
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1683907
中東欧のクーリエ・エクスプレス・パーセル(CEP):市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 中東欧のクーリエ・エクスプレス・パーセル(CEP):市場シェア分析、産業動向・統計、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年03月18日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 350 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
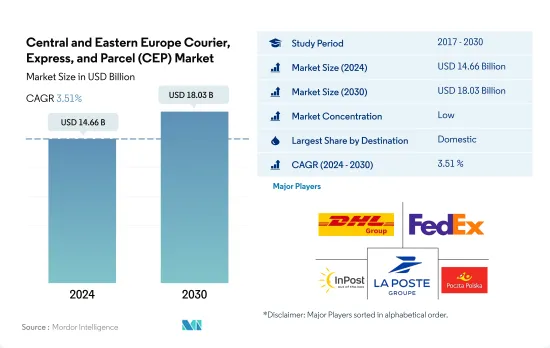
中東欧のクーリエ・エクスプレス・パーセル(CEP)市場規模は2024年に146億6,000万米ドルと推定・予測され、2030年には180億3,000万米ドルに達し、予測期間中(2024~2030年)のCAGRは3.51%で成長すると予測されます。
サービス拡大、料金引き下げ、eコマース利用の拡大により、CEP分野は同地域で開発中
- 2022年、ハンガリーのCEP事業者は同分野の開発に乗り出しました。例えば、ハンガリーの事業者であるMagyar Posta社は、2022年にLeonardo社の新しい仕分けシステムを導入し、物流能力を増強しました。レオナルドは、小包や小包の自動化ソリューションの大手プロバイダーです。2023年中に供給されるこのシステムは、国内および国際小包を処理するように設計されており、年間最大1億個の小包を処理できる可能性があります。また、ハンガリーを拠点とするFoxPostは、ハンガリーで2万社の企業にサービスを提供しており、ハンガリー国内に2500の小包ロッカーがあります。
- 欧州の主要オンライン・ファッション・ライフスタイル・プラットフォームであるZalandoは、2021年にチェコの物流・テクノロジー企業Zasilkovnaと提携しました。この動きは、チェコの4人に1人が受け取り場所を選び、小包ロッカーでの受け取りを好む傾向が3年間で0%から6%に上昇したというチェコの顧客の嗜好の変化に対応するものです。この提携により、Zalandoの顧客は1,500カ所のZasilkovnaロッカーと4,700カ所のピックアップポイントを利用することができ、支払い方法の1つとして代金引換を選択することができます。その目的は、チェコの顧客の嗜好に対応し、チェコの顧客に利便性を提供することです。また、ウクライナの大手郵便事業者であるノヴァ・ポシュタ社は、2022年にポーランドへ個人的な物品を送る際の関税を2.5倍に引き下げたが、これは戦争の影響でポーランドに滞在するウクライナ人の数が増加したためです。
- eコマースは、この地域におけるCEP需要の主要な推進力です。例えば、スロバキアのオンライン消費者の85.07%は、2022年にオンラインで購入する可能性が最も高いです。ルーマニアとブルガリアのインターネット・ユーザーのシェアは、2022年にそれぞれ51.46%と48.78%に達しました。スロバキアでは2027年までにeコマースユーザーの普及率が318万人に達するため、CEPの需要も同地域で増加すると予測されます。
CEE地域のeコマース市場は2022年に346億3,000万米ドルに達し、CEP配送の需要を生み出します。
- CEE地域のeコマース市場は2022年に346億3,000万米ドルに達し、ファッション分野が31.68%、エレクトロニクス分野が28.10%で収益シェアをリードしています。2022年には、ポーランド(278億米ドル)のeコマースシェアが同地域で最も高く、チェコ(130億米ドル)がこれに続きます。2022年には、スロバキアの住民(85%)がCEE諸国で最もオンラインショッピングを利用する可能性が高いです。スロバキアの人々がオンラインで買い物をする割合は、2022年のEU平均と比べて10%高かったです。チェコ、ハンガリー、エストニアは、EU27カ国の中でeコマースの利用率が平均以上と評価されました。
- ポーランドもまた、この地域で国内および国際エクスプレス・デリバリー・サービスを提供している国です。国営郵便サービスであるPoczta Polskaは、速達郵便サービス(EMS)を通じてこれらのサービスを提供しています。Poczta Polskaは、170カ国以上にEMSによるドアツードアの国際エクスプレス配達を提供しています。国内および国際貨物の最大重量は20kgです。チェコ共和国とスロバキアは近いため、国営郵便はチェコ共和国とスロバキアに配達されるEMS貨物の料金を特別に安くしています。
- 需要の増加により、ルーマニアはこの地域で国内および国際エクスプレス配達サービスを提供している国のひとつとなっています。ルーマニアの国営郵便であるルーマニア郵便は、EMSを通じてこのサービスを提供しています。国内配送の重量制限は、通常の小包で15キロ、目に見えない内容物で20キロです。国際スピード郵便は、ルーマニアから約105カ国への国際配達に対応しています。国際宅配便は、ルーマニアから約105カ国への配達が可能で、配達時の最大重量は31.5kgです。
中東欧のクーリエ・エクスプレス・パーセル(CEP)市場動向
アルバニアは世界的課題の中で成長鈍化に直面、一方ブルガリア、チェコ、ポーランドはインパクトの大きいインフラ投資を強化
- 世界銀行は、アルバニアの2023年の経済成長率をわずか2.2%と予測しています。ウクライナ戦争やエネルギー危機の深刻化、ユーロ圏の景気後退を引き起こし、輸送コストが上昇する可能性があるため、アルバニアの経済成長は2024年にはさらに弱まる可能性があります。しかしブルガリアは、ブルガリアの復興・強靭化計画(RRP)に割り当てられた15億米ドルに加え、11億米ドルと4億3,100万米ドルを国家基金から拠出し、3つのプロジェクトに投資しました。これには、ルセ郊外に2026年までに完成する予定の地域間ハブの建設が含まれます。
- 2023年、チェコ共和国は、100km以上の高速道路と18kmのi級道路の建設計画を含む、最大118kmの新しい高速道路を開通させる予定でした。この戦略により、交通渋滞の緩和、移動時間の短縮、交通安全の向上が期待されます。また、高速道路や道路建設プロジェクトは、新たな雇用を創出し、国の経済成長を後押しするなど、大きな経済効果をもたらす可能性があります。交通インフラが改善されれば、アクセシビリティとコネクティビティも向上し、企業が国中を商品やサービスを移動しやすくなる可能性もあります。
- ポーランド政府は、鉄道インフラに175億米ドル、道路インフラに366億米ドルの投資を計画しています。国道・自動車道総局(GDDKiA)、ポーランド鉄道PKP SA、ポーランド鉄道ネットワーク(PKP-PLK)、経済開発・技術省、インフラストラクチャー省などの主な組織が、全国または特定地域にまたがるプロジェクトを担当しています。
ブルガリアの公益事業規制当局の承認後、ガス料金は税抜きで30.7%値下げ
- ハンガリーは、エネルギー価格を低く抑えるための価格規制策を実施し、その結果、欧州で最も安いガス・電気料金の1つとなっています。ハンガリーのガス料金は、年間1,729立方メートルまで約0.25ユーロ(0.26米ドル)の割引単価で購入できます。一方、ユーロ圏で最もインフレ率の高いエストニアは、エネルギーコストの上昇に苦慮しており、政府は2024年4月まで電力と燃料の物品税を凍結し、燃料への減税など他の対策を検討することで、家計への影響を緩和する計画です。
- 2021年、天然ガス価格は2020年から49.41%上昇しました。ロシア・ウクライナ戦争の影響で天然ガス価格は約7倍、石炭価格は約4倍に上昇し、エネルギー情勢が不安定になり、特にエストニア、リトアニア、ラトビアのバルト3国では消費者物価のインフレが進みました。2023年6月には、エストニアが1リットル当たり1.84米ドルと中東欧諸国の中で最も高いガソリン価格を記録し、アルバニアが1リットル当たり1.79米ドルでこれに続いた。
- 2023年、ブルガリアの公益事業規制当局は、2月の規制ガス価格の30.7%引き下げを承認し、その結果、新価格は1MWh当たり124.34BGN(67.8米ドル)となった(輸送費、物品税、付加価値税を除く)。今回の値下げは、欧州の温暖な気候と十分なガス貯蔵量を背景に、国際ガス市場の価格が低下したことによる。この値下げは多くの消費者に恩恵をもたらすと予想され、規制当局は冬の暖房シーズンの残りの期間、セントラルヒーティングの価格を維持することを決定しました。
中東欧のクーリエ・エクスプレス・パーセル(CEP)業界概要
中東欧のクーリエ・エクスプレス・パーセル(CEP)市場は断片化されており、上位5社で31.80%を占めています。この市場の主要企業は以下の通り。 DHL Group, FedEx, InPost, La Poste Group and Poczta Polska SA(sorted alphabetically).
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- アナリストによる3ヶ月間のサポート
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリーと主な調査結果
第2章 レポートのオファー
第3章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場定義
- 調査範囲
- 調査手法
第4章 主要産業動向
- 人口動態
- 経済活動別GDP分布
- 経済活動別GDP成長率
- インフレ率
- 経済パフォーマンスとプロファイル
- eコマース産業の動向
- 製造業の動向
- 運輸・倉庫業のGDP
- 輸出動向
- 輸入動向
- 燃料価格
- 物流実績
- インフラ
- 規制の枠組み
- 中東欧(CEE)
- バリューチェーンと流通チャネル分析
第5章 市場セグメンテーション
- 仕向地
- 国内
- 国際
- 配達速度
- エクスプレス
- 非エクスプレス
- モデル
- 企業間(B2B)
- 企業対消費者(B2C)
- 消費者間(C2C)
- 出荷重量
- 重量貨物
- 軽量貨物
- 中量貨物
- 輸送形態
- 航空便
- 道路
- その他
- エンドユーザー
- eコマース
- 金融サービス(BFSI)
- ヘルスケア
- 製造業
- 第一次産業
- 卸売・小売業(オフライン)
- その他
- 国名
- アルバニア
- ブルガリア
- クロアチア
- チェコ共和国
- エストニア
- ハンガリー
- ラトビア
- リトアニア
- ポーランド
- ルーマニア
- スロバキア共和国
- スロベニア
- その他のCEE
第6章 競争情勢
- 主要な戦略的動き
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業情勢
- 企業プロファイル
- CARGUS SRL
- DHL Group
- Fan Courier
- FedEx
- InPost
- International Distributions Services(including GLS)
- La Poste Group
- Poczta Polska SA
- Posta Romana SA
第7章 CEOへの主な戦略的質問
第8章 付録
- 世界概要
- 概要
- ファイブフォース分析フレームワーク
- 世界のバリューチェーン分析
- 市場力学(DROs)
- 技術の進歩
- 情報源と参考文献
- 図表リスト
- 主要洞察
- データパック
- 用語集
The Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market size is estimated at 14.66 billion USD in 2024, and is expected to reach 18.03 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 3.51% during the forecast period (2024-2030).

Developing CEP segment in the region owing to services expansion, reducing tariffs, and growing e-commerce usage
- In 2022, CEP players in Hungary have taken the initiative to develop the segment. For instance, Hungarian operator Magyar Posta increased its distribution capacity with Leonardo's new sorting system in 2022. Leonardo is a major provider of automated solutions for small packets and parcels. The system, which would be supplied during 2023, is designed to process domestic and international parcels, wherein it could potentially process up to 100 million parcels a year. Also, Hungary-based FoxPost serves 20,000 businesses in Hungary, with 2,500 parcel lockers in Hungary.
- Zalando, Europe's leading online fashion and lifestyle platform, partnered with local logistics and technology Czech company Zasilkovna in 2021. The move responds to the shift in preferences of Czech customers wherein 1 in 4 Czechs chose pick-up points, and the preference for pick-up via parcel lockers rose from 0% to 6% in 3 years. Through the partnership, Zalando customers can use 1,500 Zasilkovna lockers and 4,700 pick-up points, with cash on delivery as one of the payment options. The aim is to cater to local customer preferences and provide convenience to Czech customers. Also, Nova Poshta, a major Ukrainian postal carrier, made a 2.5-fold reduction in tariffs for sending personal items to Poland in 2022, and this was done owing to the rise in the number of Ukrainians in Poland due to the war.
- E-commerce is a major driver for CEP demand in the region. For instance, 85.07% of online consumers in Slovakia were most likely to make purchases online in 2022. Share of internet users in Romania and Bulgaria stood at 51.46% and 48.78%, respectively, in 2022. With e-commerce user penetration to touch 3.18 million by 2027 in Slovakia, the demand for CEP is also projected to rise in the region.
E-commerce market in the CEE region hit USD 34.63 billion in 2022 generating the demand for CEP deliveries
- The e-commerce market in the CEE region reached a value of USD 34.63 billion in 2022, with the fashion and electronics segments leading the revenue shares with 31.68% and 28.10%, respectively. In 2022, Poland (USD 27.80 billion) had the highest e-commerce share in the region, followed by Czechia (USD 13 billion). In 2022, residents of Slovakia (85%) were the most likely to shop online in CEE countries. The percentage of people in Slovakia shopping online was 10% higher compared to the EU average in 2022. Czechia, Hungary, and Estonia were rated above average for using e-commerce among the 27 EU countries.
- Poland is another country in the region providing domestic and international express delivery services. Poczta Polska, the national postal service, provides these services via express mail service (EMS). Poczta Polska facilitates door-to-door international express deliveries via EMS to over 170 countries. The maximum weight of shipments of domestic and international goods is 20 kg. The national postal service has special lowered rates for EMS shipments being delivered to the Czech Republic and Slovakia due to their proximity.
- Due to increased demand, Romania is one of the countries in the region providing domestic and international express delivery services. The Romanian Post, the national postal service, provides this service via its EMS. The domestic delivery weight limit is 15 kg for ordinary parcels and 20 kg for invisible contents. The express delivery service can cater to international deliveries to about 105 countries from Romania. The maximum weight of parcels for these shipments at the time of posting and delivery should be 31.5 kg.
Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market Trends
Albania faces slower growth amid global challenges, while Bulgaria, Czech Republic, and Poland ramp up high-impact infrastructure investments
- The World Bank predicts that Albania's economy will grow by only 2.2% in 2023. Albania's economic growth may be even weaker in 2024 due to the war in Ukraine and the energy crisis deepening and causing an economic downturn in the eurozone, which may increase transportation costs. However, Bulgaria invested in three projects with USD 1.5 billion allocated to Bulgaria's Recovery and Resilience Plan (RRP), along with USD 1.1 billion and USD 431 million from National Funding. This includes the construction of an intermodular regional hub outside of Rousse, which is expected to be finished by 2026.
- In 2023, the Czech Republic was expected to open up to 118 km of new highway stretches, including a plan to build over 100 km of highway and 18 km of Class I road. This strategy is expected to reduce traffic congestion, reduce travel time, and improve road safety. The highway and road construction projects may also have a significant economic impact, creating new jobs and boosting the country's economic growth. Improved transportation infrastructure may also enhance accessibility and connectivity, making it easier for businesses to move goods and services across the country.
- The Polish government plans to invest USD 17.5 billion in railway infrastructure and USD 36.6 billion in road infrastructure. The key organizations, such as the General Directorate of National Roads and Motorways (GDDKiA), Polish Railway PKP SA, Polish Railway Networks (PKP-PLK), and the Ministry of Economic Development and Technology and the Ministry of Infrastructure, are taking charge of projects spanning across the nation or specific regions.
Post approval from Bulgaria's utilities regulator, gas prices reduced by 30.7%, excluding taxes
- Hungary has implemented price regulation measures to keep energy prices low, resulting in one of the lowest gas and electricity prices in Europe. Gas prices in Hungary are available at a reduced unit price of approximately EUR 0.25 (USD 0.26) for up to 1,729 cubic meters per year. On the other hand, Estonia, which has the highest inflation rate in the Eurozone, struggles with rising energy costs, and the government plans to alleviate the impact on households by freezing excise duty on electricity and fuel until April 2024 and considering other measures, such as reducing taxes on fuels.
- In 2021, the price of natural gas increased by 49.41%, up from 2020. The price of natural gas increased by almost seven times, and coal prices quadrupled due to the Russian-Ukraine War, leading to an unstable energy situation and increased consumer price inflation, particularly in the Baltic countries of Estonia, Lithuania, and Latvia. In June 2023, Estonia recorded the highest gasoline prices among Central and Eastern European countries, at 1.84 USD per liter, followed by Albania at 1.79 USD/liter.
- In 2023, Bulgaria's utilities regulator gave its approval for a reduction of 30.7% in the regulated gas price for February, resulting in a new price of BGN 124.34 (USD 67.8) per MWh (excluding transportation costs, excise, and value-added tax). The price reduction is attributed to the lower prices in international gas markets, owing to warm weather and sufficient gas storage in Europe. This price reduction is expected to benefit significant consumers, and the regulator has decided to maintain central heating prices for the rest of the winter heating season.
Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Industry Overview
The Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 31.80%. The major players in this market are DHL Group, FedEx, InPost, La Poste Group and Poczta Polska SA (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Demographics
- 4.2 GDP Distribution By Economic Activity
- 4.3 GDP Growth By Economic Activity
- 4.4 Inflation
- 4.5 Economic Performance And Profile
- 4.5.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.5.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6 Transport And Storage Sector GDP
- 4.7 Export Trends
- 4.8 Import Trends
- 4.9 Fuel Price
- 4.10 Logistics Performance
- 4.11 Infrastructure
- 4.12 Regulatory Framework
- 4.12.1 Central and Eastern Europe (CEE)
- 4.13 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes Market Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed Of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode Of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
- 5.7 Country
- 5.7.1 Albania
- 5.7.2 Bulgaria
- 5.7.3 Croatia
- 5.7.4 Czech Republic
- 5.7.5 Estonia
- 5.7.6 Hungary
- 5.7.7 Latvia
- 5.7.8 Lithuania
- 5.7.9 Poland
- 5.7.10 Romania
- 5.7.11 Slovak Republic
- 5.7.12 Slovenia
- 5.7.13 Rest of CEE
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 CARGUS SRL
- 6.4.2 DHL Group
- 6.4.3 Fan Courier
- 6.4.4 FedEx
- 6.4.5 InPost
- 6.4.6 International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- 6.4.7 La Poste Group
- 6.4.8 Poczta Polska SA
- 6.4.9 Posta Romana SA
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR CEP CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.1.5 Technological Advancements
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms


