
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1645120
アフリカの食品コールドチェーン物流-市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Africa Food Cold Chain Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| アフリカの食品コールドチェーン物流-市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年01月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 150 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
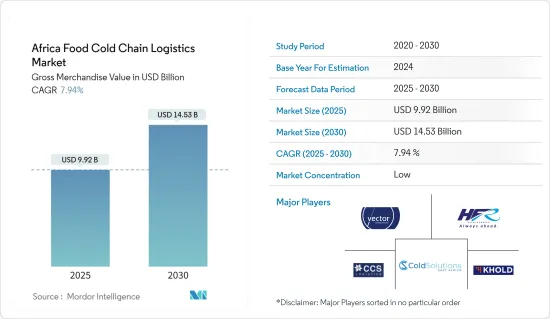
アフリカの食品コールドチェーン物流市場規模は、商品総額ベースで2025年の99億2,000万米ドルから2030年には145億3,000万米ドルに成長し、予測期間(2025~2030年)のCAGRは7.94%になると予測されます。
ライフスタイルの変化と都市化が加工食品の国内消費の増加に寄与し、人々の健康志向の高まり、食品浪費への対処、食料安全保障の確保が必要となるにつれて、新鮮果物の消費増加を含む消費パターンの変化が市場の成長を支える要因となっています。
気候変動の危機は、アフリカにおける悲惨な食糧不安と食糧浪費に大きく寄与しています。アフリカで生産される食料の3分の1以上が、腐敗や廃棄によって失われていると推定されています。国連食糧農業機関の推定によると、サハラ以南のアフリカでは40%以上の食料が消費者に届く前に失われています。これは、サハラ以南のアフリカにおける生鮮食品の場合、60%にも達します。
食品廃棄の主要原因は、特に温度に敏感な食品の保存期間を延ばすための低温貯蔵施設の不足による腐敗です。アフリカの農業従事者や農業業者は、その場しのぎのクーラーや時代遅れの一般的な冷蔵室に頼っています。これらのシステムは信頼性が低く、メンテナンスも不十分で、運用コストも高いです。
冷蔵倉庫やコールドサプライチェーン製品は腐敗を抑え、品質と有効性を維持するのに役立ちますが、効果的に機能させるには十分な電力が必要です。アフリカ開発銀行(AfDB)によると、アフリカでは6億4,000万人以上の人々が電気に手が届かず、一定の低温を持続的に維持することが課題となっています。アフリカでは、食料や医薬品の損失に対処するため、弾力性があり、信頼性が高く、サステイナブルコールドチェーンを展開することが急務となっています。
アフリカではいくつかの新興企業が、新たな課題に対応するためのデジタルソリューションを革新しています。これらの新興企業は、エネルギー効率に優れ、輸出規格に準拠したコールド保管製品やソリューションを提供しています。また、価格も手ごろで、温度や性能のモニタリングシステムも充実しています。
コールドチェーン保管産業の報告書によると、コールドチェーンインフラは東アフリカで開発が進んでおり、南部アフリカのコールドチェーンインフラはより発展して輸出業者向けとなっています。
アフリカの食品コールドチェーン物流市場動向
電力危機が南アフリカの食品コールドチェーン物流市場にマイナスの影響
南アフリカは現在、アフリカ大陸のコールド保管能力の大半を擁しており、多くのプラス(生鮮果物、野菜)とマイナス(魚、肉)のコールド保管・オプションを包含しています。アフリカで事業を展開する数多くのコールドチェーン物流・プロバイダーが南アフリカに本社を置いています。しかし、同国は大幅な電力不足に悩まされており、その結果、様々な地域で毎日10時間にも及ぶ広範囲な停電が発生しています。鉱物資源エネルギー省によると、南アフリカの国内総発電容量は58,095メガワット(MW)です。石炭は依然として主要なエネルギー源であり、同国のエネルギーミックスの約80%を占めています。それにもかかわらず、一部の石炭発電所の老朽化と状態の悪化により、実際の発電量は大幅に不足し、4,000~6,000MWの不足が生じています。
この不足分は、「負荷減」とも呼ばれる深刻な停電につながっています。コールドチェーンを維持するためには、信頼できる安定したエネルギー供給が不可欠です。電力が安定しない、あるいは信頼できない地域では、温度管理された環境に支障をきたすリスクが高まります。こうした停電は農業部門のコールドチェーンに悪影響を及ぼし、特に生鮮食品の保管や輸送に影響を与えています。報告によると、配送の遅れやコールドチェーンの混乱が原因で生鮮食品を拒否した小売業者もあり、気温の高い時期には状況が悪化します。このエネルギー危機は、南アフリカの食品コールドチェーン物流市場にとって重大な課題です。
生鮮果実の輸出が市場の成長に貢献
エジプトはこの地域で最大の果物・野菜輸出国です。年間、エジプトは様々な生鮮、乾燥、冷凍の果物・野菜製品の輸出から約30億米ドルの収入を得ています。国際市場に輸出される主要製品には、オレンジ、ジャガイモ、冷凍イチゴ、テーブルブドウ、生タマネギなどがあります。南アフリカは輸出市場でも重要な役割を果たしています。南アフリカの農業部門は明らかに輸出中心で、生産物の約半分が金額ベースで輸出されています。南アフリカの果実産業は、同国の農産物輸出において圧倒的な力を持っており、生鮮果実は南アフリカの農産物輸出の約35%を占めています。数十年にわたる研究開発と、生産者や産業団体のための能力開発イニシアティブが、世界的に効果的に競争できる高品質の果物の生産に役立っています。
