|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1794020
電気小型商用車の世界市場:車両タイプ別、推進方式別、GVWR別、バッテリータイプ別、バッテリー容量別、航続距離別、最終用途別、地域別 - 予測(~2032年)Electric Light Commercial Vehicle Market by Vehicle Type (Pickup Truck, Van), Propulsion (BEV, PHEV), GVWR (< 6,000 lbs, and 6,001 to 10,000 lbs), Battery Type (LFP, NMC, Others), Battery Capacity, Range, End Use, And Region - Global Forecast to 2032 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
|
|||||||
| 電気小型商用車の世界市場:車両タイプ別、推進方式別、GVWR別、バッテリータイプ別、バッテリー容量別、航続距離別、最終用途別、地域別 - 予測(~2032年) |
|
出版日: 2025年08月13日
発行: MarketsandMarkets
ページ情報: 英文 286 Pages
納期: 即納可能
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
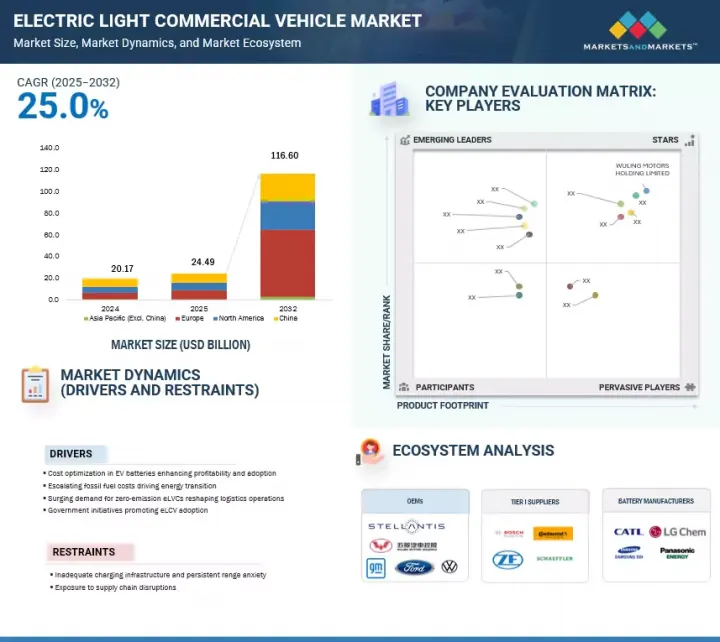
世界の電気小型商用車の市場規模は、2025年に推定244億9,000万米ドルであり、2032年までに1,166億米ドルに達すると予測され、2025年~2032年にCAGRで25.0%の成長が見込まれます。
| 調査範囲 | |
|---|---|
| 調査対象年 | 2021年~2032年 |
| 基準年 | 2024年 |
| 予測期間 | 2025年~2032年 |
| 単位 | 金額(10億米ドル)、数量(1,000台) |
| セグメント | 車両タイプ、航続距離、バッテリータイプ、バッテリー容量、推進力、最終用途、GVWR、地域 |
| 対象地域 | 中国、アジア太平洋(中国を除く)、欧州、北米 |
この急拡大は、排出ガス削減を求める規制圧力や、eコマースの成長による都市のロジスティクスへの需要の高まり、取得コストを削減する政府の優遇措置によるものです。例えば、米国とカナダでは、電気商用バンやピックアップの急速な普及が、厳しい排出規制(EPA 2027基準など)や、強力な購入インセンティブ(米国では最高4万米ドル、カナダではiMHZEVで最高14万6,000米ドル)、州や準州のリベートによって推進されています。
これは、eコマースの成長による都市のロジスティクスへの需要の高まりが、電動ドライブトレインへのシフトを加速させていることによっても後押しされています。欧州は依然として、ドイツ、フランス、英国、オランダなどの国々が主導する重要な採用国であり、中国は強力な国内の補助金と垂直統合されたEVサプライチェーンから恩恵を受けています。インドと東南アジアでは、それぞれFAME-IIのような政府制度と商用車需要の増加に支えられて、採用が勢いを増しています。バッテリー化学(LFP/NMC)の技術的進歩、フリートデポへのDC急速充電インフラの展開、テレマティクスとフリート管理システムの統合は、e-LCVの実現可能性をさらに高めています。Stellantis、Ford、Renault、Wuling Motorsなどの主要OEMが生産を拡大しているため、市場はニッチから主流へと移行しつつあり、2トン未満のミニLCVと、都市や地域の多様なロジスティクスニーズに対応する2~3.5トンのデリバリーバンとの間に正確なセグメンテーションが生まれつつあります。
「プラグインハイブリッド電気自動車は、予測期間にバッテリー電気自動車よりも急成長する推進力セグメントになります。」
電気小型商用車市場のプラグインハイブリッド電気自動車セグメントは、主に充電インフラが安定していない地域での運用の柔軟性により、人気を集めています。2025年4月、Fordはオーストラリア初のプラグインハイブリッドバン、2025 Ford Transit Custom PHEVの発売を発表しました。PHEVモデルは、Trend LWBとSport SWBです。このプラグインハイブリッドモデルは、都市部の低排出ガス地帯では電気のみで運行し、地方での長距離ルートではICEのバックアップを維持するという利点をフリートへ提供します。さらに、電気小型商用車の航続距離の不安の低減は、特に充電インフラが拡大し、バッテリー技術が向上するにつれて、フリート採用の重要な促進要因となっています。この保証により、ロジスティクスやラストマイル配送企業は、都市部や半都市部のルートにeLCVを混乱なく自信を持って展開することができます。
「50kWh以下が予測期間に大きな市場シェアを占めます。」
電気小型商用車市場の50kWh以下のバッテリー容量セグメントは、主に短距離の都市内ロジスティクスに最適化された小型配送バンの需要の高まりによって牽引されています。これらのバッテリーパックは、特に1日の走行距離が150km未満で、頻繁にストップアンドゴーを繰り返すような人口密集地において、都市のフリートにコスト効率の高いソリューションを提供します。BYD(中国)は、バッテリー容量43kWhのT3小型電気トラックを提供しています。Workhorse Group(米国)は、バッテリー容量50kWhの電気トラックW-15を提供しています。インド、日本、インドネシアなどの国々では、Tata Ace EVやSuzuki Every EVのような、30~50kWh未満のバッテリーパックを搭載した、短距離ロジスティクスや小企業向けに調整されたコンパクトなeLCVの採用が増加しています。これらの車両は、政府が支援する電化プログラムや都市モビリティの目標に合致しており、新興経済圏の商用フリート運用者にとって重大な要素である、低い総所有コストと限られた充電インフラへの適合性を提供します。
当レポートでは、世界の電気小型商用車市場について調査分析し、主な促進要因と抑制要因、競合情勢、将来の動向などの情報を提供しています。
目次
第1章 イントロダクション
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 重要な知見
- 電気小型商用車市場の企業にとって魅力的な機会
- 電気小型商用車市場:車両タイプ別
- 電気小型商用車市場:GVWR別
- 電気小型商用車市場:推進力別
- 電気小型商用車市場:航続距離別
- 電気小型商用車市場:バッテリータイプ別
- 電気小型商用車市場:バッテリー容量別
- 電気小型商用車市場:用途別
- 電気小型商用車市場:地域別
第5章 市場の概要
- イントロダクション
- 市場力学
- 促進要因
- 抑制要因
- 機会
- 課題
- 市場力学の影響
- カスタマービジネスに影響を与える動向/混乱
- 価格設定の分析
- 車両タイプの平均販売価格の動向:主要メーカー別
- 平均販売価格の動向:地域別(2022年~2024年)
- エコシステム分析
- OEM
- 原材料サプライヤー
- Tier 1サプライヤー
- Tier 2サプライヤー
- 部品メーカー
- EV充電インフラプロバイダー
- サプライチェーン分析
- 規制情勢
- 規制:国別
- 規制機関、政府機関、その他の組織
- 主な会議とイベント(2025年~2026年)
- ケーススタディ分析
- FEDEXの持続可能なロジスティクスへの飛躍
- SCOTTISH WATERの電気バン採用成功
- KENT COUNTY COUNCILによる企業向け電気バンの試験導入
- 投資と資金調達のシナリオ
- 特許分析
- HSコード(8702):電気小型商用車
- 電気小型商用車市場の輸入シナリオ
- 電気小型商用車市場の輸出シナリオ
- AI/生成AIの影響
- 技術分析
- 主要技術
- 補完技術
- 隣接技術
- 今後の自動車の発売、主要OEMの投資、電化目標に関するMNMの見解
- 今後の車両モデルの発売
- OEMの目標と投資
- OEMのeLCVプラットフォーム戦略に関する考察
- 電気ピックアップトラックとバンのバッテリースワッピングに関する戦略的考察
- 電気ピックアップトラックとバンのビジネスケースの分析
- フリートの所有・運用
- Fleet as a Service(FaaS)
- プラットフォームとエコシステムの提携
- 従量課金モデル
- 部品表
- 総所有コスト
- 電気小型商用車の主な性能の比較
- 航続距離/バッテリー容量
- 航続距離と最終用途
- バッテリー容量と最終用途
- 出力と充電時間
- 主なステークホルダーと購入基準
第6章 電気小型商用車市場:車両タイプ別
- イントロダクション
- ピックアップトラック
- バン
- 重要な知見
第7章 電気小型商用車市場:推進力別
- イントロダクション
- バッテリー電気自動車
- プラグインハイブリッド電気自動車
- 重要な知見
第8章 電気小型商用車市場:バッテリー容量別
- イントロダクション
- 50kWh以下
- 50~100kWh
- 100~150kWh
- 重要な知見
第9章 電気小型商用車市場:バッテリータイプ別
- イントロダクション
- リン酸鉄リチウム(LFP)
- ニッケルマンガンコバルト(NMC)
- 全固体電池
- その他
- 重要な知見
第10章 電気小型商用車市場:用途別
- イントロダクション
- ラストマイル配送
- フィールドサービス
- 配送サービス
- 主な産業考察
第11章 電気小型商用車市場:GVWR別
- イントロダクション
- 6,000ポンド未満
- 6,001~1万ポンド
- 重要な知見
第12章 電気小型商用車市場:車両タイプ別
- イントロダクション
- 100マイル以下
- 100~200マイル
- 200マイル超
- 重要な知見
第13章 電気小型商用車市場:地域別
- イントロダクション
- 中国
- アジア太平洋(中国を除く)
- マクロ経済の見通し
- 日本
- インド
- 韓国
- 欧州
- マクロ経済の見通し
- フランス
- ドイツ
- スペイン
- オーストリア
- ノルウェー
- スウェーデン
- オランダ
- 英国
- イタリア
- その他の欧州
- 北米
- マクロ経済の見通し
- 米国
- カナダ
第14章 競合情勢
- 概要
- 主要参入企業の戦略/強み
- 市場シェア分析(2024年)
- 収益分析(2020年~2024年)
- 企業の評価と財務指標
- ブランド/製品の比較
- 企業の評価マトリクス:主要企業(2024年)
- 企業の評価マトリクス:スタートアップ/中小企業(2024年)
- 競合シナリオ
第15章 企業プロファイル
- 主要企業
- WULING MOTORS HOLDINGS LIMITED
- FORD MOTOR COMPANY
- GENERAL MOTORS
- STELLANTIS N.V.
- RENAULT GROUP
- TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION
- BYD COMPANY LTD.
- NISSAN MOTOR CO., LTD.
- IVECO GROUP N.V.
- FLEXIS
- RIVIAN
- FOTON INTERNATIONAL
- TATA MOTORS LIMITED
- MAXUS ELECTRIC VEHICLES AND VANS
- MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION
- その他の企業
- SWITCH MOBILITY
- EULER MOTORS
- TELO TRUCKS
- OMEGA SEIKI MOBILITY
- SLATE
- EVUM MOTORS
- ARRIVAL UK LTD.
- EKA MOBILITY
- NU RIDE INC.
- MULLEN AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
- EVAGE
- QUCEV
- KAIYUN MOTORS
第16章 MARKETSANDMARKETSによる提言
- 中国は電気小型商用車の主要市場となる
- 6,001~1万ポンドセグメントは予測期間に成長が見込まれる
- ADAS(先進運転支援システム)の統合
- 結論
第17章 付録
List of Tables
- TABLE 1 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET DEFINITION, BY PROPULSION
- TABLE 2 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET DEFINITION, BY END USE
- TABLE 3 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET DEFINITION, BY BATTERY TYPE
- TABLE 4 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET DEFINITION, BY VEHICLE TYPE
- TABLE 5 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET DEFINITION, BY GVWR
- TABLE 6 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- TABLE 7 USD EXCHANGE RATES, 2021-2025
- TABLE 8 ZERO-EMISSION LIGHT-DUTY VEHICLE POLICIES AND INCENTIVES IN SELECTED COUNTRIES
- TABLE 9 EV CHARGER DENSITY, BY KEY COUNTRIES, 2024
- TABLE 10 LITHIUM AVAILABILITY VS. DEMAND FOR EV BATTERIES, 2020-2030
- TABLE 11 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND OF ELECTRIC VANS, BY KEY PLAYERS, 2024 (USD)
- TABLE 12 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE OF ELECTRIC PICKUP TRUCKS, BY KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- TABLE 13 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2022-2024 (USD)
- TABLE 14 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND, BY REGION, 2022-2024 (USD)
- TABLE 15 ROLE OF COMPANIES IN ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET ECOSYSTEM
- TABLE 16 NETHERLANDS: ELECTRIC VEHICLE INCENTIVES
- TABLE 17 NETHERLANDS: ELECTRIC VEHICLE CHARGING STATION INCENTIVES
- TABLE 18 GERMANY: ELECTRIC VEHICLE INCENTIVES
- TABLE 19 GERMANY: ELECTRIC VEHICLE CHARGING STATION INCENTIVES
- TABLE 20 FRANCE: ELECTRIC VEHICLE INCENTIVES
- TABLE 21 FRANCE: ELECTRIC VEHICLE CHARGING STATION INCENTIVES
- TABLE 22 UK: ELECTRIC VEHICLE INCENTIVES
- TABLE 23 UK: ELECTRIC VEHICLE CHARGING STATION INCENTIVES
- TABLE 24 CHINA: ELECTRIC VEHICLE INCENTIVES
- TABLE 25 CHINA: ELECTRIC VEHICLE CHARGING STATION INCENTIVES
- TABLE 26 US: ELECTRIC VEHICLE INCENTIVES
- TABLE 27 US: ELECTRIC VEHICLE CHARGING STATION INCENTIVES
- TABLE 28 ASIA PACIFIC: REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- TABLE 29 NORTH AMERICA: REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- TABLE 30 EUROPE: REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- TABLE 31 REST OF THE WORLD: REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- TABLE 32 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2025-2026
- TABLE 33 LIST OF FUNDING, APRIL 2024-MARCH 2025
- TABLE 34 PATENT REGISTRATIONS RELATED TO ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, APRIL 2024-FEBRUARY 2025
- TABLE 35 IMPORT DATA FOR HS CODE 8702, BY COUNTRY, 2020-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 36 EXPORT DATA FOR HS CODE 8702, BY COUNTRY, 2020-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 37 VEHICLE MODEL EQUIPPED WITH V2X TECHNOLOGY
- TABLE 38 UPCOMING ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES, 2025-2026
- TABLE 39 OEM TARGETS AND INVESTMENT
- TABLE 40 OEM STRATEGIES AND EV PLATFORMS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES
- TABLE 41 OEM INITIATIVES TOWARD BATTERY SWAPPING
- TABLE 42 KEY ELECTRIC VANS AND PICKUP TRUCKS FOR FLEET APPLICATIONS
- TABLE 43 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES: RANGE VS. BATTERY CAPACITY
- TABLE 44 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES: RANGE VS. END USE
- TABLE 45 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES: BATTERY CAPACITY VS. END USE
- TABLE 46 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES: POWER VS. CHARGING DURATION
- TABLE 47 INFLUENCE OF STAKEHOLDERS ON BUYING PROCESS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES, BY VEHICLE TYPE
- TABLE 48 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 49 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 50 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 51 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 52 ELECTRIC PICKUP TRUCK MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 53 ELECTRIC PICKUP TRUCK MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 54 ELECTRIC PICKUP TRUCK MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 55 ELECTRIC PICKUP TRUCK MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 56 ELECTRIC VAN MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 57 ELECTRIC VAN MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 58 ELECTRIC VAN MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 59 ELECTRIC VAN MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 60 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY PROPULSION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 61 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY PROPULSION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 62 BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 63 BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 64 PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 65 PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 66 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY CAPACITY, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 67 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY CAPACITY, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 68 UP TO 50 KWH: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 69 UP TO 50 KWH: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 70 50 TO 100 KWH: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 71 50 TO 100 KWH: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 72 100 TO 150 KWH: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 73 100 TO 150 KWH: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 74 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 75 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 76 LFP: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 77 LFP: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 78 NMC: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 79 NMC: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 80 SOLID-STATE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 81 OTHERS: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 82 OTHERS: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 83 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY END USE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 84 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY END USE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 85 LAST-MILE DELIVERY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 86 LAST-MILE DELIVERY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 87 FIELD SERVICES: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 88 FIELD SERVICES: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 89 DISTRIBUTION SERVICES: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 90 DISTRIBUTION SERVICES: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 91 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY GVWR, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 92 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY GVWR, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 93 BELOW 6,000 LBS ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 94 BELOW 6,000 LBS ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 95 6,001-10,000 LBS ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 96 6,001-10,000 LBS ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 97 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY RANGE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 98 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY RANGE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 99 UP TO 100 MILES: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 100 UP TO 100 MILES: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 101 100 TO 200 MILES: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 102 100 TO 200 MILES: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 103 ABOVE 200 MILES: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 104 ABOVE 200 MILES: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 105 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 106 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 107 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 108 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY/REGION, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 109 CHINA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 110 CHINA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 111 CHINA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 112 CHINA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 113 ASIA PACIFIC (EXCL. CHINA): ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 114 ASIA PACIFIC (EXCL. CHINA): ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 115 ASIA PACIFIC (EXCL. CHINA): ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 116 ASIA PACIFIC (EXCL. CHINA): ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 117 JAPAN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 118 JAPAN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 119 JAPAN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 120 JAPAN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 121 INDIA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 122 INDIA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 123 INDIA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 124 INDIA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 125 SOUTH KOREA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 126 SOUTH KOREA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 127 SOUTH KOREA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 128 SOUTH KOREA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 129 EUROPE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 130 EUROPE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 131 EUROPE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 132 EUROPE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 133 FRANCE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 134 FRANCE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 135 FRANCE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 136 FRANCE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 137 GERMANY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 138 GERMANY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 139 