|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1565350
RIS(Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface)の世界市場(2025年~2035年)The Global Market for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) 2025-2035 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| RIS(Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface)の世界市場(2025年~2035年) |
|
出版日: 2024年11月05日
発行: Future Markets, Inc.
ページ情報: 英文 172 Pages, 95 Tables, 46 Figures
納期: 即納可能
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
RISは、IRS(Intelligent Reflecting Surface)またはソフトウェア制御メタサーフェスとしても知られ、電磁波を操作するために電子的に制御できる多数の小さな受動素子で構成された人工構造です。これらの表面は、受信信号を希望する方向に反射、屈折、吸収、集束させることができ、無線伝搬環境を効果的に形成することができます。近年のメタマテリアルの進歩により、RISは将来の6G無線通信の有望な技術として浮上しています。高アレイゲイン、低コスト、低消費電力という利点を持つRISは、信号のカバー範囲を大幅に拡大し、システムの処理能力を向上させ、エネルギー効率を高めると予測されます。
RIS技術は、電磁波の操作において画期的な能力を提供し、無線ネットワークにおけるカバー範囲、処理能力、エネルギー効率の向上を可能にします。5Gネットワークが拡大し、6Gの開発が加速するなか、RISは無線通信における現在の限界を克服する上で重要な役割を果たすと予測されます。主な用途は、通信、スマートシティ、産業用IoT、医療、自動車、航空宇宙、コンシューマーエレクトロニクスなど多岐にわたります。市場は、高速・低遅延通信への需要の高まりや、IoTの採用の拡大、エネルギー効率の高い無線ソリューションへのニーズによって牽引されています。しかし、高い初期費用や、大規模展開における技術的複雑性、標準化の問題などが課題となっています。
当レポートでは、世界のRIS(Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface)市場について調査分析し、市場規模と成長予測、技術の詳細、応用分野、競合情勢、将来の見通しなどの情報を提供しています。
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリー
- RIS(Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface)の概要
- 主な市場の促進要因と課題
- 技術と市場動向
- RISの鍵となるメタマテリアル
- 市場規模と成長予測
- 競合情勢の概要
- 将来の見通しと機会
第2章 イントロダクション
- 技術の概要
- システムアーキテクチャ
- 現代の無線通信における重要性
- 従来の無線技術に対する利点
- 現在の制限と課題
- その他のスマート電磁(EM)デバイスとの比較
第3章 RIS技術
- メタサーフェス
- 液晶ベースのRIS
- MEMSベースのRIS
- バラクタダイオードベースのRIS
- PINダイオードベースのRIS
- その他の材料
- RIS技術の比較
第4章 無線通信システムにおけるリスク
- 5G
- 6G以降
- MIMOシステムとRIS
- ビームフォーミングとRIS
- 無線ネットワークのエネルギー効率
第5章 市場と用途
- 通信
- スマートシティ、IoT
- 産業用IoT、インダストリー4.0
- 医療用途
- 自動車、輸送
- 航空宇宙、防衛
- スマートホーム、コンシューマーエレクトロニクス
第6章 市場の分析と動向
- 世界の市場規模と成長予測
- 市場セグメンテーション:技術別
- 市場セグメンテーション:市場別
- 市場セグメンテーション:地域別
- 主な市場促進要因
- 高速・低遅延通信への需要の増加
- IoTとスマートデバイスの採用の増加
- 5Gと6G技術の進歩
- エネルギー効率の高い無線ソリューションへのニーズ
- その他の促進要因
- 市場の課題と障壁
- 高い初期実装費用
- 大規模展開における技術的な複雑性
- 標準化と相互運用性の問題
- 規制とコンプライアンスの課題
- その他の課題と障壁
- 新興市場の機会
- エッジコンピューティングとの統合
- 衛星、宇宙通信向けRIS
- RIS向け先進材料
- AIと機械学習の統合
- 量子RISコンセプト
- 認知RIS
- 自己構成、自己修復RIS
- 安全な通信に向けたブロックチェーンとの統合
- 将来の見通し
- 6G以降のRIS
- ホログラフィック通信
- 宇宙ベースのRISネットワーク
- RIS制御におけるAIと機械学習
- テラヘルツ、光無線通信向けRIS
- 大規模RIS展開の生物学的、健康的影響
第7章 標準化と規制環境
- RISに関連する現在の標準
- 周波数の割り当てと管理
第8章 環境と持続可能性に関する考慮
- RIS対応ネットワークのエネルギー効率
- RIS技術のライフサイクルアセスメント
- 電子廃棄物の管理とリサイクル
- 持続可能な生産方式
- スマートグリッドとエネルギー管理におけるRISの役割
- 大規模RIS展開の環境に対する影響
第9章 課題と限界
- RIS実装における技術的課題
- 生産規模の拡大とコスト削減
- 既存のインフラとの統合
- 複雑な環境でのパフォーマンス
- セキュリティとプライバシーに関する懸念
第10章 企業プロファイル(企業20社のプロファイル)
第11章 付録
第12章 参考文献
List of Tables
- Table 1. Key Market Drivers and Challenges in RIS
- Table 2. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) Technology and Market Trends
- Table 3. Future Outlook and Opportunities in RIS
- Table 4. Overview of different RIS types
- Table 5. RIS operation phases
- Table 6. RIS Hardware
- Table 7. Comparison of different RIS techniques
- Table 8. RIS functionalities
- Table 9. Challenges for fully functionalized RIS environments
- Table 10. Comparison of Reflection Coefficient Across Different RIS Technologies
- Table 11. Benchmarking of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) types
- Table 12. Comparison of Key Performance Metrics for Different RIS Technologies
- Table 13.Comparison of Phase Shift Range Across Different RIS Technologies
- Table 14. Bandwidth and Frequency Ranges for Various RIS Technologies
- Table 15. Power Consumption Comparison of RIS Technologies
- Table 16. Energy Efficiency Comparison: RIS-enabled vs. Traditional Wireless Networks
- Table 17. Reconfiguration Speed Comparison Across Different RIS Types
- Table 18. Integration Considerations
- Table 19. Advantages Over Traditional Wireless Technologies
- Table 20. Current Limitations and Challenges
- Table 21. RIS vs Other Smart Electromagnetic (EM) Devices
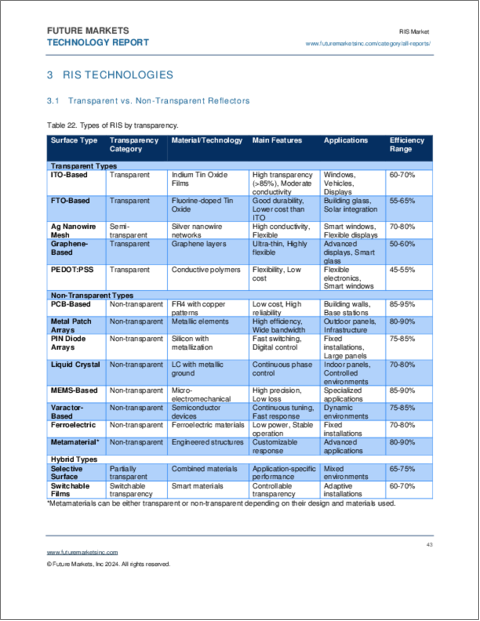
- Table 22.Types of Metasurfaces
- Table 23. Metasurface fabrication techniques
- Table 24. Distinguishing between conductive and optical metamaterials
- Table 25. Advantages and Limitations of Liquid Crystal-based RIS
- Table 26. MEMS-based RIS Technology Performance Metrics
- Table 27. Comparison of RIS Performance in Different Environmental Conditions
- Table 28. Cost Analysis
- Table 29. Market drivers for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces in 5G
- Table 30. Coverage Enhancement Metrics
- Table 31. Energy Efficiency Metrics
- Table 32. Cost Optimization Metrics
- Table 33. Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) - applications in 5G
- Table 34. RIS operation phases
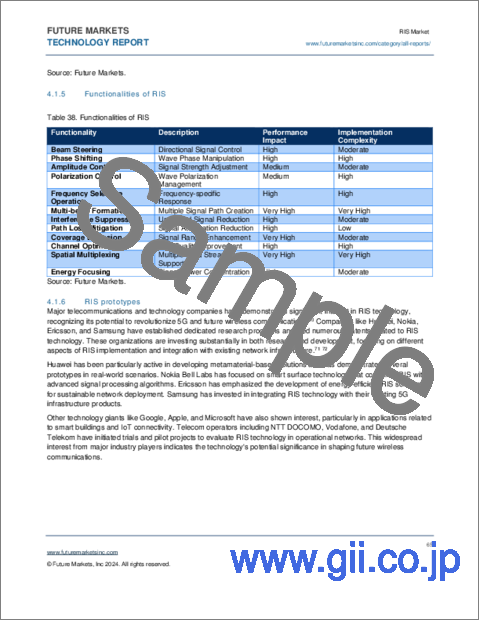
- Table 35. Functionalities of RIS
- Table 36. RIS 5G Prototypes
- Table 37. 5G Network Requirements
- Table 38. RIS applications in wireless networks
- Table 39. Network integration strategies for RIS technology
- Table 40. Integration with Existing Infrastructure
- Table 41. Performance Metrics in 5G Network Integration
- Table 42. Path Loss Models
- Table 43. Channel Estimation Techniques
- Table 44. Multi-user Scenarios
- Table 45. Precoding Techniques
- Table 46. Integration Challenges and Solutions
- Table 47. Coverage Extension Methods
- Table 48. Indoor Coverage Solutions
- Table 49. Capacity Enhancement
- Table 50. Energy Efficiency
- Table 51. Power Consumption Analysis
- Table 52. High-Frequency Challenges
- Table 53. RIS Solutions for mmWave
- Table 54. Performance Analysis
- Table 55. Implementation Challenges
- Table 56. Technical Challenges for RIS
- Table 57. Hardware Limitations for RIS in 5G
- Table 58. Standardization Challenges
- Table 59. RIS Materials Applications
- Table 60. RIS costs in volume
- Table 61. RIS formulations
- Table 62. Adaptive Beamforming Techniques
- Table 63. Global market forecast for RIS Adoption in 5G/6G Networks (2025-2035), Millions USD
- Table 64. Urban Environment Monitoring Applications
- Table 65. Smart Transportation Applications
- Table 66. Energy Management Applications
- Table 67. Global market forecast for RIS Adoption in Smart Cities and IoT (2025-2035), Millions USD
- Table 68.Industrial IoT Applications
- Table 69. Process Control Applications
- Table 70. Global market forecast for RIS Adoption in Industrial IoT and Industry 4.0 Applications (2025-2035), Millions USD
- Table 71. Wireless Body Area Networks Applications
- Table 72. Remote Patient Monitoring Applications
- Table 73. Global Market Forecast for RIS Adoption in Healthcare/Medical (2025-2035), Millions USD
- Table 74.Automotive and Transportation Applications
- Table 75. Global market forecast for RIS Adoption in Automotive and Transportation (2025-2035), Millions USD
- Table 76. Augmented and Virtual Reality Applications
- Table 77. Global RIS Market Size, by Technology Type, 2025-2035 (USD Million)
- Table 78. Global RIS Market Size, by market, 2025-2035 (USD Million)
- Table 79. Global RIS Market Size, by Region, 2025-2035 (USD Million)
- Table 80. Applications in Satellite and Space Communications
- Table 81.RIS Material Types and Applications
- Table 82. Quantum RIS Concepts
- Table 83. Biological and Health Implications
- Table 84. Safety and Electromagnetic Compatibility Regulations
- Table 85. Data Privacy and Security Considerations
- Table 86. Environmental Impact Comparison: RIS vs. Traditional Wireless Infrastructure
- Table 87. Energy Efficiency Metrics
- Table 88. Life Cycle Assessment of RIS Technologies
- Table 89. E-waste Management and Recycling
- Table 90. Sustainable Manufacturing for RIS Technology
- Table 91. Smart Grid Integration
- Table 92. Environmental Impact of Large-Scale RIS Deployment
- Table 93. Technical Challenges in RIS Implementation
- Table 94. Glossary of Terms
- Table 95. List of Abbreviations
List of Figures
- Figure 1. A typical use case of an RIS, where it receives a signal from the transmitter and re-radiates it focused on the receiver
- Figure 2. Basic RIS application: coverage extension in a cellular network
- Figure 3. Comparison of different wireless systems
- Figure 4. Schematic Diagram of a Typical RIS Structure
- Figure 5. Intelligent reflection and refraction
- Figure 6. Hardware architecture of RIS
- Figure 7. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of several metalens antenna forms
- Figure 8. Transparent and flexible metamaterial film developed by Sekishi Chemical
- Figure 9. The structure of a three-layered PIN diode based 2-bit RIS panel
- Figure 10. NTT DOCOMO transparent RIS
- Figure 11. Meta Nanoweb-R
- Figure 12. RIS mmWave communication
- Figure 13. RIS in 5G Market and technology roadmap
- Figure 14. Comparison between 5G and 6G wireless systems in terms of key-performance indicators
- Figure 15. RIS-assisted wireless communication
- Figure 16. RIS-enabled, self-sufficient ultra-massive 6G UM-MIMO base station design
- Figure 17. Active and passive beamforming in RIS-assisted cell-free massive MIMO
- Figure 18. Lumotive advanced beam steering concept
- Figure 19. Deployment of RIS in a building for communication
- Figure 20. RIS-assisted indoor enhancement of outdoor macro station coverage
- Figure 21. Global market forecast for RIS Adoption in 5G/6G Networks (2025-2035), Millions USD
- Figure 22. Global market forecast for RIS Adoption in Smart Cities and IoT (2025-2035), Millions USD
