
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1851423
廃棄物エネルギー(WTE):市場シェア分析、産業動向、統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Waste To Energy (WTE) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 廃棄物エネルギー(WTE):市場シェア分析、産業動向、統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年07月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 125 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
2025年の廃棄物エネルギー(WTE)市場規模は454億2,000万米ドルと推計され、2030年にはCAGR 11.22%で773億米ドルに達すると予測されます。
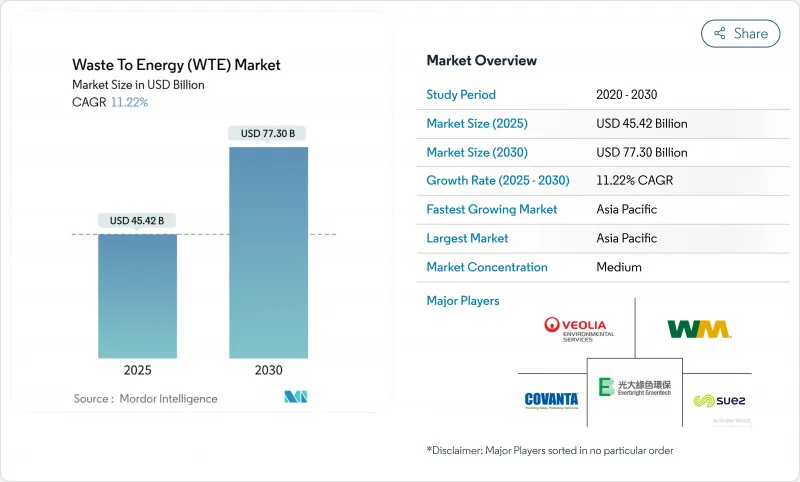
成長の背景には、都市廃棄物の増大と低炭素電力への世界的な要請という2つの圧力があります。火力発電技術は依然として設備増設の基幹技術であるが、投資はプラズマアークや改良型嫌気性消化法などの先進的で低排出ガスなソリューションへとシフトしています。韓国と欧州連合(EU)の積極的な炭素価格制度がプロジェクトの経済性を再構築している一方、インドの第2級都市では埋め立てが禁止され、原料の入手が加速しています。ユーティリティ企業、環境サービス企業、技術スペシャリストの戦略的統合が続き、デジタル最適化ツールは、新設・改修プラント全体の運転マージンとコンプライアンス性能を引き上げています。このような力が相まって、銀行取引可能なプロジェクトの強固なパイプラインが維持され、廃棄物発電市場が循環型経済の極めて重要な要素として位置づけられています。
世界の廃棄物エネルギー(WTE)市場動向と洞察
中国大湾岸地域におけるEfW官民パートナーシップ・パイプラインの急速な展開
350億人民元を超える投資により、先進的な排出モニタリングと材料回収設計を導入する80以上のプロジェクトに資金が供給されています。新しいプラントは、毎日40万トン以上を処理する大容量のクラスターを形成し、この地域の拡張可能な都市廃棄物ソリューションのひな型を固めています。WTEを含むクリーンな電力源からの発電量は、2024年には前年比16.4%増となり、政策の勢いと投資家の信頼を裏付けています。
レガシー焼却炉のレトロフィットを加速するEUグリーン税制優遇措置
グリーン税制は、融資を厳格なエネルギー効率指標にリンクさせ、排ガスシステムのアップグレードと原料再利用の拡大を組み合わせた改修工事に対して約3億ユーロの資金を提供します。これを遵守する事業者は、資金調達コストの削減と優先的な送電網の利用が可能となり、西欧および北欧全域の廃棄物発電市場が強化されます。
ダイオキシン排出規制強化でドイツの火炉改修許可が延期に
2024年産業排出指令は規制を強化し、2035年までに電子許可を義務付けるもので、古いプラントの操業者は大気汚染防止システムの再設計を余儀なくされます。コンプライアンスコストと承認に時間がかかるため、容量のアップグレードが遅れ、欧州最大の経済圏の廃棄物発電市場が低迷しています。
セグメント分析
焼却は、実績のある操業の歴史と、欧州と東アジア全域の地域熱インフラとの統合に支えられ、2024年の廃棄物エネルギー化市場シェアの65%を維持。年産20万トン以上の工場では、予測可能な運転時間と確立されたサプライヤー・ネットワークにより、引き続き火格子炉設計が採用されています。とはいえ、プラズマアーク炉の生産能力は、廃棄物からシンガスへの変換効率が99%に達し、ダイオキシン生成量が大幅に減少するため、2030年までにCAGR 16%を記録すると予測されています。低排出量と高い金属回収率に見合う補助金制度は、特に人口密度の高いアジアの都市部では、プロジェクトのパイプラインをプラズマアークへとさらに傾ける。そのため、先進的な熱プラットフォームと結びついた廃棄物発電の市場規模は、ヘッドラインレートを上回るペースで加速しています。