GERMANY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 140 GERMANY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 141 SPAIN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 142 SPAIN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 143 SPAIN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 144 SPAIN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 145 AUSTRIA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 146 AUSTRIA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 147 AUSTRIA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 148 AUSTRIA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 149 NORWAY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 150 NORWAY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 151 NORWAY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 152 NORWAY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 153 SWEDEN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 154 SWEDEN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 155 SWEDEN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 156 SWEDEN: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 157 NETHERLANDS: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 158 NETHERLANDS: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 159 NETHERLANDS: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 160 NETHERLANDS: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 161 UK: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 162 UK: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 163 UK: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 164 UK: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 165 ITALY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 166 ITALY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 167 ITALY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 168 ITALY: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 169 REST OF EUROPE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 170 REST OF EUROPE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 171 REST OF EUROPE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 172 REST OF EUROPE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 173 NORTH AMERICA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 174 NORTH AMERICA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 175 NORTH AMERICA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 176 NORTH AMERICA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 177 US: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 178 US: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 179 US: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 180 US: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 181 CANADA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 182 CANADA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- TABLE 183 CANADA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2021-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 184 CANADA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025-2032 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 185 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN, JANUARY 2021-JUNE 2025
- TABLE 186 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET SHARE OF TOP 5 PLAYERS, 2024
- TABLE 187 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: REGION FOOTPRINT, 2024
- TABLE 188 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: VEHICLE TYPE FOOTPRINT, 2024
- TABLE 189 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: LIST OF STARTUPS/SMES
- TABLE 190 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING OF STARTUPS/SMES
- TABLE 191 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: PRODUCT LAUNCHES, JANUARY 2021-JUNE 2025
- TABLE 192 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: DEALS, JANUARY 2021-JULY 2025
- TABLE 193 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: EXPANSIONS, JANUARY 2021-JULY 2025
- TABLE 194 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: OTHER DEVELOPMENTS, JANUARY 2021-JULY 2025
- TABLE 195 WULING MOTORS HOLDINGS LIMITED: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 196 WULING MOTORS HOLDINGS LIMITED: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 197 WULING MOTORS HOLDINGS LIMITED: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 198 WULING MOTORS HOLDINGS LIMITED: DEALS
- TABLE 199 FORD MOTOR COMPANY: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 200 FORD MOTOR COMPANY: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 201 FORD MOTOR COMPANY: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 202 FORD MOTOR COMPANY: DEALS
- TABLE 203 FORD MOTOR COMPANY: EXPANSIONS
- TABLE 204 FORD MOTOR COMPANY: OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
- TABLE 205 GENERAL MOTORS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 206 GENERAL MOTORS: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 207 GENERAL MOTORS: DEALS
- TABLE 208 STELLANTIS N.V.: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 209 STELLANTIS N.V.: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 210 STELLANTIS N.V.: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 211 STELLANTIS N.V.: DEALS
- TABLE 212 RENAULT GROUP: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 213 RENAULT GROUP: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 214 RENAULT GROUP: PRODUCT DEVELOPMENTS
- TABLE 215 RENAULT GROUP: DEALS
- TABLE 216 TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 217 TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 218 TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION: DEALS
- TABLE 219 TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION: OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
- TABLE 220 BYD COMPANY LTD.: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 221 BYD COMPANY LTD.: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 222 BYD COMPANY LTD.: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 223 BYD COMPANY LTD.: DEALS
- TABLE 224 BYD COMPANY LTD.: EXPANSIONS
- TABLE 225 NISSAN MOTOR CO., LTD.: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 226 NISSAN MOTOR CO., LTD.: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 227 NISSAN MOTOR CO., LTD.: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 228 NISSAN MOTOR CO., LTD.: DEALS
- TABLE 229 IVECO GROUP N.V.: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 230 IVECO GROUP N.V.: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 231 IVECO GROUP N.V.: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 232 IVECO GROUP N.V.: DEALS
- TABLE 233 FLEXIS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 234 FLEXIS: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 235 FLEXIS: DEALS
- TABLE 236 RIVIAN: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 237 RIVIAN: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 238 RIVIAN: PRODUCT ENHANCEMENTS/LAUNCHES
- TABLE 239 RIVIAN: DEALS
- TABLE 240 RIVIAN: OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
- TABLE 241 FOTON INTERNATIONAL: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 242 FOTON INTERNATIONAL: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 243 FOTON INTERNATIONAL: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 244 FOTON INTERNATIONAL: DEALS
- TABLE 245 FOTON INTERNATIONAL: OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
- TABLE 246 TATA MOTORS LIMITED: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 247 TATA MOTORS LIMITED: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 248 TATA MOTORS LIMITED: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 249 TATA MOTORS LIMITED: DEALS
- TABLE 250 MAXUS ELECTRIC VEHICLES AND VANS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 251 MAXUS ELECTRIC VEHICLES AND VANS: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 252 MAXUS ELECTRIC VEHICLES AND VANS: PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- TABLE 253 MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 254 MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION: PRODUCTS OFFERED
- TABLE 255 MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION: DEALS
- TABLE 256 MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION: OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
- TABLE 257 SWITCH MOBILITY: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 258 EULER MOTORS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 259 TELO TRUCKS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 260 OMEGA SEIKI MOBILITY: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 261 SLATE: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 262 EVUM MOTORS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 263 ARRIVAL UK LTD.: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 264 EKA MOBILITY: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 265 NU RIDE INC.: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 266 MULLEN AUTOMOTIVE, INC.: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 267 EVAGE: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 268 QUCEV: COMPANY OVERVIEW
- TABLE 269 KAIYUN MOTORS: COMPANY OVERVIEW
List of Figures
- FIGURE 1 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET SEGMENTATION
- FIGURE 2 RESEARCH DESIGN
- FIGURE 3 RESEARCH DESIGN MODEL
- FIGURE 4 BREAKDOWN OF PRIMARY INTERVIEWS
- FIGURE 5 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY: HYPOTHESIS BUILDING
- FIGURE 6 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- FIGURE 7 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- FIGURE 8 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET ESTIMATION NOTES
- FIGURE 9 DATA TRIANGULATION
- FIGURE 10 MARKET GROWTH PROJECTIONS FROM DEMAND-SIDE DRIVERS
- FIGURE 11 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET OVERVIEW
- FIGURE 12 CHINA TO HOLD PROMINENT MARKET SHARE IN 2032
- FIGURE 13 ELECTRIC VAN SEGMENT TO HOLD DOMINANT MARKET SHARE IN 2032
- FIGURE 14 6,001 TO 10,000 LBS TO GROW AT HIGHER CAGR THAN BELOW 6,000 LBS DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 15 RISING DEMAND FOR ELECTRIC VANS IN CHINA TO DRIVE MARKET
- FIGURE 16 ELECTRIC VAN SEGMENT TO HOLD DOMINANT MARKET SHARE IN 2032
- FIGURE 17 6,001-10,000 LBS TO BE DOMINANT SEGMENT DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 18 BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLE SEGMENT TO SECURE LEADING POSITION DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 19 UP TO 100 MILES SEGMENT TO GROW AT HIGHEST CAGR DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 20 LFP BATTERIES TO DOMINATE MARKET IN 2032
- FIGURE 21 50 TO 100 KWH SEGMENT TO GROW AT HIGHEST CAGR DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 22 LAST-MILE DELIVERY SEGMENT TO HOLD LARGEST MARKET SHARE IN 2032
- FIGURE 23 EUROPE TO BE FASTEST-GROWING ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- FIGURE 24 DRIVERS, RESTRAINTS, OPPORTUNITIES, AND CHALLENGES IN ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET
- FIGURE 25 PRICE TRENDS OF SELECTED BATTERY METALS AND LITHIUM-ION BATTERY PACK, 2020-2025
- FIGURE 26 AVERAGE GLOBAL PETROL PRICES, 2001 VS. 2011 VS. 2024 VS. 2025
- FIGURE 27 OPERATING COST COMPARISON OF ELECTRIC AND ICE VEHICLES
- FIGURE 28 GLOBAL ELECTRIFICATION TARGETS, 2025-2050
- FIGURE 29 PRIVATE, SEMI-PUBLIC, AND PUBLIC CHARGING OWNERSHIP
- FIGURE 30 BATTERY-LEASING SERVICE MODEL FOR LIGHT-DUTY COMMERCIAL VEHICLES
- FIGURE 31 WIRELESS CHARGING FOR ELECTRIC PICKUP TRUCKS
- FIGURE 32 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
- FIGURE 33 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2022-2024 (USD)
- FIGURE 34 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND, BY REGION, 2022-2024 (USD)
- FIGURE 35 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET ECOSYSTEM
- FIGURE 36 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET MAP
- FIGURE 37 SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS OF ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET
- FIGURE 38 INVESTMENT SCENARIO, JANUARY 2022-JULY 2025
- FIGURE 39 PATENT ANALYSIS, JANUARY 2015-JULY 2025
- FIGURE 40 IMPORT DATA FOR HS CODE 8702, BY COUNTRY, 2020-2024 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 41 EXPORT DATA FOR HS CODE 8702, BY COUNTRY, 2020-2024 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 42 ELECTRIC VAN EQUIPPED WITH WIRELESS CHARGING TECHNOLOGY
- FIGURE 43 BILL OF MATERIALS: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES
- FIGURE 44 BILL OF MATERIALS: BATTERY VS. NON-BATTERY COMPONENTS (USD)
- FIGURE 45 TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP: FORD ELECTRIC TRANSIT VS. ICE TRANSIT 3.5-TON MODELS
- FIGURE 46 INFLUENCE OF STAKEHOLDERS ON BUYING PROCESS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES, BY VEHICLE TYPE
- FIGURE 47 KEY BUYING CRITERIA FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE TYPES
- FIGURE 48 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025 VS. 2032 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 49 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY PROPULSION, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- FIGURE 50 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY CAPACITY, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- FIGURE 51 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY TYPE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- FIGURE 52 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY END USE, 2025 VS. 2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- FIGURE 53 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY GVWR, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- FIGURE 54 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY RANGE, 2025-2032 (THOUSAND UNITS)
- FIGURE 55 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY REGION, 2025 VS. 2032 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 56 CHINA: REAL GDP GROWTH RATE, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 57 CHINA: GDP PER CAPITA, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 58 CHINA: INFLATION RATE AVERAGE CONSUMER PRICES, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 59 CHINA: MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY'S CONTRIBUTION TO GDP, 2024
- FIGURE 60 CHINA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE, 2025 VS. 2032
- FIGURE 61 ASIA PACIFIC (EXCL. CHINA): REAL GDP GROWTH RATE, BY COUNTRY, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 62 ASIA PACIFIC (EXCL. CHINA): GDP PER CAPITA, BY COUNTRY, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 63 ASIA PACIFIC (EXCL. CHINA): INFLATION RATE AVERAGE CONSUMER PRICES, BY COUNTRY, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 64 ASIA PACIFIC (EXCL. CHINA): MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY'S CONTRIBUTION TO GDP, 2024
- FIGURE 65 ASIA PACIFIC (EXCL. CHINA): ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 66 EUROPE: REAL GDP GROWTH RATE, BY COUNTRY, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 67 EUROPE: GDP PER CAPITA, BY COUNTRY, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 68 EUROPE: INFLATION RATE AVERAGE CONSUMER PRICES, BY COUNTRY, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 69 EUROPE: MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY'S CONTRIBUTION TO GDP, 2024
- FIGURE 70 EUROPE: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2025 VS. 2032 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 71 NORTH AMERICA: REAL GDP GROWTH RATE, BY COUNTRY, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 72 NORTH AMERICA: GDP PER CAPITA, BY COUNTRY, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 73 NORTH AMERICA: CPI INFLATION RATE, BY COUNTRY, 2024-2026
- FIGURE 74 NORTH AMERICA: MANUFACTURING INDUSTRY'S CONTRIBUTION TO GDP, 2024
