
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1850179
欧州のスマートマニュファクチャリング:市場シェア分析、産業動向、統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Europe Smart Manufacturing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 欧州のスマートマニュファクチャリング:市場シェア分析、産業動向、統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年06月26日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 120 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
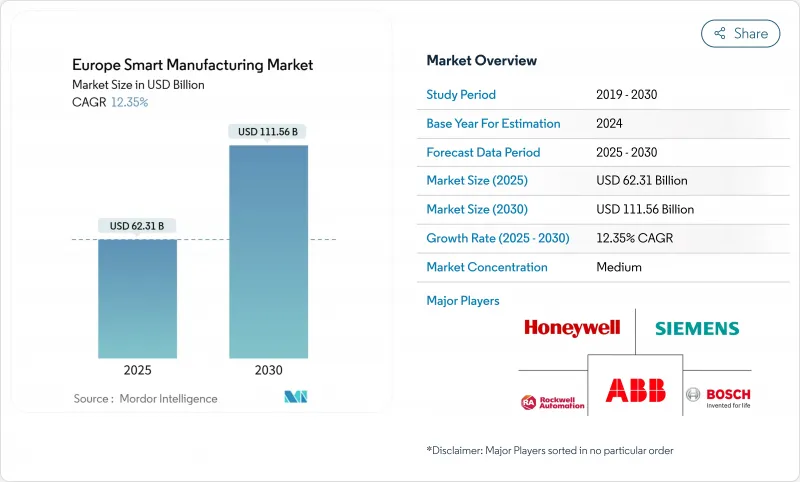
欧州のスマートマニュファクチャリングの市場規模は2025年に623億1,000万米ドル、2030年には1,115億6,000万米ドルに達し、CAGR 12.35%で拡大すると予測されています。
人件費インフレの激化、2,000億ユーロ(2,130億米ドル)のInvestAIプログラムのような注目度の高い公的資金、サイバーレジリエンス法に基づく規制圧力の高まりが、総じてコネクテッド生産技術の採用を加速させています。産業用ロボティクスが引き続き工場現場の自動化を支える一方で、エッジAIとデジタルツインの導入が、資産活用を拡大するリアルタイムのプロセスインサイトを解き放ちます。企業は、制御ハードウェア、IIoTコネクティビティ、分析ソフトウェアを融合したプラットフォームベースのエコシステムを追求することで、エネルギー消費を抑制し、ネットゼロの義務に準拠することができます。既存企業がAIのスペシャリストを吸収し、政府が財政的インセンティブを地域のデータ主権保護に結びつけることで、競争は激化し、欧州のスマートマニュファクチャリング市場は経済回復力の戦略的支柱となります。
欧州のスマートマニュファクチャリング市場の動向と洞察
EUのインダストリー4.0資金調達スキーム
欧州の強力な資金提供により、デジタル変革のための前例のない資金が引き出されます。ドイツのManufacturing-Xプログラムは、相互運用可能な産業データスペースの構築に1億5,000万ユーロ(1億6,000万米ドル)を供給し、より広範なInvestAIアーキテクチャはAIインフラ全体に2,000億ユーロ(2,130億米ドル)を動員しています。中小企業がマッチング・グラントを利用することで、参入障壁が低くなります。英国のMade Smarterパイロットでは、すでに2,200万ポンド(2,800万米ドル)を350の技術プロジェクトに投入し、1,600人の新規雇用を創出しました。ベンチャー企業の勢いは公的資金に追随するもので、ドイツではAIを活用した製造業のスタートアップ企業が67%急増し、AWS、マイクロソフト、アップルがハイパースケーラーを提供することを表明しています。こうした資本の流れにより、欧州のスマートマニュファクチャリング市場は、地域の技術主権を守りつつ、アジアの受託製造に代わる信頼できる市場として位置づけられています。
人件費上昇圧力が工場の自動化を促進
EUの時間当たり平均人件費は、2024年には前年比5%増の33.5ユーロ(35.7米ドル)となり、西欧と低賃金地域とのデルタが拡大します。ルクセンブルクの時給は55.2ユーロ(58.8米ドル)でEU圏のトップであり、プレミアム生産者の自動化に対する競争上の緊急性が高まっています。また、雇用主は深刻な人材格差に直面しています。21カ国の調査対象企業の75%が、熟練した職務の充足が困難であると報告しています。このようなプレッシャーが絡み合うことで、自動化は裁量的な効率化手段から必要不可欠な要件へと変化し、スマートマニュファクチャリング市場全体において、反復作業をロボットやコンピュータ・ビジョン・システムに置き換える動きが加速しています。
サイバーセキュリティとデータ主権への懸念
サイバーレジリエンス法は、リスク段階的な適合性評価を実施し、最高1,500万ユーロ(1,600万米ドル)または世界売上高の2.5%の罰則を課すことができます。GDPRとNIS 2の規則が重なり合うことで、特にサイバーチームが限られている中小企業にとっては、文書化作業がエスカレートします。域外へのデータ転送を恐れるあまり、EU域外でホストされるハイパースケールプラットフォームへの移行が遅れ、サプライヤーはソブリンクラウドやエッジアナリティクスアプライアンスを提供せざるを得なくなります。こうしたコンプライアンスコストが導入サイクルを長期化させ、欧州のスマートマニュファクチャリング市場の短期的な成長ペースを抑制しています。
セグメント分析
