|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1693938
欧州の衛星打ち上げロケット-市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Europe Satellite Launch Vehicle - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 欧州の衛星打ち上げロケット-市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 161 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
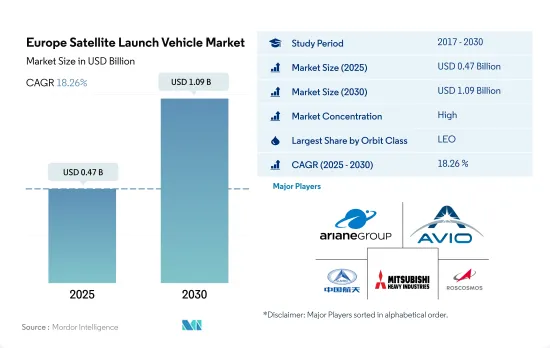
欧州の衛星打上げロケット市場規模は、2025年に4億7,000万米ドルと推定・予測され、2030年には10億9,000万米ドルに達し、予測期間(2025~2030年)のCAGRは18.26%で成長すると予測されています。
欧州における軌道打上げシステムの需要増加
- 打ち上げの際、衛星や宇宙船は通常、地球を周回する多くの特別な軌道の1つに配置されます。多くの気象衛星や通信衛星は、地表から最も遠い地球高軌道をとる傾向があります。地球の平均軌道(中軌道)にある衛星には、特定の地域をモニタリングするように設計された航法衛星や特殊衛星が含まれます。ESAの地球観測システムチームを含むほとんどの科学衛星は、地球低軌道にあります。
- 小型ロケットは従来の大型ロケットと異なり、機体の性能は、特定の軌道まで持ち上げることができるペイロードの量と打ち上げコストに依存します。小型衛星の能力拡大に伴い、宇宙産業は戦略的有用性を発展させており、その結果、政府、宇宙機関、非公開会社を含む様々な利害関係者を活用して拡大しています。小型衛星ロケットは、次世代の将来を担うものとして期待されています。この種のロケットは、人工衛星の打ち上げ、科学ミッションの遂行、国際宇宙ステーションへの補給に不可欠です。宇宙活動の活発化により軌道に打ち上げられる衛星の数が増加していることが、中距離ロケットの需要を牽引しています。
- 2022年10月、欧州宇宙機関は、日常機器により正確な位置データを提供するため、既存の衛星よりもはるかに地球に近い軌道を周回する新しい航法衛星の検査を計画しました。全地球測位衛星システムは通常、地表から約(1万~2万km)の地球中間軌道に配置されます。2017~2022年の間に、この地域では合計590以上の衛星が打ち上げられました。同市場は、2023~2029年の予測期間中に210%の成長が見込まれています。
低コストの打上げシステムに対する需要が高まっており、同地域の市場成長を後押ししています。
- 打上げ装置産業は、欧州では商業衛星の開発に次いで2番目に大きな宇宙製造活動であり、これが欧州市場の成長を後押ししています。アリアン5、ソユーズ、ヴェガはフランス領ギアナにある欧州の宇宙港から飛び立ちます。欧州は、欧州政府のあらゆるニーズと商業市場の大半を満たす能力と柔軟性を備えたこの一連のロケットから恩恵を受けており、それによって欧州の社会経済的利益と宇宙へのアクセスを高めています。
- 欧州の衛星打上げロケット市場の特徴は、複数の参入企業が存在することです。この地域の主要な打上げロケットには、アリアン5、ソユーズ、ベガなどがあります。EASAのような宇宙機関はSpaceXのような民間企業と衛星の製造と打ち上げのセグメントで提携しています。
- 衛星打上げロケット産業は、軍事モニタリング、通信、ナビゲーションから地球観測に至るまで、幅広い用途の衛星需要によって牽引されています。その結果、民間/政府、商業、軍事セグメントからの衛星需要が増加しています。これに基づき、2017~2022年の間に、この地域では合計570以上の衛星が打ち上げられました。COVID-19パンデミックの影響を受けた後の2020~2021年に打ち上げられた衛星数の伸びは140%です。
- 国が運用する衛星の数では、2017~2022年の間に打ち上げられた衛星が462機以上で英国がトップ、次いでロシアが65機、ドイツが34機となっています。宇宙機関や非公開会社は近年、衛星打ち上げシステムのコスト削減に努めています。2023~2029年にかけて、予測期間中に市場は213%急増すると予想されます。
欧州の衛星打上げロケット市場動向
欧州ロケット市場における需要の高まりと競合
- 欧州のロケットは、様々な軌道に様々なペイロードを打ち上げることができる汎用性の高さで知られています。欧州のロケットの需要を牽引している主要因は、商業宇宙産業の成長です。衛星やその他の宇宙資産を軌道に打ち上げようとする企業が増えるにつれ、信頼性が高く費用対効果の高いソリューションとして欧州のロケットが注目されています。欧州のロケット会社は、再使用可能なロケット、電気推進システム、人工知能などの新技術に投資し、打ち上げ能力を向上させ、市場での競合を維持しています。例えば、アリアングループは再使用可能なアリアン・ネクスト・ロケットを開発しており、Airbusはアリアン・ロケットの再使用可能な第1段を含むアデラインコンセプトを開発しています。
- さらに、小型衛星打ち上げの需要が増加しており、これが欧州企業による小型ロケットの開発を後押ししています。例えば、PLDスペース社は小型衛星打ち上げ用のミウラ1ロケットとミウラ5ロケットを開発しており、イザール・エアロスペース社も同じ目的でスペクトラムロケットを開発しています。宇宙産業では国際協力の傾向が強まっており、欧州のロケットメーカーは世界中の企業や組織と提携しています。この背景には、宇宙ミッションの複雑化に加え、リソースや専門知識を共有する必要性があります。アリアンスペース社は欧州宇宙機関とフランス宇宙庁と、PLDスペース社は欧州宇宙機関とスペイン政府と提携しています。
欧州の衛星打上げロケット市場における投資機会の増加が要因
- 欧州諸国は、宇宙セグメントにおける様々な投資の重要性を認識しています。世界の宇宙産業で競合と革新性を維持するため、さまざまな宇宙プログラムへの支出を増やしています。2022年11月、欧州宇宙機関(ESA)は、2023~2025年に185億ユーロの予算を支援するよう22カ国に要請したと発表しました。欧州は2023年第4四半期に、次世代宇宙ロケットであるアリアン6の初号機の打ち上げを計画しています。39億米ドル弱を投じて開発され、当初は2020年7月の初打ち上げを予定していたこのプロジェクトは、相次ぐ延期に見舞われています。フランス、ドイツ、イタリアの3カ国政府は、欧州のロケット競合を強化すると同時に、欧州の独立系宇宙へのアクセスを確保するため、「欧州におけるロケット開発の将来」に関する協定に署名したと発表しました。
- 2022年9月、フランス政府は、過去3年間で約25%増となる90億米ドル以上を宇宙活動に充てる予定であると発表しました。2022年11月、ドイツはさまざまな宇宙関連プロジェクトに約23億7,000万ユーロを割り当てると発表しました。同国は、2023年末からアリアン6が宇宙へペイロードを運ぶ新しい欧州のロケットになる見込みであると述べました。ドイツはアリアン6のさらなる開発と市場導入に総額1億6,200万ユーロを拠出します。同国は、ランポルトハウゼンにあるDLRのロケットエンジン検査施設の運営を含む、オプションのLEAP(Launchers Exploitation Accompaniment)プログラムに約5,200万ユーロを投資しています。
欧州の衛星打ち上げロケット産業概要
欧州の衛星打ち上げロケット市場はかなり統合されており、上位5社で99.01%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は、Ariane Group、Avio、China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)、Mitsubishi Heavy Industries、ROSCOSMOSです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主要調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 衛星の小型化
- ロケットの所有者
- 宇宙開発への支出
- 規制の枠組み
- フランス
- ドイツ
- ロシア
- 英国
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 軌道クラス
- GEO
- LEO
- MEO
- ロケット
- 大型
- 小型
- 中型
- 打上げ国
- ロシア
第6章 競合情勢
- 主要な戦略動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Ariane Group
- Avio
- Blue Origin
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation(CASC)
- Indian Space Research Organisation(ISRO)
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Rocket Lab USA, Inc.
- ROSCOSMOS
- Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- The Boeing Company
- Virgin Orbit
第7章 CEOへの主要戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表一覧
- 主要な洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
The Europe Satellite Launch Vehicle Market size is estimated at 0.47 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 1.09 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 18.26% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Rising demand for orbital launch systems in Europe
- At launch, a satellite or spacecraft is usually placed into one of many special orbits around the Earth, or it can be launched into an interplanetary journey. Many weather and communication satellites tend to have high Earth orbits farthest from the surface. Satellites in the mean (medium) Earth orbit include navigational and specialized satellites that are designed to monitor a specific area. Most science satellites, including ESA's Earth Observation System team, are in low Earth orbit
- Light launchers differ from conventional heavy launchers in the vehicle's performance, which depends on the amount of payload the vehicle can lift to a particular orbit and the launch cost. With the expansion of the capabilities of small satellites, the space industry is developing strategic utility, which, in turn, leverages various stakeholders, including governments, space agencies, and private companies, to expand. Small satellite launchers are expected to be the future of the next generation. These types of launchers are essential for launching satellites, carrying out science missions, and resupplying the International Space Station. The increasing number of satellites being launched into orbit due to increased space activities is driving the demand for medium-range launch vehicles.
- In October 2022, the European Space Agency planned to test new navigation satellites that would orbit much closer to Earth than existing ones to provide more accurate position data for everyday devices. The Global Positioning Satellite System is typically placed in mid-Earth orbit about (10,000 to 20,000 km) from the Earth's surface. During 2017-2022, a total of 590+ satellites were launched in the region. The market is expected to witness a growth of 210% during the forecast period between 2023 and 2029.