- FIGURE 75 NORTH AMERICA: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 76 US: ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE DEMAND, BY END USER
- FIGURE 77 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2024
- FIGURE 78 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: REVENUE ANALYSIS OF TOP LISTED PLAYERS, 2020-2024
- FIGURE 79 COMPANY VALUATION OF KEY PLAYERS, JULY 2025 (USD BILLION)
- FIGURE 80 FINANCIAL METRICS OF KEY PLAYERS, JULY 2025 (EV/EBITDA)
- FIGURE 81 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- FIGURE 82 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX (KEY PLAYERS), 2024
- FIGURE 83 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: COMPANY FOOTPRINT, 2024
- FIGURE 84 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET: COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX (STARTUPS/SMES), 2024
- FIGURE 85 WULING MOTORS HOLDINGS LIMITED: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 86 FORD MOTOR COMPANY: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 87 GENERAL MOTORS: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 88 STELLANTIS N.V.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 89 RENAULT GROUP: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 90 TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 91 BYD COMPANY LTD.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 92 NISSAN MOTOR CO., LTD.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 93 IVECO GROUP N.V.: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 94 RIVIAN: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 95 FOTON INTERNATIONAL: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
- FIGURE 96 TATA MOTORS LIMITED: COMPANY SNAPSHOT
The electric light commercial vehicle market is estimated at USD 24.49 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 116.60 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 25.0% from 2025 to 2032.
| Scope of the Report | |
|---|---|
| Years Considered for the Study | 2021-2032 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2032 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Billion), Volume (Thousand Units) |
| Segments | Vehicle Type, Range, Battery Type, Battery Capacity, Propulsion, End Use, GVWR, and Region |
| Regions covered | China, Asia Pacific (excl. China), Europe, and North America |
This rapid expansion is driven by regulatory pressure to cut emissions, rising urban logistics demand due to e-commerce growth, and favorable government incentives that reduce acquisition costs. For instance, in the US and Canada, rapid adoption of electric commercial vans and pickups is driven by strict emission norms (e.g., EPA 2027 standards) and strong purchase incentives up to USD 40,000 in the US and up to USD 146,000 in Canada (iMHZEV), with additional state and provincial rebates.

This is further supported by rising urban logistics demand due to e-commerce growth, accelerating the shift to electric drivetrains. Europe remains a key adopter, led by countries like Germany, France, the UK, and the Netherlands, while China benefits from strong domestic subsidies and vertically integrated EV supply chains. In India and Southeast Asia, adoption is gaining momentum, supported by government schemes like FAME-II and increasing commercial fleet demand, respectively. Technological advancements in battery chemistries (LFP/NMC), deployment of DC fast-charging infrastructure at fleet depots, and integration of telematics and fleet management systems further enhance the viability of e-LCVs. With major OEMs such as Stellantis, Ford, Renault, and Wuling Motors scaling production, the market is transitioning from niche to mainstream, with a precise segmentation emerging between sub-2-ton mini-LCVs and 2-3.5-ton delivery vans for diverse urban and regional logistics needs.
"Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle to be faster-growing propulsion segment than battery electric vehicle segment during forecast period"
The plug-in hybrid electric vehicle segment of the electric light commercial vehicle market is gaining traction primarily due to its operational flexibility in regions with inconsistent charging infrastructure. In April 2025, Ford announced the launch of Australia's first plug-in hybrid van, the 2025 Ford Transit Custom PHEV, arriving in October alongside its full-electric sibling. The PHEV models are Trend LWB and Sport SWB. This plug-in hybrid model offers fleets the benefit of electric-only operation in urban low-emission zones, while retaining ICE backup for extended rural routes. Additionally, lower range anxiety in electric light commercial vehicles is a key driver for fleet adoption, especially as charging infrastructure expands and battery technologies improve. This assurance enables logistics and last-mile delivery companies to deploy eLCVs across urban and semi-urban routes without disruption, confidently.
"Up to 50 kWh to hold significant market share during forecast period"
The up to 50 kWh battery capacity segment of the electric light commercial vehicle market is primarily driven by the growing demand for compact delivery vans optimized for short-distance, intra-city logistics. These battery packs offer a cost-effective solution for urban fleets, especially in densely populated regions where daily routes are under 150 km and frequent stop-and-go driving is common. BYD (China) offers T3 light-duty electric trucks with a battery capacity of 43 kWh. The offerings of Workhorse Group (US) include its electric truck W-15 with a battery capacity of 50 kWh. Countries like India, Japan, and Indonesia are witnessing increased adoption of compact eLCVs such as Tata Ace EV and Suzuki Every EV, equipped with battery packs under 30-50 kWh, tailored for short-haul logistics and small business use. These vehicles align with government-supported electrification programs and urban mobility goals, offering lower total cost of ownership and compatibility with limited charging infrastructure, factors critical to commercial fleet operators in emerging economies.
"North America to hold second-largest market share during forecast period"
North America is home to renowned OEMs that specialize in producing high-quality and high-performance vehicles, driving the electric light commercial vehicle market. These manufacturers, including Ford Motor Company (US), GMC (US), and General Motors (US), are increasingly focusing on developing faster, cleaner, and more efficient electric light commercial vehicles. In North America, governments at both the federal and state levels are offering incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles, including electric light commercial vehicles. For instance, under the US Federal Commercial Clean Vehicle Credit (IRC 45W), businesses can receive up to USD 7,500 for light commercial EVs, and state programs like California's HVIP offer up to USD 60,000 per vehicle for zero-emission vans and trucks, with tiered reductions for large fleets. These incentives include tax credits, rebates, grants, and infrastructure investments. For instance, the US federal government's investments in charging infrastructure and tax incentives for EV purchases have stimulated growth in the electric light commercial vehicle market. The expansion of charging infrastructure is critical for the widespread adoption of electric light commercial vehicles. In North America, there has been significant investment in charging networks, including fast-charging stations along major transportation routes and in urban areas. For instance, in January 2024, the US government invested USD 623 million in charging infrastructure. In February 2024, the first public 500 kW charging station for North America was unveiled at Mercedes-Benz USA Headquarters in Sandy Springs, Georgia.
Breakup of Primaries:
In-depth interviews were conducted with CEOs, marketing directors, other innovation and technology directors, and executives from various key organizations operating in this market.
