
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1690959
英国のサイバー(賠償責任)保険:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)UK Cyber (Liability) Insurance - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 英国のサイバー(賠償責任)保険:市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 145 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
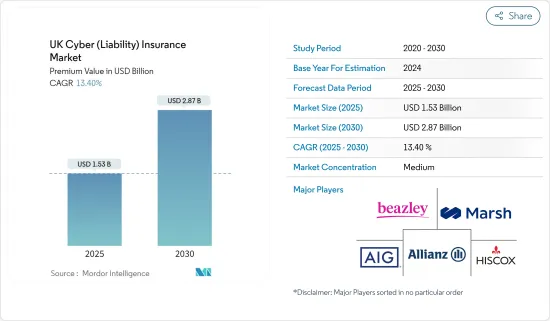
英国のサイバー保険の市場規模は、保険料ベースで2025年の15億3,000万米ドルから2030年には28億7,000万米ドルに成長し、予測期間(2025-2030年)のCAGRは13.4%となる見込みです。
保険の概念とリスク軽減という機能は時代とともに変わっていないが、保険は関連性を保ち、リスクの性質の変化に対応するために適応しなければならなくなりました。これには、保険会社が従来のように保険金を支払うだけでなく、保険契約を通じてサービスを提供することも含まれます。このような進化の結果、いくつかの新しい形態の保険が登場しました。サイバーリスクは、この10~20年の間に開発され、注目されるようになったが、これは、テクノロジーと接続性への依存度が高まっていることを考慮したものです。サイバー保険はさまざまなリスクに対応しています。一方の端には、データ詐欺、盗難、その他のプライバシー侵害など、頻度の高い「日常生活」タイプのリスクがあります。もう一方の端には、NotPetyaやWannacryのような「極端なシナリオ」タイプのリスクがあり、多くの企業に深刻な混乱をもたらす可能性があります。NotPetya攻撃では、ウイルスがユーザーのコンピューターを凍結させ、身代金の支払いを要求しました。英国のReckitt Benckiser社、オランダの配送会社TNT社、デンマークの海運大手Maersk社など、ウクライナと強い貿易関係を持つ企業が影響を受けました。 e WannaCryランサムウェア暗号ワームは、少なくとも150カ国にまたがる23万台以上のコンピュータを攻撃したと推定されています。この攻撃は、マイクロソフト・ウィンドウズの特定の脆弱性を利用してデータを暗号化し、身代金の支払いを要求しました。被害を受けたさまざまな部門や業界の中でも、最も大きな被害を受けた機関のひとつがNHSでした。NHSは、いまだに旧式のソフトウェアやオペレーティング・システムに大きく依存しており、攻撃に対して脆弱でした。
サイバー保険は、英国企業への直接的な利益だけでなく、広く経済への影響を通じて、英国経済において重要な役割を果たしてきたし、今後も果たしていくと思われます。今後数年間、サイバー保険市場は大きな開拓と急成長を続けると予想されます。これは、リスクに対する意識の高まりと、COVID-19の大流行によって一段と加速したビジネスのデジタル化という広範な傾向によるサイバー事象の発生頻度の増加を反映しています。このことは、サイバー犯罪の影響を受けやすいデータの量が増加するにつれて、データ・セキュリティに課題を突きつけています。コネクティビティの向上から生じる課題に取り組むため、サイバーリスクの範囲は拡大し続けることが予想されます。これを反映して、経済全体の機能におけるサイバー保険の関連性と重要性が大幅に高まることが予想されます。
英国のサイバー保険会社は、(英国のサイバー・セキュリティ企業とともに)リスク軽減と封じ込めのプロセスを適応させ、改善しています。こうした手法を企業と共有することで、英国のサイバー保険会社はサイバーインシデントがもたらすリスクの軽減に貢献することができます。サイバーリスクが複雑であることは、再保険がサイバー保険の供給を拡大する上で重要な役割を果たすことも意味します。
英国のサイバー保険市場の動向
サイバー保険のカバー範囲
最近まで、事業中断損失や物理的損害をカバーするサイバー保険商品は、一部の保険会社によってのみ提供されていました。しかし現在では、96%の保険会社が事業中断損失をカバーしており、第一当事者の損失もカバーする保険会社が増えています。サイバーリスクのダイナミックな性質や動向を反映して、補償内容は絶えず変化し、拡大しています。サイバー保険がカバーできるサイバーインシデントや損害の種類が増えるにつれ、英国企業がサイバー保険に投資するメリットも増加すると思われます。また、サイバー保険会社やブローカーは、特定の企業の保険ニーズを理解し、カバーを適切に調整できるようになってきています。サイバー保険の中には、被保険者が特定のサイバーセキュリティ基準を満たすこと、あるいはセキュリティ慣行の改善を証明することを求めるものもあります。これらの要件を満たさない場合、補償に影響が出る可能性があります。
破壊的なサイバーセキュリティ侵害が企業に与える影響
サイバー保険は通常、重大な侵害に関連するコストを完全にカバーできない可能性のある補償限度額を設定しています。企業は、保険限度額を超えても一定の費用を負担する責任を負う可能性があります。ほとんどのサイバー保険には免責金額が設定されており、保険が適用される前に企業が一定額を負担しなければなりません。免責金額の大きさは、組織の財政負担に大きく影響します。サイバー保険に加入していても、大規模なデータ漏洩は企業の評判を傷つける可能性があります。顧客やパートナーは組織に対する信頼を失い、ビジネスの損失や長期的な損害につながる可能性があります。サイバー保険は、情報漏えいに起因する一定の法的費用や罰金をカバーする可能性がありますが、すべての費用がカバーされるとは限りません。規制上の罰金や法的な和解は、依然として組織に大きな財務的影響を与える可能性があります。サイバー保険は、インシデント対応、フォレンジック調査、復旧作業のコストをカバーするのに役立ちます。しかし、これらのコストの全容を予測することは困難であり、保険は一部の側面しかカバーしない可能性があります。
英国のサイバー保険業界の概要
英国のサイバー保険業界は、既存の大手保険会社、サイバー専門の保険会社、インシュアテックの新興企業、仲介業者が混在し、サイバー賠償責任保険に対する需要の高まりに対応しているのが特徴でした。市場の競争は、サイバー脅威がもたらす特有の課題に対応するための保険設計やリスク評価手法の革新を促していました。技術的プラットフォームの採用と新技術へのアップグレードは、サイバー犯罪の脅威の増大につながります。COVID-19や都市化が一般市民を襲い、サイバー犯罪の脅威による損失リスクを軽減するためにサイバー保険を採用するようになると、イノベーションと技術進歩が加速しました。世界中の企業がこの分野の市場に巨額の投資を行っています。英国では、サイバー(賠償)保険市場には多くの企業があり、そのシェアは微々たるものです。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリスト・サポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場の洞察と力学
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- データプライバシー規制
- ビジネスの中断
- 市場抑制要因
- 複雑さと理解不足
- 補償コスト
- バリューチェーン分析
- 市場機会
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手/消費者の交渉力
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
- 市場における技術革新に関する洞察
- 消費者行動分析に関する洞察
- 市場における政府の規制
- COVID-19の市場への影響
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 製品タイプ別
- パッケージ
- スタンドアロン
- 用途タイプ別
- 銀行・金融サービス
- IT&テレコム
- ヘルスケア
- 小売
- その他
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度の概要
- 企業プロファイル
- AIG
- Allianz
- Beazley
- Hiscox
- Marsh
- Tokio Marine Kiln
- AXA XL
- CFC Underwriting
- NIG
- Zurich*
第7章 市場機会と今後の動向
第8章 免責事項
The UK Cyber Insurance Market size in terms of premium value is expected to grow from USD 1.53 billion in 2025 to USD 2.87 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 13.4% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

While the concept of insurance and its function of risk mitigation has remained the same over time, policies have had to adapt to stay relevant and accommodate the changing nature of risks. This includes insurance firms providing services throughout an insurance contract beyond solely paying out for claims as was traditionally the case. As a result of this evolution, several new forms of insurance have emerged-cyber insurance being one of them. Cyber risks have developed and gained increasing attention over the last 10-20 years, considering our increasing reliance on technology and connectivity. Cyber insurance caters to a spectrum of risks. At one end, there are higher-frequency, 'daily life '-type risks, such as data fraud, theft, or other privacy breaches. On the other end, there are 'extreme scenario '-type risks, such as NotPetya and Wannacry, which can result in severe disruption to many businesses. In the NotPetya attack, the virus froze the user's computer and demanded a ransom to be paid. Businesses with strong trade links with Ukraine, such as the UK's Reckitt Benckiser, Dutch delivery firm TNT, and Danish shipping giant Maersk, were affected. e WannaCry ransomware crypto-worm, which is estimated to have hit over 230,000 computers across at least 150 countries. The attack used a specific Microsoft Windows vulnerability to encrypt data and demand ransom payments. Among the range of sectors and industries hit, one of the largest agencies to suffer was the NHS, which was still largely reliant on outdated software and operating systems, making it vulnerable to attack.
Cyber insurance has and will continue to play an important role in the UK economy, both through the direct benefits to the UK business as well as the impact on the economy more broadly. Looking ahead, the cyber insurance market is expected to continue to undergo major development and rapid growth over the next few years, reflecting the increased awareness of risks as well as the likely increase in the frequency of cyber events driven by the broader trend of increasing digitization of businesses, which in part, were hastened by the COVID-19 pandemic. This poses challenges for data security as the quantity of data susceptible to cyber-crime increases. To tackle the challenges that arise from increasing connectivity, it is expected that coverage of cyber risks will continue to expand. To reflect this, the relevance and importance of cyber coverage in the overall functioning of the economy is expected to increase significantly.
The UK cyber insurers are adapting and improving their risk mitigation and containment processes (alongside UK cyber security firms). By sharing these techniques with businesses, UK cyber insurers can help to reduce the risks posed by cyber incidents. The complexity of cyber risks also means that reinsurance can play an important role in expanding the supply of cyber insurance.
UK Cyber Insurance Market Trends
Impact of Cyber Insurance Policy Coverage
Until recently, cyber insurance products covering business interruption losses and physical damage were only offered by a few insurers. Now, however, 96% of insurers cover business interruption losses, and an increasing number of insurers are also offering coverage for first-party losses. Coverage is continually changing and expanding to reflect the dynamic nature of cyber risks and trends. As the variety of cyber incidents and types of losses that cyber insurance increases can cover, the benefit to UK businesses of investing in cyber insurance will also likely increase. Cyber insurers and brokers are also becoming better able to understand a particular company's insurance needs, tailoring cover appropriately. Some cyber insurance policies may require the insured organization to meet specific cybersecurity standards or demonstrate improvements in security practices. Failing to meet these requirements could affect coverage.
Impact of Disruptive Cyber Security Breach for Businesses
Cyber insurance policies typically have coverage limits that may not fully cover the costs associated with a severe breach. Businesses may still be responsible for covering certain expenses beyond the policy limits. Most cyber insurance policies have deductibles, which means the business must pay a certain amount out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. The size of the deductible can significantly impact the financial burden on the organization. Even with cyber insurance, a major data breach can harm a business's reputation. Customers and partners may lose trust in the organization, leading to a loss of business and long-term damage. Cyber insurance may cover certain legal expenses and fines resulting from a breach, but not all costs may be covered. Regulatory fines and legal settlements can still have a significant financial impact on the organization. Cyber insurance can help cover the costs of incident response, forensic investigations, and recovery efforts. However, the full extent of these costs can be challenging to predict, and insurance may only cover some aspects.
UK Cyber Insurance Industry Overview
The UK cyber insurance landscape was characterized by a mix of established insurance giants, specialized cyber insurers, insurtech startups, and intermediaries working together to address the growing demand for cyber liability coverage. The market's competitive nature was driving innovation in policy design and risk assessment methodologies to meet the unique challenges posed by cyber threats. Adoption of technological platforms and up-gradation to new technology leads to an increase in the threat of cybercrimes. Innovation and technological advancement took pace as COVID-19 and urbanization struck general people to the adoption of cyber insurance to mitigate the risk of loss due to the threat of cybercrimes. Companies across the world have huge investments in this segment of the market. In the United Kingdom, the Cyber (liability) insurance market has many companies fragmented over minor shares. Swiss Re, Allianz, Beazley, Hiscox, Marsh, Tokio Marine Kiln, and AXA XL are among the cyber insurance companies.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS AND DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Data Privacy Regulations
- 4.2.2 Business Interruption
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Complexity and Lack of Understanding
- 4.3.2 Cost of Coverage
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Market Opportunities
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 Insights on Technological Innovations in the Market
- 4.8 Insights on Consumer Behavior Analysis
- 4.9 Government Regulation in Market
- 4.10 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Packaged
- 5.1.2 Standalone
- 5.2 By Application Type
- 5.2.1 Banking & Financial Services
- 5.2.2 IT & Telecom
- 5.2.3 Healthcare
- 5.2.4 Retail
- 5.2.5 Other Application Types
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 AIG
- 6.2.2 Allianz
- 6.2.3 Beazley
- 6.2.4 Hiscox
- 6.2.5 Marsh
- 6.2.6 Tokio Marine Kiln
- 6.2.7 AXA XL
- 6.2.8 CFC Underwriting
- 6.2.9 NIG
- 6.2.10 Zurich*


