|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1803903
ゼロトラストセキュリティの世界市場(~2035年):認証タイプ別、ソリューション別、展開別、提供別、サービスタイプ別、セキュリティ機能タイプ別、エンドユーザータイプ別、企業規模別、主要地域別、産業動向、予測Zero Trust Security Market, Till 2035: Distribution by Type of Authentication, Solution, Deployment, Offering, Type of Service, Type of Security Feature, Type of End User, Company Size, and Key Geographical Regions: Industry Trends and Global Forecasts |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| ゼロトラストセキュリティの世界市場(~2035年):認証タイプ別、ソリューション別、展開別、提供別、サービスタイプ別、セキュリティ機能タイプ別、エンドユーザータイプ別、企業規模別、主要地域別、産業動向、予測 |
|
出版日: 2025年09月03日
発行: Roots Analysis
ページ情報: 英文 248 Pages
納期: 7~10営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
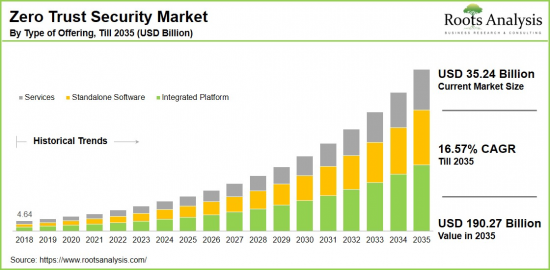
世界のゼロトラストセキュリティの市場規模は、現在の352億4,000万米ドルから2035年までに1,902億7,000万米ドルに達すると予測され、2035年までの予測期間にCAGRで16.57%の成長が見込まれます。
ゼロトラストセキュリティ市場:成長と動向
ゼロトラストとは、決して信用せず、常に検証するという概念に根ざしたサイバーセキュリティのフレームワークです。ゼロトラストアーキテクチャやパラメーターレスセキュリティと呼ばれることも多く、ITシステムの戦略立案、設計、実装のアプローチを表しています。
ゼロトラストセキュリティモデルでは、組織はユーザーやデバイスを自動的に信用することを控え、脅威はネットワークの外部と内部の両方から発生する可能性があるという前提条件で運用します。その結果、ユーザーやデバイスの場所や企業の内外にかかわらず、その信頼性を継続的に評価します。さらに、今日のデジタル時代において、サイバーセキュリティの脅威が頻発していることから、今日の複雑で進化するIT情勢において、データ侵害のリスクを低減し、機密情報を保護する上で、ゼロトラスト技術の重要性が浮き彫りになっています。この技術は、継続的なモニタリングと分析を通じて、本人確認、デバイス確認、マイクロセグメンテーションを採用し、異常な活動を特定することで機能します。
ゼロトラストソリューションへの需要が高まる中、ステークホルダーは先進技術を活用して、ID管理、デバイス検証、アクセス制御、持続的モニタリングなどのさまざまなセキュリティ要素を組み込んだ包括的なゼロトラストプラットフォームを開発しています。これらのプラットフォームは、まとまったソリューションを提供することでゼロトラストの実装を合理化します。強化されたサイバーセキュリティ対策に対する需要の高まり、IT環境の複雑化、IoT技術の利用の拡大により、ゼロトラストセキュリティ市場は予測期間に大幅に成長する見込みです。
当レポートでは、世界のゼロトラストセキュリティ市場について調査分析し、市場規模の推計と機会の分析、競合情勢、企業プロファイルなどの情報を提供しています。
目次
第1章 序文
第2章 調査手法
第3章 経済的考慮事項、その他のプロジェクト特有の考慮事項
第4章 マクロ経済指標
第5章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第6章 イントロダクション
第7章 競合情勢
第8章 企業プロファイル
- 章の概要
- Akamai Technologies
- Broadcom
- Centrify Corporation
- Cisco Systems
- CyberArk Software
- F5 Networks
- Illumio
- Microsoft
- Palo Alto Networks
- Pulse Secure
- Sophos Group
- Trend Micro
- VMware
第9章 バリューチェーンの分析
第10章 SWOTの分析
第11章 世界のゼロトラストセキュリティ市場
第12章 市場機会:認証タイプ別
第13章 市場機会:ソリューションタイプ別
第14章 市場機会:展開タイプ別
第15章 市場機会:提供タイプ別
第16章 市場機会:サービスタイプ別
第17章 市場機会:セキュリティ機能タイプ別
第18章 市場機会:エンドユーザータイプ別
第19章 市場機会:企業規模別
第20章 北米のゼロトラストセキュリティ市場の機会
第21章 欧州のゼロトラストセキュリティ市場の機会
第22章 アジアのゼロトラストセキュリティ市場の機会
第23章 中東・北アフリカ(MENA)のゼロトラストセキュリティ市場の機会
第24章 ラテンアメリカのゼロトラストセキュリティ市場の機会
第25章 その他の地域のゼロトラストセキュリティ市場の機会
第26章 表形式データ
第27章 企業・団体のリスト
第28章 カスタマイズの機会
第29章 Rootsのサブスクリプションサービス
第30章 著者詳細
Zero Trust Security Market Overview
As per Roots Analysis, the global zero trust security market size is estimated to grow from USD 35.24 billion in the current year to USD 190.27 billion by 2035, at a CAGR of 16.57% during the forecast period, till 2035.

The opportunity for zero trust security market has been distributed across the following segments:
Type of Authentication
- Multi-factor Authentication
- Single-factor Authentication
Type of Solution
- API Security
- Cloud Security
- Data Security
- Endpoint Security
- Network Security
- Others
Type of Deployment
- Cloud-based
- On-Premise
Type of Offering
- Integrated Platform
- Standalone Software
- Services
Type of Service
- Consulting and Advisory Service
- Implementation and Integration Service
- Managed Service
- Training and Support Service
Type of Security Feature
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
- Micro-Segmentation
- Network Segmentation
- Privileged Access Management (PAM)
- Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR)
- Others
Type of End-User
- Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI)
- Energy and Power
- Government and Defense
- Healthcare
- IT and Telecom
- Manufacturing
- Retail
- Other End-user Industries
Company Size
- Small and Medium Enterprises
- Large Enterprises
Geographical Regions
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
- Other North American countries
- Europe
- Austria
- Belgium
- Denmark
- France
- Germany
- Ireland
- Italy
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Russia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- UK
- Other European countries
- Asia
- China
- India
- Japan
- Singapore
- South Korea
- Other Asian countries
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Chile
- Colombia
- Venezuela
- Other Latin American countries
- Middle East and North Africa
- Egypt
- Iran
- Iraq
- Israel
- Kuwait
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Other MENA countries
- Rest of the World
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Other countries
Zero Trust Security Market: Growth and Trends
Zero trust constitutes a cybersecurity framework rooted in the notion of never trusting and always verifying. It is often referred to as zero trust architecture or parameter less security, describing an approach to strategizing, designing, and implementing IT systems.
Within the zero trust security model, organizations refrain from automatically trusting users or devices, operating under the premise that threats may arise from both outside and within the network. As a result, it continuously assesses the trustworthiness of users and devices, regardless of their location or whether they fall inside or outside the corporate perimeter. Additionally, in today's digital age, the increasing frequency of cybersecurity threats highlights the importance of zero trust technology in reducing the risk of data breaches and protecting sensitive information within today's complex and evolving IT landscapes. This technology functions through ongoing monitoring and analysis to identify any unusual activity, employing identity verification, device verification, and micro-segmentation.
With the growing demand for zero trust solutions, stakeholders are utilizing advanced technology to develop comprehensive zero trust platforms that incorporate various security elements, including identity management, device verification, access control, and continuous monitoring. These platforms streamline the implementation of zero trust by providing a cohesive solution. Owing to the rising demand for enhanced cybersecurity measures, increasing complexity of IT environments, and the expanding use of IoT technology, the zero trust security market is expected to experience significant growth during the forecast period.
Zero Trust Security Market: Key Segments
Market Share by Type of Authentication
Based on type of authentication, the global zero trust security market is segmented into single-factor authentication and multi-factor authentication. According to our estimates, currently, the multi-factor authentication segment captures the majority share of the market. This can be attributed to the advanced capabilities of zero trust security solutions that enhance security, as multi-factor authentication necessitates two or more verification methods.
However, the multi-factor authentication segment is expected to grow at a higher CAGR during the forecast period, due to its advanced security, adherence to compliance, and alignment with contemporary cybersecurity demands.
Market Share by Type of Solution
Based on type of solution, the zero trust security market is segmented into network security, data security, endpoint security, API security, cloud security, and others. According to our estimates, currently, the network security segment captures the majority of the market. Additionally, this segment is expected to grow at a higher CAGR during the forecast period. This growth can be attributed to the key features of zero trust security, such as micro-segmentation, network access control, and ongoing monitoring. These features are integral to zero trust security policies, which enhance the demand for network security solutions.
However, the data security segment is expected to grow at a higher CAGR during the forecast period, due to the increasing frequency of data breaches and cyber-attacks.
Market Share by Type of Deployment
Based on type of deployment, the zero trust security market is segmented into cloud-based and on-premises. According to our estimates, currently, the cloud-based segment captures the majority share of the market, due to the scalability and adaptability of cloud solutions, enabling organizations to modify resources as needed. Further, the capability of these solutions to integrate seamlessly with other cloud services and applications ensures centralized security management across hybrid and multi-cloud environments, driving the growth of this segment.
However, the on-premises segment is expected to grow at a higher CAGR during the forecast period. This can be attributed to the regulatory requirements, legacy systems, or the need for strict control over sensitive data in industries such as finance and healthcare, where on-premises security infrastructure is essential.
Market Share by Type of Offering
Based on type of offering, the zero trust security market is segmented into integrated platforms, standalone software, and services. According to our estimates, currently, the integrated platform captures the majority share of the market. This is due to the increasing demand for comprehensive solutions that offer a variety of security features, such as next-generation firewalls, identity and access management, and data loss prevention, all through a single platform.
However, the service segment is expected to grow at a higher CAGR during the forecast period, driven by the escalating need for expertise and managed security solutions in the coming years.
Market Share by Type of Service
Based on type of service, the zero trust security market is segmented into consulting and advisory services, implementation and integration services, managed services, training and support services. According to our estimates, currently, the implementation and integration segment captures the majority share of the market.
This is due to the benefits of this service in establishing identity and access management systems, network segmentation, and continuous monitoring tools ensure that zero trust security principles are effectively implemented. Given the increasing need for implementation and integration services, this segment is projected to experience significant growth during the forecast period.
Market Share by Type of Security Feature
Based on type of security feature, the zero trust security market is segmented into micro-segmentation, privileged access management (PAM), network segmentation, endpoint detection and response (EDR), cloud security posture management (CSPM), security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR). According to our estimates, currently, the privileged access management (PAM) captures the majority share of the market. This is due to their vital role in safeguarding sensitive data and minimizing insider threats by overseeing and controlling privileged accounts.
However, the endpoint detection and response (EDR) segment is expected to grow at a higher CAGR during the forecast period. This can be attributed to the escalating complexity and sophistication of cyber threats, which require advanced EDR solutions for real-time detection, investigation, and response to malicious activities.
Market Share by Type of End User
Based on type of end user, the zero trust security market is segmented into IT and telecoms, BFSI, manufacturing, healthcare, energy and power, retail, government, and others. According to our estimates, currently, the BFSI segment captures the majority share of the market. This is due to its heightened vulnerability to cybersecurity threats and stringent regulatory requirements. Additionally, the vast amount of sensitive information, from personal identification to financial transactions within the BFSI sector, makes it a prime target for cyberattacks.
However, the IT and telecom sector is expected to grow at a higher CAGR during the forecast period, as it emerges as a key industry for zero trust security solutions, with tech companies and telecom providers increasingly implementing these solutions to safeguard against industrial espionage and cyber threats aimed at their infrastructure.
