
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1911294
日本の電力:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年)Japan Power - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 日本の電力:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年) |
|
出版日: 2026年01月12日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 110 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
2026年の日本の電力の市場規模は397.34ギガワットと推定され、2025年の393.33ギガワットから成長が見込まれます。
2031年の予測値は417.99ギガワットで、2026年から2031年にかけてCAGR1.02%で拡大する見通しです。
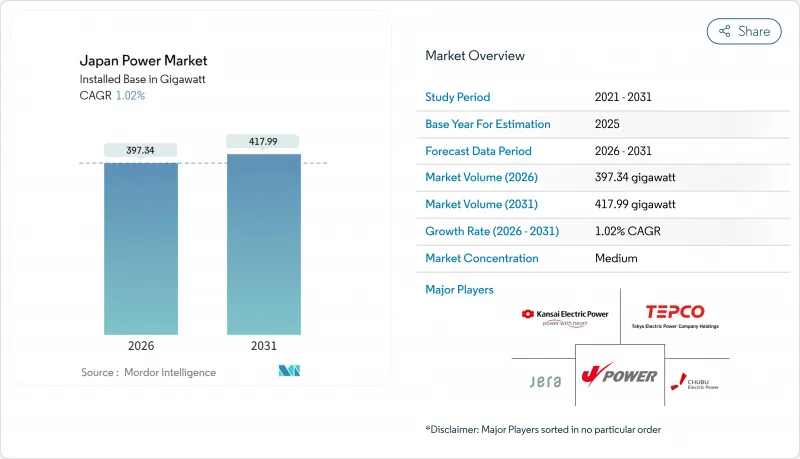
着実な成長率の背後には構造的変化が隠れています。政策により、1兆米ドル規模のグリーン・トランスフォーメーション(GX)予算が再生可能エネルギーの拡大、原子力発電所の再稼働、そして歴史的に分断されていた50Hz/60Hzの送電網を単一の商業市場に統合する高電圧直流送電(HVDC)連系網に投入されています。太陽光発電(PV)コストの低下、洋上風力入札の勢い、グリッド規模の蓄電池導入加速が、従来型液化天然ガス(LNG)プラントへの競合圧力を強めています。一方、水素・アンモニア混焼パイロット事業が燃料価格リスクのヘッジを開始しています。エネルギー貯蔵ニュース。同時に、日本の内閣は、エネルギー集約型の半導体および人工知能クラスターへの供給を確保するため、2040年までに再生可能エネルギー比率40~50%、原子力発電比率20%を目標としています。人口減少にもかかわらず消費ピークが続く都市部回廊では、企業間電力購入契約(PPA)、スマートメーターデータ分析、デマンドレスポンスプログラムが、系統の柔軟性を収益化することで、これらの変化をさらに加速させています。
日本の電力市場の動向と洞察
太陽光モジュールおよび設置コストの低下
モジュール価格は2018年の17.6円/kWhから、2024年の複数入札では8円/kWhを下回る水準まで下落し、補助金を必要としない卸売市場での競争が可能となりました。ハードウェアのデフレとソフトコストの効率化により、この技術は固定価格買取制度への依存から、入札ベースの価格形成へと移行しつつあります。このコスト曲線は、土地不足を回避する屋上設置型やアグリボルタイク(農業と太陽光発電の複合)の導入と相まって進展しています。村田製作所などのメーカーは、RE100目標達成のため仮想PPA(電力購入契約)を通じて70MWを確保し、産業回廊における需要を定着させました。蓄電池価格の低下に伴い、昼間の太陽光発電ピークが夕方の需要へと移行する傾向が強まり、ピーク対応発電所の利益率を圧迫するとともに、容量市場力学を再構築しています。
洋上風力入札パイプラインの拡大
2024年12月の第3次入札では1GWがkWh当たり3円(約30円)で落札され、従来型発電とのコスト競争力達成が確認されました。浮体式基礎技術により沿岸水深制約を回避し深海域開発が可能となり、JERA主導グループは台風耐性プラットフォームの開発を進めています。政府の送電網確保指針により海底リースと送電網整備が連動し、従来のボトルネックが解消されつつあります。欧州の開発業者は過酷な環境下でのノウハウを移転し、日本の商社はプロジェクトファイナンスを供給するハイブリッドモデルにより、国内サプライチェーンを構築しています。漁業関係者との協議の解決と港湾インフラの整備が、2030年までに10GWという目標達成の可否を決定づけるでしょう。
LNG価格変動と輸入依存度
日本のエネルギー輸入依存度は96%に達するため、LNGスポット価格の急騰により翌日電力価格が1kWhあたり1米ドルを超える事態が発生し、電力会社の利益率を圧迫しました。2014年以降の原子力発電再開によりLNG消費量は25%削減されましたが、依然として依存度は残存しています。商社は契約貨物を海外転売する動きを見せており、構造的な需要減退を示唆しています。一方、九州電力は変動リスクヘッジのため、米国輸出ターミナルへの上流投資を進めています。アンモニアや水素の混焼試験は実施中ですが、商業規模には至っていません。
セグメント分析