南アフリカは、世界第2位の柑橘類輸出国、世界第6位の洋ナシ生産国、世界第7位のブドウ輸出国、世界第8位のリンゴ輸出国、世界第9位のアボカド輸出国など、世界の果実生産において重要な地位を誇っています。輸出市場に関しては、南アフリカの果実産業は、欧州連合(EU)、英国、米国内の伝統的市場を維持し、最大化することを目指しています。さらに、東アジアと中東の新市場へのアクセスを獲得することに戦略的重点が置かれています。アフリカは、南アフリカ産の様々な種類の果物にとって、かなりの潜在的輸出市場です。現在、西アフリカと東アフリカでは、リンゴとナシが好調です。アフリカ内外へのこれらの果物の輸出は、コールドチェーン物流の重要な需要ドライバーであり、コールドチェーンインフラの継続的開発の重要性を強調しています。
アフリカの食品コールドチェーン物流産業概要
アフリカ大陸の多様性を考慮すると、地元と地域の物流・プロバイダーが重要な役割を果たしています。地域業者は、アフリカの食品コールドチェーン物流市場における主要な参入企業です。これらの企業は、現地の市場力学、規制、インフラの課題をよりよく理解しています。コールドチェーン物流事業はアフリカ大陸の南部地域に集中しています。輸送、倉庫保管、流通を含む統合的なコールドチェーンサービスを提供する企業は競争上優位にあります。これらのサービスのシームレスな連携は、温度に敏感な食品の完全性を維持するために不可欠です。CCS Logistics、Khold、Cold Solutions East Africa、Vector Logistics、HFR Transportなどが市場の主要企業です。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場洞察
- 市場概要
- バリューチェーン/サプライチェーン分析
- 産業における政府の規制と取り組み
- 市場における技術開拓
- 市場の革新的新興企業に関する洞察(Solar Freeze、InspiraFarms、Coldbox Store、ColdHubs、Freezelink)
- COVID-19パンデミックの市場への影響
第5章 市場力学
- 促進要因
- 果物輸出の増加
- 抑制要因
- 電力危機
- 機会
- 冷蔵施設不足による食品廃棄
- 産業の魅力-ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
第6章 市場セグメンテーション
- サービス別
- 保管
- 輸送
- 付加価値サービス(ブラスト冷凍、ラベリング、在庫管理など)
- 温度別
- 冷蔵
- 冷凍
- 常温
- 製品カテゴリー別
- 園芸(生鮮果物・野菜)
- 乳製品(牛乳、アイスクリーム、バターなど)
- 肉、鶏肉、魚介類
- 加工食品
- その他
- 国別
- エジプト
- ナイジェリア
- 南アフリカ
- その他の国
第7章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 企業プロファイル
- CCS Logistics
- Khold
- Cold Solutions East Africa
- Vector Logistics
- HFR Transport
- Africa Cold Chain Limited
- African Perishable Logistics
- Unitrans
- Africa Global Logistics (AGL)
- Go Global
- Lieben Logistics
- BigCold Kenya Ltd
- Southern Shipping Services Ltd (SSSL)*
- その他の企業
第8章 市場の将来
第9章 付録
The Africa Food Cold Chain Logistics Market size in terms of gross merchandise value is expected to grow from USD 9.92 billion in 2025 to USD 14.53 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 7.94% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Changes in lifestyle and urbanization contributing to increased domestic consumption of processed foods and a shift in consumption patterns, including increased consumption of fresh fruits, as people become more health concerned, need to address food wastage and ensure food security, are the factors assisting the market's growth.
