 Sierra Nevada Corporation
- 6.4.10 Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- 6.4.11 Thales
- 6.4.12 The Boeing Company
- 6.4.13 United Launch Alliance, LLC.
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