There is a rising demand for low-cost launch systems aiding the market growth in the region
- The launch equipment industry is the second-largest space manufacturing activity in Europe after the development of commercial satellites, which is aiding the growth of the European market. Ariane 5, Soyuz, and Vega take off from Europe's spaceport in French Guiana. Europe benefits from this line of launchers with the ability and flexibility to meet all the needs of the European government and most of the commercial market, thereby increasing its socioeconomic benefits and access to space in Europe
- The European satellite launch vehicles market is characterized by the presence of several players. The major launch vehicles in this region are Ariane 5, Soyuz, and Vega, among others. Space organizations like EASA have partnered with private players like SpaceX in the production and launch of satellites in the field.
- The satellite launch vehicle industry is driven by demand for satellites for applications ranging from military surveillance, communications, and navigation to Earth observation. As a result, the demand for satellites from the civilian/government, commercial and military sectors is increasing. On this basis, during the period 2017-2022, a total of more than 570+ satellites were launched in the region. The growth in the number of satellites launched from 2020 to 2021 is 140% after the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- In terms of the number of satellites operated by a country, the United Kingdom leads with more than 462 satellites launched between 2017 and 2022, followed by Russia and Germany with 65 and 34, respectively. Space agencies and private companies have tried to reduce the cost of satellite launch systems in recent years. Between 2023 and 2029, the market is expected to surge by 213% during the forecast period.
Europe Satellite Launch Vehicle Market Trends
Growing demand and competition in the European launch vehicle market
- European launch vehicles are known for their versatility, capable of launching a wide range of payloads into various orbits. A key factor driving the demand for European launch vehicles is the growing commercial space industry. As more and more companies seek to launch satellites and other space-based assets into orbit, they are turning to European launch vehicles as a reliable and cost-effective solution. European launch companies are investing in new technologies, such as reusable launch vehicles, electric propulsion systems, and artificial intelligence, to improve their launch capabilities and stay competitive in the market. For example, ArianeGroup is developing the Ariane Next reusable rocket, and Airbus is developing the Adeline concept, which involves a reusable first stage for the Ariane rocket.
- Additionally, the demand for small satellite launches is increasing, which is driving the development of smaller launch vehicles by European companies. For example, PLD Space is developing the Miura 1 and Miura 5 rockets for small satellite launches, while Isar Aerospace is developing the Spectrum rocket for the same purpose. There is a growing trend toward international collaboration in the space industry, with European launch vehicle manufacturers partnering with companies and organizations across the world. This is driven by the increasing complexity of space missions, as well as the need to share resources and expertise. On this note, Arianespace has partnerships with the European Space Agency and the French Space Agency, and PLD Space is working with the European Space Agency and the Spanish government.
Increasing investment opportunities in the European satellite launch vehicle market is the driver
- European countries are recognizing the importance of various investments in the space domain. They are increasing their spending on various space programs to stay competitive and innovative in the global space industry. In November 2022, the European Space Agency (ESA) announced that it requested its 22 nations to back a budget of EUR 18.5 billion for 2023-2025. Europe plans to launch the first Ariane 6 rocket, its next-generation space launcher, in the fourth quarter of 2023. Developed at a cost of just under USD 3.9 billion and originally set for an inaugural launch in July 2020, the project has been hit by a series of delays. The governments of France, Germany, and Italy announced that they had signed an agreement on "the future of launcher exploitation in Europe" to enhance the competitiveness of European vehicles while also ensuring independent European access to space.
- In September 2022, the French government announced that it is planning to allocate more than USD 9 billion to space activities, an increase of about 25% over the past three years. In November 2022, Germany announced that about EUR 2.37 billion was allocated for various space-related projects. The country mentioned that from the end of 2023, Ariane 6 is expected to be the new European launcher to carry payloads into space. Germany is contributing a total of EUR 162 million to the further development of Ariane 6 and its market introduction. The country is investing around EUR 52 million in the optional LEAP (Launchers Exploitation Accompaniment) program, which also includes the operation of DLR's test facility for rocket engines in Lampoldshausen.
Europe Satellite Launch Vehicle Industry Overview
The Europe Satellite Launch Vehicle Market is fairly consolidated, with the top five companies occupying 99.01%. The major players in this market are Ariane Group, Avio, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and ROSCOSMOS (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Satellite Miniaturization
- 4.2 Owner Of Launch Vehicle
- 4.3 Spending On Space Programs
- 4.4 Regulatory Framework
- 4.4.1 France
- 4.4.2 Germany
- 4.4.3 Russia
- 4.4.4 United Kingdom
- 4.5 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes market size in Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Orbit Class
- 5.1.1 GEO
- 5.1.2 LEO
- 5.1.3 MEO
- 5.2 Launch Vehicle Mtow
- 5.2.1 Heavy
- 5.2.2 Light
- 5.2.3 Medium
- 5.3 Country
- 5.3.1 Russia
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Ariane Group
- 6.4.2 Avio
- 6.4.3 Blue Origin
- 6.4.4 China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- 6.4.5 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
- 6.4.6 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- 6.4.7 Rocket Lab USA, Inc.
- 6.4.8 ROSCOSMOS
- 6.4.9 Space Exploration Technologies Corp.
- 6.4.10 The Boeing Company
- 6.4.11 Virgin Orbit
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR SATELLITE CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms