
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1640605
アジア太平洋のインフラセクター-市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025年~2030年)Infrastructure Sector In Asia Pacific - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| アジア太平洋のインフラセクター-市場シェア分析、産業動向、成長予測(2025年~2030年) |
|
出版日: 2025年01月05日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 120 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
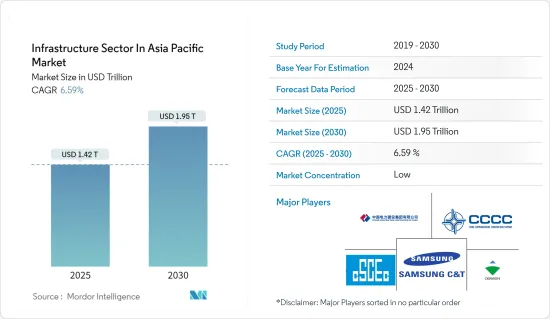
アジア太平洋のインフラセクター市場規模は2025年に1兆4,200億米ドルと推定され、予測期間(2025~2030年)のCAGRは6.59%で、2030年には1兆9,500億米ドルに達すると予測されます。
東南アジアではインフラセクターブームが起きており、ベトナム、タイ、フィリピン、マレーシア、インドネシアで大規模なプロジェクトが受け入れられています。それらは多くの場合、日本と中国による融資やその他の支援によって支えられています。日本と中国の東南アジアへの1年間の投資の区別は、ストーリーの一部に過ぎないです。中国のASEANインフラセクターへの投資は、近年急速に増加しています。
インド経済の屋台骨であるインフラセクター部門は、国家全体の開発向上に不可欠です。その他の産業サブセグメントには、電話、電力、道路、港湾などが含まれます。インドは、2025年の経済成長目標である5兆米ドルを達成するために、インフラセクターを強化しなければならないです。国家インフラセクターパイプライン(NIP)は、「Make in India」や生産連動型インセンティブ(PLI)プログラムなどの他のイニシアチブとともに、インフラセクター産業の拡大を促進するために政府によって開始されました。PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan(NMP)の下、44の中央省庁と36の州/UTが参加し、合計1,614のデータレイヤーが統合されました。データの正確性を維持するため、主要なインフラセクター省庁は、3階層システムの中で標準作業手順書(SOP)を制定しました。SOPは8つのインフラセクター省庁と15の社会セクター省庁に正式に通知されており、その他の省庁や州・自治体については開発作業が進行中です。
日本の国土交通省(MLIT)は、国のインフラセクター管理において極めて重要な役割を果たしています。国土交通省によれば、リスクのあるインフラセクターを積極的に検知し対処することで、重大事故を未然に防ぎ、保守・更新コストを47%削減することができ、2048年までに460億米ドルの節約の可能性があるといいます。これを踏まえ、国土交通省は2021年からインフラセクターのデジタルトランスフォーメーション(DX)を提唱し、インフラセクター管理の責任主体である自治体に対し、先進的な点検技術の採用と導入を促しています。2023年には、73万を超える橋梁、1万1,000のトンネル、1万の水門、47万メートルの下水道管、5,000の港湾岸壁が50年の節目を迎えます。この老朽化したインフラセクターがもたらす課題は、関連する事故と相まって、政府と国民の両方からのモニタリングを強めています。
全体として、地域のインフラセクター投資の展望は非常に有望です。COVID-19は、この地域全体のインフラセクター開発と資金調達にかなりの影響を与えたが、その変化の一部は、プロジェクトの貸し手や投資家にとって有益です。疫病の流行は、低炭素で気候変動に強いインフラセクターや、インターネット接続や公衆衛生を改善する取り組みへの投資を急がせた。ESGとデジタル化という2つのセグメントは、当分の間、インフラセクターセグメントを支配し続けると考えられます。
アジア太平洋のインフラセクター市場の動向
交通インフラセクターセグメントへの投資の増加
最先端の交通インフラセクターで有名な日本は、長期的なインフラセクター需要のための資金確保に大胆な動きを見せています。日本は、整備された道路や効率的な空港とともに、新幹線という大規模な高速鉄道網を誇っています。現在進行中の投資は、これらのシステムの拡大と近代化を目指しています。東京の羽田空港と成田空港は、航空交通量の増加と観光客の増加に対応するため、大幅な拡大と改修が行われています。強化の焦点は、旅客施設のアップグレードと滑走路容量の増強です。トラック運転手不足に対処するため、日本は、東京から大阪まで伸びる「ベルトコンベアロード」と呼ばれる自動貨物輸送回廊の建設を計画しています。間もなく試運転が開始され、2030年代半ばにはフル稼働する予定です。この最新鋭の回廊は、空港、鉄道、港をシームレスに結ぶ無人自動輸送システムを特徴とします。
Parvatmala Pariyojana全国ロープウェイ開発計画の下、インド政府は200以上のプロジェクトを発表しており、今後5年間の割り当て総額は12億5,000万インドルピー(147億7,000万米ドル)です。2024年、連邦内閣は、パンジャブ州とラジャスタン州の国境地帯に2,280kmの道路を建設することを目的とした440億6,000万インドルピー(5億2,000万米ドル)の構想を承認しました。インドでは、道路と高速道路が交通部門の大半を占め、鉄道と都市公共交通が僅差でこれに続きます。政府は、2025年までに2,000kmの国道網を開発し、空港の数を220に拡大するなど、交通部門に野心的な目標を設定しています。さらに、2030年までに23の水路を開通させ、35の複合一貫物流パーク(MMLP)を開発する計画もあります。インフラセクター関連省庁の予算支出総額は、23年度の約37億インドルピー(437億4,000万米ドル)から24年度には51億インドルピー(591億1,000万米ドル)に増加し、さまざまな交通サブセグメントで民間セクターに投資機会をもたらしています。
著しい成長を遂げる中国のインフラセクター
2023年の時点で、中国の農村道路は合計460万kmに及んでいた。このうち舗装道路は422万kmに及び、農村部の道路網全体の91.8%を占めています。これは過去10年間で27.2%の大幅な増加を示しています。さらに、約3万の鎮と50万を超える行政村に舗装道路が整備され、農村部におけるアクセシビリティの向上を裏付けています。
中国の最新の再生可能エネルギー構想は、2025年と2030年の大胆な消費目標を設定しています。単に容量を導入することを中心とした以前の計画とは異なり、この新しいアプローチは、再生可能エネルギーの利用を強化することを優先しています。これは、インフラセクターを改善し、輸送、農業、製造業などさまざまなセグメントに自然エネルギーを統合することで達成されます。この戦略的軸足の結果、グリーン技術、送電網の近代化、広範なクリーンエネルギーセグメントで、大きなビジネス展望が期待されます。
しかし、中国は2024年、債務処理の課題の高まりに悩む12地域でインフラセクター支出を縮小しました。中央政府は地方政府の債務リスクの抑制を優先しています。今年初め、中央政府はこれらの12地域に対し、政府主導の特定のインフラセクター構想を延期または中止するよう指示し、債務問題の深刻化を緩和することを目指しました。
アジア太平洋のインフラセクター産業概要
市場はセグメント化されており、新規参入企業の多くが、市場の主要企業としての地位を強化するため、プロジェクトの獲得に注力しています。
市場の主要企業は、China State Construction Engineering、China Communications Construction Company、Power Construction Corporation of China、Samsung C&T、Obayashi Corporationです。
その他の特典
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- 3ヶ月間のアナリストサポート
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の成果
- 調査の前提
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場洞察
- 市場概要
- 産業の規制と施策
- 政府の規制と取り組み
- サプライチェーン/バリューチェーン分析
- アジア太平洋のインフラセクターセグメントにおける技術革新に関する洞察
- 地政学とパンデミックが市場に与える影響
第5章 市場力学
- 市場促進要因
- 各国政府からの旺盛な投資流入
- アジア太平洋諸国の人口増加
- 市場抑制要因
- 限られた公共予算と民間投資の誘致難
- 土地取得の遅れ
- 市場機会
- モバイルとインターネットの急速な普及
- 強力な都市化プロジェクトのパイプライン
- 産業の魅力-ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 買い手/消費者の交渉力
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係の強さ
第6章 市場セグメンテーション
- 社会インフラセクター
- 学校
- 病院
- 国防
- その他の社会インフラセクター
- 交通インフラセクター
- 鉄道
- 道路
- 空港
- 水路
- 採掘インフラセクター
- 発電
- 送電・配電
- 水
- ガス
- 通信
- 製造インフラセクター
- 金属・鉱石生産
- 石油精製
- 化学製造
- 工業団地とクラスター
- その他の製造インフラセクター
- 国名
- 中国
- インド
- フィリピン
- 日本
- 韓国
- その他のアジア太平洋
第7章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度概要
- 企業プロファイル
- China State Construction Engineering
- China Communications Construction Company
- Power Construction Corporation of China
- Samsung C&T
- Obayashi Corporation
- Shanghai Construction Group
- Hyundai E&C
- China Petroleum Engineering Corporation
- L&T
- China Metallurgical Group*
- その他の企業
第8章 市場機会と今後の動向
第9章 付録
- マクロ経済指標(GDP分布、活動別)
- 経済統計-運輸・倉庫業の経済への貢献
- 対外貿易統計-輸出・輸入(製品別)
The Infrastructure Sector In Asia Pacific Market size is estimated at USD 1.42 trillion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 1.95 trillion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.59% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Southeast Asia is experiencing a boom in infrastructure, with major projects in Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Indonesia accepted. Those were supported in many cases by loans and other assistance provided by Japan and China. The distinction between Japan and China's one-year investment in Southeast Asia represents just part of the story. China's investments in ASEAN infrastructure have risen rapidly in recent years.
The backbone of the Indian economy, the infrastructure sector, is essential to improving the nation's overall development. Other industry sub-segments include telephony, power, roads, ports, etc. India has to enhance its infrastructure to reach its 2025 economic growth target of USD 5 trillion. The National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), along with other initiatives like "Make in India" and the production-linked incentives (PLI) program, was launched by the government to promote the expansion of the infrastructure industry. Under the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP), 44 Central Ministries and 36 States/UTs have come on board, integrating a total of 1,614 data layers. To uphold data accuracy, key infrastructure ministries have established Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) within a three-tier system. SOPs have been officially notified for 8 infrastructure ministries and 15 social sector ministries, while development efforts are ongoing for additional ministries and States/UTs.
Japan's Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transportation (MLIT) plays a pivotal role in managing the nation's infrastructure. According to MLIT, proactively detecting and addressing at-risk infrastructure can prevent severe incidents and cut maintenance and renewal costs by an impressive 47%, translating to a potential savings of USD 46 billion by 2048. In light of this, MLIT has been championing Digital Transformation (DX) for infrastructure since 2021, urging municipalities, the entities responsible for managing infrastructure, to adopt and implement advanced inspection technologies. In 2023, over 730,000 bridges, 11,000 tunnels, 10,000 water gates, 470,000 meters of sewage pipes, and 5,000 harbor quays have surpassed the 50-year mark. The challenges posed by this aging infrastructure, coupled with related accidents, have garnered heightened scrutiny from both the government and the public.
Overall, the prospects for regional infrastructure investment are highly promising. While COVID-19 has had a considerable influence on infrastructure development and finance throughout the area, part of that change is beneficial to project lenders and investors. The epidemic has hastened investment in low-carbon, climate-resilient infrastructure, as well as initiatives that improve internet connection and public health. The two areas-ESG and digitalization-will continue to dominate the infrastructure sector for the foreseeable future.
APAC Infrastructure Market Trends
Increasing Investments in Transport Infrastructure Sector
Japan, renowned for its cutting-edge transportation infrastructure, is making bold moves to secure financing for its long-term infrastructure needs. The nation boasts an extensive high-speed railway network, the Shinkansen, alongside well-maintained roads and efficient airports. Ongoing investments aim to expand and modernize these systems. Tokyo's Haneda and Narita airports are undergoing significant expansions and renovations to better accommodate rising air traffic and tourism. Enhancements focus on upgrading passenger facilities and boosting runway capacity. To tackle a truck driver shortage, Japan plans to build an automated cargo transport corridor, dubbed the "conveyor belt road," stretching from Tokyo to Osaka. Set to begin trial runs soon, the corridor anticipates full operations by the mid-2030s. This state-of-the-art corridor will feature unmanned, automated transport systems, seamlessly linking airports, railways, and ports.
Under the "Parvatmala Pariyojana" National Ropeways Development Programme, the Government of India has announced more than 200 projects, with a total allocation of INR 1.25 lakh crore (USD 14.77 billion) for the upcoming five years. In 2024, the Union Cabinet has approved INR 4,406 crore (USD 0.52 billion) initiative aimed at constructing 2,280 km of roads in the border areas of Punjab and Rajasthan. In India, roads & highways dominate the transport sector, followed closely by railways and urban public transport. The government has set ambitious targets for the transport sector, including the development of a 2 lakh-km national highway network by 2025 and expanding the number of airports to 220. Additionally, plans include operationalizing 23 waterways by 2030 and developing 35 Multi-Modal Logistics Parks (MMLPs). The total budgetary outlay for infrastructure-related ministries increased from around INR 3.7 lakh crore (USD 43.74 billion) in FY23 to INR 5 lakh crore (USD 59.11 billion) in FY24, presenting investment opportunities for the private sector across various transport sub-segments.
China Infrastructure is Witnessing Significant Growth
As 2023 concluded, rural roads in China spanned a total of 4.6 million kilometers. Of these, paved roads stretched across 4.22 million kilometers, making up 91.8% of the total rural road network. This marks a significant rise of 27.2% over the last decade. Furthermore, paved roads have been established in approximately 30,000 towns and townships, as well as in over 500,000 administrative villages, underscoring the growing accessibility in rural regions.
China's latest renewable energy initiative sets bold consumption targets for 2025 and 2030. Departing from earlier plans that centered on merely installing capacity, this new approach prioritizes enhancing the utilization of renewable energy. This will be achieved through upgrading infrastructure and integrating renewables across various sectors, such as transportation, agriculture, and manufacturing. As a result of this strategic pivot, significant business prospects are anticipated in green technologies, grid modernization, and the broader clean energy arena
However, in 2024, China scaled back infrastructure spending in 12 regions grappling with heightened debt-servicing challenges. The central government is prioritizing the containment of local-government debt risks. Earlier this year, the central government directed these 12 regions to either delay or halt specific government-led infrastructure initiatives, aiming to mitigate their escalating debt challenges.
APAC Infrastructure Industry Overview
The market is fragmented, as many new entrants focus on bagging projects to strengthen their positions among the market's key players and are expected to grow during the forecast period due to private and venture capital investment.
Key players in the market are China State Construction Engineering, China Communications Construction Company, Power Construction Corporation of China, Samsung C&T, and Obayashi Corporation.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Policies and Regulations
- 4.3 Government Regulations and Initiatives
- 4.4 Supply Chain/Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Insights into Technological Innovation in the APAC Infrastructure Sector
- 4.6 Impact of Geopolitics and Pandemic on the Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Strong investment inflow from governments
- 5.1.2 Rising population of APAC nations
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 Limited public budget and difficulty in attracting private investment
- 5.2.2 Delay in land acquisition
- 5.3 Market Opportunities
- 5.3.1 Rapid growth of mobile and internet usage
- 5.3.2 Strong pipeline of urbanization projects
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 5.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 Social Infrastructure
- 6.1.1 Schools
- 6.1.2 Hospitals
- 6.1.3 Defence
- 6.1.4 Other social infrastructures
- 6.2 Transportation Infrastructure
- 6.2.1 Railways
- 6.2.2 Roadways
- 6.2.3 Airports
- 6.2.4 Waterways
- 6.3 Extraction Infrastructure
- 6.3.1 Power Generation
- 6.3.2 Electricity Transmission & Distribution
- 6.3.3 Water
- 6.3.4 Gas
- 6.3.5 Telecoms
- 6.4 Manufacturing Infrastructure
- 6.4.1 Metal and Ore Production
- 6.4.2 Petroleum Refining
- 6.4.3 Chemical Manufacturing
- 6.4.4 Industrial Parks and Clusters
- 6.4.5 Other manufacturing infrastructures
- 6.5 Country
- 6.5.1 China
- 6.5.2 India
- 6.5.3 Philippines
- 6.5.4 Japan
- 6.5.5 South Korea
- 6.5.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 China State Construction Engineering
- 7.2.2 China Communications Construction Company
- 7.2.3 Power Construction Corporation of China
- 7.2.4 Samsung C&T
- 7.2.5 Obayashi Corporation
- 7.2.6 Shanghai Construction Group
- 7.2.7 Hyundai E&C
- 7.2.8 China Petroleum Engineering Corporation
- 7.2.9 L&T
- 7.2.10 China Metallurgical Group*
- 7.3 Other Companies
8 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
9 APPENDIX
- 9.1 Macroeconomic Indicators (GDP Distribution, by Activity)
- 9.2 Economic Statistics - Transport and Storage Sector Contribution to the Economy
- 9.3 External Trade Statistics - Export and Import, by Product


