|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1522941
電気自動車向けLFP・NMC電池技術の技術経済比較:性能、バリューチェーン分析、成長機会、2024~2030年Techno-economic Comparison of LFP and NMC Battery Technologies for Electric Vehicle Applications: Performance, Value Chain Analysis, and Growth Opportunities, 2024-2030 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| 電気自動車向けLFP・NMC電池技術の技術経済比較:性能、バリューチェーン分析、成長機会、2024~2030年 |
|
出版日: 2024年07月04日
発行: Frost & Sullivan
ページ情報: 英文 42 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
LFP・NMC電池は、両ケミストリーが示す性能の違いにより、明確な価値提案を提供します。
次世代の電気自動車(EV)を開発するためには、電池技術の急速な進歩が不可欠です。現在、リチウムイオン(Li-ion)電池のニッケルマンガンコバルト(NMC)とリチウム鉄・リン酸塩(LFP)がEV電池パックの市場をリードしており、LFP電池はここ数年で普及が進んでいます。これは、ニッケルやコバルトといったNMC電池に使用される重要な材料の使用や、これらの金属(特にコバルト)の確保に関連するサプライチェーンの不確実性や採掘の課題によって悪化しています。
LFP・NMC電池は、正極にリチウムイオンを閉じ込めるために、異なるインターカレーションメカニズムを採用しています。NMC電池はこれらのイオンを2次元層間化合物内に貯蔵するが、LFP電池は正極材料格子内の3次元構造内にイオンを貯蔵します。この重要な結果として、LFP電池の安全性が向上し、サイクル寿命が長くなります。さらに、LFP電池は製造時に希少材料の使用を避けることで、NMC電池よりも低価格を実現しています。
当レポートでは以下のトピックを取り上げます:技術情勢では、LFP・NMC電池の主な相違点と、その製造に使用される様々な構成材料を取り上げています。
LFP・NMC電池の比較分析では、エネルギー密度、コスト、サイクル寿命など、さまざまな性能パラメータを取り上げます。また、両電池のアプリケーションマッピングも掲載しています。
資金調達分析では、LFP・NMC電池に関する利害関係者の主な資金調達事例を取り上げます。
特許情勢と成長機会では、両電池の主要成長分野を分析しています。
目次
戦略的課題
- なぜ成長が難しくなっているのか?
- The Strategic Imperative 8(TM)
- 電気自動車産業向けLFP・NMC電池における戦略的重要課題上位3のインパクト
- 成長機会がGrowth Pipeline Engine(TM)を促進
- 調査手法
成長機会分析
- 分析範囲
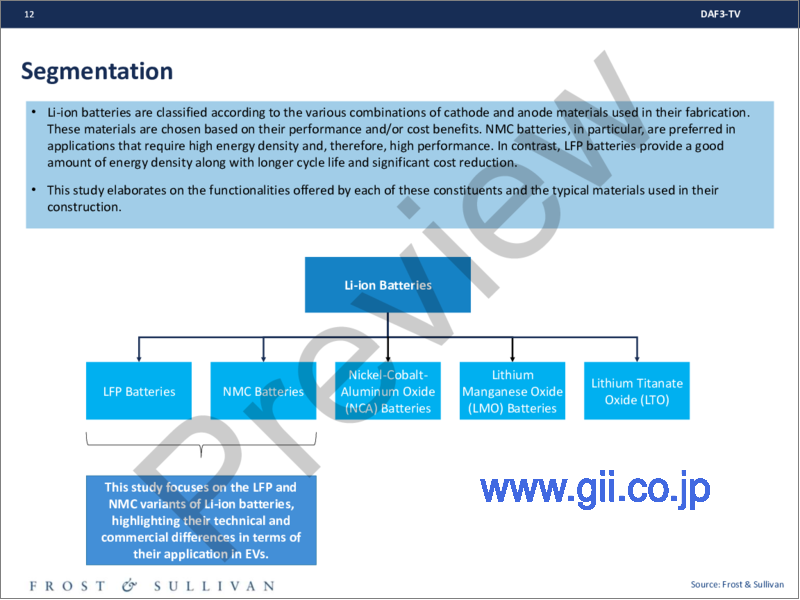
- セグメンテーション
成長要因
- 成長促進要因
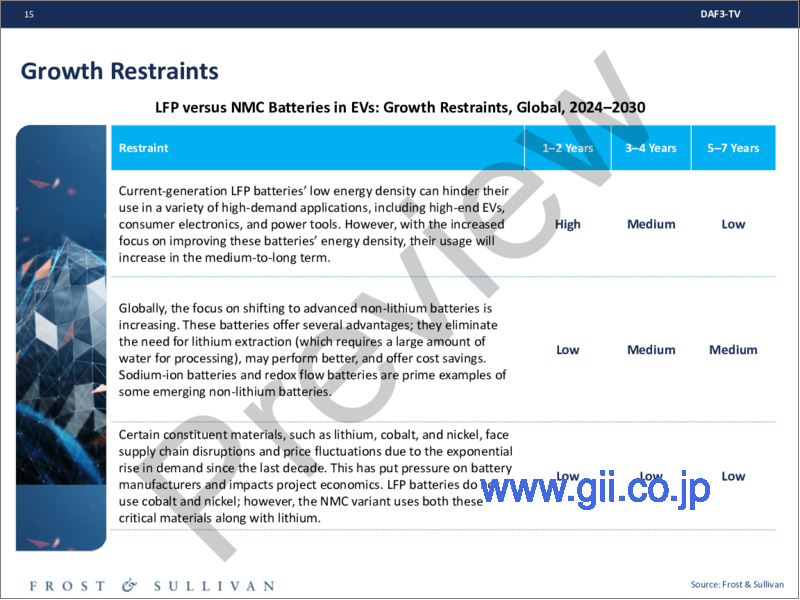
- 成長抑制要因
技術スナップショット
- EV向け電池パックではNMCとLFPが人気
- EVは世界中で指数関数的な成長軌道にある
- LFP・NMC電池の比較:正極材料の違いが電池性能に影響
- NMC正極とLFP正極は相反するインターカレーションを示す
- LFPとNMC電池の比較:性能パラメータ
- LFP電池は近年採用が急増している
イノベーションエコシステム
- Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Ltd (CATL)、中国
- LG Chemical Ltd.、韓国
- その他のLFP・NMC電池企業
- 特許事情
- LFP・NMC電池メーカー:資金調達情報
成長要因
- 成長機会1:コスト効率に優れたEVの大衆市場投入の促進
- 成長機会2:高い需要が見込まれる用途の電動化への道を開くNMC電池の強化
- 成長機会3:LFP電池のエネルギー密度を向上させ、総合的に優れたソリューションとして浮上させる
付録
- 技術成熟度(TRL):解説
次のステップ
- 成長機会の利点と影響
- 次のステップ
- 次のステップへ
- 免責事項
LFP and NMC batteries provide distinct value propositions due to the performance differences exhibited by both chemistries
Rapid advancements in battery technology are imperative to develop the next generation of electric vehicles (EVs). Currently, the nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) and lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) variants of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries lead the market for EV battery packs, with LFP batteries witnessing increased penetration over the past few years. This is exacerbated by the use of critical materials, such as nickel and cobalt, used in NMC variants, as well as supply chain uncertainties and mining challenges associated with securing these metals, especially cobalt, which is concentrated in a few African countries and is an important human rights issue.
