|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1654716
有機農業の世界市場:2025年~2032年Global Organic Farming Market - 2025-2032 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 有機農業の世界市場:2025年~2032年 |
|
出版日: 2025年02月13日
発行: DataM Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 201 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
世界の有機農業市場は、2024年に1,715億米ドルに達し、2032年までには2,873億米ドルに達すると予測され、予測期間中の2025年から2032年のCAGRは6.7%です。
世界の有機農業部門は、最近の動向で著しい上昇を続けています。2023年には、有機栽培の総面積は9,640万ヘクタールを超え、2022年から2,000万ヘクタール以上増加しました。この成長の主因は、オーストラリアとインドにおける大幅な拡大です。オーストラリアは有機栽培面積5,300万ヘクタールで首位を維持し、インドは470万ヘクタールで2位に浮上しました。
世界の有機生産者数も顕著に増加し、2022年末までに450万人を突破しました。この増加は、現在約250万人の有機生産者を占めるインドの大幅な増加によるところが大きいです。こうした前向きな動向にもかかわらず、有機部門は、市場の変動や地域によって異なる消費者需要などの課題に直面しています。とはいえ、生産量と市場価格の両方が持続的に伸びていることは、有機農業とその原則に対する世界のコミットメントの高まりを強調しています。
ダイナミクス
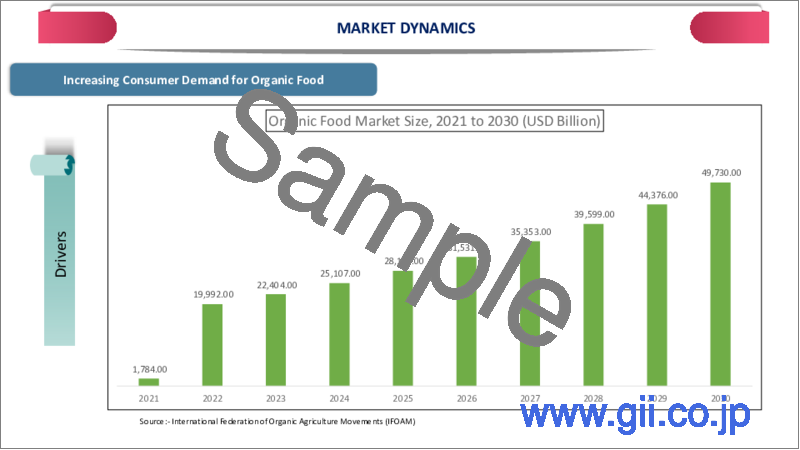
有機製品に対する消費者需要の高まり
世界の有機農業市場は、有機製品に対する消費者需要の高まりに後押しされ、近年著しい成長を遂げています。この動向は、健康上の利点、環境の持続可能性、自然で化学薬品を使用しない方法で生産された食品への要望に対する意識の高まりを反映しています。これらの要因は、生産、市場価値、政府の取り組みが顕著に拡大する中で、世界の有機農業の軌道を形成する上で重要な役割を果たしました。
2024年、世界の有機農業セクターは安定した成長を続け、有機管理下の土地面積は9,800万ヘクタールを超えました。これは、有機製品に対する消費者の選好の高まりに後押しされ、以前と比べて大幅な伸びを示しました。2022年の世界の有機市場の売上高は1,350億ユーロに達し、米国が最大の有機市場として566億ユーロの売上高を計上しました。この成長は、ドイツ、中国、カナダを含む他の主要市場でも同様で、消費者の優先順位の幅広いシフトを反映しています。
政府の支援政策と補助金
政府の支援政策と補助金は、世界の有機農業市場を推進する上で極めて重要です。こうしたイニシアティブは、財政支援、研究開発資金、市場開拓支援を提供し、農家が有機農法を採用し、有機製品に対する消費者需要の高まりに対応することを奨励してきました。
2024年、米国農務省(USDA)は、有機酪農生産者を支援するため、有機酪農マーケティング支援プログラム(ODMAP)を通じて5,800万米ドルを利用可能にすると発表しました。この資金は、有機酪農の市場を拡大し、消費を拡大することで、有機酪農の経済性を強化することを目的としています。さらに米国農務省は、2024年に主要な保全プログラムとセーフティネット・プログラムを通じて、農業生産者と土地所有者に21億4,000万米ドル以上の支払いを開始しました。これらのプログラムは、自然資源を保護し、有機農業の原則に沿った家族経営の農場を支援することを目的としています。
欧州連合(EU)では、共通農業政策(CAP)が有機農業の重要な推進力となってきました。しかし、最近の報告書では、補助金と環境目標との整合性を高める改革の必要性が強調されています。欧州監査院(European Court of Auditors)による2024年の報告書では、EUの農業奨励策とグリーンディールの目標との間にギャップがあることが指摘され、有機農業を含む持続可能な慣行に対する、より的を絞った支援の必要性が強調されています。
さらに、米国農務省の有機農業プログラムは、有機産業が米国農業の中で最も急成長している分野であると認識しており、食品と非食品の総売上高は2021年に575億米ドルに達するとしています。この認識により、リスク管理オプションの拡大や保険料補助など、有機生産者への支援が強化されています。
慣行農法に比べ低収量
世界の有機農業市場は、持続可能な方法で生産された食品に対する消費者の需要の高まりに後押しされて拡大してきました。しかし、有機農業の成長を阻む重大な課題は、慣行農法に比べて有機農業の収量が低いことです。この収量の差は、食糧供給、土地利用、有機農業の経済的実現性に影響を及ぼします。
