
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1685720
マレーシアの不動産:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Malaysia Real Estate - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| マレーシアの不動産:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 150 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
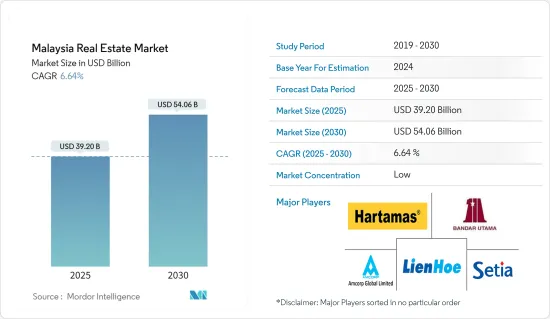
マレーシアの不動産市場規模は2025年に392億米ドルと推定され、予測期間(2025-2030年)のCAGRは6.64%で、2030年には540億6,000万米ドルに達すると予測されます。
主なハイライト
- COVID-19の大流行は需要を麻痺させ、住宅価格に下落圧力を加えました。その結果、マレーシアの住宅価格指数は2021年第1四半期までの1年間で0.3%上昇と、前年の前年同期比1.9%上昇から微減となりました。これは2010年から2019年までの年間7.5%の価格上昇から急減速しました。インフレ調整後では、2021年第1四半期の住宅価格は前年同期比1.3%下落しました。
- 2022年のマレーシアの不動産市場は、より多くの需要が手頃な価格の住宅に偏ったため、回復しました。開発業者は、若年層の不動産需要が旺盛である可能性が高いことから、中長期的な不動産見通しについて慎重に楽観視しています。
- 現時点での金利は引き続き良好と予想されます。2022年予算では、不動産譲渡益税(RPGT)が個人・法人ともにそれぞれ0%、5.0%に戻る以外は、与えられるものがほとんどなかったため、2022年は2021年から引き続き厳しい年となりました。
マレーシア不動産市場の動向
供給過剰が引き起こす問題
10年にわたる住宅価格ブームの後、マレーシアの住宅市場は過去2年間、大量の供給過剰により冷え込んでいます。昨年、マレーシアの主要都市で売れ残ったマンションは184億8,000万リンギ(44億1,000万米ドル)相当だったが、これは最近のブームで最高級物件が深刻な過剰建築となった結果です。
この過剰建築に対抗するため、政府は投機を抑制し、開発業者の過剰建築を抑制するための複数の措置を導入しました。100万リンギ(23万8,578米ドル)以上の物件の印紙税は3%から4%に引き上げられました。
政府はまた、6年以上所有する不動産の売却に対して5%の不動産譲渡益課税(RPGT)を追加導入しました。しかし、これらの措置は、パンデミックによる不動産市場への影響に対処するため、一時的に緩和されました。
グレーター・クアラルンプールのオフィススペースが拡大
グレーター・クアラルンプールのオフィス市場は、2021年第3四半期末時点で累積供給が1億3,600万平方フィートを超え、うち67%がWPクアラルンプール(9,170万平方フィート)に立地しています。これは累計で2.1%の成長であり、2021年末までにさらに多くのオフィスが完成するため、4.4%の成長で今年を終える見込みです。
グレーターKLでは、2021年1~9月に9件のオフィスビルが竣工しました。そのうち6棟はWPクアラルンプールにあり、Menara Legasi、Menara Permata Sapura KLCC、TSLaw Tower、The Five at Kompleks Pejabat Damansara、Plaza Conlay、Menara Great Eastern 2で、206万平方フィートです。
一方、アウターKLでは、Qタワー、イマジム・アット・ダマンサラ・アップタウン、クイル9アネックスの3棟の新規オフィスビルが竣工し、総面積は69万平方フィートとなりました。グレーターKLでは、2023年までに990万平方フィートの新規オフィスビルが竣工すると予想され、既存の水準からさらに7%供給が増加することになるが、そのうちWPクアラルンプールが84%、約830万平方フィートを占めています。
マレーシア不動産業界の概要
マレーシアの住宅不動産市場は非常に断片化されています。本調査では、マレーシア不動産セクターの上位参加者を取り上げます。大企業は資金力を強みとしているが、中小企業は地元市場で専門知識を築くことで効果的に競争できます。
市場参加者間の競争激化が販売価格や地価に影響を与え、市場の供給過剰をさらに招いています。さらに、市場は少数の汎インド・ブランド・プレーヤーと複数の地元プレーヤーによって支配されています。
Hartamas Real Estate(Malaysia)Sdn Bhd、Bandar Utama City Sdn Bhd、S P Setia Bhd、Lien Hoe Corporation Berhad、Amcorp Properties Berhadなどが著名な企業です。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリスト・サポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場洞察
- 経済と市場の概要
- 不動産購入動向- 社会経済的・人口統計的洞察
- 住宅不動産セクターに対する政府の取り組みと規制の側面
- 不動産融資の規模と融資額の動向に関する洞察
- 不動産における技術革新、新興企業、プロップテックへの注目
- サウジアラビアと主要都市における不動産需要と供給
- 不動産セグメントの賃貸利回りに関する洞察
- 不動産における資本市場の浸透とREITの存在に関する洞察
- 政府と官民パートナーシップによる廉価住宅支援に関する洞察
- COVID-19の市場への影響
第5章 市場力学
- 促進要因
- 抑制要因
- 機会
- 業界の魅力-ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手・消費者の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
第6章 市場セグメンテーション
- タイプ別
- 住宅用不動産
- 別荘
- アパート
- その他のタイプ
- 商業用不動産
- オフィス
- 小売
- ホスピタリティ
- 工業用
- その他のタイプ
- 住宅用不動産
第7章 競合情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- Hartamas Real Estate(Malaysia)Sdn Bhd
- Bandar Utama City Sdn Bhd
- S P Setia Bhd
- Lien Hoe Corporation Berhad
- Amcorp Properties Berhad
- Tanming Berhad
- Hap Seng Realty Sdn Bhd
- Cornerstone Xstate
- Berjaya Corporation Berhad
- IJM Corporation Berhad*
第8章 市場の将来
第9章 付録
The Malaysia Real Estate Market size is estimated at USD 39.20 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 54.06 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.64% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- The COVID-19 pandemic crippled demand, adding downward pressure on house prices. As a result, Malaysia's house price index rose a minuscule 0.3% during the year to Q1 2021, down from the previous year's 1.9% Y-o-Y increase. This was a sharp slowdown from the annual price growth of 7.5% from 2010 to 2019. When adjusted for inflation, house prices fell by 1.3% Y-o-Y in Q1 2021.
