
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1635528
アジア太平洋地域の製造住宅市場:市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Asia Pacific Manufactured Homes - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| アジア太平洋地域の製造住宅市場:市場シェア分析、産業動向と統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年01月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 120 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
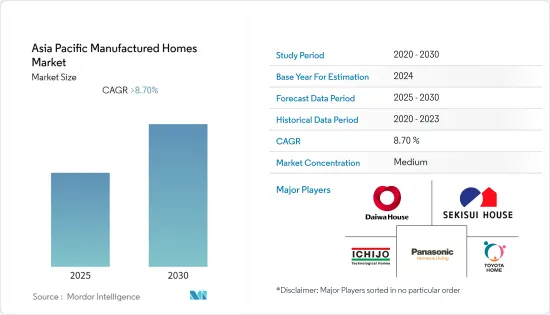
アジア太平洋地域の製造住宅市場は予測期間中に8.7%以上のCAGRで推移する見込みです。
主なハイライト
- 人口増加のニーズに対応するため、グリーンインフラや持続可能な生活への関心が高まっていることも、この市場を動かす要因のひとつです。モジュール式住宅の必要性がより緊急性を帯びている特定の状況があります。製造住宅は、アジアの低所得者層に低コスト住宅を提供する一方で、災難や過酷な条件から彼らを守ることができます。
- 高級住宅市場は現在、プレハブ住宅を単なる住宅ソリューション以上のものとしてアジア太平洋地域と欧米の双方に提示しています。高級モジュール式住宅の設計者は、欧米以外にインスピレーションを求めるようになってきています。製造された建築システムにとって最も有利な市場はアジア太平洋地域と予想され、この動向は当面続くと思われます。中国、韓国、インドを含むアジア太平洋地域諸国では、ここ数年モジュラーハウスの市場が大幅に拡大しています。このことが、持続可能な建築システム市場に確かな後押しを与えています。
- インド、中国、日本の住宅部門からの需要が急速に高まっているため、アジア太平洋地域の製造住宅市場は予測期間中に大幅に拡大すると予測されます。アジア太平洋地域の製造住宅市場は、中国とインドがインフラ整備に多額の投資を行った結果、急速に拡大すると予想されます。
アジア太平洋地域の製造住宅市場の動向
オーストラリアにおける住宅セクターの成長とイノベーションを支える投資
オーストラリアには、低所得世帯向けに手頃な価格の住宅を最近生産し、このサービスを拡大しようとしている非営利団体が約40あります。このカテゴリーには11の著名な非営利デベロッパーがあり、いずれも高い実績を持ち、最近の動向も良好です。オーストラリアを代表する非営利デベロッパーは、入居者の同意を得た上で、費用対効果が高く、目的に応じて設計された様々な住宅を建設するスキルを築き始めています。
最近、オーストラリアの全ての政府が、非営利団体に手頃な価格の住宅を建設させるための資金調達、立法、規制の方法を導入するための措置を講じています。活動のレベルは管轄区域によって異なるが、政府からの資金提供は、大量の供給を行ったり、民間投資を大幅に増やしたりするには、一般的に十分ではないです。オーストラリアでは、より大きな財政的インセンティブを与えたり、非営利セクターに対する全国的な一貫性のある規制を推進するなど、連邦政府の新たな施策によって、この開発活動がさらに勢いを増す可能性があります。
最近、オーストラリアのすべての政府が、非営利団体に手頃な価格の住宅を建設させるための資金調達、立法、規制の方法を導入するための措置を講じています。活動のレベルは管轄区域によって異なるが、政府資金は通常、膨大な供給量を提供したり、民間投資を大幅に増加させたりするには十分ではないです。オーストラリアでは、より大きな財政的インセンティブを与えたり、非営利セクターに対する全国的な一貫性のある規制を推進するなど、連邦政府の新たな施策によって、この開発活動がさらに勢いを増すかもしれないです。
オーストラリア政府は、建築・建設・製造業への支援、プレハブ建築分野への支援を約束しました。オーストラリア政府は、より経済的で環境的に持続可能でありながら、建設時間を大幅に短縮できる斬新なプレハブ建築物を製造するメーカーを支援するため、新たなコラボレーション・ラボの開設を発表しました。
オーストラリア政府は、構造物を改良し、より手頃な価格で効果的かつ安全なものにするため、業界の業界団体であるPrefabAusに2,127万米ドルを提供しました。このプログラムにより、プロジェクトの遅延が40%削減され、CO2排出量が50%削減され、建築廃棄物が80%削減されます。オーストラリア研究評議会は、メルボルン大学が運営するARC Training Centre for Advanced Manufacturing of Prefabricated Housingに多額の投資を行い、4年間で600万米ドルの融資を受けました。
日本のプレハブ住宅産業は技術革新で世界をリードしている
日本では、プレハブ建築が全新築住宅の15%を占めています。プレハブ建築を採用する日本の家庭では、50年から100年の耐久性を想定しているにもかかわらず、30年ごとに家を建て替えることが多いです。プレハブ建築の利用は国によって異なるが、日本のように他の産業部門とのつながりの恩恵を受けている市場もあり、人気を博しています。
プレハブ住宅は、調査期間中、日本の全建築物に占める割合とほぼ同じで、14%から15%の間でした。2019年現在、東京(18,683戸)が日本で最も多くのプレハブ建築物を有し、神奈川(10,864戸)、愛知(10,655戸)、千葉(8,970戸)、埼玉(8,898戸)と続いています。