LFP and NMC batteries follow a distinct intercalation mechanism to trap lithium ions in their cathodes. NMC batteries store these ions within 2D interlayers, while LFP batteries store ions within 3D structures in the cathode material lattice. An important result of this is enhanced safety and a longer cycle life for LFP batteries. In addition, LFP batteries, by avoiding the use of rare materials during fabrication, come at a lower price point than the NMC variant, which is a critical parameter for their accelerated adoption in key global markets.
This study covers the following topics: The technology landscape covers the major differences between LFP and MNC batteries as well as the various constituent materials used in their fabrication.
The comparative analysis of LFP and NMC batteries covers various performance parameters, including energy density, cost, and cycle life. The section also includes the application mapping for both battery variants.
The funding analysis covers stakeholders' major funding instances for LFP and NMC batteries.
The patent landscape and growth opportunities analyze the key growth areas for both battery variants.
Table of Contents
Strategic Imperatives
- Why Is It Increasingly Difficult to Grow?
- The Strategic Imperative 8™
- The Impact of the Top 3 Strategic Imperatives on LFP and NMC Batteries for the EV Industry
- Growth Opportunities Fuel the Growth Pipeline Engine™
- Research Methodology
Growth Opportunity Analysis
- Scope of Analysis
- Segmentation
Growth Generator
- Growth Drivers
- Growth Restraints
Technology Snapshot
- The NMC and LFP Variants are Popular in EV Battery Packs
- EVs are on an Exponential Growth Trajectory Across the World
- LFP Versus NMC Batteries: Distinct Constituent Cathode Materials Influence Battery Performance
- NMC and LFP Cathodes Exhibit Contrary Intercalation
- LFP Versus NMC Batteries: Performance Parameters
- LFP Batteries Have Seen an Uptick in Adoption in Recent Years
Innovation Ecosystem
- Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Ltd (CATL), China
- LG Chemical Ltd., South Korea
- Other Prominent LFP and NMC Battery Companies
- Patent Landscape
- LFP and NMC Battery Manufacturers: Funding Information
Growth Generator
- Growth Opportunity 1: Facilitate the Launch of Cost-efficient EVs for Mass-market Adoption
- Growth Opportunity 2: Enhance NMC Batteries to Pave the Way for the Electrification of Applications Witnessing High Demand
- Growth Opportunity 3: Improve LFP Batteries' Energy Density to Help Them Emerge as a Comprehensively Superior Solution
Appendix
- Technology Readiness Levels (TRL): Explanation
Next Steps
- Benefits and Impacts of Growth Opportunities
- Next Steps
- Take the Next Step
- Legal Disclaimer