
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1693932
アジア太平洋の衛星打ち上げロケット-市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Asia-Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| アジア太平洋の衛星打ち上げロケット-市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 152 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
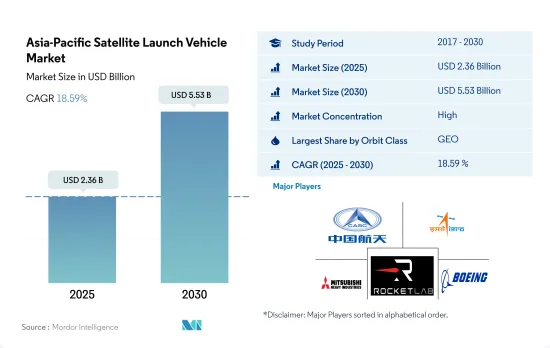
アジア太平洋の衛星打上げロケット市場規模は、2025年には23億6,000万米ドルと予測され、2030年には55億3,000万米ドルに達し、予測期間(2025~2030年)のCAGRは18.59%で成長すると予測されています。
アジア太平洋の軌道打上げシステム需要はLEO衛星が牽引
- アジア太平洋では、LEOベースの軌道打ち上げシステムの需要が増加しています。中国、インド、日本、韓国、オーストラリア、台湾などの国々は、さまざまな用途の衛星をLEOに配備するために、軌道打ち上げシステムを積極的に開発・活用しています。例えば、中国の長征ロケットシリーズ、インドのPSLVとGSLV、日本のH-IIAロケットとH3ロケット、韓国の韓国宇宙ロケットII(KSLV-II)は、地球観測、リモートセンシング、気象モニタリング、通信目的の衛星をLEOに打ち上げるために使用されてきました。
- MEOは、GNSSや衛星通信などの用途に適しています。この地域では、中国の長征3Bと長征3B/G2が、MEOに衛星を配備するためにこの地域の国々が開発または利用している打ち上げシステムの一部です。これらの衛星は、中国が開発した北斗航法衛星システム(BDS)のような衛星ベースのナビゲーションシステム、遠隔地や農村部向けの通信サービス、海事・航空産業、災害管理などのサービスを記載しています。
- GEOにある衛星は地球に対して静止しているように見えるため、通信、放送、気象観測などの用途には理想的です。中国の長征3B/G2、インドのGSLV Mk III、日本のH3、韓国のKSLV-IIは、通信、放送、気象観測の目的でGEOに衛星を打ち上げるために利用されるいくつかの打ち上げシステムです。全体として、市場は今後数年間で、2023年と比較して2029年には219%成長すると予想されます。
中国の衛星産業は大幅な成長が見込まれる
- アジア太平洋は近年、衛星の主要市場として台頭してきました。この市場は、地球観測、通信、科学研究の需要増に牽引され、急成長が予測されます。
- 中国は圧倒的な宇宙大国になるべく歩みを進めています。2020年10月、中国は2024年以降の野心的な月探査計画を発表しました。中国は、2020年末までに月の裏側からサンプルを採取するミッションを打ち上げる予定です。
- インド宇宙研究機関(ISRO)は小型衛星打ち上げロケット(SSLV)の開発に取り組んでいます。SSLVは固体燃料のみを動力源とする3段式の打ち上げプラットフォームで、打ち上げ質量は120トン、LEOまで500kg、太陽同期軌道まで300kgの打ち上げが可能です。2021年3月に実施されたSS1の最初の静止発射検査は失敗に終わりました。最初の実証飛行は2021年10月に行われる予定でした。
- NewSpace India Limitedは、インド宇宙庁が新たに設立した商業部門であり、インド産業がインドの宇宙開発のためのハイテク製造・生産拠点を拡大できるようにすることを任務としています。民間セクタと協力してSSLVの製造に携わる予定です。
- 韓国の宇宙開発は、他国がコア技術の移転に消極的なため、遅々として進んでいないです。2021年2月、科学情報通信省は、人工衛星、ロケット、その他の重要な宇宙機器の製造のために5億5,310万米ドルの宇宙予算を発表しました。このような構想は、予測期間中、アジア太平洋におけるロケット需要を促進すると考えられます。
アジア太平洋の衛星打ち上げロケット市場動向
アジア太平洋のロケット市場における需要の高まりと競合
- アジア太平洋は最近の宇宙産業の動向において著しい成長を遂げており、多くの企業がロケットの開発・配備における主要企業として台頭してきています。CASCは、世界で最も信頼性の高いロケットとなった長征ロケットシリーズを含む、さまざまなロケットを開発しました。2017~2022年にかけて、CASCの長征ロケットは世界中の様々な衛星事業者のために約372基の衛星を宇宙に打ち上げました。ロシアのロスコスモス国営企業はソユーズロケットとプロトンロケットの開発を担当しており、これらのロケットはさまざまな衛星や有人宇宙ミッションの打ち上げに使用されています。2017~2022年にかけて、ソユーズロケットは世界中の様々な衛星運用者のために約611個の衛星を宇宙に打ち上げました。
- 宇宙航空研究開発機構(JAXA)は、H-IIAロケットやH-IIBロケットなど、数多くのロケットを開発してきました。2017~2022年にかけて、JAXAのH-IIAロケットは、世界中のさまざまな衛星事業者のために約25基の衛星を宇宙に打ち上げました。インドのISROは、同国のロケット開発において重要な役割を果たしています。ISROは、PSLVやGSLVを含むさまざまなロケットを開発し、さまざまな衛星の打ち上げに使用してきました。2017~2022年にかけて、ISROのロケットは世界中の様々な衛星事業者のために約171基の衛星を宇宙に打ち上げました。これらの既存企業に加え、ニュージーランドを拠点とし、Electronロケットを開発したRocket Labのような新興企業も数多く存在します。2017~2022年にかけて、Electronロケットは世界の様々な衛星通信事業者のために約87個の衛星を宇宙に打ち上げました。
中国、インド、日本、韓国の支出増が市場成長を牽引
- 衛星ロケットの需要は、最大1万3,000基の衛星からなる国家衛星インターネットコンステレーションの製造・打ち上げなどのプロジェクトが牽引しています。China SatNetは、Guowangコンステレーション構築の青写真を作成するため、民間企業と関わっています。そのため、この地域の複数の宇宙機関が宇宙ロケット技術を開発しています。2023年2月、インド政府は、ISROがさまざまな宇宙関連活動のために20億米ドルを受け取る見込みであると発表しました。主要計画に関する支出では、944億1,000万インドルピーの予算の一部が宇宙技術(打ち上げ活動、ロケット、エンジン、衛星などの研究開発を含む)に割り当てられています。2021年3月、日本は宇宙関連活動に41億4,000万米ドルを支出したと発表しました。同国は、H3ロケット開発に189億円を割り当てたと述べました。2020年1月、JAXAは、燃費を大幅に改善し、環境負荷を低減するコアエンジン技術の研究開発、静粛超音速機やエミッションフリー機(電気推進システム)の研究開発に36億円を充てたと発表しました。
- 2023年3月、韓国は、国内宇宙産業の拡大、次世代ロケットの開発、宇宙防衛能力の強化のため、宇宙計画に6億7,400万米ドルを投じると発表しました。約1億1,360万米ドルは、次世代キャリアロケットKSLV-2の開発に費やされます。2030年デビュー予定の新型ロケットKSLV-3は、ケロシンと液体酸素を燃料とする2段式ロケットとして設計されています。
アジア太平洋の衛星打上げロケット産業概要