- By Company Type: OEMs- 35%, Tier I- 41%, and Tier II & III- 24%
- By Designation: CXOs - 60%, Managers - 10%, and Executives- 30%
- By Region: China-20%, Asia Pacific (excl. China)-34%, Europe-23%, North America-18%
The electric light commercial vehicle market is dominated by major players, including Wuling Motors Holdings Limited (China), Ford Motor Company (US), General Motors (US), Stellantis NV (Netherlands), and Renault (France).
The study includes an in-depth competitive analysis of these key players in the electric light commercial vehicle market, with their company profiles, recent developments, and key market strategies.
Research Coverage:
This research report categorizes the electric light commercial vehicle market by vehicle type (pickup truck and van), propulsion (battery electric vehicle and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle), by battery type (LFP, NMC, solid-state, and others), battery capacity (up to 50 kWh, 50 to 100 kWh, and 100 to 150 kWh), range (up to 100 miles, 100 to 200 miles, and above 200 miles), by GVWR (Below 6,000 lbs and 6,001 to 10,000 lbs), end use (last-mile delivery, field services, and distribution services), and region (China, Asia Pacific (excl. China), Europe, and North America). The scope of the report covers detailed information regarding the major factors, such as drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities, influencing the growth of the market. A detailed analysis of the key industry players provided insights into their business overviews, solutions & services, key strategies, contracts, partnerships, agreements, product & service launches, mergers & acquisitions, and recent developments associated with the electric light commercial vehicle market. Competitive analysis of upcoming startups in the electric light commercial vehicle market ecosystem has been covered in this report.
Reasons to Buy this Report
The report will help the market leaders/new entrants in this market with information on the closest approximations of the revenue numbers for the overall electric light commercial vehicle market and the subsegments. This report will also help stakeholders understand the competitive landscape and gain more insights to position their businesses better and plan suitable go-to-market strategies. It will help stakeholders understand the pulse of the market and provide them with information on key market drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities.
The report provides insights into the following pointers:
- Analysis of key drivers (cost optimization in EV batteries enhancing profitability and adoption, Escalating fossil fuel costs driving energy transition, Surging demand for zero-emission eLVCs reshaping logistics operations, government initiatives promoting eLCV adoption), restraints (inadequate charging infrastructure and persistent range anxiety hindering market adoption, exposure to supply chain disruptions), opportunities (battery leasing and mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) models, development of wireless EV charging technology for on-the-go charging), and challenges (lack of standardization in charging protocols, low availability of lithium for EV batteries) influencing the growth of the electric light commercial vehicle market
- Product Development/Innovation: Detailed insights into upcoming technologies and research & development activities in the electric light commercial vehicle market
- Market Development: Comprehensive information about lucrative markets (the report analyses the electric light commercial vehicle market across varied regions)
- Market Diversification: Exhaustive information about new products & services, untapped geographies, recent developments, and investments in the electric light commercial vehicle market
Competitive Assessment: In-depth assessment of market shares, growth strategies, and service offerings of leading players, such as Wuling Motors Holdings Limited. (China), Ford Motor Company (US), General Motors (US), Stellantis NV (Netherlands), and Renault (France), in the electric light commercial vehicle market
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES
- 1.2 MARKET DEFINITION
- 1.3 STUDY SCOPE
- 1.3.1 MARKETS COVERED AND REGIONAL SCOPE
- 1.3.2 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS
- 1.3.3 YEARS CONSIDERED
- 1.4 CURRENCY CONSIDERED
- 1.4.1 UNITS CONSIDERED
- 1.5 STAKEHOLDERS
- 1.6 SUMMARY OF CHANGES
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 RESEARCH DATA
- 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.1.1.1 List of key secondary sources
- 2.1.1.2 Key data from secondary sources
- 2.1.2 PRIMARY DATA
- 2.1.2.1 Primary interviews: demand and supply sides
- 2.1.2.2 Primary interview participants
- 2.1.2.3 Objectives of primary research
- 2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA
- 2.2 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION
- 2.2.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH
- 2.2.2 TOP-DOWN APPROACH
- 2.3 DATA TRIANGULATION
- 2.4 FACTOR ANALYSIS
- 2.4.1 DEMAND- AND SUPPLY-SIDE FACTOR ANALYSIS
- 2.5 RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS
- 2.6 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS
- 2.7 RISK ANALYSIS
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 PREMIUM INSIGHTS
- 4.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET
- 4.2 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE
- 4.3 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY GVWR
- 4.4 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY PROPULSION
- 4.5 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY RANGE
- 4.6 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY TYPE
- 4.7 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY CAPACITY
- 4.8 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY END USE
- 4.9 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY REGION
5 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 5.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.2 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.2.1.1 Cost optimization in EV batteries enhancing profitability and adoption
- 5.2.1.2 Escalating fossil fuel costs driving energy transition
- 5.2.1.3 Surging demand for zero-emission eLCVs reshaping logistics operations
- 5.2.1.4 Government initiatives promoting eLCV adoption
- 5.2.2 RESTRAINTS
- 5.2.2.1 Inadequate charging infrastructure and persistent range anxiety hindering market adoption
- 5.2.2.2 Exposure to supply chain disruptions
- 5.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES
- 5.2.3.1 Battery leasing and mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) models
- 5.2.3.2 Development of wireless EV charging technology for on-the-go charging
- 5.2.4 CHALLENGES
- 5.2.4.1 Lack of standardization in charging protocols
- 5.2.4.2 Low availability of lithium for EV batteries
- 5.2.5 IMPACT OF MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.2.1 DRIVERS
- 5.3 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS
- 5.4 PRICING ANALYSIS
- 5.4.1 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND FOR VEHICLE TYPES, BY KEY PLAYERS, 2024 (USD)
- 5.4.2 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND, BY REGION, 2022-2024
- 5.5 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS
- 5.5.1 OEMS
- 5.5.2 RAW MATERIAL SUPPLIERS
- 5.5.3 TIER I SUPPLIERS
- 5.5.4 TIER II SUPPLIERS
- 5.5.5 COMPONENT MANUFACTURERS
- 5.5.6 EV CHARGING INFRASTRUCTURE PROVIDERS
- 5.6 SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS
- 5.7 REGULATORY LANDSCAPE
- 5.7.1 COUNTRY-WISE REGULATIONS
- 5.7.1.1 Netherlands
- 5.7.1.2 Germany
- 5.7.1.3 France
- 5.7.1.4 UK
- 5.7.1.5 China
- 5.7.1.6 US
- 5.7.2 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS
- 5.7.1 COUNTRY-WISE REGULATIONS
- 5.8 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2025-2026
- 5.9 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS
- 5.9.1 FEDEX'S LEAP INTO SUSTAINABLE LOGISTICS
- 5.9.2 SCOTTISH WATER'S SUCCESSFUL ADOPTION OF ELECTRIC VANS
- 5.9.3 ELECTRIC VAN TRIAL FOR BUSINESSES BY KENT COUNTY COUNCIL
- 5.10 INVESTMENT AND FUNDING SCENARIO
- 5.11 PATENT ANALYSIS
- 5.11.1 INTRODUCTION
- 5.12 HS CODE (8702): ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE
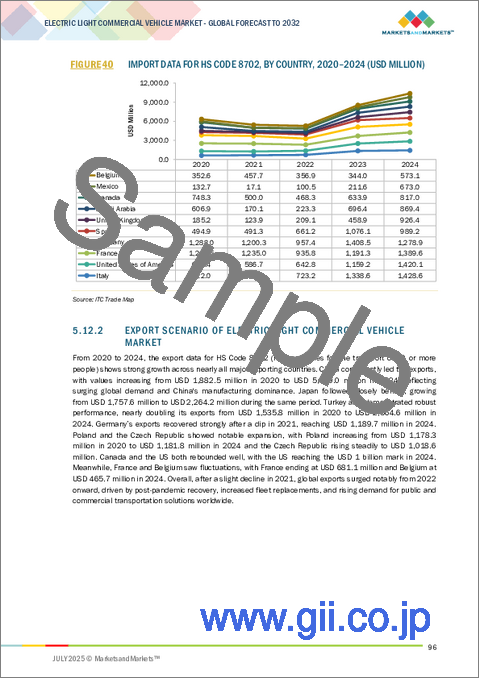
- 5.12.1 IMPORT SCENARIO OF ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET
- 5.12.2 EXPORT SCENARIO OF ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET
- 5.13 IMPACT OF AI/GEN AI
- 5.14 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS
- 5.14.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.14.1.1 Development in wireless charging technology
- 5.14.1.2 Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) integration
- 5.14.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.14.2.1 Development in solid-state batteries
- 5.14.2.2 Advanced fleet telematics systems
- 5.14.3 ADJACENT TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.14.3.1 Multi-motor configurations
- 5.14.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES
- 5.15 MNM INSIGHTS ON UPCOMING VEHICLE LAUNCHES, KEY OEM INVESTMENTS, AND TARGET FOR ELECTRIFICATION
- 5.15.1 UPCOMING VEHICLE MODEL LAUNCHES
- 5.15.2 OEM TARGETS AND INVESTMENT
- 5.16 INSIGHTS INTO OEMS' STRATEGIES FOR ELCV PLATFORMS
- 5.17 STRATEGIC INSIGHTS INTO BATTERY SWAPPING FOR ELECTRIC PICKUP TRUCKS AND VANS
- 5.18 BUSINESS CASE ANALYSIS FOR ELECTRIC PICKUP TRUCKS AND VANS
- 5.18.1 FLEET OWNERSHIP & OPERATIONS
- 5.18.2 FLEET-AS-A-SERVICE (FAAS)
- 5.18.3 PLATFORM AND ECOSYSTEM COLLABORATION
- 5.18.4 PAY-PER-USE MODEL
- 5.19 BILL OF MATERIALS
- 5.20 TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP
- 5.21 KEY PERFORMANCE COMPARISON FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES
- 5.21.1 RANGE/BATTERY CAPACITY
- 5.21.2 RANGE VS. END USE
- 5.21.3 BATTERY CAPACITY VS. END USE
- 5.21.4 POWER VS. CHARGING DURATION
- 5.22 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA
- 5.22.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS
- 5.22.2 BUYING CRITERIA
6 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY VEHICLE TYPE
- 6.1 INTRODUCTION
- 6.2 PICKUP TRUCK
- 6.2.1 RISING DEMAND FOR DUAL-PURPOSE UTILITY VEHICLES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 6.3 VAN
- 6.3.1 LOWER TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 6.3.2 CARGO VAN
- 6.3.3 PASSENGER VAN
- 6.4 KEY PRIMARY INSIGHTS
7 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY PROPULSION
- 7.1 INTRODUCTION
- 7.2 BATTERY ELECTRIC VEHICLE
- 7.2.1 LOWER TOTAL COST OF OWNERSHIP THAN ICE AND HYBRID VEHICLES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 7.3 PLUG-IN HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLE
- 7.3.1 LOWER RANGE ANXIETY AND OPERATIONAL FLEXIBILITY TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 7.4 PRIMARY INSIGHTS
8 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY CAPACITY
- 8.1 INTRODUCTION
- 8.2 UP TO 50 KWH
- 8.2.1 INCREASING ADOPTION OF COMPACT DELIVERY VANS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 8.3 50 TO 100 KWH
- 8.3.1 SUITABILITY FOR MID-RANGE LOGISTICS AND URBAN-SUBURBAN DELIVERY OPERATIONS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 8.4 100 TO 150 KWH
- 8.4.1 HIGH PAYLOAD APPLICATIONS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 8.5 PRIMARY INSIGHTS
9 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY BATTERY TYPE
- 9.1 INTRODUCTION
- 9.2 LITHIUM IRON PHOSPHATE (LFP)
- 9.2.1 HIGH ENERGY DENSITY AND FAST-CHARGING CAPABILITIES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 9.3 NICKEL MANGANESE COBALT (NMC)
- 9.3.1 LONG DRIVING RANGES FOR LOGISTICS AND DELIVERY TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 9.4 SOLID-STATE
- 9.4.1 LONGER LIFECYCLE THAN CONVENTIONAL LITHIUM-ION BATTERIES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 9.5 OTHERS
- 9.6 PRIMARY INSIGHTS
10 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY END USE
- 10.1 INTRODUCTION
- 10.2 LAST-MILE DELIVERY
- 10.2.1 RISING DEMAND FOR VEHICLE ELECTRIFICATION IN E-COMMERCE TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 10.3 FIELD SERVICES
- 10.3.1 INCREASING DEMAND FOR GREEN MOBILITY IN FIELD SERVICES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 10.4 DISTRIBUTION SERVICES
- 10.4.1 INCREASING RELIANCE ON DELIVERY SERVICES TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 10.5 KEY INDUSTRY INSIGHTS
11 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY GVWR
- 11.1 INTRODUCTION
- 11.2 BELOW 6,000 LBS
- 11.2.1 GROWING DEMAND FOR LAST-MILE DELIVERY IN URBAN AREAS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 11.3 6,001-10,000 LBS
- 11.3.1 GROWING DEMAND FOR OPTIMAL LOAD-CARRYING CAPACITY DRIVE GROWTH
- 11.4 PRIMARY INSIGHTS
12 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY RANGE
- 12.1 INTRODUCTION
- 12.2 UP TO 100 MILES
- 12.2.1 INCREASING DEMAND FROM MICRO-MOBILITY LOGISTICS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 12.3 100 TO 200 MILES
- 12.3.1 OPERATIONAL FLEXIBILITY AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 12.4 ABOVE 200 MILES
- 12.4.1 INCREASING DEMAND FOR ZERO-EMISSION CARGO VANS IN EUROPE TO DRIVE GROWTH
- 12.5 PRIMARY INSIGHTS
13 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY REGION
- 13.1 INTRODUCTION
- 13.2 CHINA
- 13.2.1 RAPID ROLLOUT OF COST-EFFECTIVE ELCVS TO DRIVE MARKET
- 13.2.2 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 13.3 ASIA PACIFIC (EXCL. CHINA)
- 13.3.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 13.3.2 JAPAN
- 13.3.2.1 Government-led decarbonization and urban logistics innovation to drive growth
- 13.3.3 INDIA
- 13.3.3.1 Urban emission norms and government push toward clean mobility to drive growth
- 13.3.4 SOUTH KOREA
- 13.3.4.1 Targeted fleet electrification initiatives to drive growth
- 13.4 EUROPE
- 13.4.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 13.4.2 FRANCE
- 13.4.2.1 Growth in e-commerce and parcel delivery to drive market
- 13.4.3 GERMANY
- 13.4.3.1 Commercial charging infrastructure development to drive growth
- 13.4.4 SPAIN
- 13.4.4.1 Government-led electrification targets and subsidies to drive growth
- 13.4.5 AUSTRIA
- 13.4.5.1 Increasing deployment of fast-charging hubs near industrial parks and logistic centers to drive growth
- 13.4.6 NORWAY
- 13.4.6.1 Zero-emission commercial transport policies to drive growth
- 13.4.7 SWEDEN
- 13.4.7.1 Government-backed green transport incentives to drive growth
- 13.4.8 NETHERLANDS
- 13.4.8.1 Stringent legislation to drive growth
- 13.4.9 UK
- 13.4.9.1 ZEV mandate to drive growth
- 13.4.10 ITALY
- 13.4.10.1 Integration of smart mobility solutions in commercial fleets to drive growth
- 13.4.11 REST OF EUROPE
- 13.5 NORTH AMERICA
- 13.5.1 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK
- 13.5.2 US
- 13.5.2.1 Rising adoption of electric pickup trucks to drive growth
- 13.5.3 CANADA
- 13.5.3.1 Government plans to electrify transit to drive growth
14 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 14.1 OVERVIEW
- 14.2 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN
- 14.3 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2024
- 14.4 REVENUE ANALYSIS, 2020-2024
- 14.5 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS
- 14.5.1 COMPANY VALUATION
- 14.5.2 FINANCIAL METRICS
- 14.6 BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON
- 14.7 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2024
- 14.7.1 STARS
- 14.7.2 EMERGING LEADERS
- 14.7.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS
- 14.7.4 PARTICIPANTS
- 14.7.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT
- 14.7.5.1 Company footprint
- 14.7.5.2 Region footprint
- 14.7.5.3 Vehicle type footprint
- 14.8 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2024
- 14.8.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES
- 14.8.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES
- 14.8.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES
- 14.8.4 STARTING BLOCKS
- 14.8.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING
- 14.8.5.1 List of startups/SMEs
- 14.8.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of startups/SMEs
- 14.9 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO
- 14.9.1 PRODUCT LAUNCHES
- 14.9.2 DEALS
- 14.9.3 EXPANSIONS
- 14.9.4 OTHER DEVELOPMENTS
15 COMPANY PROFILES
- 15.1 KEY PLAYERS
- 15.1.1 WULING MOTORS HOLDINGS LIMITED
- 15.1.1.1 Business overview
- 15.1.1.2 Products offered
- 15.1.1.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.1.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.1.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.1.4 MnM view
- 15.1.1.4.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.1.4.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.1.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 15.1.2 FORD MOTOR COMPANY
- 15.1.2.1 Business overview
- 15.1.2.2 Products offered
- 15.1.2.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.2.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.2.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.2.3.3 Expansions
- 15.1.2.3.4 Other developments
- 15.1.2.4 MnM view
- 15.1.2.4.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.2.4.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.2.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 15.1.3 GENERAL MOTORS
- 15.1.3.1 Business overview
- 15.1.3.2 Chevrolet BrightDrop
- 15.1.3.3 Products offered
- 15.1.3.4 Recent developments
- 15.1.3.4.1 Deals
- 15.1.3.5 MnM view
- 15.1.3.5.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.3.5.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.3.5.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 15.1.4 STELLANTIS N.V.
- 15.1.4.1 Business overview
- 15.1.4.2 Peugeot
- 15.1.4.3 Citroen
- 15.1.4.4 Fiat Professional
- 15.1.4.5 Vauxhall
- 15.1.4.6 Ram
- 15.1.4.7 Products offered
- 15.1.4.8 Recent developments
- 15.1.4.8.1 Product launches
- 15.1.4.8.2 Deals
- 15.1.4.9 MnM view
- 15.1.4.9.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.4.9.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.4.9.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 15.1.5 RENAULT GROUP
- 15.1.5.1 Business overview
- 15.1.5.2 Products offered
- 15.1.5.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.5.3.1 Product developments
- 15.1.5.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.5.4 MnM view
- 15.1.5.4.1 Key strengths
- 15.1.5.4.2 Strategic choices
- 15.1.5.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats
- 15.1.6 TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION
- 15.1.6.1 Business overview
- 15.1.6.2 Products offered
- 15.1.6.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.6.3.1 Deals
- 15.1.6.3.2 Other developments
- 15.1.7 BYD COMPANY LTD.
- 15.1.7.1 Business overview
- 15.1.7.2 Products offered
- 15.1.7.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.7.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.7.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.7.3.3 Expansions
- 15.1.8 NISSAN MOTOR CO., LTD.
- 15.1.8.1 Business overview
- 15.1.8.2 Products offered
- 15.1.8.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.8.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.8.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.9 IVECO GROUP N.V.
- 15.1.9.1 Business overview
- 15.1.9.2 Products offered
- 15.1.9.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.9.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.9.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.10 FLEXIS
- 15.1.10.1 Business overview
- 15.1.10.2 Products offered
- 15.1.10.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.10.3.1 Deals
- 15.1.11 RIVIAN
- 15.1.11.1 Business overview
- 15.1.11.2 Products offered
- 15.1.11.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.11.3.1 Product enhancements/launches
- 15.1.11.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.11.3.3 Other developments
- 15.1.12 FOTON INTERNATIONAL
- 15.1.12.1 Business overview
- 15.1.12.2 Products offered
- 15.1.12.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.12.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.12.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.12.3.3 Other developments
- 15.1.13 TATA MOTORS LIMITED
- 15.1.13.1 Business overview
- 15.1.13.2 Products offered
- 15.1.13.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.13.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.13.3.2 Deals
- 15.1.14 MAXUS ELECTRIC VEHICLES AND VANS
- 15.1.14.1 Business overview
- 15.1.14.2 Products offered
- 15.1.14.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.14.3.1 Product launches
- 15.1.15 MITSUBISHI FUSO TRUCK AND BUS CORPORATION
- 15.1.15.1 Business overview
- 15.1.15.2 Products offered
- 15.1.15.3 Recent developments
- 15.1.15.3.1 Deals
- 15.1.15.3.2 Other developments
- 15.1.1 WULING MOTORS HOLDINGS LIMITED
- 15.2 OTHER PLAYERS
- 15.2.1 SWITCH MOBILITY
- 15.2.2 EULER MOTORS
- 15.2.3 TELO TRUCKS
- 15.2.4 OMEGA SEIKI MOBILITY
- 15.2.5 SLATE
- 15.2.6 EVUM MOTORS
- 15.2.7 ARRIVAL UK LTD.
- 15.2.8 EKA MOBILITY
- 15.2.9 NU RIDE INC.
- 15.2.10 MULLEN AUTOMOTIVE, INC.
- 15.2.11 EVAGE
- 15.2.12 QUCEV
- 15.2.13 KAIYUN MOTORS
16 RECOMMENDATIONS BY MARKETSANDMARKETS
- 16.1 CHINA TO BE PROMINENT MARKET FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLES
- 16.2 6,001 TO 10,000 LBS SEGMENT TO WITNESS GROWTH DURING FORECAST PERIOD
- 16.3 INTEGRATION OF ADVANCED DRIVER ASSISTANCE SYSTEMS
- 16.4 CONCLUSION
17 APPENDIX
- 17.1 KEY INSIGHTS OF INDUSTRY EXPERTS
- 17.2 DISCUSSION GUIDE
- 17.3 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS' SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL
- 17.4 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS
- 17.4.1 COMPANY PROFILES
- 17.4.1.1 Profiling of Additional Market Players (Up to 5)
- 17.4.2 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY PROPULSION, AT COUNTRY LEVEL
- 17.4.3 ELECTRIC LIGHT COMMERCIAL VEHICLE MARKET, BY GVWR, AT COUNTRY LEVEL
- 17.4.1 COMPANY PROFILES
- 17.5 RELATED REPORTS
- 17.6 AUTHOR DETAILS