- Malaysia's property market rebounded in 2022 as more demand likely skewed toward affordable housing. Developers were cautiously optimistic about the property prospects in the medium to long term due to the likelihood of robust demand for properties among the young demographic.
- The interest rate at the moment is expected to remain favorable. The year 2022 continued to be challenging from 2021 as there was little to be given in the 2022 Budget except for real property gains tax (RPGT) reverting to 0% and 5.0% for both individuals and companies, respectively.
Malaysia Real Estate Market Trends
Oversupply Causing Problems
After a decade-long house price boom, Malaysia's housing market has been cooling in the past two years due to massive oversupply. There was MYR 18.48 billion (USD 4.41 billion) worth of unsold apartments in Malaysia's major cities last year, the result of a serious overbuilding of top-end properties during the recent boom.
To combat this over-building, the government introduced multiple measures to control speculation and discourage developers from over-building. Stamp duty was increased from 3% to 4% on properties worth above MYR 1 million (USD 238,578).
The government also introduced an additional 5% in real property gains tax (RPGT) on sales of properties owned for 6 years and beyond. However, these measures were temporarily relaxed to deal with the impact of the pandemic on the property market.
Greater Kuala Lumpur Increases Office Space
Greater Kuala Lumpur's office market reached a cumulative supply of over 136 million sq ft at the end of Q3/2021, of which 67% is located in WP Kuala Lumpur (91.7 million sq ft). This represented a year-to-date growth of 2.1% and was expected to close the year at 4.4% growth as more offices were completed by the end of 2021.
Nine new office completions were witnessed in the first nine months of 2021 in the Greater KL. Six of the buildings are in WP Kuala Lumpur, namely Menara Legasi, Menara Permata Sapura KLCC, TSLaw Tower, The Five at Kompleks Pejabat Damansara, Plaza Conlay, and Menara Great Eastern 2, amounting to 2.06 million sq ft.
On the other hand, Outer KL recorded three new office buildings, namely Q Tower, Imazium at Damansara Uptown, and Quill 9 Annexe, accounting for 0.69 million sq ft. Expected new office completions in Greater KL will amount to 9.9 million sq ft by 2023, representing a further supply growth of 7% from existing levels, of which WP Kuala Lumpur accounts for 84% or approximately 8.3 million sq ft.
Malaysia Real Estate Industry Overview
The residential real estate market in Malaysia is highly fragmented. The top participants in the Malaysian real estate sector are covered in this research. Large firms have financial resources to their advantage, whereas small businesses can compete effectively by building expertise in local markets.
Higher competition among market players is impacting selling prices and land prices, further leading to oversupply in the market. Furthermore, the market is dominated by a few pan-India branded players and multiple local players.
Hartamas Real Estate (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd, Bandar Utama City Sdn Bhd, S P Setia Bhd, Lien Hoe Corporation Berhad, Amcorp Properties Berhad, and others are some of the prominent companies.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Overview of the Economy and the Market
- 4.2 Real Estate Buying Trends - Socioeconomic and Demographic Insights
- 4.3 Government Initiatives and Regulatory Aspects for the Residential Real Estate Sector
- 4.4 Insights Into Size of Real Estate Lending and Loan to Value Trends
- 4.5 Focus on Technology Innovation, Startups, and Proptech in Real Estate
- 4.6 Demand for and Supply of Real Estate in Saudi Arabia and Key Cities
- 4.7 Insights into Rental Yields in the Real Estate Segment
- 4.8 Insights into Capital Market Penetration and REIT Presence in Real Estate
- 4.9 Insights into Affordable Housing Support Provided by Government and Public-private Partnerships
- 4.10 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Drivers
- 5.2 Restraints
- 5.3 Opportunities
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness- Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 5.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Type
- 6.1.1 Residential Real Estate
- 6.1.1.1 Villas
- 6.1.1.2 Apartments
- 6.1.1.3 Other Types
- 6.1.2 Commercial Real Estate
- 6.1.2.1 Offices
- 6.1.2.2 Retail
- 6.1.2.3 Hospitality
- 6.1.2.4 Industrial
- 6.1.2.5 Other Types
- 6.1.1 Residential Real Estate
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Overview (Market Concentration and Major Players)
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 Hartamas Real Estate (Malaysia) Sdn Bhd
- 7.2.2 Bandar Utama City Sdn Bhd
- 7.2.3 S P Setia Bhd
- 7.2.4 Lien Hoe Corporation Berhad
- 7.2.5 Amcorp Properties Berhad
- 7.2.6 Tanming Berhad
- 7.2.7 Hap Seng Realty Sdn Bhd
- 7.2.8 Cornerstone Xstate
- 7.2.9 Berjaya Corporation Berhad
- 7.2.10 IJM Corporation Berhad*