効果的な生産方法、的を絞ったマーケティング戦略、消費者参画、多様性と柔軟性を市場競争価格で提供する高品質設計により、日本の製造住宅事業はイノベーションの世界的パイオニアとなっています。顧客は、完全にコンピュータ化されたシステムのおかげで、標準化された部品を使って住宅を設計することができます。欧米で広く信じられているのとは反対に、日本の工場生産住宅は伝統的な建築方法よりも優れていると見なされています。
アジア太平洋地域の製造住宅産業の概要
市場では熾烈な競争が繰り広げられており、数社のみが圧倒的なシェアを占めています。市場の断片化にもかかわらず、今後数年間は成長が見込まれます。日本では、パナソニックホームズやトヨタホームをはじめとする大手メーカーが木造住宅市場に参入しています。主なプレーヤーは、大和ハウス工業、積水ハウス、一条工務店、パナソニックホームズ、トヨタホームです。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 市場の定義と範囲
- 調査の前提
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学と洞察
- 現在の市場シナリオ
- 市場力学
- 促進要因
- 抑制要因
- 機会
- 産業バリューチェーン分析
- 製造住宅市場における技術革新
- 業界における政府の規制と取り組み
- 製造住宅のコストに関する洞察
- 業界の魅力度-ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手/消費者の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
- COVID-19が市場に与える影響
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- タイプ別
- シングルファミリー
- マルチファミリー
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度の概要
- 企業プロファイル
- Daiwa House Industry
- Sekisui House
- Ichijo
- Panasonic Homes
- Toyota Housing Corporation
- Ausco Modular Construction
- Shanghai Star House
- Archiblox
- Anchor Homes
- Aussie Modular Solutions*
第7章 アジア太平洋地域の製造住宅市場の将来
第8章 付録
The Asia Pacific Manufactured Homes Market is expected to register a CAGR of greater than 8.7% during the forecast period.

Key Highlights
- The other motivating aspect will be the growing worries about green infrastructure and sustainable living to meet the needs of the expanding population. There are particular situations where the need for modular housing is more urgent. Manufactured homes can provide low-cost housing for low-income communities in Asia while safeguarding them from calamities and harsh conditions.
- The luxury market is currently presenting prefabricated homes as more than just a straightforward dwelling solution, both in the Asia Pacific and the West. High-end modular home designers are increasingly seeking inspiration outside of the West. The most lucrative market for manufactured building systems is anticipated to be Asia Pacific, and this trend is likely to stay for the foreseeable future. The market for modular homes has significantly increased over the past few years in Asia Pacific nations including China, South Korea, and India. This is giving the market for sustainable building systems a solid boost.
- Due to the rapidly rising demand from the residential sectors of India, China, and Japan, the Asia-Pacific manufactured home market is predicted to have considerable expansion over the forecast period. The Asia-Pacific manufactured homes market is expected to increase rapidly as a result of significant investments made by China and India in the development of their infrastructure.
