
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1910892
貿易金融:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年)Trade Finance - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 貿易金融:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年) |
|
出版日: 2026年01月12日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 130 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
貿易金融市場の規模は、2026年には834億2,000万米ドルと推定されており、2025年の806億4,000万米ドルから成長が見込まれます。
2031年までの予測では988億3,000万米ドルに達し、2026年から2031年にかけてCAGR3.45%で成長すると見込まれています。
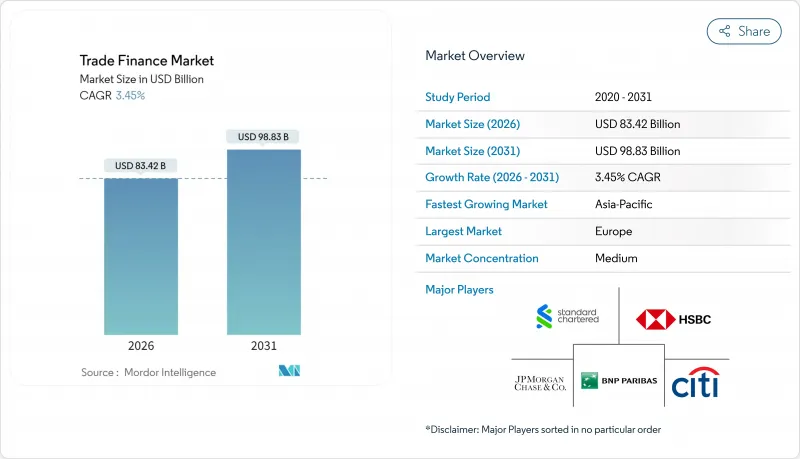
貿易金融市場における需要は、信用状が高リスク地域において依然として不可欠である一方で、デジタル化されたオープンアカウントソリューションへと移行しつつあります。電子譲渡可能記録に関するモデル法(MLETR)による規制の近代化とブロックチェーン技術の普及により、書類手続きの摩擦が軽減され、債権担保型金融商品への投資家の関心が高まっています。中小企業向け貿易金融における2兆5,000億米ドルの未解決の資金ギャップは、銀行に圧力をかけ続け、フィンテックの革新を促進しています。同時に、地政学的な緊張地域は貿易の流れを転換させ、マネーロンダリング対策(AML)のためのコンプライアンス支出を増加させています。
世界の貿易金融市場の動向と洞察
貿易のデジタル化とブロックチェーン導入
Contour社の稼働中ブロックチェーンネットワークは、信用状承認サイクルを10日間から24時間未満に短縮し、分散型台帳が具体的なプロセス効率化をもたらすことを実証しております。2025年9月にはSWIFTが、世界11,000以上の金融機関のリアルタイム決済データを記録するブロックチェーン台帳のプロトタイプを発表いたしました。トークン化により担保プールが拡大し、銀行は資本市場で貿易債権を再融資し、二次的な流動性を解放できるようになりました。こうした利点があるにもかかわらず、複数のクローズドループプラットフォームは「デジタルアイランド」を生み出し、企業はマルチネットワーク接続のために多額の統合予算を資金調達せざるを得ません。したがって、相互運用性ツールキットと共通データ標準は、ネットワーク全体の規模拡大のための前提条件となりつつあります。
越境電子商取引の拡大
B2B越境決済額は、急増するマーケットプレース調達を反映し、2030年までにCAGR5.6%で56兆米ドルに達すると予測されています。ウォルマート・ビジネスなどの小売業者は、TreviPayの信用取引条件を決済プロセスに直接組み込み、従来の銀行取引ラインを持たないサプライヤーのオンボーディング時間を短縮しています。買い手がデータ可視性を活用して支払リスクを管理するにつれ、信用状取引に代わってオープンアカウント構造が普及しつつあります。銀行にとっては、この変化に対応するため、信用判断を電子商取引ワークフローにリアルタイムでストリーミングできるAPI中心のプラットフォームが求められています。その結果、融資、決済、照合が単一のデジタルチャネルに統合された複合サービスモデルが生まれています。
厳格なAML/KYCコンプライアンス負担
大手銀行は現在、KYC審査に年間最大1億7,500万米ドルを費やしており、融資活動から資本が流れています。2025年7月に施行されるEUのAMLパッケージでは、直接的な執行権限を持つ新たな監督機関が導入され、100万ユーロを超える貿易取引の書類提出基準が引き上げられます。KYCワークフローを自動化している金融機関はわずか4%であり、このオンボーディング遅延により、67%の銀行がリスクの高い中小企業との取引を終了せざるを得ない状況です。軍民両用物品のチェックには、AIモデルによる部品表のスキャンと軍事用途のフラグ付けが求められますが、この機能は既存システムの多くが備えていません。コンプライアンス部門は高度な分析機能を統合しなければならず、さもなければデジタルネイティブの競合他社にシェアを奪われるリスクがあります。
セグメント分析
2025年時点で、貿易金融市場シェアの65.72%を書類取引商品が占めました。これは信用状が不安定な貿易ルートにおいて不可欠な不履行保護を提供するからです。しかしながら、スピードと低手数料を重視するオープンアカウント取引に後押しされ、非書類取引ソリューションはCAGR4.39%で拡大しています。非書類取引構造の貿易金融市場規模は、現在の採用曲線が維持されれば2031年までに361億米ドルを超える可能性があります。ブロックチェーン上のデジタル信用状は法的保護を維持しつつ決済期間を短縮し、オープンアカウントモデルとの効率格差を縮めています。企業が信用保険付売掛債権への信頼を高めるにつれ、成熟した貿易ルートでは書類取引への依存度が低下すると予想されます。
取引先間で確立された取引実績を共有するEU域内およびNAFTA域内の輸送ルートにおいて、オープンアカウント取引の成長が最も顕著です。サプライチェーンファイナンスプラットフォームは、紙ベースの文書取引プロセスでは非現実的な作業であった数百のサプライヤーの同時オンボーディングを簡素化します。しかしながら、新興アフリカ地域で事業を展開する輸入業者は、為替変動リスクやソブリンリスクの不確実性を軽減するため、引き続き銀行保証を要求しています。電子船荷証券データをスマートコントラクトに組み込んだハイブリッド製品は、リアルタイム貨物可視化を求める物流コングロマリット間で採用が進んでいます。接続性が向上する中、銀行は縮小する紙処理収益を補うため手数料体系の見直しを進めています。
2025年の貿易金融市場において、銀行は69.84%の収益シェアを掌握し、強固なバランスシートを活用して複数通貨にわたる高額信用状を支えました。しかしながら、フィンテック参入企業は、調達・ERPプラットフォームに組み込まれたAPI駆動型融資を提供することで、CAGR4.75%でシェアを拡大中です。フィンテック企業が提供する貿易金融市場規模は、大手銀行との提携が現在の勢いを維持すれば、2031年までに112億米ドルに達すると予測されています。銀行は規制資本とデジタルユーザー体験を融合させ、フィンテックのワークフローをホワイトラベル化するケースが増加しています。保険会社は、銀行およびフィンテックが創出したエクスポージャーの両方を支える信用リスクカバーを提供し、市場の回復力を支えています。
フィンテックプラットフォームは、代替データ分析による中小企業向けオンボーディングに優れており、本人確認(KYC)サイクル時間を数週間から数時間に短縮します。大手銀行は、機関向け事業基盤を保護しつつフィンテックのスピードに追随するため、トークン対応預金サービスへ投資しています。シティグループがFnalityの2025年シリーズCラウンドへ出資した事例のように、戦略的株式取得により、バランスシート規模とブロックチェーン技術革新を両立させています。このハイブリッド型エコシステムでは、銀行がプラットフォーム運営者となり、フィンテック企業が規制ライセンスを借り受けることで、競合の境界線が曖昧になります。貿易金融業界の融合が加速する可能性が高く、ネットワーク効果が強化され、新規参入スタートアップの参入障壁が高まるでしょう。
地域別分析
アジア太平洋地域は2025年に貿易金融市場シェアの38.12%を占め、地域の製造業基盤の厚さと先進的なデジタル貿易枠組みに支えられ、2031年までCAGR5.68%で推移すると予測されています。シンガポールのMLETR(電子貿易文書法)に基づく電子貿易文書の採用は、銀行がトークン化されたサプライチェーンプログラムを拡大する法的確実性を提供します。日本のTradeWaltzコンソーシアムは商社と保険会社を単一台帳に統合し、エンドツーエンドのデジタル化に向けた業界横断的な取り組みを示しています。中国の「一帯一路」プロジェクトは地政学的監視が高まる中でもインフラ関連融資を維持しています。インドの生産連動型奨励策(PLI)は輸出志向型製造業を加速させ、出荷前融資に対する国内需要を拡大しています。
北米は、米ドルの準備通貨としての役割と強力なフィンテック革新エコシステムにより、貿易金融市場で相当な取引量を占めています。GENIUS法はドル建てステーブルコイン決済に規制上の確実性を与え、現在平均7%の越境決済手数料を削減する可能性があります。メキシコはニアショアリング拠点として台頭しており、マキラドーラ輸出が運転資金需要の増加を牽引しています。カナダ銀行はNAFTA回廊の貿易データを活用し、世界の競合他社よりも競争力のある条件で売掛債権割引を引受けています。同地域の金融引き締め姿勢は無担保融資を制約する可能性がありますが、資産担保型融資構造は引き続き堅調に支えられています。
欧州では、AML(資金洗浄対策)監視の強化と決済分野における戦略的自律性推進という二重の課題に直面しています。9行からなるユーロ建てステーブルコインコンソーシアムは、2026年にMiCA準拠トークンを導入し商業決済に活用することで、ドル依存度の低減を目指しています。BNPパリバは欧州域内貿易金融の主導的立場を維持し、ブロックチェーン実証プログラムへ多額の投資を継続しています。ブレグジットの影響で資金の流れが再編される中、英国金融機関はアジア・中東との連携強化を推進しています。中東・アフリカ地域は高成長のニッチ市場であり、特にドバイのDIFCではトークン化された金が構造化信用状と取引されています。ただし、政治リスクプレミアムが広範な地域的な普及を抑制しています。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- アナリストによる3ヶ月間のサポート
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 貿易のデジタル化とブロックチェーン導入
- 越境電子商取引の拡大
- 世界の商品貿易量の増加
- 貿易債権の資本市場における証券化
- 電子貿易文書の法的承認(例:MLETR法)
- 組み込み型B2B決済及びバーチャルカードによる運転資金プログラム
- 市場抑制要因
- 厳格なAML/KYCコンプライアンス負担
- 地政学的貿易摩擦及び制裁
- フロンティア市場におけるコルレス銀行ネットワークの縮小
- 貿易信用保険料の上昇
- バリュー/サプライチェーン分析
- 規制情勢
- テクノロジーの展望
- ポーターのファイブフォース
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
第5章 市場規模と成長予測
- 製品タイプ別
- ドキュメンタリー
- ノンドキュメンタリー
- サービスプロバイダー別
- 銀行
- 貿易金融会社
- 保険会社
- その他のサービスプロバイダー
- 用途別
- 国内
- 国際
- 企業規模別
- 大企業
- 中小企業(SME)
- 資金調達構造別
- 構造化貿易金融
- 非構造化貿易金融
- 地域別
- 北米
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- 南米
- ブラジル
- ペルー
- チリ
- アルゼンチン
- その他南米
- 欧州
- 英国
- ドイツ
- フランス
- スペイン
- イタリア
- ベネルクス(ベルギー、オランダ、ルクセンブルク)
- 北欧諸国(デンマーク、フィンランド、アイスランド、ノルウェー、スウェーデン)
- その他欧州
- アジア太平洋
- インド
- 中国
- 日本
- オーストラリア
- 韓国
- 東南アジア(シンガポール、マレーシア、タイ、インドネシア、ベトナム、フィリピン)
- その他アジア太平洋
- 中東・アフリカ
- アラブ首長国連邦
- サウジアラビア
- 南アフリカ
- ナイジェリア
- その他中東・アフリカ
- 北米
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 戦略的動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- HSBC Holdings plc
- Citigroup Inc.
- BNP Paribas SA
- Standard Chartered PLC
- JPMorgan Chase & Co.
- Bank of America Corp.
- Deutsche Bank AG
- Banco Santander SA
- Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group Inc.
- Mizuho Financial Group Inc.
- Wells Fargo & Company
- Societe Generale SA
- Barclays PLC
- UBS Group AG
- Euler Hermes(Allianz Trade)
- Atradius N.V.
- Coface SA
- Tradeteq Ltd.
- Finastra Group Holdings Ltd.
- Komgo SA