ハイブリダイゼーションの動向は、資産仕様を再構築しています。いくつかの新設プラントは、熱変換の前にリサイクル収率を高めるために、フロントエンドの機械的生物学的処理とガス化またはプラズマアークをバンドルしています。一方、嫌気性消化は、高水分の有機廃棄物が優れたバイオガス収量を適度な資本コストで提供する農業地域で、再び注目を集めています。現在では機械的、熱的、化学的前処理によってメタン生産量が25%~190%上昇し、分散型消化装置の経済的スイートスポットが広がっています。予測期間中、デジタル・ツインとAI支援燃焼制御により、熱島効率がライフサイクルベースで4~6%向上し、次世代施設の差別化がさらに進むと予想されます。
都市固形廃棄物は、着実な回収量と埋め立てからの脱却を求める規制圧力に後押しされ、2024年の廃棄物エネルギー(WTE)市場規模の70%を占めました。主要都市における高発熱の産業廃棄物および発生源分別プログラムが、堅調な原料品質を維持し、ベースロード・エネルギー生産を支えています。一方、農業・農産業残渣は、政府が農村部のサプライチェーンにおけるメタン削減を目標としているため、2030年までのCAGRが14%になると予想されます。農家が作物の茎葉や糞尿を供給するための財政的インセンティブは、これまで未開拓であったエネルギーの可能性を解き放ち、消化液利用による土壌健全性目標に合致します。
プラスチック、溶剤、高Btスラッジなどの産業廃棄物の流れは、特殊なロータリーキルンや流動床システムに対する安定した需要をもたらします。下水汚泥は、排出規制の厳格化によって追加治療が必要とされる場所で、その存在感を増しています。熱乾燥と単焼却を組み合わせることで、現在では肥料にリサイクルできるリンの豊富な灰が得られます。この動向は、廃棄物エネルギー市場におけるプラントの稼働率向上とメンテナンスサイクルの長期化を支えています。
廃棄物エネルギー(WTE)市場レポートは、技術別(物理的、熱的、生物学的)、廃棄物タイプ別(都市固形廃棄物、産業廃棄物、その他)、エネルギー出力別(電気、熱、その他)、エンドユーザー別(公益事業およびIPP、産業用キャプティブプラント、地域暖房事業者、輸送燃料販売業者)、地域別(北米、欧州、アジア太平洋、南米、中東アフリカ)に分類されています。
地域分析
アジア太平洋地域は2024年の売上高の45%を占め、2030年までの地域別CAGRは13%でポールポジションを維持します。中国だけでも日産40万トンを処理する400以上の工場が稼動しており、2025年には日産70万トンにまで能力が上昇します。インドのTier-2都市は、Swachh Bharat Mission 2.0に導かれて、300~500トン/日のモジュール式ラインを好む建設・操業・譲渡契約を結んでいます。日本は排出規制技術でリーダーシップを維持し、韓国の排出権取引スキームはモデルIRRを最大2.5ポイント引き上げ、北東アジアの廃棄物発電市場を拡大します。
欧州は、高密度の地域熱統合と厳格な環境規制を特徴とし、売上高で第2位にランクされています。デンマークとスウェーデンは、地方自治体の熱供給ネットワークにおける再生可能エネルギーの割合がすでに75%を超えており、EUのグリーン税制は、譲許的な資本をプラントの改修に回しています。ドイツはダイオキシン規制強化による改修の遅れに直面し、英国は発熱量規制により低品位RDFを国内焼却炉に振り向け、新たな地域需要を生み出しています。
北米では、米国でのユーティリティ・スケールのプロジェクトやカナダでのバイオメタンへの投資を中心に、着実な拡大が見られます。Covanta社、Waste Management社、FCC Environmental Services社が大規模な自治体との契約を争っており、最近の買収はさらなる統合を示唆しています。中南米では、ブラジルの中南部砂糖地帯でバイオガスの導入が進んでいるが、原料価格の変動がプロジェクトのパイプラインを不安定にしています。中東・アフリカでは、エジプトの1億2,000万米ドルの固形廃棄物発電所が関心の高まりを示しているが、全体的な展開はまだ初期段階です。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 中国大湾区におけるEfW官民パートナーシップパイプラインの急速な展開
