|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1486556
CTP/CTB/CTC統合型バッテリーの世界市場(2024年~2035年)Cell to Pack (CTP), Cell to Body (CTB) and Cell to Chassis (CTC) Integrated Battery Market 2024-2035 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| CTP/CTB/CTC統合型バッテリーの世界市場(2024年~2035年) |
|
出版日: 2024年07月03日
発行: Future Markets, Inc.
ページ情報: 英文 205 Pages, 61 Tables, 58 Figures
納期: 即納可能
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
EVの売上の伸びがバッテリー需要を促進しており、EV用バッテリーの市場規模は2023年に750GWhを超え、前年比で40%の増加となりました。この成長の約95%は電気自動車が占めています。EV市場は急拡大しており、長い走行距離を確保できる信頼性と安全性の高いバッテリーの開発が大きな課題の1つとなっています。電気自動車に使用されている従来のリチウムイオンバッテリーは、エネルギー密度が低い、熱安定性が低い、発火しやすいなどの限界があります。自動車メーカーとバッテリー製造企業は、電気自動車で安全に使用するために、これらの問題に対処する新しいバッテリーを開発しています。従来のリチウムイオンバッテリー技術に対するCTP(Cell To Pack) 、CTB(Cell To Body)、CTC(Cell To Chassis)バッテリー技術の主な利点は、エネルギー密度の向上と性能パラメーターの強化にあります。これらの革新的なバッテリー統合アプローチは、より高い体積エネルギー密度と重量エネルギー密度を可能にし、車両全体の重量削減に寄与すると同時に、車両のパッケージングスペースをより小さく占有する、よりコンパクトで軽量なバッテリーソリューションを可能にします。
さらに、CTP/CTB/CTC技術は、より効率的なバッテリーパッケージング設計を促し、製造工程を最小限に抑え、バッテリーパッケージング全体の容積を削減し、設計の柔軟性を高めます。これは、より安定したバッテリー特性、バッテリー寿命の延長、全体的なバッテリー性能の向上など、バッテリー寿命の延長と優れた性能指標につながります。これらの先進のバッテリー技術の大きな利点は、バッテリーのパッケージングと組み立てのコストを削減できる可能性にあります。製造プロセスを合理化し、従来の方法と比べて複雑性を軽減することで、CTP/CTB/CTCパッケージング技術は、自動車メーカーに費用対効果の高いソリューションを提供します。
当レポートでは、世界のCTP/CTB/CTC統合型バッテリー市場について調査分析し、市場の促進要因と動向、過去の需要と予測、企業プロファイルなどを提供しています。
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリー
- 市場の概要
- 市場促進要因と動向
- 近年の市場の発展と技術のハイライト
- 競合情勢
- 規制情勢
- 将来の見通しと新たな動向
- 市場予測と成長予測
- EV用バッテリー需要:EVタイプ別
- EV用バッテリー需要:地域別
- EV用バッテリー需要:バッテリータイプ別
- バッテリーセル材料
- バッテリーパック材料
第2章 技術の概要
- 統合型バッテリーシステムの概要
- 電気自動車用バッテリー材料
- セルからパックへ
- CTP、CTB、CTC
- CTM(Cell-to-Module)
- 乗用車用統合型バッテリー(シャーシ)
- 比較分析
- 電気自動車におけるCTP、CTB、CTCの重要性
- コスト分析
- CTP
- CTB
- CTC