The climate change crisis has significantly contributed to the dire food insecurity and food wastage in Africa. Over one-third of food produced in Africa is estimated to be lost to spoilage or waste. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization estimates that over 40% of food in Sub-Saharan Africa perishes before it reaches a consumer. This can be as high as 60% for fresh produce in Sub-Saharan Africa.
The leading cause of food wastage is spoilage due to the lack of cold storage facilities to extend the shelf life, especially temperature-sensitive food items. Farmers and agri-traders in Africa rely on makeshift coolers or outdated, generic cold rooms. These systems are unreliable, poorly maintained, and have high operational costs.
Cold storage or cold supply chain products can help reduce spoilage and maintain quality and efficacy, but they require sufficient electricity to work effectively. In Africa, according to the African Development Bank (AfDB), electricity is out of reach for more than 640 million people, and the ability to sustainably maintain constant cold temperatures remains a challenge. There is an urgent need to deploy resilient, reliable, and sustainable cold chains to tackle food and medicine losses in Africa.
Several startups in Africa are innovating digital solutions to respond to emerging challenges. These startups offer cold storage products and solutions that are energy-efficient and compliant with export standards. They are also affordable and well-equipped with temperature and performance monitoring systems.
According to a Cold Chain Storage industry report, the cold chain infrastructure is developing in East Africa, with cold chain infrastructure in Southern Africa being more developed and geared toward exporters.
Africa Food Cold Chain Logistics Market Trends
Electricity Crisis is Negatively Affecting the South African Food Cold Chain Logistics Market
South Africa currently hosts most of the continent's cold storage capacity, encompassing many positive (fresh fruit and vegetables) and negative (fish and meat) cold storage options. Numerous cold chain logistics providers operating in Africa are headquartered in South Africa. However, the country is grappling with significant electricity shortages, resulting in widespread daily power cuts lasting up to 10 hours in various regions. As per the Ministry of Mineral Resources and Energy, South Africa's total domestic electricity generation capacity is 58,095 megawatts (MW). Coal remains the predominant energy source, constituting approximately 80% of the country's energy mix. Nonetheless, due to the aging and deteriorating condition of some coal power stations, actual power generation falls substantially short, creating a deficit ranging between 4000 - 6000 MW.
This shortfall has led to severe power cuts, also known as 'load shedding.' A reliable and consistent energy supply is crucial for maintaining the cold chain. In regions with inconsistent or unreliable power, the risk of disruptions to temperature-controlled environments increases. These power cuts are adversely affecting the cold chains within the agricultural sector, particularly impacting the storage and transport of fresh produce. Reports indicate that some retailers have rejected fresh produce due to delivery delays and disruptions in the cold chain, exacerbating the situation during warmer months. This energy crisis is a significant challenge for the South African food cold chain logistics market.
Fresh Fruit Exports are Contributing to the Growth of the Market
Egypt holds the position of being the largest exporter of fruits and vegetables in the region. Annually, the country generates approximately USD 3 billion in revenue from exporting various fresh, dried, and frozen fruit and vegetable products. Key products exported to international markets include oranges, potatoes, frozen strawberries, table grapes, and fresh onions. South Africa also plays a vital role in the export market. The agricultural sector in South Africa is distinctly export-focused, with approximately half of its produce being exported in value terms. The South African fruit industry is a predominant force in the country's agricultural exports, with fresh fruit accounting for around 35% of South African agricultural exports. Decades of research and development and capacity-building initiatives for growers and industry associations have been instrumental in producing high-quality fruit that can compete effectively globally.
South Africa boasts significant rankings in global fruit production, including being the world's 2nd largest citrus exporter, 6th largest pear producer, 7th largest grape exporter, 8th largest apple exporter, and 9th largest avocado exporter. Regarding export markets, the South African fruit industry aims to retain and maximize its traditional markets within the European Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Additionally, there is a strategic focus on gaining access to new markets in East Asia and the Middle East. Africa represents a substantial potential export market for various types of fruit from South Africa. Presently, apples and pears are performing well in West and East Africa. The export of these fruits within and outside Africa is a significant demand driver for cold chain logistics, emphasizing the importance of ongoing development in cold chain infrastructure.
Africa Food Cold Chain Logistics Industry Overview
Given the diversity of the African continent, local and regional logistics providers play a crucial role. Regional players are the major players in the African food cold chain logistics market. They have a better understanding of local market dynamics, regulations, and infrastructure challenges. Cold Chain logistics operations are concentrated in the Southern region of the continent. Companies that offer integrated cold chain services, including transportation, warehousing, and distribution, have a competitive advantage. Seamless coordination of these services is essential for maintaining the integrity of temperature-sensitive food products. CCS Logistics, Khold, Cold Solutions East Africa, Vector Logistics, and HFR Transport are some of the key players in the market.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.3 Government Regulations and Initiatives in the Industry
- 4.4 Technological Developments in the Market
- 4.5 Insights on Innovative Startups in the Market (Solar Freeze, InspiraFarms, Coldbox Store, ColdHubs, and Freezelink)
- 4.6 Impact of the COVID - 19 Pandemic on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Drivers
- 5.1.1 Increasing Fruit Exports
- 5.2 Restraints
- 5.2.1 Electricity Crisis
- 5.3 Opportunities
- 5.3.1 Food Wastage Due to Lack of Cold Storage Facilities
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 5.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Service
- 6.1.1 Storage
- 6.1.2 Transportation
- 6.1.3 Value-added Services (Blast Freezing, Labeling, Inventory Management, etc.)
- 6.2 By Temperature
- 6.2.1 Chilled
- 6.2.2 Frozen
- 6.2.3 Ambient
- 6.3 By Product Category
- 6.3.1 Horticulture (Fresh Fruits and Vegetables)
- 6.3.2 Dairy Products (Milk, Ice Cream, Butter, etc.)
- 6.3.3 Meat, Poultry, and Seafood
- 6.3.4 Processed Food Products
- 6.3.5 Other Categories
- 6.4 By Country
- 6.4.1 Egypt
- 6.4.2 Nigeria
- 6.4.3 South Africa
- 6.4.4 Other Countries
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Concentration
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 CCS Logistics
- 7.2.2 Khold
- 7.2.3 Cold Solutions East Africa
- 7.2.4 Vector Logistics
- 7.2.5 HFR Transport
- 7.2.6
Africa Cold Chain Limited
- 7.2.7 African Perishable Logistics
- 7.2.8 Unitrans
- 7.2.9 Africa Global Logistics (AGL)
- 7.2.10 Go Global
- 7.2.11 Lieben Logistics
- 7.2.12 BigCold Kenya Ltd
- 7.2.13 Southern Shipping Services Ltd (SSSL)*
- 7.3 Other Companies