有機農業の収量は一般的に慣行農業の収量よりも低いことが、研究によって一貫して示されています。Natureに掲載された包括的なメタ分析によれば、有機農法の収量は慣行農法の収量よりも一般的に低く、その差はさまざまな要因によって5%から34%に及びます。良好な管理慣行や特定の作物の種類など特定の条件下では、有機栽培システムは慣行栽培の収量にほぼ匹敵しますが、そうでない場合もあります。
有機農業における収量の低さは、いくつかの要因に起因しています。合成肥料や農薬の使用が禁止されているため、害虫の被害が拡大したり、栄養不足に陥ったりする可能性があります。有機農家は、土壌肥沃度や病害虫を管理するために、自然の代替物や輪作に頼っていますが、これは従来の方法よりも効果が低かったり、効き目が遅かったりすることがあります。さらに有機農法では、より多様な作物輪作と休耕期間を必要とすることが多く、一定期間に栽培される市場流通可能な農産物の量が減少する可能性があります。
目次
第1章 調査手法と調査範囲
第2章 定義と概要
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場力学
- 影響要因
- 促進要因
- オーガニック製品に対する消費者の需要の高まり
- 政府の支援政策と補助金
- 抑制要因
- 従来の農業に比べて収穫量が少ない
- 機会
- 影響分析
- 促進要因
第5章 産業分析
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- サプライチェーン分析
- 価格分析
- 規制分析
- DMIの見解
第6章 製品タイプ別
- 有機種子・栽培資材
- 果物と野菜の種子
- 穀物・豆類
- 油糧種子
- 苗木・実生苗
- 有機肥料
- 有機農薬
- 土壌改良剤
- 植物成長促進剤
- 動物飼料・添加物
- その他
第7章 農業タイプ別
- 純粋有機農業
- 統合有機農業
第8章 用途別
- 作物の多様性
- 土壌管理
- 雑草管理
- その他
第9章 地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 欧州
- ドイツ
- 英国
- フランス
- イタリア
- スペイン
- その他欧州地域
- 南米
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
- その他南米
- アジア太平洋
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- オーストラリア
- その他アジア太平洋
- 中東・アフリカ
第10章 競合情勢
- 競合シナリオ
- 市況・シェア分析
- M&A分析
第11章 企業プロファイル
- Darling Ingredients Inc.
- 会社概要
- 製品ポートフォリオと概要
- 財務概要
- 主な発展
- Indigo Agriculture Inc.
- Soli Organic Inc.
- SalMar ASA
- Actagro
- Reiter Affiliated Companies, LLC.
- KORIN AGROPECUARIA LTDA
- Jain Farm Fresh Foods Limited
- Suminter India Organics
- Ambrosia Organic Farm
第12章 付録
Global Organic Farming Market reached US$ 171.5 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach US$ 287.3 billion by 2032 growing with a CAGR of 6.7% during the forecast period 2025-2032.
The global organic farming sector has continued its upward trajectory, with significant developments in recent years. In 2023, the total area under organic management crossed 96.4 million hectares, marking an increase of over 20 million hectares from 2022. This growth was predominantly driven by substantial expansions in Australia and India. Australia remains the leader with 53 million hectares under organic cultivation, while India has ascended to the second position with 4.7 million hectares.
The number of organic producers worldwide also saw a notable rise, surpassing 4.5 million by the end of 2022. This increase is largely attributed to a significant uptick in India, which now accounts for approximately 2.5 million organic producers. Despite these positive trends, the organic sector faces challenges, including market fluctuations and varying consumer demand across regions. Nevertheless, the sustained growth in both production and market value underscores the increasing global commitment to organic agriculture and its principles.
Dynamics
Rising Consumer Demand for Organic Products
The global organic farming market has experienced remarkable growth in recent years, fueled by increasing consumer demand for organic products. This trend reflects a growing awareness of health benefits, environmental sustainability and the desire for food produced through natural and chemical-free methods.These factors played a critical role in shaping the trajectory of organic farming worldwide, with notable expansions in production, market value and government initiatives.
In 2024, the global organic farming sector continued to grow steadily, with turnover of more than 98 million hectares of land under organic management. This marked a significant increase compared to previous years, driven by heightened consumer preferences for organic products. The organic market globally reached sales of EUR 135 billion in 2022, with US leading as the largest organic market, generating EUR 56.6 billion in sales. This growth was mirrored in other major markets, including Germany, China and Canada, reflecting a broad-based shift in consumer priorities.
Supportive Government Policies and Subsidies
Supportive government policies and subsidies have been pivotal in driving the global organic farming market. The initiatives have provided financial assistance, research funding and market development support, encouraging farmers to adopt organic practices and meet the rising consumer demand for organic products.
In 2024, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) announced the availability of US$ 58 million through the Organic Dairy Marketing Assistance Program (ODMAP) to support organic dairy producers. This funding aims to expand the market for organic dairy and increase consumption, thereby strengthening the economic viability of organic dairy farming. Additionally, the USDA began issuing over US$ 2.14 billion in payments to agricultural producers and landowners through key conservation and safety-net programs in 2024. The programs are designed to conserve natural resources and support family farms, aligning with the principles of organic agriculture.
In the European Union, the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) has been a significant driver of organic farming. However, recent reports have highlighted the need for reforms to better align subsidies with environmental goals. A 2024 report by the European Court of Auditors identified gaps between EU farming incentives and the Green Deal objectives, emphasizing the need for more targeted support for sustainable practices, including organic farming.
Furthermore, the USDA's Organic Agriculture Program has recognized the organic industry as the fastest-growing segment of U.S. agriculture, with total sales of food and non-food products reaching US$ 57.5 billion in 2021. This recognition has led to increased support for organic producers, including expanded risk management options and premium subsidies.
Low Yield Compared to Conventional Farming
The global organic farming market has been expanding, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainably produced food. However, one significant challenge restraining its growth is the lower yield of organic farming compared to conventional methods. This yield gap has implications for food supply, land use and the economic viability of organic agriculture.
Studies have consistently shown that organic farming yields are generally lower than those of conventional farming. A comprehensive meta-analysis published in Nature found that organic yields are typically lower than conventional yields, with differences ranging from 5% to 34% depending on various factors. Under certain conditions, such as with good management practices and specific crop types organic systems can nearly match conventional yields, whereas under others, they cannot.
The lower yields in organic farming are attributed to several factors, including the prohibition of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, which can lead to increased pest pressures and nutrient deficiencies. Organic farmers rely on natural alternatives and crop rotations to manage soil fertility and pests, practices that can be less effective or slower-acting than conventional methods. Additionally organic farming often requires more diverse crop rotations and fallow periods, which can reduce the amount of marketable produce grown in a given time frame.
Segment Analysis
The global organic farming market is segmented based on on product type, farming type, application and region.
Shifting Consumer Preferences For Pure Organic Farming
The demand for pure organic farming methods has been a key driver of growth in the global organic farming market. This demand reflects an increasing consumer preference for health-conscious and environmentally sustainable products. In 2023, the USDA highlighted that the U.S. organic industry is the fastest-growing segment of agriculture, with organic product sales reaching $57.5 billion in 2021. This growth trend is expected to continue, supported by rising awareness of the benefits of organic products.
The USDA's Agricultural Resource Management Survey (ARMS) provides valuable data on organic practices and their economic impact. In 2023, the ARMS revealed that organic farms, particularly those practicing pure organic methods without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides, are gaining traction despite challenges such as higher production costs and lower yields compared to conventional farming. These farms, however, benefit from premium prices and significant demand in the marketplace.