- CTP技術
- 定義と概念
- 主なコンポーネントとアーキテクチャ
- CTCとCTPの比較
- セル設計の最適化
- 利点と課題
- 製造プロセス
- 設計上の考慮事項
- CTB技術
- 定義と概念
- 主なコンポーネントとアーキテクチャ
- CTBとCTPの比較
- CTBとCTCの比較
- 利点と課題
- 製造プロセス
- 設計上の考慮事項
- CTC技術
- 定義と概念
- 主なコンポーネントとアーキテクチャ
- 利点と課題
- 製造プロセス
- 設計上の考慮事項
- 熱管理システム
- 液体冷却システム
- 空気冷却システム
- 熱伝導材料
- コールドプレート、クーラントホース
- 相変化材料(PCM)
- スマート熱管理システム
- 二相冷却システム
- 直接バッテリー浸漬冷却
- 熱電冷却
- グラフェンベース熱管理
- 熱エネルギーハーベスティング
- 熱メタマテリアル
- バッテリー管理システム(BMS)
- 機能とコンポーネント
- 集中型BMS vs. 分散型BMS
- 通信プロトコル
- BMSの進歩
- 安全性と信頼性に関する考慮事項
第3章 市場の分析
- 世界の統合型バッテリー市場の概要
- 中国における生産
- 市場規模と予測(2024年~2035年)
- CTP市場
- CTB市場
- CTC市場
- 市場セグメンテーション
- 技術別(CTP、CTB、CTC)
- 車両タイプ別(乗用車、商用車、その他)
- 地域別
- 用途別(バッテリー電気自動車、ハイブリッド電気自動車、プラグインハイブリッド電気自動車)
- バッテリー化学別
- 市場促進要因
- 電気自動車の需要の増加
- 軽量で効率的なバッテリーシステムへのニーズ
- バッテリー技術の進歩
- 規制の取り組みとインセンティブ
- 政府の政策と排出目標
- 市場抑制要因
- 高い初期費用
- 技術的課題と統合の複雑性
- 安全性の懸念と信頼性の問題
- 限られたインフラと充電設備
- 機会
- 性能の向上
- コスト削減の可能性
- 設計のイノベーション
- EV市場の拡大
- 環境上の利点
- 課題
- 競合情勢
- 主な企業と戦略
- 自動車OEM
- 戦略的パートナーシップ
- 中国のバッテリー統合政策
- 規制情勢
- 安全と環境規制
- インセンティブと補助金
- リサイクルと廃棄に関する規制
- 将来の見通しと新たな動向
- バッテリー化学と材料の進歩
- AIとIoTの統合
- ワイヤレスバッテリー管理システム
- 持続可能性と循環性への注目の高まり
- 新たな用途と市場
- 航空宇宙、防衛
- エネルギー貯蔵システム
- 海事、船舶
第4章 企業プロファイル
- 24M Technologies, Inc
- Automotive Energy Supply Corporation (AESC)
- Beijing Hyundai
- BAIC BJEV
- Benteler
- BMW
- BYD
- China Aviation Lithium Battery (CALB) Technology Co., Ltd.
- CATL
- Changan Automobile
- Chery International
- EVE Energy Co., Ltd.
- Farasis Energy
- FAW
- FinDreams Battery
- Ford Motor Company
- GAC Aion
- GM
- Gotion High-Tech
- Great Wall Motor (GWM)
- Hycan
- IAT Automobile
- JAC Motors
- LG Energy
- Leap Motor
- Neta Auto
- NIO, Inc.
- Our Next Energy (ONE)
- REPT Battero
- SAIC (Shanghai Automotive Industry Corporation)
- Samsung SDI Co.
- SEVB
- SK On
- Stellantis N.V.
- StoreDot
- SVOLT Energy
- Tesla
- Tuopu Group
- Volvo
- Volkswagen
- Xiaomi Automobile
- XING Mobility
- Xpeng
- ZEEKR
第5章 調査手法
第6章 参考文献
List of Tables
- Table 1. Comparison of Advanced Battery Chemistries
- Table 2. CTP, CTB and CTC Integrated Battery Market Drivers and Trends
- Table 3. Recent CTP, CTB and CTC Integrated Battery Market Developments and Technology Highlights
- Table 4. CTP, CTB and CTC Integrated Battery Market Competitive Landscape
- Table 5. CTP, CTB and CTC Integrated Battery Market Regulations
- Table 6. Trends in CTP, CTB and CTC Integrated Batteries
- Table 7. EV Battery Demand Market Share Forecast (GWh) 2021-2035
- Table 8. EV Battery Demand Market Share Forecast (GWh) 2021-2035, by region
- Table 9. Battery Market Value Forecast for EVs 2022-2035 (Millions US$)
- Table 10. Battery Cell Materials Forecast for 2022-2035
- Table 11. Battery Cell Materials Market 2022-2035 (MT)
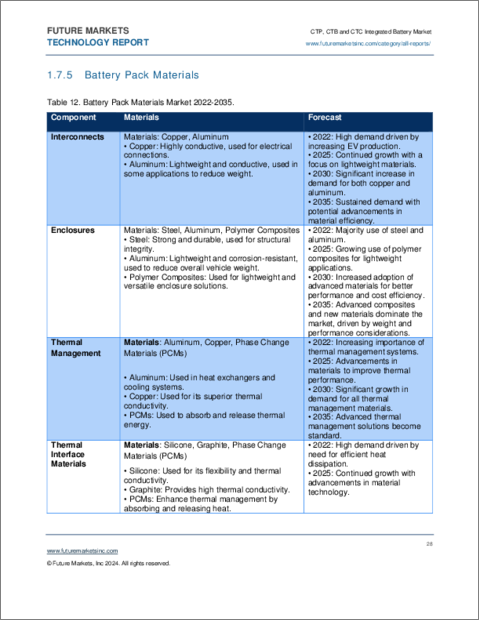
- Table 12. Battery Pack Materials Market 2022-2035
- Table 13. Total Battery Cell and Pack Materials Forecast by Vehicle Type 2022-2035 (MT)
- Table 14.Total Battery Cell and Pack Materials Market Value Forecast 2022-2035 (Millions US$)
- Table 15. Battery Materials for Electric Vehicles
- Table 16. Main types of cells used in electric vehicle batteries
- Table 17. Cell vs Pack Energy Density
- Table 18. Comparative analysis of CTP, CTB and CTC
- Table 19. Summary of Cost Impact
- Table 20. Cost Analysis for CTP, CTB and CTC Integrated Batteries
- Table 21. Comparison of CTP Mode and Conventional Battery Pack
- Table 22. Comparison between CTC and CTP
- Table 23. Cell to Pack (CTP) Advantages and Challenges
- Table 24. Manufacturing Processes for Cell-to-Pack
- Table 25. Design Considerations for Cell-to-Pack
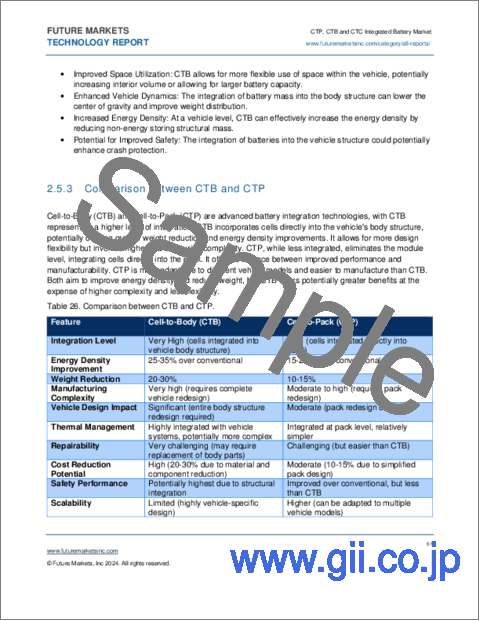
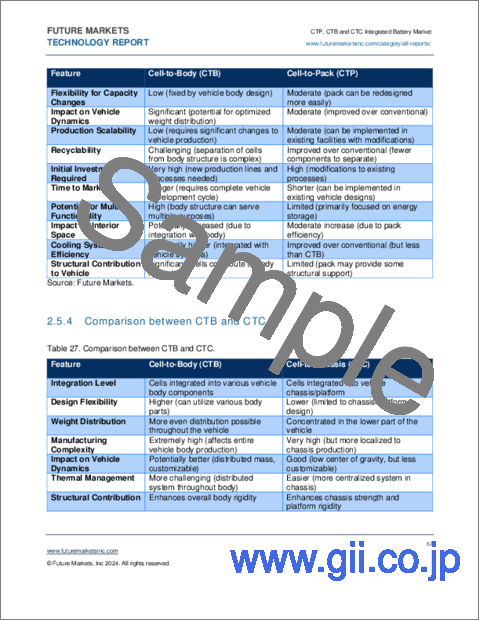
- Table 26. Comparison between CTB and CTP
- Table 27. Comparison between CTB and CTC
- Table 28. Cell to Body (CTB) Advantages and Challenges
- Table 29. Cell to Body (CTB) Manufacturing Processes
- Table 30. Cell to Body (CTB) Design Considerations
- Table 31. Cell to Chassis (CTC) Advantages and Challenges
- Table 32. Cell to Chassis (CTC) Manufacturing Processes
- Table 33. Comparison of Thermal Management Systems
- Table 34. Liquid Cooling Systems
- Table 35. Air Cooling Systems
- Table 36. TIM Application by Cell Format
- Table 37. Key Properties for TIMs in EVs
- Table 38. Key properties and characteristics of common TIM chemistries
- Table 39. Overview of the battery thermal management strategies employed by major OEMs
- Table 40. Types of PCMs
- Table 41. Comparison of Battery Management System (BMS) Architectures
- Table 42. Functions and components in Battery Management Systems (BMS) for Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Table 43. Centralized vs. Distributed BMS
- Table 44. Communication Protocols in BMS
- Table 45. Safety and Reliability Considerations
- Table 46. Global CTP Market Size and Forecast (2023-2035), billions USD
- Table 47. Global CTB Market Size and Forecast (2022-2035), Billions USD
- Table 48. Global CTC Market Size and Forecast (2024-2035), Billions USD
- Table 49. Integrated Battery Market Share by Vehicle Type, 2023-2035, Billions USD
- Table 50. Integrated Battery Market Share by Region, 2023-2035, Billions USD
- Table 51. Integrated Battery Market Share by Application, 2023-2035, Billions USD
- Table 52. Challenges in CTP, CTB and CTC Integrated Battery Market
- Table 53. Key Players in the Integrated Battery Market
- Table 54. Comparison of Automotive OEM integrated batteries
- Table 55. Strategic partnerships in the CTP, CTB and CTC Integrated Battery Market
- Table 56. Overview of key policies and initiatives in China
- Table 57. Battery Safety Standards for Integrated Batteries in EVs
- Table 58. Emissions and Fuel Economy Standards Affecting EV Battery Development
- Table 59. Environmental Impact Regulations Affecting EV Battery Production and Recycling
- Table 60. Battery Recycling Regulations
- Table 61. End-of-Life Vehicle Directives
List of Figures
- Figure 1. EV Battery Demand Market Share Forecast (GWh) 2021-2035
- Figure 2. EV Battery Demand Market Share Forecast (GWh) 2021-2035, by region
- Figure 3. Battery Market Value Forecast for EVs 2022-2035 (Millions US$)
- Figure 4. Battery Cell Materials Market 2022-2035 (MT)
- Figure 5. Battery Pack Materials Market 2022-2035 (MT)
- Figure 6. Total Battery Cell and Pack Materials Forecast by Vehicle Type 2022-2035 (MT)
- Figure 7. Total Battery Cell and Pack Materials Market Value Forecast 2022-2035 (US$)
- Figure 8. Li-ion batteries packaging schemes for EVs
- Figure 9. Types of integrated battery packs
- Figure 10. Component Breakdown of a Battery Pack
- Figure 11. CATL's CIIC skateboard chassis
- Figure 12. Battery pack with a cell-to-pack design and prismatic cells
- Figure 13. Battery pack with a cell-to-pack design and prismatic cells
- Figure 14. BYD CTP schematic
- Figure 15. Qilin battery
- Figure 16. CTP Technology Architecture
- Figure 17. The structural design of blade cell, cell arrays, and battery pack
- Figure 18. Gravimetric Energy Density and Cell-to-pack Ratio
- Figure 19. BYD Cell-to-body
- Figure 20. CATL Cell-to-chassis
- Figure 21. Tesla CTC Technology
- Figure 22. CTC Technology Architecture. The battery pack is a structural component of the vehicle, where cells are assembled directly into a car's structure
- Figure 23. Passenger NEV production in China 2020-2024
- Figure 24. Passenger BEV production in China 2020-2024
- Figure 25. Passenger PHEV production in China 2020-2024
- Figure 26. Global CTP Market Size and Forecast (2023-2035), billions USD
- Figure 27. Global CTB Market Size and Forecast (2022-2035), Billions USD
- Figure 28. Global CTC Market Size and Forecast (2024-2035), Billions USD
- Figure 29. Integrated Battery Market Share by Technology (2023-2035), Billions USD
- Figure 30. Integrated Battery Market Share by Vehicle Type, 2023-2035, Billions USD
- Figure 31. Integrated Battery Market Share by Region, 2023-2035, Billions USD
- Figure 32. Integrated Battery Market Share by Application, 2023-2035
- Figure 33. Integrated Battery Market Share by Battery Chemistry, 2023-2035, Billions USD
- Figure 34. Rolling chassis developed by BENTELER and Bosch
- Figure 35. BYD CTB technology
- Figure 36. CALB "U" type battery
- Figure 37. CATL CTP 1.0-3.0
- Figure 38. CTP 3.0: Shenxing Batteries
- Figure 39. CATL Skateboard chassis
- Figure 40. "II" Battery System
- Figure 41. Farasis Cell-to-Pack Battery System
- Figure 42. Farasis Energy Super Pouch Solution (SPS)
- Figure 43. GAC Aion's magazine battery
- Figure 44. GM Ultium
- Figure 45. Batteries with CTP mounted on a mock-up design of an automobile
- Figure 46. LG Energy's cell-to-pack technology for pouch batteries
- Figure 47. Leapmotor CTC 2.0
- Figure 48. Nio Hybrid Chemistry Cell-to-pack
- Figure 49. Our Next Energy: Aeris
- Figure 50. SAIC CTP battery design
- Figure 51. StoreDot I-BEAM XFC Cells
- Figure 52. Dragon Armor Battery
- Figure 53. Short Blade Battery LCTP Technology
- Figure 54. L400 Short Blade Batteries
- Figure 55. Tesla Cell-to-Chassis
- Figure 56. IMMERSIO(TM) Cell-to-Pack (CTP) architecture
- Figure 57. Xpeng CIB technology
- Figure 58. Gold brick battery
The growth in EV sales is driving demand for batteries, with the market for EV batteries surpassing 750 GWh in 2023, up 40% on the previous year. Electric cars account for approximately 95% of this growth. The EV market is rapidly expanding, and one of the significant challenges is the development of a reliable and safe battery that can provide a long driving range. The traditional lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles have limitations such as low energy density, poor thermal stability, and a tendency to catch fire. Vehicle OEMS and battery manufacturing companies are developing new batteries to address these issues for safe uses in electric vehicles. The key advantage of cell to pack (CTP), cell to body (CTB), and cell to chassis (CTC) battery technologies over traditional lithium-ion battery technologies lies in their improved energy density and enhanced performance parameters. These innovative battery integration approaches enable higher volumetric and gravimetric energy densities, allowing for more compact and lightweight battery solutions that occupy less vehicle packaging space while contributing to reduced overall vehicle weight.