- Figure 23. RIS-aided IoT communication
- Figure 24. Global market forecast for RIS Adoption in IoT Applications (2025-2035), Millions USD
- Figure 25. Global Market Forecast for RIS Adoption in Healthcare/Medical (2025-2035), Millions USD
- Figure 26. RIS-assisted V2V communication system
- Figure 27. RIS vehicle network communication
- Figure 28. Global market forecast for RIS Adoption in Automotive and Transportation (2025-2035), Millions USD
- Figure 29. PHY-Layer security issue scheme of RIS
- Figure 30. RIS UAV communication
- Figure 31. RIS VLC in a smart office room
- Figure 32. Global RIS Market Size, by Technology Type, 2025-2035 (USD Million)
- Figure 33. Global RIS Market Size, by Application, 2025-2035 (USD Million)
- Figure 34. Global RIS Market Size, by Region, 2025-2035 (USD Million)
- Figure 35. RIS-enabled wireless edge computing
- Figure 36. Edgehog Advanced Technologies Omnidirectional anti-reflective coating
- Figure 37. FM/R technology
- Figure 38. Metablade antenna
- Figure 39. MTenna flat panel antenna
- Figure 40. Kymeta u8 antenna installed on a vehicle
- Figure 41. LIDAR system for autonomous vehicles
- Figure 42. Light-control metasurface beam-steering chips
- Figure 43. Metaboard wireless charger
- Figure 44. Metalenz metasurface-based optics on a chip
- Figure 45. NTT DOCOMO transparent RIS
- Figure 46. ZTE dynamic reconfigurable intelligent surface 2.0 product
RIS, also known as Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS) or software-controlled metasurfaces, are artificial structures composed of a large number of small, passive elements that can be electronically controlled to manipulate electromagnetic waves. These surfaces can reflect, refract, absorb, or focus incoming signals in desired directions, effectively shaping the wireless propagation environment. Due to recent advances in metamaterials, Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) has emerged as a promising technology for future 6G wireless communications. Benefiting from its high array gain, low cost, and low power consumption, RISs are expected to greatly enlarge signal coverage, improve system capacity, and increase energy efficiency.
RIS technology offers revolutionary capabilities in manipulating electromagnetic waves, enabling enhanced coverage, capacity, and energy efficiency in wireless networks. As 5G networks expand and 6G development accelerates, RIS is expected to play a crucial role in overcoming current limitations in wireless communications. Key applications span telecommunications, smart cities, Industrial IoT, healthcare, automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. The market is driven by increasing demand for high-speed, low-latency communications, growth in IoT adoption, and the need for energy-efficient wireless solutions. However, challenges include high initial costs, technical complexities in large-scale deployment, and standardization issues.
Report contents include:
- Market Size and Growth Projections: Detailed forecasts of the RIS market size and growth rate from 2025 to 2035, segmented by technology type, application, and geography.