- EUのグリーン税制優遇措置がレガシー焼却炉のレトロフィットを加速する
- インドのTier-2都市でMSW転換を誘発する無分別埋め立ての全国的禁止
- 炭素クレジット価格の高騰で韓国のWTEプロジェクトのIRRが改善
- サーキュラーエコノミーが主導する北欧のバイオガスCPPA(企業間電力購入契約)
- ブレグジット後の英国におけるRDF輸出の発熱量基準値の義務化
- 市場抑制要因
- ダイオキシン排出規制強化でドイツの火格子炉改修許可が延期に
- 限定的な廃棄物処理料金上昇がインドネシアのプロジェクト・バンカビリティを阻害
- ブラジルの嫌気性消化法原料価格の乱高下がマージンを悪化させる
- オーストラリアの都市周辺地域におけるプラズマアーク施設に対する地域社会の反発
- サプライチェーン分析
- テクノロジーの展望
- 規制の見通し
- ポーターのファイブフォース
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 消費者の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
- 投資分析
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- 技術別
- 物理的(廃棄物由来燃料、機械的生物学的治療)
- 熱(焼却/燃焼、ガス化、熱分解、プラズマ・アーク)
- 生物学的(嫌気性消化、発酵)
- 廃棄物タイプ別
- 固形廃棄物
- 産業廃棄物
- 農業・農産業残渣
- 下水汚泥
- その他(商業、建設、危険物)
- エネルギー出力別
- 電気
- 熱
- 熱電併給(CHP)
- 輸送用燃料(バイオNG、バイオLNG、エタノール)
- エンドユーザー別
- 公益事業および独立系発電事業者(IPP)
- 産業キャプティブプラント
- 地域暖房事業者
- 輸送用燃料ディストリビューター
- 地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 欧州
- 英国
- ドイツ
- フランス
- スペイン
- 北欧諸国
- ロシア
- その他欧州地域
- アジア太平洋地域
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- 韓国
- ASEAN諸国
- その他アジア太平洋地域
- 南米
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
- コロンビア
- その他南米
- 中東・アフリカ
- アラブ首長国連邦
- サウジアラビア
- 南アフリカ
- エジプト
- その他中東・アフリカ地域
- 北米
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 戦略的な動き(M&A、パートナーシップ、PPA)
- 市場シェア分析(主要企業の市場ランク/シェア)
- 企業プロファイル
- Veolia Environnement SA
- Suez SA
- Waste Management Inc.
- Covanta Holding Corp.
- Wheelabrator Technologies Inc.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
- Hitachi Zosen Corp.
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises Inc.
- A2A SpA
- MVV Energie AG
- Martin GmbH fur Umwelt-und Energietechnik
- China Everbright Environment Group Ltd
- China Jinjiang Environment Holding Co.
- Xcel Energy Inc.
- Shenzhen Energy Group Co.
- Keppel Seghers
- Remondis SE & Co. KG
- FCC Servicios Medio Ambiente
- Enerkem Inc.
- Sembcorp Industries Ltd
- Green Conversion Systems LLC
- Fortum Oyj