The National Organic Standards Board (NOSB) plays a key role in maintaining organic standards, ensuring that only products adhering to strict organic guidelines, such as the exclusion of synthetic substances, are certified as organic. This ensures that pure organic farming practices remain the standard for products labeled as organic. In 2024, the NOSB continued its evaluation of various substances to ensure they meet the stringent criteria of organic farming.
Geographical Penetration
Significant Growth in Organic Farming Trends in Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific has experienced significant growth in organic farming, driven by increasing consumer demand for organic products and supportive government policies. In 2023, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) reported that Asia accounted for approximately 5% of the global organic agricultural land, with countries like China, India and Japan leading in organic farming area.
In 2024, the OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook projected that the Asia-Pacific region would continue to experience strong economic growth, with per capita income increasing at an average annual rate of 4.5%. This economic expansion is expected to drive higher demand for organic products, as consumers become more health-conscious and environmentally aware.
Government initiatives have played a crucial role in promoting organic farming in the region. For instance, Australia's Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry has implemented programs to support organic certification and market access for organic producers. The department's Annual Report 2023-24 highlights efforts to enhance the competitiveness of Australian organic products in both domestic and international markets.
In India, the government has launched the National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP), which provides certification and support to organic farmers. This initiative aims to increase the area under organic cultivation and improve the quality of organic products, thereby boosting consumer confidence and market growth. Overall, the combination of rising consumer demand and supportive government policies is expected to drive the continued growth of the organic farming market in the Asia-Pacific region.
Competitive Landscape
The major global players in the market include Darling Ingredients Inc., Indigo Agriculture Inc., Soli Organic Inc., SalMar ASA, Actagro, Reiter Affiliated Companies, LLC, KORIN AGROPECUARIA LTDA, Jain Farm Fresh Foods Limited, Suminter India Organics and Ambrosia Organic Farm.
By Product Type
- Organic Seeds and Planting Materials
- Fruits and vegetable seeds
- Cereal and pulse seeds
- Oilseed seeds
- Saplings and seedlings
- Organic Fertilizers
- Organic Pesticides
- Soil Conditioners
- Plant Growth Enhancers
- Animal Feed and Additives
- Others
By Farming Type
- Pure organic farming
- Integrated Organic farming
By Application
- Crop Diversity
- Soil Management
- Weed Management
- Others
By Region
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- UK
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Rest of Europe
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of South America
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- Australia
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
- Middle East and Africa
Key Developments
- In September 2024 organic Seed Alliance (OSA) and a consortium of research partners announced the launch of a major new research project aimed at advancing organic seed production practices and expanding the availability of high-quality organic seed. The project, titled "OSPREY: Organic Seed Production Research on Economics and Yield," has been awarded funding through the U.S. Department of Agriculture's (USDA) National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) Organic Research and Extension Initiative (OREI).
- In June 2024, Chandra Shekhar Azad University of Agriculture and Technology (CSAUAT) has initiated a large-scale shift towards organic farming in response to the excessive use of chemical pesticides, which is causing serious harm to human health and soil quality. In collaboration with Hindustan Insecticides Limited, the university is launching an organic farming project across 22 districts in Uttar Pradesh. This project, running from 2024 to 2028, aims to extensively educate farmers about organic farming practices.
Why Purchase the Report?
- To visualize the global organic farming market segmentation based on product type, farming type, application and region, as well as understand key commercial assets and players.
- Identify commercial opportunities by analyzing trends and co-development.
- Excel data sheet with numerous data points of the organic farming market with all segments.
- PDF report consists of a comprehensive analysis after exhaustive qualitative interviews and an in-depth study.
- Product mapping available as excel consisting of key products of all the major players.
The global organic farming market report would provide approximately 62 tables, 56 figures and 201 pages.