Market Share by Company Size
Based on company size, the zero trust security market is segmented into small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and large enterprises. According to our estimates, currently, the large enterprise segment captures the majority share of the market. This is due to their considerable investments in cutting-edge security technologies and their efforts in establishing industry standards for strong cybersecurity practices.
Additionally, their ample resources facilitate the implementation of advanced zero trust security solutions, which not only improve their own security measures but also encourage smaller businesses and security providers to embrace similar approaches.
Market Share by Geographical Regions
Based on geographical regions, the zero trust security market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia, Latin America, Middle East and North Africa, and the rest of the world. According to our estimates, currently, North America captures the majority share of the market, due to the increased awareness of cybersecurity threats and the early adoption of innovative technologies in the region.
Meanwhile, Asia is projected to experience the highest compound annual growth rate during the forecast period, fueled by rapid digital transformation. In addition, a rise in cybersecurity incidents, increased government initiatives that emphasize zero trust security frameworks for safeguarding sensitive data, and significant investments in advanced security solutions are further driving the market in this region.
Example Players in Zero Trust Security Market
- Akamai Technologies
- Broadcom
- Centrify Corporation
- Check Point Software Technologies
- Cisco Systems
- CyberArk Software
- F5 Networks
- Fortinet
- Illumio
- Microsoft
- Okta
- Palo Alto Networks
- Proofpoint
- Pulse Secure
- SailPoint Technologies Holdings
- Sophos Group
- Symantec Corporation
- Trend Micro
- VMware
Zero Trust Security Market: Research Coverage
The report on the zero trust security market features insights on various sections, including:
- Market Sizing and Opportunity Analysis: An in-depth analysis of the zero trust security market, focusing on key market segments, including [A] type of authentication, [B] type of solution, [C] type of deployment, [D] type of offering, [E] type of service, [F] type of security feature, [G] type of end user, [H] company size, and [I] key geographical regions.
- Competitive Landscape: A comprehensive analysis of the companies engaged in the zero trust security market, based on several relevant parameters, such as [A] year of establishment, [B] company size, [C] location of headquarters and [D] ownership structure.
- Company Profiles: Elaborate profiles of prominent players engaged in the zero trust security market, providing details on [A] location of headquarters, [B] company size, [C] company mission, [D] company footprint, [E] management team, [F] contact details, [G] financial information, [H] operating business segments, [I] zero trust security portfolio, [J] moat analysis, [K] recent developments, and an informed future outlook.
- SWOT Analysis: An insightful SWOT framework, highlighting the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats in the domain. Additionally, it provides Harvey ball analysis, highlighting the relative impact of each SWOT parameter.
- Value Chain Analysis: A comprehensive analysis of the value chain, providing information on the different phases and stakeholders involved in the zero trust security market
Key Questions Answered in this Report
- How many companies are currently engaged in zero trust security market?
- Which are the leading companies in this market?
- What factors are likely to influence the evolution of this market?
- What is the current and future market size?
- What is the CAGR of this market?
- How is the current and future market opportunity likely to be distributed across key market segments?
Reasons to Buy this Report
- The report provides a comprehensive market analysis, offering detailed revenue projections of the overall market and its specific sub-segments. This information is valuable to both established market leaders and emerging entrants.
- Stakeholders can leverage the report to gain a deeper understanding of the competitive dynamics within the market. By analyzing the competitive landscape, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their market positioning and develop effective go-to-market strategies.
- The report offers stakeholders a comprehensive overview of the market, including key drivers, barriers, opportunities, and challenges. This information empowers stakeholders to stay abreast of market trends and make data-driven decisions to capitalize on growth prospects.
Additional Benefits
- Complimentary Excel Data Packs for all Analytical Modules in the Report
- 15% Free Content Customization
- Detailed Report Walkthrough Session with Research Team
- Free Updated report if the report is 6-12 months old or older
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. PREFACE
- 1.1. Introduction
- 1.2. Market Share Insights
- 1.3. Key Market Insights
- 1.4. Report Coverage
- 1.5. Key Questions Answered
- 1.6. Chapter Outlines
2. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1. Chapter Overview
- 2.2. Research Assumptions
- 2.3. Database Building
- 2.3.1. Data Collection
- 2.3.2. Data Validation
- 2.3.3. Data Analysis
- 2.4. Project Methodology
- 2.4.1. Secondary Research
- 2.4.1.1. Annual Reports
- 2.4.1.2. Academic Research Papers
- 2.4.1.3. Company Websites
- 2.4.1.4. Investor Presentations
- 2.4.1.5. Regulatory Filings
- 2.4.1.6. White Papers
- 2.4.1.7. Industry Publications
- 2.4.1.8. Conferences and Seminars
- 2.4.1.9. Government Portals
- 2.4.1.10. Media and Press Releases
- 2.4.1.11. Newsletters
- 2.4.1.12. Industry Databases
- 2.4.1.13. Roots Proprietary Databases
- 2.4.1.14. Paid Databases and Sources
- 2.4.1.15. Social Media Portals
- 2.4.1.16. Other Secondary Sources
- 2.4.2. Primary Research
- 2.4.2.1. Introduction
- 2.4.2.2. Types
- 2.4.2.2.1. Qualitative
- 2.4.2.2.2. Quantitative
- 2.4.2.3. Advantages
- 2.4.2.4. Techniques
- 2.4.2.4.1. Interviews
- 2.4.2.4.2. Surveys
- 2.4.2.4.3. Focus Groups
- 2.4.2.4.4. Observational Research
- 2.4.2.4.5. Social Media Interactions
- 2.4.2.5. Stakeholders
- 2.4.2.5.1. Company Executives (CXOs)
- 2.4.2.5.2. Board of Directors
- 2.4.2.5.3. Company Presidents and Vice Presidents
- 2.4.2.5.4. Key Opinion Leaders
- 2.4.2.5.4. Research and Development Heads
- 2.4.2.5.2. Technical Experts
- 2.4.2.5.3. Subject Matter Experts
- 2.4.2.5.4. Scientists
- 2.4.2.5.4. Doctors and Other Healthcare Providers
- 2.4.2.6. Ethics and Integrity
- 2.4.2.6.1. Research Ethics
- 2.4.2.6.2. Data Integrity
- 2.4.3. Analytical Tools and Databases
- 2.4.1. Secondary Research
3. ECONOMIC AND OTHER PROJECT SPECIFIC CONSIDERATIONS
- 3.1. Forecast Methodology
- 3.1.1. Top-Down Approach
- 3.1.2. Bottom-Up Approach
- 3.1.3. Hybrid Approach
- 3.2. Market Assessment Framework
- 3.2.1. Total Addressable Market (TAM)
- 3.2.2. Serviceable Addressable Market (SAM)
- 3.2.3. Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM)
- 3.2.4. Currently Acquired Market (CAM)
- 3.3. Forecasting Tools and Techniques
- 3.3.1. Qualitative Forecasting
- 3.3.2. Correlation
- 3.2.3. Regression
- 3.3.4. Time Series Analysis
- 3.3.5. Extrapolation
- 3.3.6. Convergence
- 3.3.7. Forecast Error Analysis
- 3.3.8. Data Visualization
- 3.3.9. Scenario Planning
- 3.3.10. Sensitivity Analysis
- 3.4. Key Considerations
- 3.4.1. Demographics
- 3.4.2. Market Access
- 3.4.3. Reimbursement Scenarios
- 3.4.4. Industry Consolidation
- 3.5. Robust Quality Control
- 3.6. Key Market Segmentations
- 3.7 Limitations
4. MACRO-ECONOMIC INDICATORS
- 4.1. Chapter Overview
- 4.2. Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1. Time Period
- 4.2.1.1. Historical Trends
- 4.2.1.2. Current and Forecasted Estimates
- 4.2.2. Currency Coverage
- 4.2.2.1. Overview of Major Currencies Affecting the Market
- 4.2.2.2. Impact of Currency Fluctuations on the Industry
- 4.2.3. Foreign Exchange Impact
- 4.2.3.1. Evaluation of Foreign Exchange Rates and Their Impact on Market
- 4.2.3.2. Strategies for Mitigating Foreign Exchange Risk
- 4.2.4. Recession
- 4.2.4.1. Historical Analysis of Past Recessions and Lessons Learnt
- 4.2.4.2. Assessment of Current Economic Conditions and Potential Impact on the Market
- 4.2.5. Inflation
- 4.2.5.1. Measurement and Analysis of Inflationary Pressures in the Economy
- 4.2.5.2. Potential Impact of Inflation on the Market Evolution
- 4.2.6. Interest Rates
- 4.2.5.1. Overview of Interest Rates and Their Impact on the Market
- 4.2.5.2. Strategies for Managing Interest Rate Risk
- 4.2.7. Commodity Flow Analysis
- 4.2.7.1. Type of Commodity
- 4.2.7.2. Origins and Destinations
- 4.2.7.3. Values and Weights
- 4.2.7.4. Modes of Transportation
- 4.2.8. Global Trade Dynamics
- 4.2.8.1. Import Scenario
- 4.2.8.2. Export Scenario
- 4.2.9. War Impact Analysis
- 4.2.9.1. Russian-Ukraine War
- 4.2.9.2. Israel-Hamas War
- 4.2.10. COVID Impact / Related Factors
- 4.2.10.1. Global Economic Impact
- 4.2.10.2. Industry-specific Impact
- 4.2.10.3. Government Response and Stimulus Measures
- 4.2.10.4. Future Outlook and Adaptation Strategies
- 4.2.11. Other Indicators
- 4.2.11.1. Fiscal Policy
- 4.2.11.2. Consumer Spending
- 4.2.11.3. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- 4.2.11.4. Employment
- 4.2.11.5. Taxes
- 4.2.11.6. R&D Innovation
- 4.2.11.7. Stock Market Performance
- 4.2.11.8. Supply Chain
- 4.2.11.9. Cross-Border Dynamics
- 4.2.1. Time Period
5. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
6. INTRODUCTION
- 6.1. Chapter Overview
- 6.2. Overview of Zero Trust Security
- 6.2.1. Key Characteristics of Zero Trust Security
- 6.2.2. Type of Authentication
- 6.2.3. Type of Solution
- 6.2.4. Type of Deployment
- 6.2.5. Type of Offering
- 6.2.6. Type of Security Feature
- 6.3. Future Perspective
7. COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1. Chapter Overview
- 7.2. Zero Trust Security: Overall Market Landscape
- 7.2.1. Analysis by Year of Establishment
- 7.2.2. Analysis by Company Size
- 7.2.3. Analysis by Location of Headquarters
- 7.2.4. Analysis by Ownership Structure
8. COMPANY PROFILES
- 8.1. Chapter Overview
- 8.2.1. Akamai Technologies*
- 8.2.1.1. Company Overview
- 8.2.1.2. Company Mission
- 8.2.1.3. Company Footprint
- 8.2.1.4. Management Team
- 8.2.1.5. Contact Details
- 8.2.1.6. Financial Performance
- 8.2.1.7. Operating Business Segments
- 8.2.1.7. Service / Product Portfolio (project specific)
- 8.2.1.9. MOAT Analysis
- 8.2.1.10. Recent Developments and Future Outlook
- 8.2.1. Akamai Technologies*
information in the public domain
- 8.2.2. Broadcom
- 8.2.3. Centrify Corporation
- 8.2.4. Cisco Systems
- 8.2.5. CyberArk Software
- 8.2.6. F5 Networks
- 8.2.7. Google
- 8.2.8. Illumio
- 8.2.9. Microsoft
- 8.2.10. Palo Alto Networks
- 8.2.11. Pulse Secure
- 8.2.12. Sophos Group
- 8.2.13. Trend Micro
- 8.2.14. VMware
9. VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
10. SWOT ANALYSIS
11. GLOBAL ZERO TRUST SECURITY MARKET
- 11.1. Chapter Overview
- 11.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 11.3. Trends Disruption Impacting Market
- 11.4. Global Zero Trust Security Market, Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 11.5. Multivariate Scenario Analysis
- 11.5.1. Conservative Scenario
- 11.5.2. Optimistic Scenario
- 11.6. Key Market Segmentations
12. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES BASED ON TYPE OF AUTHENTICATION
- 12.1. Chapter Overview
- 12.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 12.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 12.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 12.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 12.6. Zero Trust Security Market for Multifactor Authentication: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 12.7. Zero Trust Security Market for Single-factor Authentication: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 12.8. Data Triangulation and Validation
13. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES BASED ON TYPE OF SOLUTION
- 13.1. Chapter Overview
- 13.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 13.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 13.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 13.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 13.6. Zero Trust Security Market for API Security: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 13.7. Zero Trust Security Market for Cloud Security: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 13.8. Zero Trust Security Market for Data Security: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 13.9. Zero Trust Security Market for Endpoint Security: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 13.10. Zero Trust Security Market for Network Security: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 13.11. Zero Trust Security Market for Others: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 13.12. Data Triangulation and Validation
14. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES BASED ON TYPE OF DEPLOYEMENT
- 14.1. Chapter Overview
- 14.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 14.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 14.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 14.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 14.6. Zero Trust Security Market for Cloud-based Solutions: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.7. Zero Trust Security Market for On Premise Solutions: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 14.8. Data Triangulation and Validation
15. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES BASED ON TYPE OF OFFERING
- 15.1. Chapter Overview
- 15.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 15.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 15.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 15.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 15.6. Zero Trust Security Market for Integrated Platform: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 15.7. Zero Trust Security Market for Standalone Software: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 15.8. Zero Trust Security Market for Services: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 15.9. Data Triangulation and Validation
16. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES BASED ON TYPE OF SERVICE
- 16.1. Chapter Overview
- 16.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 16.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 16.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 16.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 16.6. Zero Trust Security Market for Consulting and Advisory: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.7. Zero Trust Security Market for Implementation and Integration: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.8. Zero Trust Security Market for Managed: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.9. Zero Trust Security Market for Training and Support: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 16.10. Data Triangulation and Validation
17. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES BASED ON TYPE OF SECURITY FEATURE
- 17.1. Chapter Overview
- 17.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 17.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 17.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 17.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 17.6. Zero Trust Security Market for Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.7. Zero Trust Security Market for Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.8. Zero Trust Security Market for Micro Segmentation: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.9. Zero Trust Security Market for Network Segmentation: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.10. Zero Trust Security Market for Privileged Access Management (PAM): Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.11. Zero Trust Security Market for Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR): Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.12. Zero Trust Security Market for Other Security Features: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 17.13. Data Triangulation and Validation
18. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES BASED ON TYPE OF END USER
- 18.1. Chapter Overview
- 18.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 18.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 18.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 18.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 18.6. Zero Trust Security Market for Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI): Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 18.7. Zero Trust Security Market for Energy and Power: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 18.8. Zero Trust Security Market for Government and Defense: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 18.9. Zero Trust Security Market for Healthcare: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 18.10. Zero Trust Security Market for IT and Telecom: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 18.11. Zero Trust Security Market for Manufacturing: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 18.12. Zero Trust Security Market for Retail: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 18.18. Data Triangulation and Validation
19. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES BASED ON COMPANY SIZE
- 19.1. Chapter Overview
- 19.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 19.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 19.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 19.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 19.6. Zero Trust Security Market for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 19.7. Zero Trust Security Market for Large Enterprises: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 19.8. Data Triangulation and Validation
20. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES FOR ZERO TRUST SECURITY IN NORTH AMERICA
- 20.1. Chapter Overview
- 20.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 20.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 20.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 20.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 20.6. Zero Trust Security Market in North America: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 20.6.1. Zero Trust Security Market in the US: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 20.6.2. Zero Trust Security Market in Canada: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 20.6.3. Zero Trust Security Market in Mexico: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 20.6.4. Zero Trust Security Market in Other North American Countries: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 20.7. Data Triangulation and Validation
21. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES FOR ZERO TRUST SECURITY IN EUROPE
- 21.1. Chapter Overview
- 21.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 21.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 21.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 21.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 21.6. Zero Trust Security Market in Europe: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.1. Zero Trust Security Market in the Austria: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.2. Zero Trust Security Market in Belgium: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.3. Zero Trust Security Market in Denmark: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.4. Zero Trust Security Market in France: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.5. Zero Trust Security Market in Germany: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.6. Zero Trust Security Market in Ireland: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.7. Zero Trust Security Market in Italy: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.8. Zero Trust Security Market in Netherlands: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.9. Zero Trust Security Market in Norway: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.10. Zero Trust Security Market in Russia: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.11. Zero Trust Security Market in Spain: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.12. Zero Trust Security Market in Sweden: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.13. Zero Trust Security Market in Switzerland: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.14. Zero Trust Security Market in the UK: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.6.15. Zero Trust Security Market in Other European Countries: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 21.7. Data Triangulation and Validation
22. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES FOR ZERO TRUST SECURITY IN ASIA
- 22.1. Chapter Overview
- 22.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 22.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 22.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 22.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 22.6. Zero Trust Security Market in Asia: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 22.6.1. Zero Trust Security Market in China: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 22.6.2. Zero Trust Security Market in India: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 22.6.3. Zero Trust Security Market in Japan: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 22.6.4. Zero Trust Security Market in Singapore: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 22.6.5. Zero Trust Security Market in South Korea: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 22.6.6. Zero Trust Security Market in Other Asian Countries: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 22.7. Data Triangulation and Validation
23. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES FOR ZERO TRUST SECURITY IN MIDDLE EAST AND NORTH AFRICA (MENA)
- 23.1. Chapter Overview
- 23.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 23.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 23.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 23.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 23.6. Zero Trust Security Market in Middle East and North Africa (MENA): Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 23.6.1. Zero Trust Security Market in Egypt: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 205)
- 23.6.2. Zero Trust Security Market in Iran: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 23.6.3. Zero Trust Security Market in Iraq: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 23.6.4. Zero Trust Security Market in Israel: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 23.6.5. Zero Trust Security Market in Kuwait: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 23.6.6. Zero Trust Security Market in Saudi Arabia: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 23.6.7. Zero Trust Security Market in United Arab Emirates ( UAE): Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 23.6.8. Zero Trust Security Market in Other MENA Countries: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 23.7. Data Triangulation and Validation
24. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES FOR ZERO TRUST SECURITY IN LATIN AMERICA
- 24.1. Chapter Overview
- 24.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 24.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 24.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 24.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 24.6. Zero Trust Security Market in Latin America: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 24.6.1. Zero Trust Security Market in Argentina: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 24.6.2. Zero Trust Security Market in Brazil: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 24.6.3. Zero Trust Security Market in Chile: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 24.6.4. Zero Trust Security Market in Colombia Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 24.6.5. Zero Trust Security Market in Venezuela: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 24.6.6. Zero Trust Security Market in Other Latin American Countries: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 24.7. Data Triangulation and Validation
25. MARKET OPPORTUNITIES FOR ZERO TRUST SECURITY IN REST OF THE WORLD
- 25.1. Chapter Overview
- 25.2. Key Assumptions and Methodology
- 25.3. Revenue Shift Analysis
- 25.4. Market Movement Analysis
- 25.5. Penetration-Growth (P-G) Matrix
- 25.6. Zero Trust Security Market in Rest of the World: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 25.6.1. Zero Trust Security Market in Australia: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 25.6.2. Zero Trust Security Market in New Zealand: Historical Trends (Since 2018) and Forecasted Estimates (Till 2035)
- 25.6.3. Zero Trust Security Market in Other Countries
- 25.7. Data Triangulation and Validation