
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1907344
日本の電気自動車充電機器:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年)Japan Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 日本の電気自動車充電機器:市場シェア分析、業界動向と統計、成長予測(2026年~2031年) |
|
出版日: 2026年01月12日
発行: Mordor Intelligence
ページ情報: 英文 110 Pages
納期: 2~3営業日
|
概要
日本の電気自動車充電機器市場は、2025年に2億9,000万米ドルと評価され、2026年の4億6,000万米ドルから2031年までに46億4,000万米ドルに達すると予測されています。
予測期間(2026-2031年)におけるCAGRは58.70%と見込まれています。
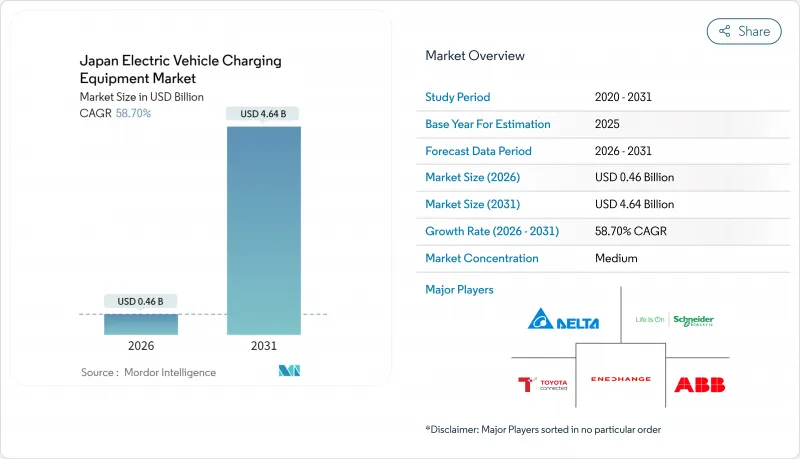
日本電気自動車充電機器市場は、2035年のガソリン車販売禁止、大規模なグリーン成長投資、双方向充電器の電力システムへの全国的な統合によって推進されています。主要な企業グループによる電気化義務化方針は、日本電気自動車充電機器市場に極めて予測可能な需要基盤をもたらし、消費者主導モデルよりも迅速なネットワーク構築と早期の規模の経済を実現しています。技術革新(特に液体冷却コード、複合ケーブル、次世代CHAdeMO/ChaoJiプロトコル)により、充電設備は単なる給油ハードウェアではなく電力網資産としての位置付けが確立されつつあります。省庁間・都道府県間の政策整合性により補助金制度が維持され、投資回収期間が短縮される一方、部品技術の革新が総所有コストの低減を推進しています。日本電気自動車充電機器市場は依然として中程度の分散状態にあるもの、電力会社は需要応答プログラムを通じた新たな収益源を開拓する、エコシステム全体の調整役として重要な役割を担い始めています。
日本の電気自動車充電機器市場の動向と洞察
2035年ガソリン車販売禁止によるEVシフトの推進
この禁止措置により政策の曖昧さが解消され、設備投資が加速します。日本の充電設備市場サプライヤーは10年間のキャッシュフローを確信を持って予測できるためです。日本政府は充電インフラ拡充に数兆円を予算化し、2030年までに公共充電ポート30万基(約8倍の拡大)の目標を設定しています。商用車両も規制対象となるため、デポ充電設備への即時需要が発生し、日本の電気自動車充電機器市場の高いCAGRを支えています。東京及び隣接県は人口密度と企業本社の集中度を反映し、初期資金の大半を集めています。
企業ESG・車隊電動化へのケイレツグループ主導の取り組み
日本特有の企業グループ(ケイレツ)システムは、電気自動車(EV)の導入を単なる消費者選択から統一的な企業戦略へと転換させ、欧米市場では見られない独自のインフラ需要パターンを生み出しています。一部の日本企業は2030年までに商用車両の完全電動化を公約しており、工場や物流拠点における長期充電器契約を確定させています。規模の経済によりポート当たりの設置コストが低下し、特に関東・関西経済圏において投資回収が加速します。
建物管理法に基づく分譲マンション改修承認の遅延
日本の「建築物管理法」では、分譲マンションにおける主要な電気設備変更には全区分所有者の同意が義務付けられています。この要件は、特に分譲マンションが主流の都市部において、住宅用充電ステーション設置の大きな障壁となっています。同法は従来の建物改修を想定して制定されたため、EVインフラ導入の特殊性を十分に考慮できていません。個々の所有者の判断が、建物の電気容量や安全システム全体に広範な影響を及ぼす可能性があります。EV普及が急増する中、こうした制約が強化され、インフラのボトルネックが生じています。その結果、多くの新規EV所有者は公共充電ソリューションに頼らざるを得ず、運用コストの増加やEV導入の魅力低下を招いています。
セグメント分析
2025年時点で乗用車は日本の電気自動車充電機器市場シェアの93.48%を占め、大半の公共ネットワークの基盤負荷を形成しています。一方、商用車は64.30%のCAGRを示しており、設備メーカーをデポ級DCブロックや高度な負荷スケジューリングソフトウェアへと導いています。フリート電動化契約は通常複数年にわたるため、サプライヤーは継続的な保守収益を確保し、部品需要をより正確に予測することが可能となります。ヤマト運輸や佐川急便などの物流企業は、メガワット級ハブをマイクログリッドとして展開し、固定型蓄電池を用いてピーク需要を削減するとともに、電力会社へ付帯サービスを販売しています。こうした大規模設備は、事業者が夜間余剰容量を一般に開放することで、個人ドライバーにも波及効果をもたらします。
また、企業向けへの転換は、コネクターの耐久性向上や決済統合の革新も促進します。フリート使用事例では数千回の接続サイクルと集中管理型課金が必要となるためです。処理能力の向上はハードウェアの交換サイクルを加速させ、ケーブル、シール、開閉装置のアフターマーケットを拡大します。ハードウェアをSaaS型フリート管理ダッシュボードとバンドルするサプライヤーは、物流ワークフローに統合されたソフトウェアの解約率が低いため、利益率の安定化を図れます。企業導入が拡大するにつれ、乗用車が数量面で優位を維持するとしても、日本電気自動車充電機器市場規模における商用セグメントのシェアは上昇すると予想されます。
その他(端子台、エネルギーメーター、安全機構等)カテゴリーは2025年に日本電気自動車充電機器市場シェアの33.62%を占めましたが、コード・ケーブルは63.90%のCAGRで成長すると予測されています。軽量複合材シースによりケーブル質量を40%削減し、作業負荷を軽減するとともに、コネクター落下に伴う保守対応件数を減少させます。国内企業は樹脂サプライヤーと共同でこれらの設計を開発し、独占供給契約を確保することで利益率を強化しています。部品の規模の経済により単価が大幅に低下し、小規模な独立事業者における導入が拡大しています。
従来の支柱型充電器は都市部の設置面積制約に直面しており、ベンダー各社は既存の駐車場照明柱にボルト固定可能なスリムな壁掛け型を投入しています。電源装置と制御盤は日本の電気自動車充電機器市場全体の成長に連動しますが、炭化ケイ素MOSFETの採用により変換効率が大幅に向上し、追加的な成長が見込まれます。相互運用性の向上はCHAdeMOの「超急」ロードマップに沿って進められ、新規ハードウェアが従来車両との下位互換性を維持します。エンドツーエンドのハードウェアスイートを提供するサプライヤーは、調達監査を簡素化するバンドル戦略により自治体入札を獲得しています。こうした部品競争は、急速に拡大する市場において、漸進的な技術改良が収益基盤を大きく左右し得ることを示しています。
その他の特典:
- エクセル形式の市場予測(ME)シート
- アナリストによる3ヶ月間のサポート
よくあるご質問
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
- 調査の前提条件と市場の定義
- 調査範囲
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概要
- 市場促進要因
- 日本の2035年ガソリン車販売禁止によるEVシフトの促進効果
- 企業ESG・財閥グループによるフリート電動化義務化
- 経済産業省グリーン成長基金による高出力充電器補助金
- 電力会社によるV2H(Vehicle-To-Home)向け割増料金
- 太陽光資源が豊富な県における双方向充電器の系統連系需要
- 2025年大阪万博に連動した路上充電器の試験導入
- 市場抑制要因
- 建築物管理法に基づく分譲マンション改修承認の遅延
- 高速道路沿いの公共急速充電施設における高い土地賃貸料
- 持続的なCHAdeMO/CCS/NACS規格の分断
- 地方充電ステーションにおける低い利用率(8%未満)
- バリュー/サプライチェーン分析
- 規制情勢
- テクノロジーの展望
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- 新規参入業者の脅威
- 供給企業の交渉力
- 買い手の交渉力
- 代替品の脅威
- 競争企業間の敵対関係
第5章 市場規模と成長予測(金額および数量)
- 車両タイプ別
- 乗用車
- 商用車
- 充電設備別
- ピラー
- コードおよびケーブル
- 制御基板
- 充電コントローラー
- 電源装置
- その他
- 充電方式別
- 交流充電ステーション
- 直流充電ステーション
- NACS(北米充電システム)
- 用途別
- 家庭充電
- 公共充電
第6章 競合情勢
- 市場集中度
- 戦略的動向
- 市場シェア分析
- 企業プロファイル
- Panasonic Corporation
- Denso Corporation
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- Delta Electronics
- Nichicon Corporation
- Fujikura Ltd.
- Toshiba Corporation
- NEC Corporation
- Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.
- Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings(TEPCO)
- ENECHANGE Ltd.
- Terra Motors Corporation
- Envision AESC Group