Target Audience 2025
- Manufacturers/ Buyers
- Industry Investors/Investment Bankers
- Research Professionals
- Emerging Companies
Table of Contents
1. Methodology and Scope
- 1.1. Research Methodology
- 1.2. Research Objective and Scope of the Report
2. Definition and Overview
3. Executive Summary
- 3.1. Snippet by Product Type
- 3.2. Snippet by Farming Type
- 3.3. Snippet by Application
- 3.4. Snippet by Region
4. Dynamics
- 4.1. Impacting Factors
- 4.1.1. Drivers
- 4.1.1.1. Rising Consumer Demand for Organic Products
- 4.1.1.2. Supportive Government Policies and Subsidies
- 4.1.2. Restraints
- 4.1.2.1. Low Yield Compared to Conventional Farming
- 4.1.3. Opportunity
- 4.1.4. Impact Analysis
- 4.1.1. Drivers
5. Industry Analysis
- 5.1. Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 5.2. Supply Chain Analysis
- 5.3. Pricing Analysis
- 5.4. Regulatory Analysis
- 5.5. DMI Opinion
6. By Product Type
- 6.1. Introduction
- 6.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Product Type
- 6.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Product Type
- 6.2. Organic Seeds and Planting Materials*
- 6.2.1. Introduction
- 6.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 6.2.3. Fruits and vegetable seeds
- 6.2.4. Cereal and pulse seeds
- 6.2.5. Oilseed seeds
- 6.2.6. Saplings and seedlings
- 6.3. Organic Fertilizers
- 6.4. Organic Pesticides
- 6.5. Soil Conditioners
- 6.6. Plant Growth Enhancers
- 6.7. Animal Feed and Additives
- 6.8. Others
7. By Farming Type
- 7.1. Introduction
- 7.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Farming Type
- 7.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Farming Type
- 7.2. Pure Organic Farming*
- 7.2.1. Introduction
- 7.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 7.3. Integrated Organic Farming
8. By Application
- 8.1. Introduction
- 8.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 8.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Application
- 8.2. Crop Diversity*
- 8.2.1. Introduction
- 8.2.2. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%)
- 8.3. Soil Management
- 8.4. Weed Management
- 8.5. Others
9. By Region
- 9.1. Introduction
- 9.1.1. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Region
- 9.1.2. Market Attractiveness Index, By Region
- 9.2. North America
- 9.2.1. Introduction
- 9.2.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 9.2.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Product Type
- 9.2.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Farming Type
- 9.2.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 9.2.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 9.2.6.1. US
- 9.2.6.2. Canada
- 9.2.6.3. Mexico
- 9.3. Europe
- 9.3.1. Introduction
- 9.3.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 9.3.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Product Type
- 9.3.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Farming Type
- 9.3.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 9.3.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 9.3.6.1. Germany
- 9.3.6.2. UK
- 9.3.6.3. France
- 9.3.6.4. Italy
- 9.3.6.5. Spain
- 9.3.6.6. Rest of Europe
- 9.4. South America
- 9.4.1. Introduction
- 9.4.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 9.4.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
- 9.4.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Product Type
- 9.4.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Farming Type
- 9.4.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 9.4.7. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 9.4.7.1. Brazil
- 9.4.7.2. Argentina
- 9.4.7.3. Rest of South America
- 9.5. Asia-Pacific
- 9.5.1. Introduction
- 9.5.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 9.5.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Product Type
- 9.5.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Farming Type
- 9.5.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 9.5.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Country
- 9.5.6.1. China
- 9.5.6.2. India
- 9.5.6.3. Japan
- 9.5.6.4. Australia
- 9.5.6.5. Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 9.6. Middle East and Africa
- 9.6.1. Introduction
- 9.6.2. Key Region-Specific Dynamics
- 9.6.3. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Product Type
- 9.6.4. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Farming Type
- 9.6.5. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Application
- 9.6.6. Market Size Analysis and Y-o-Y Growth Analysis (%), By Type
10. Competitive Landscape
- 10.1.1. Competitive Scenario
- 10.1.2. Market Positioning/Share Analysis
- 10.1.3. Mergers and Acquisitions Analysis
11. Company Profiles
- 11.1. Darling Ingredients Inc.*
- 11.1.1. Company Overview
- 11.1.2. Product Portfolio and Description
- 11.1.3. Financial Overview
- 11.1.4. Key Developments
- 11.2. Indigo Agriculture Inc.
- 11.3. Soli Organic Inc.
- 11.4. SalMar ASA
- 11.5. Actagro
- 11.6. Reiter Affiliated Companies, LLC.
- 11.7. KORIN AGROPECUARIA LTDA
- 11.8. Jain Farm Fresh Foods Limited
- 11.9. Suminter India Organics
- 11.10. Ambrosia Organic Farm
LIST NOT EXHAUSTIVE
12. Appendix
- 12.1. About Us and Services
- 12.2. Contact Us