- Technology Deep Dive: Comprehensive analysis of various RIS technologies, including metasurfaces, liquid crystal-based RIS, MEMS-based RIS, and emerging approaches.
- Application Landscape:Exploration of key application areas such as 5G/6G networks, IoT, smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and aerospace communications.
- Competitive Landscape: Profiles of leading companies and emerging players in the RIS space, including their technologies, strategies, and market positioning. Companies profiled include Alcan Systems, Alphacore Inc., Edgehog Advanced Technologies, Evolv Technologies Inc., Fractal Antenna Systems Inc., Greenerwave, Huawei, Kymeta Corporation, Leadoptik Inc., Lumotive, META, Metaboards Limited, Metawave Corporation, Nokia, NTT DOCOMO, Pivotal Commware Inc., SK Telecom, Teraview Limited, and ZTE Corporation.
- Future Outlook: Assessment of emerging trends, potential disruptions, and long-term prospects for RIS technology.
- Developments in RIS technology, including:
- Integration with AI and machine learning for adaptive control
- Quantum RIS concepts pushing the boundaries of performance
- Self-configuring and self-healing RIS for enhanced reliability
- Holographic radio and terahertz communications enabled by RIS
- Market Drivers and Opportunities
- Challenges and Market Dynamics
- Technology Benchmarking and Performance Analysis
- Comprehensive comparison of different RIS technologies.
- Integration with Wireless Communication Systems.
- Environmental and Sustainability Considerations.
- Standardization and Regulatory Landscape.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- 1.1. Overview of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS)
- 1.2. Key Market Drivers and Challenges
- 1.3. Technology and Market Trends
- 1.4. Metamaterials key to RIS
- 1.5. Market Size and Growth Projections
- 1.6. Competitive Landscape Overview
- 1.7. Future Outlook and Opportunities
2. INTRODUCTION
- 2.1. Technology overview
- 2.1.1. Key features and functionality
- 2.1.2. Frequencies
- 2.1.3. Physics of Electromagnetic Wave Manipulation
- 2.1.3.1. Reflection
- 2.1.3.2. Refraction
- 2.1.3.3. Diffraction
- 2.1.3.4. Absorption
- 2.1.4. RIS Operating Principles
- 2.1.4.1. Passive RIS
- 2.1.4.2. Active RIS
- 2.1.4.3. Hybrid RIS
- 2.1.5. Key Performance Parameters
- 2.1.5.1. Reflection Coefficient
- 2.1.5.2. Phase Shift Range
- 2.1.5.3. Bandwidth
- 2.1.5.4. Power Consumption
- 2.1.5.5. Reconfiguration Speed
- 2.1.6. Design Considerations for RIS
- 2.1.6.1. Surface Element Design
- 2.1.6.2. Array Configuration
- 2.1.6.3. Control Mechanisms
- 2.1.6.4. Integration with Existing Infrastructure
- 2.2. System Architecture
- 2.3. Importance in Modern Wireless Communications
- 2.4. Advantages Over Traditional Wireless Technologies
- 2.5. Current Limitations and Challenges
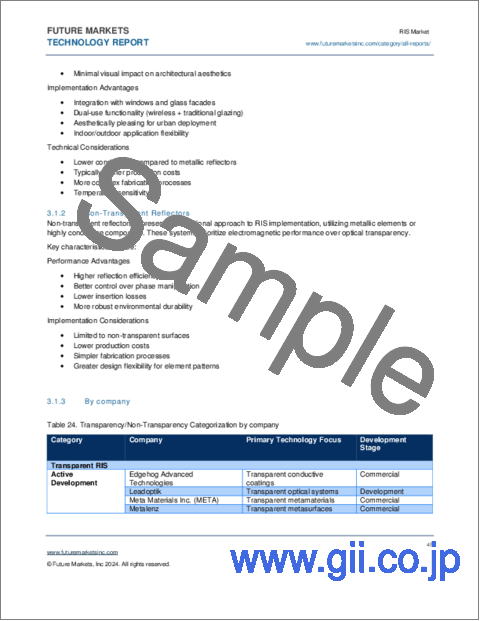
- 2.6. Comparison with Other Smart Electromagnetic (EM) Devices
3. RIS TECHNOLOGIES
- 3.1. Metasurfaces
- 3.1.1. Principles of Metasurfaces
- 3.1.2. Types of Metasurfaces
- 3.1.2.1. Meta-Lens
- 3.1.2.2. Metasurface holograms
- 3.1.2.3. Flexible metasurfaces
- 3.1.3. Fabrication Techniques
- 3.1.4. Characteristics
- 3.2. Liquid Crystal-based RIS
- 3.2.1. Operating Principles
- 3.2.2. Advantages and Limitations
- 3.3. MEMS-based RIS
- 3.3.1. MEMS Technology Overview
- 3.3.2. Design and Fabrication
- 3.3.3. Performance Metrics
- 3.4. Varactor Diode-based RIS
- 3.4.1. Overview
- 3.5. PIN Diode-based RIS
- 3.5.1. Overview
- 3.6. Other Materials
- 3.6.1. Ferroelectric materials
- 3.6.2. Phase Change Materials
- 3.6.3. Graphene
- 3.7. Comparison of RIS Technologies
- 3.7.1. Performance Metrics
- 3.7.2. Cost Analysis
- 3.7.3. Scalability and Manufacturing Considerations
4. RIS IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- 4.1. 5G
- 4.1.1. Overview
- 4.1.2. Market drivers
- 4.1.2.1. Coverage Enhancement Needs
- 4.1.2.2. Energy Efficiency Requirements
- 4.1.2.3. Capacity Improvement Demands
- 4.1.2.4. Cost Optimization Goals
- 4.1.3. Applications
- 4.1.4. RIS operation phases
- 4.1.5. Functionalities of RIS
- 4.1.6. RIS prototypes
- 4.1.7. 5G Network Requirements
- 4.1.8. RIS Role in 5G Infrastructure
- 4.1.9. Integration with 5G Networks
- 4.1.9.1. Network Integration Strategies
- 4.1.9.2. Channel Modeling
- 4.1.9.3. Signal Processing
- 4.1.9.4. Integration Challenges and Solutions
- 4.1.10. Performance Enhancement
- 4.1.10.1. Coverage Optimization
- 4.1.10.2. Capacity Enhancement
- 4.1.10.3. Energy Efficiency
- 4.1.11. Advanced Applications
- 4.1.11.1. mmWave Communications
- 4.1.11.2. Massive MIMO Systems
- 4.1.11.3. IoT Applications
- 4.1.12. Implementation Challenges
- 4.1.12.1. Technical Challenges
- 4.1.12.2. Standardization
- 4.1.13. Future Directions
- 4.1.13.1. Hardware Advancements
- 4.1.13.2. Control Systems
- 4.1.13.3. Integration Capabilities
- 4.1.13.4. Performance Enhancement
- 4.1.14. Market and technology roadmap
- 4.2. 6G and Beyond
- 4.2.1. 6G Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces and metamaterials opportunities
- 4.2.2. RIS materials applications
- 4.2.3. RIS costs in volume
- 4.2.4. RIS formulations
- 4.2.5. RIS in Terahertz Communications
- 4.2.6. Holographic Radio
- 4.2.7. Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces for Satellite Communications
- 4.3. MIMO Systems and RIS
- 4.3.1. RIS-assisted MIMO
- 4.3.2. RIS-based Massive MIMO
- 4.3.3. Performance Enhancements and Challenges
- 4.4. Beamforming and RIS
- 4.4.1. Passive Beamforming
- 4.4.2. Hybrid Beamforming with RIS
- 4.4.3. Adaptive Beamforming Techniques
- 4.5. Energy Efficiency in Wireless Networks
- 4.5.1. RIS for Green Communications
- 4.5.2. Energy Harvesting with RIS
5. MARKET AND APPLICATIONS
- 5.1. Telecommunications
- 5.1.1. Coverage Enhancement
- 5.1.2. Capacity Improvement
- 5.1.3. Interference Mitigation
- 5.1.4. Market forecast
- 5.2. Smart Cities and IoT
- 5.2.1. Urban Environment Monitoring
- 5.2.2. Smart Transportation Systems
- 5.2.3. Energy Management in Buildings
- 5.2.4. Market forecast
- 5.3. Industrial IoT and Industry 4.0
- 5.3.1. Factory Automation
- 5.3.2. Warehouse Management
- 5.3.3. Process Control and Monitoring
- 5.3.4. Market forecast
- 5.4. Healthcare and Medical Applications
- 5.4.1. Wireless Body Area Networks