アジア太平洋の衛星ロケット市場はかなり統合されており、上位5社が100%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は、China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)、Indian Space Research Organisation(ISRO)、Mitsubishi Heavy Industries、Rocket Lab USA, Inc.、The Boeing Companyです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主要調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の小型化
- ロケットの所有者
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- オーストラリア
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- ニュージーランド
- シンガポール
- 韓国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 軌道クラス
- GEO
- LEO
- MEO
- ロケットMtow
- 大型
- 小型
- 中型
- 打上げ国
- 中国
- インド
- ニュージーランド
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Ariane Group
- Blue Origin
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)
- Indian Space Research Organisation(ISRO)
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Rocket Lab USA, Inc.
- Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- The Boeing Company
第7章 CEOへの主要戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要な洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
The Asia-Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle Market size is estimated at 2.36 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 5.53 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 18.59% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The demand for orbital launch systems in Asia-Pacific is driven by LEO satellites
- In Asia-Pacific, the demand for LEO-based orbital launch systems has been on the rise. Countries such as China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia, and Taiwan have been actively developing and utilizing orbital launch systems to deploy satellites into LEO for various applications. For instance, China's Long March series of rockets, India's PSLV and GSLV, Japan's H-IIA and H3 rockets, and South Korea's Korea Space Launch Vehicle-II (KSLV-II) have been used to launch satellites for Earth observation, remote sensing, weather monitoring, and communication purposes in LEO.
- MEO is well-suited for applications such as GNSS and satellite-based communications. In the region, China's Long March 3B and Long March 3B/G2 are some of the launch systems being developed or utilized by countries in the region to deploy satellites into MEO. These satellites provide services such as satellite-based navigation systems like the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) developed by China, communication services for remote and rural areas, maritime and aviation industries, and disaster management.
- GEO is ideal for applications such as telecommunications, broadcasting, and meteorological observations, as satellites in GEO appear to be stationary relative to Earth. China's Long March 3B/G2, India's GSLV Mk III, Japan's H3, and South Korea's KSLV-II are some launch systems utilized for launching satellites into GEO for telecommunications, broadcasting, and meteorological observation purposes. Overall, the market is expected to grow in the coming years by 219% in 2029 compared to 2023.
China's satellite industry is expected to witness significant growth
- Asia-Pacific has emerged as a leading market for satellites in recent years. This market is projected to grow rapidly, driven by increasing demand for Earth observation, communication, and scientific research.
- China is stepping up to become a dominant space power. Hence, in October 2020, the country unveiled its ambitious moon mission slated for 2024 and beyond. On this note, China planned to launch a mission to collect samples from the far side of the moon by the end of 2020.
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is working on its Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV). The SSLV is a three-stage launch platform powered entirely by solid fuel, with a lift-off mass of 120 metric tons and capable of lifting 500 kg to LEO and 300 kg to the sun-synchronous orbit. The first static fire test of SS1 conducted in March 2021 was unsuccessful. The first demonstration flight was expected to take place in October 2021.
- NewSpace India Limited, a newly formed commercial arm of the Indian space agency, is tasked with enabling the Indian industry to scale up high-technology manufacturing and production base for Indian space efforts. It will be involved in the manufacture of SSLV in collaboration with the private sector.
- South Korea's space program has seen slow progress as other countries are reluctant to transfer core technologies. In February 2021, the Ministry of Science and ICT announced a space budget of USD 553.1 million for manufacturing satellites, rockets, and other key space equipment. Such initiatives will drive the demand for launch vehicles in Asia-Pacific during the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle Market Trends
Growing demand and competition in the Asia-Pacific launch vehicle market
- Asia-Pacific has witnessed significant growth in the space industry in recent years, with a number of companies emerging as major players in the development and deployment of launch vehicles. CASC developed a range of launch vehicles, including the Long March series, which has become one of the most reliable launch vehicles in the world. During 2017-2022, CASC's Long March rocket launched approximately 372 satellites into space for various satellite operators across the world. Russia's Roscosmos State Corporation is responsible for the development of the Soyuz and Proton rockets, which have been used to launch a range of satellites and crewed missions to space. During 2017-2022, the Soyuz rocket launched approximately 611 satellites into space for various satellite operators across the world.
- The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) has developed a number of launch vehicles, including the H-IIA and H-IIB rockets. During 2017-2022, JAXA's H-IIA rockets launched approximately 25 satellites into space for various satellite operators across the world. India's ISRO is playing a key role in the development of the country's launch vehicles. ISRO has developed a range of launch vehicles, including the PSLV and the GSLV, which have been used to launch a range of satellites. During 2017-2022, ISRO's rockets launched approximately 171 satellites into space for various satellite operators across the world. In addition to these established players, there are also a number of emerging companies, such as Rocket Lab, which is based in New Zealand and has developed the Electron rocket. During 2017-2022, the Electron rocket launched approximately 87 satellites into space for various satellite operators globally.
Increased spending by China, India, Japan, and South Korea is driving the market's growth
- The demand for satellite launch vehicles is driven by projects such as manufacturing and launching a national satellite internet constellation of up to 13,000 satellites. China SatNet has been engaging with commercial companies as it develops a blueprint for constructing the Guowang constellation. Hence, several space agencies in the region are developing space launch vehicle technologies. In February 2023, the Indian government announced that ISRO is expected to receive USD 2 billion for various space-related activities. Under the outlay on major schemes, a partial split up of the budget of INR 9441 crore has been allocated for space technology (including launch activity, R&D on rockets, engines, satellites, etc.). In March 2021, Japan announced that it expended USD 4.14 billion for space-related activities. The country mentioned that it had allocated JPY 18.9 billion for the H3 rocket development. In January 2020, JAXA mentioned that JPY 3.6 billion was allocated to fund the research and development of core engine technologies that significantly improve fuel consumption and reduce environmental burden, as well as the research and development of the silent supersonic airplane and emission-free aircraft (electric-powered propulsion systems).
- In March 2023, South Korea announced that it would spend USD 674 million on space programs to expand its domestic space industry, develop a next-generation launch vehicle, and bolster space defense capabilities. Approximately USD 113.6 million will be expended on developing a next-generation carrier rocket, the KSLV-2. The new rocket KSLV-3, expected to debut in 2030, is designed to be a kerosene and liquid oxygen-fueled two-stage vehicle.
Asia-Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle Industry Overview
The Asia-Pacific Satellite Launch Vehicle Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 100%. The major players in this market are China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Rocket Lab USA, Inc. and The Boeing Company (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Miniaturization
- 4.2 Owner Of Launch Vehicle
- 4.3 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.4.1 Australia
- 4.4.2 China
- 4.4.3 India
- 4.4.4 Japan
- 4.4.5 New Zealand
- 4.4.6 Singapore
- 4.4.7 South Korea
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Orbit Class
- 5.1.1 GEO
- 5.1.2 LEO
- 5.1.3 MEO
- 5.2 Launch Vehicle Mtow
- 5.2.1 Heavy
- 5.2.2 Light
- 5.2.3 Medium
- 5.3 Country
- 5.3.1 China
- 5.3.2 India
- 5.3.3 New Zealand
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Ariane Group
- 6.4.2 Blue Origin
- 6.4.3 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- 6.4.4 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- 6.4.5 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- 6.4.6 Rocket Lab USA, Inc.
- 6.4.7 Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- 6.4.8 The Boeing Company
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