Moreover, CTP, CTB, and CTC technologies facilitate more efficient battery packaging designs, minimizing manufacturing steps, reducing overall battery packaging volume, and enabling greater design flexibility. This translates into longer battery life and superior performance metrics, such as more stable battery characteristics, extended battery lifespans, and improved overall battery performance. A significant advantage of these advanced battery technologies lies in their potential to lower battery packaging and assembly costs. By streamlining manufacturing processes and reducing complexity compared to traditional methods, CTP, CTB, and CTC packaging techniques offer cost-effective solutions for automotive manufacturers.
"Cell to Pack (CTP), Cell to Body (CTB) and Cell to Chassis (CTC) Integrated Battery Market Report 2024-2035" covers the latest technologies, key applications, manufacturing processes, advantages, challenges, and opportunities within this rapidly evolving industry across major global regions. The integration of batteries directly into vehicle bodies and chassis represents a transformative shift in automotive design and engineering. This report meticulously evaluates the technological capabilities, real-world applicability, advantages, disadvantages, and tangible benefits CTP, CTB and CTC offer the entire automotive value chain.
The report assesses the pivotal battery technology trends propelling advancements in on-road and off-road automotive and aerospace vehicles utilizing CTP, CTB and CTC integrated solutions. This comprehensive evaluation illuminates the key commercial opportunities and strategic entry points across different vehicle segments. Also covered are emerging next-generation battery chemistries, materials, and architectures poised to disrupt the market further. The role of transformative technologies like AI, IoT, and wireless battery management systems in optimizing performance, safety, and sustainability is examined in detail. Report contents include:
Technology Overview including in-depth technical specifications on:
- Cell-to-Pack (CTP) Technology
- Cell-to-Body (CTB) Technology
- Cell-to-Chassis (CTC) Technology
- Thermal Management Systems
- Battery Management Systems (BMS)
Market Analysis
- Global Market Overview
- Market Size and Forecast
- Market Segmentation
- Market Drivers
- Market Restraints
- Opportunities
- Challenges
Competitive Landscape
- Key Players and Strategies
- Automotive OEMs
- Strategic Partnerships
Regulatory Landscape
- Safety and Environmental Regulations
- Incentives and Subsidies
- Recycling and Disposal Regulations
Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
- Battery Chemistry and Materials Advancements
- AI and IoT Integration
- Wireless Battery Management Systems
- Sustainability and Circularity Initiatives
- Emerging Applications and Markets
Profiles of 44 companies including Company Overview, Product Portfolio and Recent Developments and Initiatives. Companies profiled include BYD, CALB, CATL, EVE Energy, GM, LG Energy, Leap Motor, NIO, Stellantis, StoreDot and SVOLT Energy (Full list of companies profiled in table of contents).
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- 1.1. Market Overview
- 1.2. Market Drivers and Trends
- 1.3. Recent Market Developments and Technology Highlights
- 1.4. Competitive Landscape
- 1.5. Regulatory Landscape
- 1.6. Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
- 1.7. Market Forecast and Growth Projections
- 1.7.1. EV Battery Demand, By EV Type
- 1.7.2. EV Battery Demand, By Region
- 1.7.3. EV Battery Demand, By Battery Type
- 1.7.4. Battery Cell Materials
- 1.7.5. Battery Pack Materials
2. TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW
- 2.1. Overview of Integrated Battery Systems
- 2.1.1. Battery Materials for Electric Vehicles
- 2.1.2. From Cell to Pack
- 2.1.3. Cell-to-Pack (CTP), Cell-to-Body (CTB), and Cell-to-Chassis (CTC)
- 2.1.4. Cell-to-Module (CTM)
- 2.1.5. Passenger Car Integrated Battery (Chassis)
- 2.1.6. Comparative Analysis
- 2.2. Importance of CTP, CTB, and CTC in Electric Vehicles
- 2.3. Cost analysis
- 2.3.1. CTP (Cell to Pack)
- 2.3.2. CTB (Cell to Body)
- 2.3.3. CTC (Cell to Chassis)
- 2.4. Cell-to-Pack (CTP) Technology
- 2.4.1. Definition and Concept
- 2.4.2. Key Components and Architecture
- 2.4.3. Comparison between CTC and CTP
- 2.4.4. Cell Design Optimization
- 2.4.5. Advantages and Challenges
- 2.4.6. Manufacturing Processes
- 2.4.7. Design Considerations
- 2.5. Cell-to-Body (CTB) Technology
- 2.5.1. Definition and Concept
- 2.5.2. Key Components and Architecture
- 2.5.3. Comparison between CTB and CTP
- 2.5.4. Comparison between CTB and CTC
- 2.5.5. Advantages and Challenges
- 2.5.6. Manufacturing Processes
- 2.5.7. Design Considerations
- 2.6. Cell-to-Chassis (CTC) Technology
- 2.6.1. Definition and Concept
- 2.6.2. Key Components and Architecture
- 2.6.3. Advantages and Challenges
- 2.6.4. Manufacturing Processes
- 2.6.5. Design Considerations
- 2.7. Thermal Management Systems
- 2.7.1. Liquid Cooling Systems
- 2.7.2. Air Cooling Systems
- 2.7.3. Thermal Interface Materials
- 2.7.3.1. Properties for TIMs in EVs
- 2.7.3.2. Gap Pads in EV Batteries
- 2.7.3.3. Gap Fillers
- 2.7.3.4. Thermally Conductive Adhesives
- 2.7.3.5. Chemistry Comparison
- 2.7.3.6. Gap Filler to Thermally Conductive Adhesives
- 2.7.4. Cold Plates and Coolant Hoses
- 2.7.4.1. Coolant Fluids in EVs
- 2.7.4.2. Inter-cell Heat Spreaders or Cooling Plates
- 2.7.4.3. Advanced Cold Plate Design
- 2.7.4.4. Coolant Hoses for EVs
- 2.7.5. Phase Change Materials (PCMs)
- 2.7.6. Smart Thermal Management Systems
- 2.7.7. Two-Phase Cooling Systems:
- 2.7.8. Direct Battery Immersion Cooling
- 2.7.9. Thermoelectric Cooling
- 2.7.10. Graphene-based Thermal Management
- 2.7.11. Thermal Energy Harvesting
- 2.7.12. Thermal Metamaterials
- 2.8. Battery Management Systems (BMS)
- 2.8.1. Functions and Components
- 2.8.2. Centralized vs. Distributed BMS
- 2.8.3. Communication Protocols
- 2.8.4. Advancements in BMS
- 2.8.5. Safety and Reliability Considerations
3. MARKET ANALYSIS
- 3.1. Global Integrated Battery Market Overview
- 3.1.1. Production in China
- 3.2. Market Size and Forecast (2024-2035)
- 3.2.1. CTP Market
- 3.2.2. CTB Market
- 3.2.3. CTC Market
- 3.3. Market Segmentation
- 3.3.1. By Technology (CTP, CTB, CTC)
- 3.3.2. By Vehicle Type (Passenger Cars, Commercial Vehicles, Others)
- 3.3.3. By Region
- 3.3.4. By Application (Battery Electric Vehicles, Hybrid Electric Vehicles, Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles)
- 3.3.5. By Battery Chemistry
- 3.4. Market Drivers
- 3.4.1. Increasing Demand for Electric Vehicles
- 3.4.2. Need for Lightweight and Efficient Battery Systems
- 3.4.3. Advancements in Battery Technology
- 3.4.4. Regulatory Initiatives and Incentives
- 3.4.5. Government Policies and Emissions Targets
- 3.5. Market Restraints
- 3.5.1. High Initial Costs
- 3.5.2. Technical Challenges and Integration Complexities
- 3.5.3. Safety Concerns and Reliability Issues
- 3.5.4. Limited Infrastructure and Charging Facilities
- 3.6. Opportunities
- 3.6.1. Performance Improvements
- 3.6.2. Cost Reduction Potential
- 3.6.3. Design Innovation
- 3.6.4. EV Market Expansion
- 3.6.5. Environmental Benefits
- 3.7. Challenges
- 3.8. Competitive Landscape
- 3.8.1. Key Players and Strategies
- 3.8.2. Automotive OEMS
- 3.8.3. Strategic partnerships
- 3.8.4. Battery Integration Policies in China
- 3.9. Regulatory Landscape
- 3.9.1. Safety and Environmental Regulations
- 3.9.1.1. Battery Safety Standards
- 3.9.1.2. Emissions and Fuel Economy Standards
- 3.9.1.3. Environmental Impact Regulations
- 3.9.2. Incentives and Subsidies
- 3.9.2.1. Government Incentives
- 3.9.3. Recycling and Disposal Regulations
- 3.9.3.1. Battery Recycling Regulations
- 3.9.3.2. End-of-Life Vehicle Directives
- 3.9.1. Safety and Environmental Regulations
- 3.10. Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
- 3.10.1. Advancements in Battery Chemistry and Materials
- 3.10.1.1. Solid-State Batteries
- 3.10.1.2. Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
- 3.10.1.3. Sodium-ion Batteries
- 3.10.1.4. Silicon Anodes
- 3.10.2. Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things (IoT)
- 3.10.2.1. Predictive Maintenance
- 3.10.2.2. Smart Battery Management Systems
- 3.10.3. Wireless Battery Management Systems
- 3.10.4. Increasing Focus on Sustainability and Circularity
- 3.10.4.1. Sustainable Battery Materials
- 3.10.4.2. Battery Recycling and Reuse
- 3.10.1. Advancements in Battery Chemistry and Materials
- 3.11. Emerging Applications and Markets
- 3.11.1. Aerospace and Defense
- 3.11.2. Energy Storage Systems
- 3.11.3. Marine and Shipping
4. COMPANY PROFILES
- 4.1 24M Technologies, Inc,
- 4.2. Automotive Energy Supply Corporation (AESC)
- 4.3. Beijing Hyundai
- 4.4. BAIC BJEV
- 4.5. Benteler
- 4.6. BMW
- 4.7. BYD
- 4.8. China Aviation Lithium Battery (CALB) Technology Co., Ltd.
- 4.9. CATL
- 4.10. Changan Automobile
- 4.11. Chery International
- 4.12. EVE Energy Co., Ltd.
- 4.13. Farasis Energy
- 4.14. FAW
- 4.15. FinDreams Battery
- 4.16. Ford Motor Company
- 4.17. GAC Aion
- 4.18. GM
- 4.19. Gotion High-Tech
- 4.20. Great Wall Motor (GWM)
- 4.21. Hycan
- 4.22. IAT Automobile
- 4.23. JAC Motors
- 4.24. LG Energy
- 4.25. Leap Motor
- 4.26. Neta Auto
- 4.27. NIO, Inc.
- 4.28. Our Next Energy (ONE)
- 4.29. REPT Battero
- 4.30. SAIC (Shanghai Automotive Industry Corporation)
- 4.31. Samsung SDI Co.
- 4.32. SEVB
- 4.33. SK On
- 4.34. Stellantis N.V.
- 4.35. StoreDot
- 4.36. SVOLT Energy
- 4.37. Tesla
- 4.38. Tuopu Group
- 4.39. Volvo
- 4.40. Volkswagen
- 4.41. Xiaomi Automobile
- 4.42. XING Mobility
- 4.43. Xpeng
- 4.44. ZEEKR