日本の電力市場規模における再生可能エネルギーの割合は、太陽光と洋上風力の急速な拡大により、2025年に40.05%に達し、2031年までCAGR3.72%で推移する見込みです。太陽光発電はモジュール価格の低下とマーチャントPPAの普及により、累積導入容量が91GWに達しました。洋上風力は稼働資産がわずか0.3GWですが、2030年までに10GW、2040年までに最大45GWという政府支援目標が設定され、全電源の中で最も急速な絶対的成長が見込まれます。地熱とバイオマスは、許可制の制約と輸入原料コストによりニッチな分野にとどまっています。
火力発電は2025年に日本の電力市場シェア51.80%を維持しましたが、炭素価格の高騰とアンモニア混焼義務化が長期的な経済性に圧力をかけています。JERAが4.1GWの碧南石炭火力発電所で実施したパイロット事業では20%のアンモニア混焼に成功し、政府は2030年までに全発電所での導入を目指しており、年間300万トンの輸入が必要となります。原子力発電は2024年に826MWの再稼働を実現し、地域社会の理解が深まれば20%の発電シェア目標に向けて増加が見込まれます。水力発電は約50GWで横ばい状態が続いており、新規ダム建設地が環境規制に直面しているためです。これらのシェア変動は、日本の電力市場において投資が脱炭素化設備へ傾いていることを示しています。
日本の電力市場レポートは、電源別(火力、原子力、再生可能エネルギー)および最終ユーザー別(電力会社、商業・産業、住宅)に分類されています。市場規模と予測は、設備容量(GW)単位で提供されます。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- アナリストによる3ヶ月間のサポート
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 太陽光モジュールおよび設置コストの低下
- 洋上風力発電入札パイプラインの拡充
- GX政策下における原子炉再稼働
- グリッド規模の蓄電池コストの低下
- 重工業からの企業間電力購入契約(PPA)需要
- スマートメーター導入とデマンドレスポンスの潜在的可能性
- 市場抑制要因
- LNG価格の変動性および輸入依存度
- ユーティリティソーラー向け陸上用地の不足
- 老朽化した送電設備と許可手続きの遅延
- 新規高圧送電線に対する地域住民の反対
- サプライチェーン分析
- 規制情勢
- テクノロジーの展望
- ポーターのファイブフォース
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
- PESTEL分析
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- 電源別
- 火力(石炭、天然ガス、石油・ガス、軽油)
- 原子力
- 再生可能エネルギー(太陽光、風力、水力、地熱、バイオマス・廃棄物、潮力)
- エンドユーザー別
- ユーティリティ
- 商業・産業用
- 住宅用
- 送配電・電圧レベル別(定性分析のみ)
- 高電圧送電(230kV以上)
- 二次送電(69~161kV)
- 中電圧送電(13.2~34.5kV)
- 低電圧送電(1kV以下)
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 戦略的取り組み(M&A、パートナーシップ、PPA)
- 市場シェア分析(主要企業の市場順位・シェア)
- 企業プロファイル
- Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings(TEPCO)
- Kansai Electric Power Company
- Chubu Electric Power
- Hokkaido Electric Power
- Tohoku Electric Power
- Hokuriku Electric Power
- Chugoku Electric Power
- Shikoku Electric Power
- Kyushu Electric Power
- Okinawa Electric Power
- JERA Co., Inc.
- Electric Power Development Co.(J-POWER)
- Japan Renewable Energy Corporation
- Hitachi Energy
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions
- Sumitomo Corporation(Renewables)
- Marubeni Corporation(Power)
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries(Energy)
- Orsted Japan K.K.


