|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1348563
リチウム硫黄電池:技術の進歩、新たな用途、成長機会Lithium-sulfur Batteries: Technological Advancements, Emerging Applications, and Growth Opportunities |
||||||
|
|||||||
| リチウム硫黄電池:技術の進歩、新たな用途、成長機会 |
|
出版日: 2023年08月24日
発行: Frost & Sullivan
ページ情報: 英文 43 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
- 全表示
- 概要
- 目次
高いエネルギー密度と費用対効果の可能性により、市場を破壊する可能性を秘めたリチウム硫黄電池
リチウムイオン電池(LIB)は、世界のエネルギー貯蔵と電化革命をリードしているが、これらの電池の大規模製造に携わる商業参加者は、ある種の限界とリスクに直面しています。LIBのエネルギー密度はここ数年で頭打ちとなっており、今日、世界はより高いエネルギー密度を実現するエネルギー貯蔵ソリューションを必要としています。加えて、電気自動車(EV)の1回の充電による航続距離に関する問題を解消し、LIBを斬新な民生用電子機器用途に使用できるようにすることが重要です。さらに、LIB製造に使用されるコバルトやニッケルのような特定の金属は、採掘問題や価格変動に直面し、電池メーカーやエンドユーザーの事業経済性に打撃を与えています。リチウム硫黄(Li-S)電池は、製造にこれらの微量元素を必要としないため、関連するリスクがないです。
さらに、Li-S電池は、500Wh/kgを超えるエネルギー密度を提供することで、卓越した利点を提供します。これは、LIBを含む現在市販されている電池化学物質では達成できない偉業です。これらの並外れたエネルギー貯蔵能力は、電動モビリティ、家電、ヘルスケア、電力機器など、他の産業に革命をもたらす可能性も秘めています。
このFrost &Sullivanの調査では、Li-S電池の動作メカニズムや製造時に使用される代表的な材料など、Li-S電池の技術状況について説明しています。また、成長促進要因と阻害要因を評価し、LIB、ナトリウムイオン電池、バナジウムレドックスフロー電池などの既存電池技術との比較分析も行っています(比較パラメータはエネルギー密度、安全性、コスト、往復効率など)。また、特許分析、企業の技術革新状況、Li-S採用の鍵となる成長機会の詳細についても論じています。
目次
戦略的課題
- なぜ成長が難しくなっているのか?The Strategic Imperative 8(TM):成長を阻む要因
- The Strategic Imperative 8(TM)
- リチウム硫黄電池業界における戦略的課題トップ3のインパクト
- Growth Pipeline Engine(TM):成長機会の促進
- 調査手法
成長機会分析
- 分析範囲
- セグメンテーション
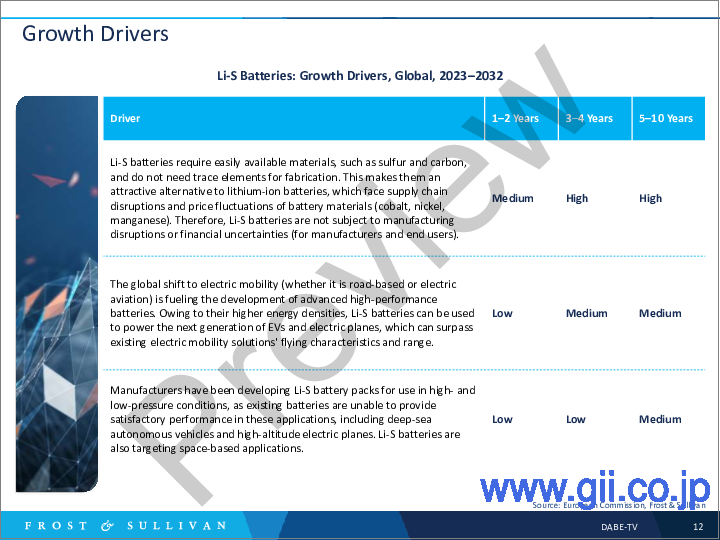
- 成長促進要因
- 成長阻害要因
技術スナップショット
- リチウムS電池イントロダクションと作動メカニズム
- Li-S電池:利点と課題
- Li-S電池:材料とコンポーネント
- Li-S電池:現在主流のリチウムイオン電池との比較分析
- Li-S電池:既存の電池化学物質との比較分析
イノベーション・エコシステム
- Li-S電池将来のアプリケーション
- Li-S電池:現世代リチウムイオン電池が直面するサプライチェーン問題の緩和
- リチウムイオン電池の開発世界の主な利害関係者
- ゼータ・エナジー(米国)
- ザイオン(ドイツ)
- その他の主なリチウムイオン電池開発企業
- リチウムS電池特許情勢
- リチウムS電池メーカーの資金調達情報
成長機会の世界
- 成長機会1:Li-S電池を使用する実現可能な電気航空ソリューションの出現
- 成長機会2:Li-S電池と高度なワイヤレスBMSを組み合わせたデータ分析を行うためのデジタルツールの利用
- 成長機会3:次世代ソフトエレクトロニクスを可能にするLi-S電池製造における先進ナノ材料の利用
付録
- 技術成熟度レベル(TRL):説明
次のステップ
- 次のステップ
- なぜフロストなのか、なぜ今なのか?