APAC Manufactured Homes Market Trends
Investment to Support the Growth and Innovation in the Housing Sector in Australia
In Australia, there are about 40 not-for-profit organizations that have recently produced affordable homes for lower-income households and are looking to extend this service. There are eleven prominent not-for-profit developers in this category, all of whom have a strong track record and recent expansion. Leading Australian not-for-profit developers are starting to build their skills in creating a range of cost-effective, purpose-designed affordable housing options that have the consent of their tenants.
All Australian governments have lately taken steps to implement financing, legislative, and regulatory methods that let not-for-profit organizations build affordable homes. Although activity levels vary between jurisdictions, governmental funding has typically not been adequate to provide a huge volume of supply or significantly increase private investment. This developing activity might be given more momentum in Australia by new Commonwealth measures, such as providing a larger financial incentive and pushing for nationally consistent regulation of the not-for-profit sector.
All Australian governments have lately taken steps to implement financing, legislative, and regulatory methods that let not-for-profit organisations build affordable homes.Although activity levels vary between jurisdictions, governmental funding has typically not been adequate to provide a huge volume of supply or significantly increase private investment. This developing activity might be given more momentum in Australia by new Commonwealth measures, such as providing a larger financial incentive and pushing for nationally consistent regulation of the not-for-profit sector.
The Australian government pledged help for the building, construction, and manufacturing industries, as well as support for the prefabricated building sector. It has announced the opening of a new collaboration lab to assist manufacturers in creating novel prefabricated buildings that are more economical and environmentally sustainable while also drastically cutting down on construction time.
The Australian government gave USD 21.27 million to PrefabAus, the industry's trade association, to improve structures and make them more affordable, effective, and secure. This programme will result in a 40% reduction in project delays, a 50% reduction in CO2 emissions, and an 80% reduction in building waste. The Australian Research Council made a sizeable investment in the ARC Training Centre for Advanced Manufacturing of Prefabricated Housing, which is run by the University of Melbourne and has received financing of USD 6 million over four years.
Japan's prefabricated-housing industry is a world leader in innovation
In Japan, prefabricated building accounts for 15% of all new dwelling construction. Japanese families who employ prefabricated constructions frequently rebuild their homes every 30 years because they view them as depreciating, even though they are intended to endure between 50 and 100 years. While the use of prefabricated building varied by country, it has gained popularity in some markets, such as Japan, which has benefited from connections with other industrial sectors.
Prefabricated dwelling units made up about the same percentage of all Japanese construction buildings over the study period-between 14% and 15%. As of 2019, Tokyo (18,683 units) had the most prefabricated buildings in Japan, followed by Kanagawa (10,864 units), Aichi (10,655 units), Chiba (8,970 units), and Saitama (8,898 units).
With effective production methods, targeted marketing strategies, consumer engagement, and high-quality designs that offer diversity and flexibility at competitive rates, Japan's manufactured home business is a global pioneer in innovation. Customers can design their homes with standardised components thanks to a completely computerised system. Contrary to popular belief in the West, factory-built homes in Japan are seen as being superior than those that are traditionally constructed.
APAC Manufactured Homes Industry Overview
There is fierce competition in the market, and only a few companies hold the lion's share. Despite market fragmentation, growth is anticipated over the coming years. Major manufactured home companies in japan are getting into the wooden housing market, including Panasonic Homes and Toyota Homes, while local power builders and construction firms are growing in influence. Major players are Daiwa House Industry, Sekisui House, Ichijo, Panasonic Homes, and Toyota Housing Corporation.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Market Definition and Scope
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS AND INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.2.2 Restraints
- 4.2.3 Opportunities
- 4.3 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Technological Innovations in the Manufactured Homes Market
- 4.5 Government Regulations and Initiatives in the Industry
- 4.6 Insights into Manufactured House Costs
- 4.7 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of the COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Type
- 5.1.1 Single Family
- 5.1.2 Multi Family
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Daiwa House Industry
- 6.2.2 Sekisui House
- 6.2.3 Ichijo
- 6.2.4 Panasonic Homes
- 6.2.5 Toyota Housing Corporation
- 6.2.6 Ausco Modular Construction
- 6.2.7 Shanghai Star House
- 6.2.8 Archiblox
- 6.2.9 Anchor Homes
- 6.2.10 Aussie Modular Solutions*


