|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1803783
核融合エネルギー市場:技術、燃料タイプ、エンドユーザー別-2025-2030年の世界予測Fusion Energy Market by Technology, Fuel Type, End-User - Global Forecast 2025-2030 |
||||||
カスタマイズ可能
適宜更新あり
|
|||||||
| 核融合エネルギー市場:技術、燃料タイプ、エンドユーザー別-2025-2030年の世界予測 |
|
出版日: 2025年08月28日
発行: 360iResearch
ページ情報: 英文 180 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
核融合エネルギー市場は、2024年には276億3,000万米ドルとなり、2025年には293億8,000万米ドル、CAGR6.58%で成長し、2030年には405億3,000万米ドルに達すると予測されています。
| 主な市場の統計 | |
|---|---|
| 基準年2024 | 276億3,000万米ドル |
| 推定年2025 | 293億8,000万米ドル |
| 予測年2030 | 405億3,000万米ドル |
| CAGR(%) | 6.58% |
世界のエネルギー情勢と技術フロンティアを一変させる革命的電源としての核融合エネルギーの台頭を理解する
核融合エネルギーが数十年にわたる研究から、ネット・プラス発電の具体的な実証へと姿を現すにつれ、世界のエネルギー部門は重大な変革の危機に瀕しています。二酸化炭素排出に対する懸念の高まり、化石燃料供給を混乱させる地政学的緊張、信頼性の高いベースロード電力に対する需要の急増が、核融合を理論的な有望性から短期的な商業的実現可能性へと押し上げる要因となっています。プラズマ閉じ込めと持続的な高温運転における工学的マイルストーンの達成により、核融合は、最小限の環境フットプリントで豊富なゼロ炭素エネルギーを供給するという、永続的な使命を果たす態勢が整いつつあります。
核融合エネルギーを商業的実現に近づける重要な技術的強化と新たな規制的枠組みの特定
近年、核融合エネルギーを商業化に向けて推進する一連の変革的な変化が起きています。高温超伝導体の技術的進歩は、より小型で効率的な磁気閉じ込め装置を可能にし、建設面積と運転コストの両方を削減しました。同時に、新しいレーザーシステムは、エネルギー供給能力を前例のないレベルまで拡大し、慣性閉じ込めアプローチを強化し、点火への代替経路を提供しています。
米国の新たな関税措置が、国際的な核融合エネルギーのサプライチェーンとイノベーションの道筋をどのように再構築するかを検証します
2025年に発効する米国の新たな関税措置の導入は、世界の核融合エネルギーサプライチェーンにとって重要な転換点となります。輸入される高強度合金、特殊超電導線材、磁石製造に不可欠なレアアース部品に関税を課すことで、これらの関税は国内生産能力を強化することを目的としています。しかし、この関税は、ニッチ材料や精密加工をこれまで海外の定評あるサプライヤーに依存してきた原子炉開発企業にとって、短期的なコスト圧力に拍車をかけるものでもあります。
核融合エネルギー採用を形成する原子炉プラットフォーム燃料様式と多様なエンドユーザー用途にわたる市場セグメンテーション洞察の公開
核融合エネルギー市場は、慣性閉じ込めと磁気閉じ込めという2つの主要な原子炉技術によって二分されます。慣性閉じ込めシステムは、高出力レーザーや粒子ビームを利用して燃料ペレットを急速に圧縮し、核融合に必要な温度と圧力を発生させる。一方、磁気閉じ込め炉は、強力な磁場を利用してプラズマをトロイダルチャンバーやステラレーターチャンバー内に閉じ込める。エンジニアリングの複雑さ、スケーラビリティ、運転時間効率といった点で、これらのプラットフォーム間に内在するトレードオフが、業界全体で異なる開発スケジュールと商業化戦略を推進しています。
核融合エネルギー開発の軌道を左右するアジア太平洋地域ダイナミクスの分析
核融合エネルギー展開のペースと性格を決定する上で、地域ダイナミクスの役割は非常に大きいです。南北アメリカでは、米国は深いベンチャーキャピタル市場、広範な国立研究所ネットワーク、そして民間の技術革新に報いる連邦政府の支援プログラムから恩恵を受けています。カナダは強磁場超伝導の専門家として貢献し、次世代設計のテストベッドとなる研究炉を維持しています。大陸を越えた開発協力は、共同開発ベンチャーや二国間資金援助イニシアティブを生み出しています。
進化する核融合エネルギー分野におけるリーダーシップを定義する戦略的企業イニシアティブと協力的エコシステムのハイライト
大手核融合開発者は、技術的リーダーシップと市場でのポジショニングを確保するために、それぞれ独自の戦略を実行しています。ある企業は、モジュール化されたコンポーネント化された原子炉アーキテクチャに重点を置き、迅速なプロトタイプの反復とコスト効率の良いスケーリングを可能にしています。また、超伝導マグネットの製造からプラズマ診断、制御ソフトウェアに至るまで、すべてをコントロールする垂直統合型のバリューチェーンに集中する企業もあります。選ばれた企業は、原子炉の寿命を延ばし、メンテナンスの中断を減らすために、先進的な材料研究に資源を投入し、並行して、リアルタイムのプラズマ安定化を達成するために、AI主導の運転モデルを最適化しています。
サプライチェーンを強化し、規制当局を巻き込み、商業展開を加速するために、核融合エネルギーの利害関係者に戦略的アクションプランを提供します
核融合エネルギーの可能性を最大限に活用するために、業界のリーダーたちは、技術的進歩と戦略的利害関係者の関与のバランスをとる多方面からのアプローチを採用すべきです。第一に、組織は国内サプライチェーンの弾力性への投資を深化させ、変動する関税の中で重要な材料と製造能力へのアクセスを確保しなければならないです。地域の鋳造所や専門部品メーカーとの関係を深めることで、調達リスクを軽減し、機敏なスケーリングを支援します。
包括的な融合分析のための専門家インタビューデータ分析とシナリオプランニングを組み合わせた頑健な混合法調査フレームワークの概説
本調査では、包括的かつ信頼性の高い知見を確保するため、混合法のアプローチを統合しました。一次データは、核融合エネルギーのエコシステム全体にわたる経営幹部、技術責任者、政策アドバイザーとの一対一のインタビューを通じて収集され、技術ロードマップ、資金戦略、規制の優先順位に関する直接の視点を捉えました。これらの定性的な知見は、オープンソースの技術論文、特許申請、政府の政策文書、投資開示の広範なレビューによって補完され、業界の進歩に関する客観的な物語を構築しました。
核融合エネルギー発展の戦略的重要性を明らかにするために、技術の進歩、規制の変化、市場力学に関する統合された洞察を引き出します
本レポートは、核融合エネルギーの技術的進歩、関税動向、セグメンテーションのニュアンス、地域ダイナミックス、企業戦略を統合することで、核融合エネルギーが実験室の好奇心から信頼できる商業的競争相手へと変遷していることを強調しています。超伝導磁石、レーザー閉じ込め、原子炉材料におけるブレークスルーは、民間部門の技術革新のための肥沃な土壌を作り出すために、支援的な政策環境と融合しました。同時に、新たな関税制度や地域的な投資パターンによって、適応力のあるサプライチェーン戦略や国境を越えた協力体制が必要とされています。
目次
第1章 序文
第2章 調査手法
第3章 エグゼクティブサマリー
第4章 市場の概要
第5章 市場力学
- トカマクの性能を向上させる高温超伝導磁石の進歩
- 民間資金の拡大により小型核融合炉の開発が加速
- 予測的なプラズマ制御とリアルタイム最適化のための人工知能の統合
- ステラレータや慣性核融合推進装置などの代替閉じ込め手法の出現
- 核融合炉部品の重要な材料への依存度を低減するサプライチェーンの革新
第6章 市場洞察
- ポーターのファイブフォース分析
- PESTEL分析
第7章 米国の関税の累積的な影響2025
第8章 核融合エネルギー市場:技術別
- 慣性閉じ込め
- 磁気閉じ込め
第9章 核融合エネルギー市場:燃料の種類別
- 重水素-重水素
- 重水素-三重水素
- ヘリウム3
- 陽子-ホウ素
第10章 核融合エネルギー市場:エンドユーザー別
- 航空宇宙
- 農業
- 商業用
- 産業
- 軍事・防衛
- 住宅用
- 運輸部門
第11章 南北アメリカの核融合エネルギー市場
- 米国
- カナダ
- メキシコ
- ブラジル
- アルゼンチン
第12章 欧州・中東・アフリカの核融合エネルギー市場
- 英国
- ドイツ
- フランス
- ロシア
- イタリア
- スペイン
- アラブ首長国連邦
- サウジアラビア
- 南アフリカ
- デンマーク
- オランダ
- カタール
- フィンランド
- スウェーデン
- ナイジェリア
- エジプト
- トルコ
- イスラエル
- ノルウェー
- ポーランド
- スイス
第13章 アジア太平洋地域の核融合エネルギー市場
- 中国
- インド
- 日本
- オーストラリア
- 韓国
- インドネシア
- タイ
- フィリピン
- マレーシア
- シンガポール
- ベトナム
- 台湾
第14章 競合情勢
- 市場シェア分析, 2024
- FPNVポジショニングマトリックス, 2024
- 競合分析
- Commonwealth Fusion Systems
- TAE Technologies, Inc.
- Commonwealth Fusion Systems, LLC
- Elytt Energy, Inc.
- First Light Fusion Ltd.
- Fuse
- Fusion Industry Association, Inc.
- General Fusion Inc.
- HB11 Energy Holdings Pty Ltd
- Helion Energy, Inc.
- Hyperjet Fusion Corporation
- Kyoto Fusioneering Ltd.
- Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC
- LPPFusion, Inc.
- Magneto-Inertial Fusion Technologies, Inc.
- Marvel Fusion GmbH
- MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD.