- 免責事項
Higher Energy Density and Potential for Cost-Effectiveness Provide Lithium-sulfur Batteries with Market Disruption Potential
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) lead the global energy storage and electrification revolution; however, commercial participants involved in these batteries' large-scale manufacturing face certain limitations and risks. LIBs' energy density has plateaued over the past few years, and, today, the world requires an energy storage solution that delivers higher energy density. In addition, it is important to eliminate woes pertaining to the range electric vehicles (EVs) offer from a single charge and ensure that LIBs can be used in novel consumer electronic applications. Furthermore, certain metals, such as cobalt and nickel, which are used in LIB fabrication, face mining issues as well as price fluctuations, hurting the economics of operations for battery manufacturers and end users. Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries do not require these trace elements in their fabrication, thereby eliminating the associated risks.
Moreover, Li-S batteries offer an exceptional advantage by providing energy densities that exceed 500Wh/kg, a feat not achievable by today's commercially available battery chemistries, including LIBs. These extraordinary energy storage capabilities also help these batteries to potentially revolutionize other industries, including electric mobility, consumer electronics, healthcare, and power equipment.
This Frost & Sullivan study describes Li-S batteries' technology landscape, including their working mechanism and the typical materials used during fabrication. It also evaluates growth drivers and restraints and offers a comparative analysis with incumbent battery technologies, such as LIBs, sodium-ion batteries, and vanadium redox flow batteries (parameters compared include energy density, safety, cost, and round-trip efficiency). The study also discusses the patent analysis and the company innovation landscape and details growth opportunities that act as key enablers for Li-S adoption.
Table of Contents
Strategic Imperatives
- Why Is It Increasingly Difficult to Grow?The Strategic Imperative 8™: Factors Creating Pressure on Growth
- The Strategic Imperative 8™
- The Impact of the Top 3 Strategic Imperatives on the Lithium-sulfur Battery Industry
- Growth Opportunities Fuel the Growth Pipeline Engine™
- Research Methodology
Growth Opportunity Analysis
- Scope of Analysis
- Segmentation
- Growth Drivers
- Growth Restraints
Technology Snapshot
- Li-S Batteries: Introduction and Working Mechanism
- Li-S Batteries: Advantages and Challenges
- Li-S Batteries: Materials and Components
- Li-S Batteries: Comparative Analysis with Currently Dominant Lithium-ion Batteries
- Li-S Batteries: Comparative Analysis with Incumbent Battery Chemistries
Innovation Ecosystem
- Li-S Batteries: Prospective Applications
- Li-S Batteries: Mitigating Supply Chain Issues Current-generation Lithium-ion Batteries are Facing
- Li-S Battery Development: Prominent Global Stakeholders
- Zeta Energy, the United States
- Theion, Germany
- Other Key Li-S Battery Developers
- Li-S Batteries: Patent Landscape
- Li-S Batteries: Manufacturers' Funding Information
Growth Opportunity Universe
- Growth Opportunity 1: Emergence of Feasible Electric Aviation Solutions that Use Li-S Batteries
- Growth Opportunity 2: Using Digital Tools to Perform Data Analytics by Coupling Li-S Batteries with Advanced Wireless BMS
- Growth Opportunity 3: Using Advanced Nanomaterials in Li-S Battery Fabrication to Enable the Next Generation of Soft Electronics
Appendix
- Technology Readiness Levels (TRL): Explanation
Next Steps
- Your Next Steps
- Why Frost, Why Now?
- Legal Disclaimer