2024年の欧州のスマートマニュファクチャリング市場シェアは産業用ロボットが28%を占め、自動車最終組立自動化と標準化された溶接セルがこれを支えます。ファナックのスペイン進出は、南欧の未開拓クラスターの開拓を示唆しており、防爆仕様の協働塗装ロボットは危険環境アプリケーションを開拓します。デジタルツイン&シミュレーションプラットフォームはCAGR16.8%で拡大しており、AIとともに物理ベースのモデルを組み込んで資産の挙動を予測し、試運転間隔を短縮しています。シミュレーションとMESの融合がクローズドループの最適化を可能にし、デジタルツインを欧州のスマートマニュファクチャリング市場で最速のテコとして位置づける。
オートメーション制御システム(PLC、SCADA、DCS)は、プラントがイーサネットベースのフィールドバスに移行するのに伴い、更新需要が発生します。ハネウェルのエクスペリオン・オペレーション・アシスタント(Experion Operations Assistant)のようなAIで拡張されたHMIレイヤーは、アラームの疲労を軽減する文脈に沿った推奨を表示します。MESは、Valmet-FactoryPalのような買収を通じて急速に浸透し、OEEダッシュボードを処方的洞察で充実させる。アディティブ・マニュファクチャリングは、形状の複雑さが量的経済性を凌駕する、スペアパーツ・フルフィルメントにおけるニッチな足場を維持します。このようなツールセットの拡大により、欧州のスマートマニュファクチャリング市場の収益源は多様化しています。
欧州のスマートマニュファクチャリング市場は、技術別(自動制御システム、産業用ロボットなど)、コンポーネント別(ハードウェア、ソフトウェア、サービス)、エンドユーザー産業別(自動車、航空宇宙・防衛、化学・石油化学など)、国別に分類されています。市場規模および予測は金額(米ドル)で提供されます。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- EUインダストリー4.0資金スキーム
- 工場の自動化を推進する労働コストの圧力の高まり
- IIoT接続の急速な導入
- ネットゼロ義務化によりエネルギー最適化ソリューションが加速
- 欧州中小企業におけるエッジAI品質検査の導入
- 産業グレードの5Gプライベートネットワークの展開
- 市場抑制要因
- サイバーセキュリティとデータ主権に関する懸念
- ブラウンフィールド統合CAPEXの高水準
- CEEプラントにおける断片化されたレガシーマシンプロトコル
- デジタルツインエンジニアリングの人材不足
- バリュー/サプライチェーン分析
- 規制状況(EUデジタル10年、Gaia-X)
- 技術展望(IIoT、デジタルツイン、5G、エッジAI)
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- 技術別
- 自動化制御システム(PLC、SCADA、DCS)
- 産業用ロボット
- 産業用IoTプラットフォーム
- ヒューマンマシンインターフェース(HMI)
- 製造実行システム(MES)
- 製品ライフサイクル管理(PLM)
- デジタルツインとシミュレーション
- 積層造形/3Dプリンティング
- コンポーネント別
- ハードウェア
- センサー
- コントローラー/IPC
- エッジコンピューティングデバイス
- マシンビジョンシステム
- ロボティクス
- ソフトウェア
- SCADAおよびHMIソフトウェア
- 分析とAIソフトウェア
- ERPおよびPLMソフトウェア
- サービス
- 統合とコンサルティング
- メンテナンスとサポート
- マネージドサービス
- ハードウェア
- エンドユーザー業界別
- 自動車
- 航空宇宙および防衛
- 化学および石油化学製品
- 食品・飲料
- 医薬品とバイオテクノロジー
- 金属および鉱業
- エレクトロニクスおよび半導体
- 石油・ガス
- 公益事業とエネルギー
- 国別
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- イタリア
- スペイン
- ロシア
- オランダ
- スウェーデン
- ポーランド
- ベルギー
- オーストリア
- スイス
- ノルウェー
- フィンランド
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 戦略的動向
- Market-share Analysis
- 企業プロファイル
- ABB Ltd
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- General Electric Co.
- Robert Bosch GmbH
- FANUC Corporation
- IBM Corporation
- Dassault Systems SE
- SAP SE
- Mitsubishi Electric Corp.
- KUKA AG
- Yokogawa Electric Corp.
- PTC Inc.
- Hexagon AB
- Omron Corp.
- Beckhoff Automation GmbH
- Endress+Hauser AG