- Oklo Inc.
- Proxima Fusion GmbH
- Renaissance Fusion
- Thea Energy Inc.
- Tokamak Energy Ltd.
- Tokamak Energy Ltd.
- Woodruff Scientific, Inc.
- Xcimer Energy, Inc.
- Zap Energy, Inc.
第15章 リサーチAI
第16章 リサーチ統計
第17章 リサーチコンタクト
第18章 リサーチ記事
第19章 付録
LIST OF FIGURES
- FIGURE 1. FUSION ENERGY MARKET RESEARCH PROCESS
- FIGURE 2. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, 2018-2030 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 3. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2024 VS 2025 VS 2030 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 4. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2024 VS 2025 VS 2030 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 5. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2024 VS 2030 (%)
- FIGURE 6. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2024 VS 2025 VS 2030 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 7. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2024 VS 2030 (%)
- FIGURE 8. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2024 VS 2025 VS 2030 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 9. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2024 VS 2030 (%)
- FIGURE 10. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2024 VS 2025 VS 2030 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 11. AMERICAS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2024 VS 2030 (%)
- FIGURE 12. AMERICAS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2024 VS 2025 VS 2030 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 13. UNITED STATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY STATE, 2024 VS 2030 (%)
- FIGURE 14. UNITED STATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY STATE, 2024 VS 2025 VS 2030 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 15. EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2024 VS 2030 (%)
- FIGURE 16. EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2024 VS 2025 VS 2030 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 17. ASIA-PACIFIC FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2024 VS 2030 (%)
- FIGURE 18. ASIA-PACIFIC FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2024 VS 2025 VS 2030 (USD MILLION)
- FIGURE 19. FUSION ENERGY MARKET SHARE, BY KEY PLAYER, 2024
- FIGURE 20. FUSION ENERGY MARKET, FPNV POSITIONING MATRIX, 2024
- FIGURE 21. FUSION ENERGY MARKET: RESEARCHAI
- FIGURE 22. FUSION ENERGY MARKET: RESEARCHSTATISTICS
- FIGURE 23. FUSION ENERGY MARKET: RESEARCHCONTACTS
- FIGURE 24. FUSION ENERGY MARKET: RESEARCHARTICLES
LIST OF TABLES
- TABLE 1. FUSION ENERGY MARKET SEGMENTATION & COVERAGE
- TABLE 2. UNITED STATES DOLLAR EXCHANGE RATE, 2018-2024
- TABLE 3. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 4. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 5. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 6. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 7. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 8. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 9. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 10. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 11. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY INERTIAL CONFINEMENT, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 12. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY INERTIAL CONFINEMENT, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 13. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY MAGNETIC CONFINEMENT, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 14. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY MAGNETIC CONFINEMENT, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 15. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 16. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 17. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY DEUTERIUM-DEUTERIUM, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 18. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY DEUTERIUM-DEUTERIUM, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 19. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY DEUTERIUM-TRITIUM, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 20. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY DEUTERIUM-TRITIUM, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 21. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY HELIUM-3, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 22. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY HELIUM-3, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 23. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY PROTON-BORON, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 24. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY PROTON-BORON, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 25. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 26. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 27. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY AEROSPACE, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 28. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY AEROSPACE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 29. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY AGRICULTURE, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 30. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY AGRICULTURE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 31. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COMMERCIAL, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 32. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COMMERCIAL, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 33. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY INDUSTRIAL, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 34. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY INDUSTRIAL, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 35. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY MILITARY & DEFENSE, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 36. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY MILITARY & DEFENSE, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 37. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY RESIDENTIAL, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 38. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY RESIDENTIAL, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 39. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TRANSPORTATION SECTOR, BY REGION, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 40. GLOBAL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TRANSPORTATION SECTOR, BY REGION, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 41. AMERICAS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 42. AMERICAS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 43. AMERICAS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 44. AMERICAS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 45. AMERICAS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 46. AMERICAS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 47. AMERICAS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 48. AMERICAS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 49. UNITED STATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 50. UNITED STATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 51. UNITED STATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 52. UNITED STATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 53. UNITED STATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 54. UNITED STATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 55. UNITED STATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY STATE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 56. UNITED STATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY STATE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 57. CANADA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 58. CANADA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 59. CANADA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 60. CANADA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 61. CANADA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 62. CANADA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 63. MEXICO FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 64. MEXICO FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 65. MEXICO FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 66. MEXICO FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 67. MEXICO FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 68. MEXICO FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 69. BRAZIL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 70. BRAZIL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 71. BRAZIL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 72. BRAZIL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 73. BRAZIL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 74. BRAZIL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 75. ARGENTINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 76. ARGENTINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 77. ARGENTINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 78. ARGENTINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 79. ARGENTINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 80. ARGENTINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 81. EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 82. EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 83. EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 84. EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 85. EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 86. EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 87. EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 88. EUROPE, MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 89. UNITED KINGDOM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 90. UNITED KINGDOM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 91. UNITED KINGDOM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 92. UNITED KINGDOM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 93. UNITED KINGDOM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 94. UNITED KINGDOM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 95. GERMANY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 96. GERMANY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 97. GERMANY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 98. GERMANY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 99. GERMANY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 100. GERMANY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 101. FRANCE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 102. FRANCE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 103. FRANCE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 104. FRANCE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 105. FRANCE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 106. FRANCE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 107. RUSSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 108. RUSSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 109. RUSSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 110. RUSSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 111. RUSSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 112. RUSSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 113. ITALY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 114. ITALY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 115. ITALY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 116. ITALY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 117. ITALY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 118. ITALY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 119. SPAIN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 120. SPAIN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 121. SPAIN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 122. SPAIN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 123. SPAIN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 124. SPAIN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 125. UNITED ARAB EMIRATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 126. UNITED ARAB EMIRATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 127. UNITED ARAB EMIRATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 128. UNITED ARAB EMIRATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 129. UNITED ARAB EMIRATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 130. UNITED ARAB EMIRATES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 131. SAUDI ARABIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 132. SAUDI ARABIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 133. SAUDI ARABIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 134. SAUDI ARABIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 135. SAUDI ARABIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 136. SAUDI ARABIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 137. SOUTH AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 138. SOUTH AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 139. SOUTH AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 140. SOUTH AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 141. SOUTH AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 142. SOUTH AFRICA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 143. DENMARK FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 144. DENMARK FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 145. DENMARK FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 146. DENMARK FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 147. DENMARK FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 148. DENMARK FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 149. NETHERLANDS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 150. NETHERLANDS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 151. NETHERLANDS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 152. NETHERLANDS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 153. NETHERLANDS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 154. NETHERLANDS FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 155. QATAR FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 156. QATAR FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 157. QATAR FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 158. QATAR FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 159. QATAR FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 160. QATAR FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 161. FINLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 162. FINLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 163. FINLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 164. FINLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 165. FINLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 166. FINLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 167. SWEDEN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 168. SWEDEN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 169. SWEDEN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 170. SWEDEN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 171. SWEDEN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 172. SWEDEN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 173. NIGERIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 174. NIGERIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 175. NIGERIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 176. NIGERIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 177. NIGERIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 178. NIGERIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 179. EGYPT FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 180. EGYPT FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 181. EGYPT FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 182. EGYPT FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 183. EGYPT FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 184. EGYPT FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 185. TURKEY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 186. TURKEY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 187. TURKEY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 188. TURKEY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 189. TURKEY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 190. TURKEY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 191. ISRAEL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 192. ISRAEL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 193. ISRAEL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 194. ISRAEL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 195. ISRAEL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 196. ISRAEL FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 197. NORWAY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 198. NORWAY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 199. NORWAY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 200. NORWAY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 201. NORWAY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 202. NORWAY FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 203. POLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 204. POLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 205. POLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 206. POLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 207. POLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 208. POLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 209. SWITZERLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 210. SWITZERLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 211. SWITZERLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 212. SWITZERLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 213. SWITZERLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 214. SWITZERLAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 215. ASIA-PACIFIC FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 216. ASIA-PACIFIC FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 217. ASIA-PACIFIC FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 218. ASIA-PACIFIC FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 219. ASIA-PACIFIC FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 220. ASIA-PACIFIC FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 221. ASIA-PACIFIC FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 222. ASIA-PACIFIC FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY COUNTRY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 223. CHINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 224. CHINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 225. CHINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 226. CHINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 227. CHINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 228. CHINA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 229. INDIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 230. INDIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 231. INDIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 232. INDIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 233. INDIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 234. INDIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 235. JAPAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 236. JAPAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 237. JAPAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 238. JAPAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 239. JAPAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 240. JAPAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 241. AUSTRALIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 242. AUSTRALIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 243. AUSTRALIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 244. AUSTRALIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 245. AUSTRALIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 246. AUSTRALIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 247. SOUTH KOREA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 248. SOUTH KOREA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 249. SOUTH KOREA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 250. SOUTH KOREA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 251. SOUTH KOREA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 252. SOUTH KOREA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 253. INDONESIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 254. INDONESIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 255. INDONESIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 256. INDONESIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 257. INDONESIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 258. INDONESIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 259. THAILAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 260. THAILAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 261. THAILAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 262. THAILAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 263. THAILAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 264. THAILAND FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 265. PHILIPPINES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 266. PHILIPPINES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 267. PHILIPPINES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 268. PHILIPPINES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 269. PHILIPPINES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 270. PHILIPPINES FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 271. MALAYSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 272. MALAYSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 273. MALAYSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 274. MALAYSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 275. MALAYSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 276. MALAYSIA FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 277. SINGAPORE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 278. SINGAPORE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 279. SINGAPORE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 280. SINGAPORE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 281. SINGAPORE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 282. SINGAPORE FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 283. VIETNAM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 284. VIETNAM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 285. VIETNAM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 286. VIETNAM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 287. VIETNAM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 288. VIETNAM FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 289. TAIWAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 290. TAIWAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY TECHNOLOGY, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 291. TAIWAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 292. TAIWAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY FUEL TYPE, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 293. TAIWAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2018-2024 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 294. TAIWAN FUSION ENERGY MARKET SIZE, BY END-USER, 2025-2030 (USD MILLION)
- TABLE 295. FUSION ENERGY MARKET SHARE, BY KEY PLAYER, 2024
- TABLE 296. FUSION ENERGY MARKET, FPNV POSITIONING MATRIX, 2024
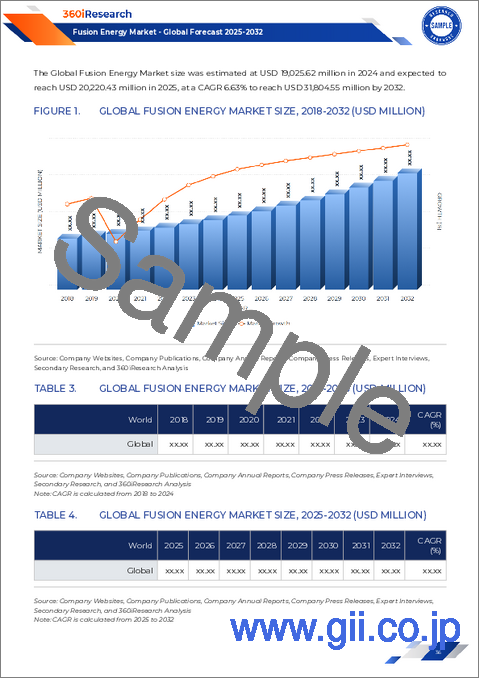
The Fusion Energy Market was valued at USD 27.63 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 29.38 billion in 2025, with a CAGR of 6.58%, reaching USD 40.53 billion by 2030.
| KEY MARKET STATISTICS | |
|---|---|
| Base Year [2024] | USD 27.63 billion |
| Estimated Year [2025] | USD 29.38 billion |
| Forecast Year [2030] | USD 40.53 billion |
| CAGR (%) | 6.58% |
Understanding the Imminent Rise of Fusion Energy as a Revolutionary Power Source Transforming Global Energy Landscapes and Technological Frontiers
The global energy sector stands on the cusp of a profound transformation as fusion energy emerges from decades of research into tangible demonstrations of net-positive power generation. Rising concerns over carbon emissions, geopolitical tensions disrupting fossil fuel supply, and surging demand for reliable baseload electricity have converged to elevate fusion from theoretical promise to near-term commercial viability. With engineering milestones achieved in plasma confinement and sustained high-temperature operation, fusion is poised to fulfill an enduring mandate: delivering abundant, zero-carbon energy with minimal environmental footprint.
This report initiates with a detailed examination of the current fusion landscape, tracing the critical breakthroughs in superconducting magnet technology, high-power lasers, and advanced materials that have accelerated progress. It also considers the pivotal role of public-private partnerships, government funding increases, and international collaborations that have de-risked projects and attracted unprecedented venture capital investment. By situating these developments within the broader context of energy security concerns and decarbonization mandates, the analysis highlights why fusion now commands the attention of policymakers, utilities, and forward-looking corporations seeking stable, scalable power solutions.
As a result, decision-makers are confronted with both remarkable opportunity and complex challenges. This introduction sets the stage for subsequent sections, which delve into regulatory shifts, tariff impacts, segmentation nuances, regional dynamics, competitive positioning, and actionable recommendations. The insights offered here will equip executives and stakeholders with the knowledge required to navigate an industry on the brink of revolution.
Identifying Key Technological Enhancements and Emerging Regulatory Frameworks That Propel Fusion Energy Closer to Commercial Realization
Recent years have witnessed a series of transformative shifts that have collectively propelled fusion energy toward commercialization. Technological advancements in high-temperature superconductors have enabled more compact and efficient magnetic confinement devices, reducing both construction footprints and operating costs. Simultaneously, novel laser systems have scaled their energy delivery capability to unprecedented levels, enhancing inertial confinement approaches and offering alternative pathways to ignition.
Regulatory ecosystems have adapted in parallel. Several national authorities have introduced fast-track permitting processes for fusion pilot plants, while cross-border frameworks are being negotiated to standardize licensing and safety protocols. This regulatory harmonization reduces project lead times and clarifies compliance requirements for private developers. Moreover, governments in key markets have unveiled incentive structures, including tax credits and milestone-based grants, specifically designed to accelerate private investment and de-risk early prototypes.
Collectively, these shifts underscore a pivotal moment in energy innovation. Technological readiness has converged with supportive policy frameworks, ushering in an era where fusion is no longer an abstract aspiration but an achievable industrial endeavor. The interplay between rapid hardware improvements, evolving regulatory landscapes, and intensified stakeholder collaboration sets the stage for the next wave of commercial fusion projects.