- 5.4.2. Remote Patient Monitoring
- 5.4.3. Medical Imaging Enhancement
- 5.4.4. Market forecast
- 5.5. Automotive and Transportation
- 5.5.1. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communications
- 5.5.2. Autonomous Vehicles
- 5.5.3. Intelligent Transportation Systems
- 5.5.4. Market forecast (IoT)
- 5.6. Aerospace and Defense
- 5.6.1. Radar Systems Enhancement
- 5.6.2. Secure Communications
- 5.6.3. Stealth Technology
- 5.6.4. UAVs
- 5.7. Smart Home and Consumer Electronics
- 5.7.1. In-home Wireless Coverage Optimization
- 5.7.2. Device-to-Device Communications
- 5.7.3. Augmented and Virtual Reality Applications
6. MARKET ANALYSIS AND TRENDS
- 6.1. Global Market Size and Growth Projections
- 6.1.1. Market Segmentation by Technology
- 6.1.2. Market Segmentation by Market
- 6.1.3. Market Segmentation by Geography
- 6.2. Key Market Drivers
- 6.2.1. Increasing Demand for High-Speed, Low-Latency Communications
- 6.2.2. Growth in IoT and Smart Device Adoption
- 6.2.3. Advancements in 5G and 6G Technologies
- 6.2.4. Need for Energy-Efficient Wireless Solutions
- 6.2.5. Other drivers
- 6.3. Market Challenges and Barriers
- 6.3.1. High Initial Implementation Costs
- 6.3.2. Technical Complexities in Large-Scale Deployment
- 6.3.3. Standardization and Interoperability Issues
- 6.3.4. Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
- 6.3.5. Other challenges and barriers
- 6.4. Emerging Market Opportunities
- 6.4.1. Integration with Edge Computing
- 6.4.2. RIS for Satellite and Space Communications
- 6.4.3. Advanced Materials for RIS
- 6.4.4. AI and Machine Learning Integration
- 6.4.5. Quantum RIS Concepts
- 6.4.6. Cognitive RIS
- 6.4.7. Self-configuring and Self-healing RIS
- 6.4.8. Integration with Blockchain for Secure Communications
- 6.5. Future Outlook
- 6.5.1. RIS in 6G and Beyond
- 6.5.2. Holographic Communications
- 6.5.3. Space-based RIS Networks
- 6.5.4. AI and Machine Learning in RIS Control
- 6.5.5. RIS for Terahertz and Optical Wireless Communications
- 6.5.6. Biological and Health Implications of Large-Scale RIS Deployment
7. STANDARDIZATION AND REGULATORY ENVIRONMENT
- 7.1. Current Standards Related to RIS
- 7.1.1. IEEE Standards
- 7.1.2. 3GPP Specifications
- 7.1.3. ETSI Standards
- 7.2. Spectrum Allocation and Management
- 7.2.1. Safety and Electromagnetic Compatibility Regulations
- 7.2.2. Data Privacy and Security Considerations
8. ENVIRONMENTAL AND SUSTAINABILITY CONSIDERATIONS
- 8.1. Energy Efficiency of RIS-enabled Networks
- 8.2. Life Cycle Assessment of RIS Technologies
- 8.3. E-waste Management and Recycling
- 8.4. Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
- 8.5. RIS Role in Smart Grid and Energy Management
- 8.6. Environmental Impact of Large-Scale RIS Deployment
9. CHALLENGES AND LIMITATIONS
- 9.1. Technical Challenges in RIS Implementation
- 9.2. Scaling Up Production and Cost Reduction
- 9.3. Integration with Existing Infrastructure
- 9.4. Performance in Complex Environments
- 9.5. Security and Privacy Concerns
10. COMPANY PROFILES (20 company profiles)
11. APPENDICES
- 11.1. Glossary of Terms
- 11.2. List of Abbreviations
- 11.3. Research Methodology