Examining How New United States Tariff Measures Will Reshape International Fusion Energy Supply Chains and Innovation Pathways
The introduction of new United States tariff measures effective in 2025 represents a significant inflection point for global fusion energy supply chains. By imposing duties on imported high-strength alloys, specialized superconducting wire, and select rare earth components critical to magnet manufacture, these tariffs aim to strengthen domestic production capabilities. However, they also catalyze near-term cost pressures for reactor developers that have historically relied on established overseas suppliers for niche materials and precision fabrication.
In response, several fusion enterprises are accelerating onshore partnerships with domestic foundries and forging co-investment agreements to localize critical imports. This strategic supply chain realignment mitigates exposure to tariffs but can entail longer development timelines as new vendors scale up expertise. At the same time, tariff-driven increases in upstream component pricing threaten to erode project budgets, compelling stakeholders to reevaluate capital allocation and financing structures.
Despite these headwinds, the policy has spurred a renaissance in U.S. manufacturing innovation. Tier-one industrial players are deploying advanced metallurgy processes and automated production lines to meet rising demand for superconducting materials. Concurrently, dialogue between industry consortia and federal regulators has intensified around refining tariff schedules to balance domestic capacity building with international collaboration. By reshaping procurement strategies and fostering public-private partnerships, the 2025 tariff regime introduces both challenges and incentives that will redefine the pace and geography of fusion deployment.
Unveiling Market Segmentation Insights Across Reactor Platforms Fuel Modalities and Diverse End User Applications Shaping Fusion Energy Adoption
The fusion energy market bifurcates according to two primary reactor technologies: inertial confinement and magnetic confinement. Inertial confinement systems leverage high-power lasers or particle beams to compress fuel pellets rapidly, generating the necessary temperatures and pressures for fusion. Magnetic confinement reactors, in contrast, use intense magnetic fields to contain plasma within toroidal or stellarator chambers. The inherent trade-offs between these platforms-in terms of engineering complexity, scalability, and runtime efficiency-drive divergent development timelines and commercialization strategies across the industry.
Fuel type further nuances market dynamics. Deuterium-deuterium reactions offer the advantage of abundant raw materials but demand higher ignition energies. Deuterium-tritium cycles, currently the most mature pathway, benefit from relatively lower threshold conditions and established research infrastructure, albeit with tritium's supply constraints. Emerging modalities such as helium-3 fusion and proton-boron reactions promise reduced neutron generation and simplified waste profiles, yet they face steeper scientific hurdles and require breakthroughs in fuel sourcing or acceleration technologies to achieve parity with more conventional cycles.
Beyond reactor architecture and fuel selection, end-user applications play a pivotal role in guiding near-term adoption. Aerospace entities are investigating compact fusion units to power satellites and deep-space missions, while agricultural ventures explore high-intensity plasma for novel nitrogen fixation methods. Commercial developers envision grid-scale fusion plants that co-generate heat and electricity. Industrial operations seek on-site fusion to decarbonize heavy processes. Defense agencies evaluate mobile fusion modules for remote installations, and residential as well as transportation stakeholders are monitoring compact reactor prototypes for distributed power generation. This multi-dimensional segmentation underscores the need for tailored strategies that align technological readiness with sector-specific requirements.
Analyzing Regional Dynamics Across the Americas Europe Middle East Africa and Asia Pacific That Influence Fusion Energy Development Trajectories
Regional dynamics play an outsized role in determining the pace and character of fusion energy deployment. In the Americas, the United States benefits from deep venture capital markets, extensive national laboratory networks, and supportive federal programs that reward private innovation. Canada contributes specialized talent in high-field superconductivity and maintains research reactors that serve as testbeds for next-generation designs. Collaboration across the continent has spawned joint development ventures and bilateral funding initiatives.
Across Europe, Middle East, and Africa, a patchwork of national approaches is emerging under a broader regulatory framework designed to harmonize safety standards and streamline cross-border project approvals. European member states are leveraging existing large accelerator facilities and nuclear research infrastructures to advance magnetic confinement prototypes. Meanwhile, Gulf Cooperation Council nations are investing heavily in alternative energy futures, positioning fusion as part of diversified decarbonization strategies. African research institutions, though at earlier stages, are forging partnerships with international consortia to build local expertise.
Asia-Pacific markets represent a dynamic frontier. China has announced flagship fusion demonstration reactors backed by state-owned enterprises, while South Korea and Japan pursue parallel tokamak and stellarator advancements through national labs and industrial alliances. Australia leverages its helium-3 reserves to explore isotopic fusion pathways, and Southeast Asian economies evaluate the potential for fusion to support emerging smart grid deployments. The region's combination of scale, funding commitment, and technological ambition makes it a crucible for the next generation of fusion breakthroughs.
Highlighting Strategic Corporate Initiatives and Collaborative Ecosystems That Define Leadership in the Evolving Fusion Energy Sector
Leading fusion developers are executing distinct strategies to secure technological leadership and market positioning. Some firms focus on modular, componentized reactor architectures, enabling rapid prototype iteration and cost-effective scaling. Others concentrate on vertically integrated value chains, controlling everything from superconducting magnet fabrication to plasma diagnostics and control software. Select enterprises are channeling resources into advanced materials research to enhance reactor longevity and reduce maintenance interruptions, while a parallel cohort is optimizing AI-driven operational models to achieve real-time plasma stabilization.
Strategic collaborations have emerged as a critical competitive lever. Partnerships between fusion startups and established engineering conglomerates allow access to industrial manufacturing expertise and global supply networks. Joint ventures with utilities facilitate integrated grid demonstrations that validate load-following capabilities and revenue models. Alliances with academic institutions accelerate talent pipelines and grant developers access to specialized facilities, such as high-power laser laboratories and cryogenic test chambers.
Intellectual property portfolios provide further differentiation. Organizations that secure key patents around superconducting coil winding techniques, radiation-hard materials, or plasma confinement algorithms strengthen their negotiating positions when engaging potential investors or strategic acquirers. As the industry matures, mergers and acquisitions activity is expected to consolidate these innovations under a narrower set of stakeholders, reinforcing the importance of early IP development and cross-licensing strategies.
Delivering Strategic Action Plans for Fusion Energy Stakeholders to Strengthen Supply Chains Engage Regulators and Accelerate Commercial Deployment
To harness the full potential of fusion energy, industry leaders should adopt a multi-pronged approach that balances technological advancement with strategic stakeholder engagement. First, organizations must deepen investments in domestic supply chain resilience, ensuring access to critical materials and fabrication capabilities amidst fluctuating tariff landscapes. Cultivating relationships with regional foundries and specialized component manufacturers will mitigate procurement risks and support agile scaling.
Second, stakeholders should proactively engage with regulators to co-create predictable policy frameworks. Early participation in standards bodies and licensing dialogues will help align safety protocols with emerging reactor designs and secure fast-track approvals. Concurrently, forming consortiums that span universities, utilities, and government agencies can leverage combined resources to de-risk demonstration projects and share best practices.
Third, fusion developers must prioritize workforce development, partnering with academic institutions to establish specialized training programs in plasma physics, cryogenics, and advanced manufacturing. Building a robust talent pipeline will address looming skill shortages and facilitate technology transfer from lab to commercial settings.
Lastly, organizations should adopt modular business models that allow phased deployment, enabling early revenue generation through pilot installations while iterating on next-generation designs. By maintaining a balance between ambitious long-term R&D and near-term commercialization pilots, industry leaders can sustain momentum and build market confidence in the transformative promise of fusion energy.
Outlining a Robust Mixed Method Research Framework Combining Expert Interviews Data Analytics and Scenario Planning for Comprehensive Fusion Analysis
This research integrates a mixed-methods approach to ensure comprehensive and reliable insights. Primary data was gathered through one-on-one interviews with executives, technical directors, and policy advisors across the fusion energy ecosystem, capturing firsthand perspectives on technology roadmaps, funding strategies, and regulatory priorities. These qualitative findings were supplemented by an extensive review of open-source technical papers, patent filings, government policy documents, and investment disclosures to construct an objective narrative of industry progress.
Quantitative analysis entailed the aggregation of public and proprietary datasets covering R&D expenditures, manufacturing capacity indicators, and tariff schedules. Statistical techniques, including trend extrapolation and sensitivity modeling, were applied to assess the impact of regulatory shifts and supply chain dynamics on technology deployment timelines. Scenario planning workshops with cross-functional experts then stress-tested key assumptions, generating multiple pathways that reflect varying levels of policy support, capital availability, and technological breakthroughs.
Rigorous data triangulation and iterative peer review processes were employed to validate findings. By combining qualitative richness with quantitative rigor, this methodology provides decision-makers with a nuanced understanding of risks, opportunities, and strategic imperatives in the rapidly evolving fusion energy landscape.
Drawing Integrated Insights on Technology Progress Regulatory Shifts and Market Dynamics to Illuminate the Strategic Imperatives for Fusion Energy Advancement
In synthesizing technological advancements, tariff landscapes, segmentation nuances, regional dynamics, and corporate strategies, this report underscores fusion energy's transition from laboratory curiosity to credible commercial contender. Breakthroughs in superconducting magnets, laser confinement, and reactor materials have converged with supportive policy environments to create a fertile ground for private-sector innovation. At the same time, new tariff regimes and regional investment patterns necessitate adaptive supply chain strategies and cross-border collaborations.
Segmentation across reactor technology, fuel type, and end-user application reveals that no single pathway will dominate; rather, a mosaic of specialized solutions will emerge to address diverse market requirements. Regional leadership in the Americas, coordinated frameworks in Europe, Middle East & Africa, and rapid scaling in Asia Pacific will collectively drive global progress. Industry leaders who forge strong ecosystem partnerships, invest in IP and workforce development, and engage proactively with regulators will capture first-mover advantages.
Ultimately, fusion energy promises to redefine power generation by offering scalable, zero-carbon baseload capacity. The insights contained herein equip stakeholders with the strategic context and actionable intelligence necessary to navigate this inflection point and shape the future of energy.
Table of Contents
1. Preface
- 1.1. Objectives of the Study
- 1.2. Market Segmentation & Coverage
- 1.3. Years Considered for the Study
- 1.4. Currency & Pricing
- 1.5. Language
- 1.6. Stakeholders
2. Research Methodology
- 2.1. Define: Research Objective
- 2.2. Determine: Research Design
- 2.3. Prepare: Research Instrument
- 2.4. Collect: Data Source
- 2.5. Analyze: Data Interpretation
- 2.6. Formulate: Data Verification
- 2.7. Publish: Research Report
- 2.8. Repeat: Report Update
3. Executive Summary
4. Market Overview
- 4.1. Introduction
- 4.2. Market Sizing & Forecasting
5. Market Dynamics
- 5.1. Advancements in high-temperature superconducting magnets improving tokamak performance
- 5.2. Expanding private sector funding accelerating development of compact fusion reactors
- 5.3. Integration of artificial intelligence for predictive plasma control and real time optimization
- 5.4. Emergence of alternative confinement approaches such as stellarators and inertial fusion drivers
- 5.5. Supply chain innovations reducing critical material dependencies for fusion reactor components
6. Market Insights
- 6.1. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 6.2. PESTLE Analysis
7. Cumulative Impact of United States Tariffs 2025
8. Fusion Energy Market, by Technology
- 8.1. Introduction
- 8.2. Inertial Confinement
- 8.3. Magnetic Confinement
9. Fusion Energy Market, by Fuel Type
- 9.1. Introduction
- 9.2. Deuterium-Deuterium
- 9.3. Deuterium-Tritium
- 9.4. Helium-3
- 9.5. Proton-Boron
10. Fusion Energy Market, by End-User
- 10.1. Introduction
- 10.2. Aerospace
- 10.3. Agriculture
- 10.4. Commercial
- 10.5. Industrial
- 10.6. Military & Defense
- 10.7. Residential
- 10.8. Transportation Sector
11. Americas Fusion Energy Market
- 11.1. Introduction
- 11.2. United States
- 11.3. Canada
- 11.4. Mexico
- 11.5. Brazil
- 11.6. Argentina
12. Europe, Middle East & Africa Fusion Energy Market
- 12.1. Introduction
- 12.2. United Kingdom
- 12.3. Germany
- 12.4. France
- 12.5. Russia
- 12.6. Italy
- 12.7. Spain
- 12.8. United Arab Emirates
- 12.9. Saudi Arabia
- 12.10. South Africa
- 12.11. Denmark
- 12.12. Netherlands
- 12.13. Qatar
- 12.14. Finland
- 12.15. Sweden
- 12.16. Nigeria
- 12.17. Egypt
- 12.18. Turkey
- 12.19. Israel
- 12.20. Norway
- 12.21. Poland
- 12.22. Switzerland
13. Asia-Pacific Fusion Energy Market
- 13.1. Introduction
- 13.2. China
- 13.3. India
- 13.4. Japan
- 13.5. Australia
- 13.6. South Korea
- 13.7. Indonesia
- 13.8. Thailand
- 13.9. Philippines
- 13.10. Malaysia
- 13.11. Singapore
- 13.12. Vietnam
- 13.13. Taiwan
14. Competitive Landscape
- 14.1. Market Share Analysis, 2024
- 14.2. FPNV Positioning Matrix, 2024
- 14.3. Competitive Analysis
- 14.3.1. Commonwealth Fusion Systems
- 14.3.2. TAE Technologies, Inc.
- 14.3.3. Commonwealth Fusion Systems, LLC
- 14.3.4. Elytt Energy, Inc.
- 14.3.5. First Light Fusion Ltd.
- 14.3.6. Fuse
- 14.3.7. Fusion Industry Association, Inc.
- 14.3.8. General Fusion Inc.
- 14.3.9. HB11 Energy Holdings Pty Ltd
- 14.3.10. Helion Energy, Inc.
- 14.3.11. Hyperjet Fusion Corporation
- 14.3.12. Kyoto Fusioneering Ltd.
- 14.3.13. Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC
- 14.3.14. LPPFusion, Inc.
- 14.3.15. Magneto-Inertial Fusion Technologies, Inc.
- 14.3.16. Marvel Fusion GmbH
- 14.3.17. MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD.
- 14.3.18. Oklo Inc.
- 14.3.19. Proxima Fusion GmbH
- 14.3.20. Renaissance Fusion
- 14.3.21. Thea Energy Inc.
- 14.3.22. Tokamak Energy Ltd.
- 14.3.23. Tokamak Energy Ltd.
- 14.3.24. Woodruff Scientific, Inc.
- 14.3.25. Xcimer Energy, Inc.
- 14.3.26. Zap Energy, Inc.