|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1642229
ペロブスカイト材料・技術の世界市場(2025年~2035年)The Global Market for Perovskite Materials and Technologies 2025-2035 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| ペロブスカイト材料・技術の世界市場(2025年~2035年) |
|
出版日: 2025年01月29日
発行: Future Markets, Inc.
ページ情報: 英文 177 Pages, 57 Tables, 48 Figures
納期: 即納可能
|
全表示
- 概要
- 図表
- 目次
世界のペロブスカイト材料・技術市場は急速な成長を示しており、世界中の研究者、産業、投資家から大きな注目を集めています。ペロブスカイトは、ユニークな結晶構造を持つ材料の一種であり、その卓越した光電子特性、低コスト生産、汎用性により、さまざまな用途の有望なソリューションとして浮上しています。ペロブスカイト市場の主な促進要因は、高効率で費用対効果が高く、持続可能なエネルギーソリューションに対する需要の高まりです。ペロブスカイト太陽電池(PSC)は近年大きく進歩し、実験室環境での電力変換効率は現在25%(2009年の3%から)を超えています。このことは、PSCを従来のシリコンベースの太陽光発電に対する有力な挑戦者として位置づけています。低温、溶液ベースのプロセスでペロブスカイト膜を生産できるため、スケーラブル製造やフレキシブル基板との統合に魅力的です。生産コストが低く、エネルギー効率が高く、フレキシブル基板やガラス基板への適応性も高いです。
ペロブスカイトは、太陽光発電以外にも、発光素子(LED)、光検出器、センサー、トランジスター、記憶装置、触媒などの分野でも応用されています。PeLEDとして知られるペロブスカイトLEDは、色純度が高く、調整可能で、低コストで製造できるため、ディスプレイや照明用途に適しています。ペロブスカイトをベースとする光検出器やセンサーは、高感度、広範なスペクトル応答、高速応答時間を示し、イメージング、監視、環境モニタリングへの応用が期待されています。
ペロブスカイト市場はまだ初期段階にあります。しかし、ペロブスカイトをベースとした製品の採用が増え、製造プロセスの規模が拡大していることから、市場は今後数年で大きく成長すると予測されます。世界のペロブスカイトの市場規模は2035年までに100億米ドルを超え、太陽光発電セグメントが最大のシェアを占める見込みです。ペロブスカイト材料と技術の将来見通しは有望で、安定性、耐久性、性能の向上に焦点を当てた研究が進行中です。ペロブスカイトをシリコンやCIGSのような他の確立された技術と組み合わせたタンデムアーキテクチャは、電力変換効率を押し上げると予測されています。太陽光で動作する衣服やセンサーなど、フレキシブルなウェアラブルペロブスカイトデバイスも視野に入っています。ペロブスカイト量子ドットは、従来の材料に比べて色域やエネルギー効率が改善され、ディスプレイや照明用途での可能性が注目されています。
しかし、長期的な安定性や効率、スケーラビリティ、ペロブスカイト製剤に含まれる有毒な鉛の存在などの課題が残されています。研究者たちは、これらの懸念に対処するため、鉛フリーの代替品やカプセル化技術を積極的に模索しています。
当レポートでは、世界のペロブスカイト材料・技術市場について調査分析し、ペロブスカイト材料とその特性、用途、合成法、市場の促進要因と抑制要因、各地域の市場予測、競合情勢、将来の機会などの情報を提供しています。
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリー
- 市場の概要
- 技術ロードマップ
- 市場の促進要因と抑制要因
- 市場の機会と将来の動向
- 市場予測
- 規制
第2章 イントロダクション
第3章 ペロブスカイト材料
- 無機ペロブスカイト
- 有機無機ハイブリッドペロブスカイト
第4章 ペロブスカイトの合成法と加工法
- 概要
- 溶液ベースの方法
- 蒸着法
- その他の合成法
- スケーラブルな加工に利用する成膜技術
- ロールツーロール加工
- 合成後加工技術
- 成膜方法の比較
第5章 ペロブスカイトの用途と最終用途市場
- 太陽光発電
- 発光素子
- 光検出器、センサー
- トランジスター、記憶装置
- 触媒、光触媒
- 熱電
- その他の新用途
第6章 企業プロファイル(企業65社のプロファイル)
第7章 付録
第8章 参考文献
List of Tables
- Table 1. Market overview for Perovskite Materials and Technologies
- Table 2. Market drivers for perovskite materials and technologies
- Table 3. Production Cost of Perovskites
- Table 4. Market restraints for perovskite materials and technologies:
- Table 5. Perovskite materials and technologies versus established technologies, by market
- Table 6. Global Perovskite Market Size (Billion USD)
- Table 7. Perovskite Materials and Technologies Market Forecasts by Application, 2022-2035 (Millions USD)
- Table 8. Perovskite Materials and Technologies Market Forecasts by Region, 2022-2035 (Millions USD)
- Table 9. Perovskite PV companies in China
- Table 10. Regulations and Standards for Perovskite Materials
- Table 11. Disposal and Recycling Strategies
- Table 12. Occupational Health and Safety Measures
- Table 13. Types of Perovskites
- Table 14. Perovskite Properties
- Table 15. Advantages of Perovskite Materials
- Table 16. Challenges and Limitations
- Table 17. Perovskite quantum dots (PQDs) overview
- Table 18. Comparative properties of conventional QDs and Perovskite QDs
- Table 19. Synthesis Methods for Perovskite Quantum Dots
- Table 20. Applications of perovskite QDs
- Table 21. Properties of perovskite QLEDs comparative to OLED and QLED
- Table 22. Perovskite-based QD producers
- Table 23. Perovskite synthesis and processing methods
- Table 24. Perovskite Deposition Methods Comparison
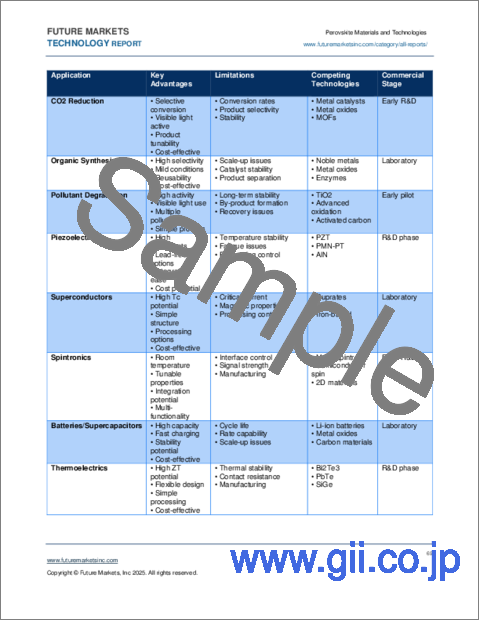
- Table 25. Overview of Perovskite Materials and Technologies Applications
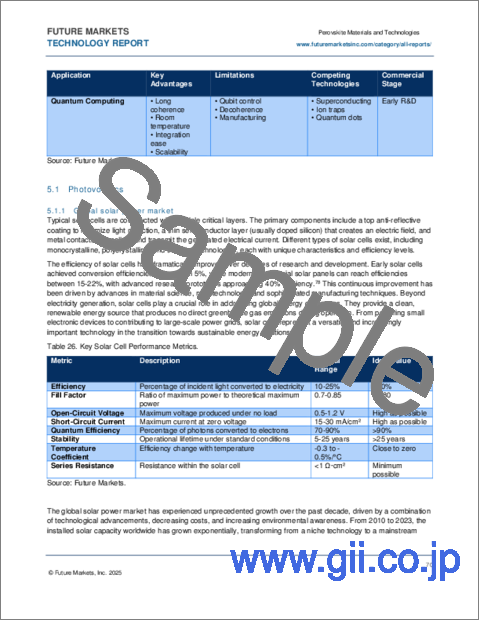
- Table 26. Key Solar Cell Performance Metrics
- Table 27. Total installed solar capacity by technology type, 2024-2035
- Table 28. Global Solar Installations by Region (2023)
- Table 29. Thin Film Technology Comparison
- Table 30. Benchmarking of solar technologies
- Table 31. Solar Technology Development Status Roadmap (2020-2035)
- Table 32. Perovskite solar power funding and projects
- Table 33. n-i-p vs p-i-n configurations
- Table 34. Perovskite vs. Other Thin Film Technologies Comparison
- Table 35. Thin-film perovskite cost breakdown
- Table 36. Applications of perovskite/silicon tandem PV
- Table 37. Thin film vs tandem perovskite PV
- Table 38. Tandem cell fabrication process:
- Table 39. Perovskite/silicon tandem PV market players
- Table 40. Companies in all-perovskite tandem technology
- Table 41. Materials for Perovskite PV
- Table 42. Substrate materials for solar cells
- Table 43. Cost and Performance Comparison of Substrate Materials
- Table 44. Benchmarking of Substrate Materials for Perovskite PV
- Table 45. TCF Material Options and Key Properties
- Table 46. Perovskite PV Market Players Overview
- Table 47. Global installed perovskite PV capacity by application, 2023-2035
- Table 48. Global perovskite PV annual revenues, 2023-2035 (Millions USD)
- Table 49. Global solar farm installation capacity, 2024-2035 (GW)
- Table 50. Global Perovskite Residential Rooftop PV Revenues (Million USD)
- Table 51. Applications of Perovskites in Light-Emitting Devices
- Table 52. Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes (PeLEDs) Properties and Applications
- Table 53. Applications of Perovskites in Photodetectors and Sensors
- Table 54. Photodetector applications
- Table 55. Applications of Perovskites in Transistors and Memory Devices
- Table 56. Applications of Perovskites in Catalysis and Photocatalysis
- Table 57. List of Terms and Abbreviations
List of Figures
- Figure 1. Technology roadmap for perovskite materials
- Figure 2. Global Perovskite Market Size (Billion USD)
- Figure 3. Perovskite Materials and Technologies Market Forecasts by Application, 2022-2035
- Figure 4. Perovskite Materials and Technologies Market Forecasts by Region, 2022-2035
- Figure 5. Perovskite solution
- Figure 6. Perovskite structure
- Figure 7. Perovskite solar cell by Toshiba
- Figure 8. A pQLED device structure
- Figure 9. Roadmap for perovskite QDs
- Figure 10. SWOT analysis for perovskite QDs
- Figure 11. Perovskite quantum dots under UV light
- Figure 12. Roll-to-roll manufacturing process
- Figure 13. Total installed solar capacity by technology type, 2024-2035
- Figure 14. Thin Film Perovskite PV Roadmap
- Figure 15. Perovskite solar cell
- Figure 16. Devices structure for a mesoporous perovskite solar cell structure. In the inset, the electron charge transport processes for injecting and non-injecting mesoporous materials are represented and b structure of a thin film-like perovskite solar cells
- Figure 17. SWOT analysis of thin film perovskite PV
- Figure 18. Comparison of silicon-based solar cells and perovskite solar cells
- Figure 19. Perovskite PV value chain
- Figure 20. Perovskite/silicon tandem PV roadmap
- Figure 21. Perovskite/silicon tandem PV SWOT analysis
- Figure 22. Shape of the deployment module in which the "space tandem flexible solar cell" panel developed by Hanwha System's in-house venture Flexel Space is unfolded like a scroll
- Figure 23. Lightyear O solar powered car
- Figure 24. Global installed perovskite PV capacity by application, 2023-2035
- Figure 25. Global perovskite PV annual revenues, 2023-2035
- Figure 26. Global solar farm installation capacity, 2024-2035
- Figure 27. Global Perovskite residential rooftop PV revenues, 2024-2035
- Figure 28. Working principle of perovskite LEDs
- Figure 29. Perovskite absorption spectrum
- Figure 30. Active Surfaces 4-by-4-inch photovoltaic devices
- Figure 31. Aisin spray perovskite materials solar cell. (Source) Aisin Corporation
- Figure 32. Anker solar umbrella
- Figure 33. Caelux perovskite solar cell
- Figure 34. Perovskite solar cells (left) could achieve mass production by adding a coating developed by Canon to their structure (right)
- Figure 35. EneCoat Technologies Co., Ltd. perovskite solar cells
- Figure 36. EMC Transparent Conductor Printing
- Figure 37. QD Barrier film
- Figure 38. Kaneka Corporation built-in perovskite solar cells
- Figure 39. Mellow Energy ML-Flex panel
- Figure 40. Perovskia Solar printed perovskite cells
- Figure 41. PXP Corporation flexible chalcopyrite photovoltaic modules
- Figure 42. PESL (Perovskite Electronic Shelf Label)
- Figure 43. Uchisaiwaicho 1-chome Urban District Development Project
- Figure 44. Sekisui film-type perovskite solar cells
- Figure 45. Solar Ink(TM)
- Figure 46. Swift Solar panel
- Figure 47. Tandem metal-halide perovskite solar panels
- Figure 48. UtmoLight 450W perovskite solar module
The global market for perovskite materials and technologies is experiencing rapid growth and attracting significant attention from researchers, industries, and investors worldwide. Perovskites, a class of materials with a unique crystalline structure, have emerged as a promising solution for various applications due to their exceptional optoelectronic properties, low-cost production, and versatility. The primary driver of the perovskite market is the increasing demand for high-efficiency, cost-effective, and sustainable energy solutions. Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have demonstrated remarkable progress in recent years, with power conversion efficiencies now exceeding 25% (from 3% in 2009) in laboratory settings. This positions PSCs as a potential challenger to traditional silicon-based photovoltaics. The ability to produce perovskite films through low-temperature, solution-based processes makes them attractive for scalable manufacturing and integration with flexible substrates. They offer low production costs, high energy efficiency, and adaptability for flexible and glass substrates.
Beyond photovoltaics, perovskites are finding applications in light-emitting devices (LEDs), photodetectors, sensors, transistors, memory devices, and catalysis. Perovskite LEDs, known as PeLEDs, offer high color purity, tunability, and low-cost fabrication, making them suitable for display and lighting applications. Perovskite-based photodetectors and sensors exhibit high sensitivity, wide spectral response, and fast response times, with potential uses in imaging, surveillance, and environmental monitoring.
The perovskite market is still in its early stages. However, the market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by the increasing adoption of perovskite-based products and the scaling up of manufacturing processes. The global perovskite market will exceed $10 billion by 2035, with the photovoltaics segment accounting for the largest share. The future outlook for perovskite materials and technologies is promising, with ongoing research focused on improving stability, durability, and performance. Tandem architectures, combining perovskites with other established technologies like silicon or CIGS, are expected to push power conversion efficiencies. Flexible and wearable perovskite devices, such as solar-powered clothing and sensors, are also on the horizon. Perovskite quantum dots are attracting interest for their potential in display and lighting applications, offering improved color gamut and energy efficiency compared to conventional materials.
However, challenges remain in terms of long-term stability/efficiency, scalability, and the presence of toxic lead in some perovskite formulations. Researchers are actively exploring lead-free alternatives and encapsulation techniques to address these concerns.
The report covers the following key aspects:
- Overview of perovskite materials and their unique properties
- Types of perovskites: inorganic, hybrid organic-inorganic, and perovskite quantum dots
- Advantages of perovskites over traditional materials
- Perovskite applications and end-use markets
- Photovoltaics: perovskite solar cells (PSCs), tandem solar cells, and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV)
- Light-emitting devices: perovskite LEDs (PeLEDs), white light-emitting devices, lasers, and optical amplifiers
- Photodetectors and sensors: visible light, X-ray, gamma-ray, chemical, and humidity sensors
- Transistors and memory devices: field-effect transistors (FETs) and resistive random-access memory (RRAM)
- Catalysis and photocatalysis: water splitting, hydrogen production, CO2 reduction, and pollutant degradation
- Thermoelectrics and other emerging applications
- Perovskite synthesis and processing methods
- Solution-based methods: one-step deposition, two-step sequential deposition, and anti-solvent assisted crystallization
- Vapor deposition methods: thermal evaporation, co-evaporation, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD)
- Scalable processing techniques: inkjet printing, blade coating, slot-die coating, and spray coating
- Roll-to-roll processing for high-volume production and cost reduction
- Post-synthesis processing techniques: thermal annealing, solvent annealing, and pressure-assisted annealing
- Market drivers and restraints
- Market forecasts and regional analysis
- Global perovskite materials and technologies market size and growth rate from 2025 to 2035
- Market segmentation by application, material type, and geographic region
- Detailed market forecasts for North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Rest of the World
- Competitive landscape and company profiles
- Profiles of over 65 key players in the perovskite industry, including material suppliers and device manufacturers. Companies profiled include Aisin Corporation, Anker, Ascent Solar, Astronergy, Avantama, Beyond Silicon, Caelux, BrightComSol, Canadian Solar, Canon, China Huaneng Group Co., Ltd., Cosmos Innovation, CubicPV, DaZheng, Dyenamo, EneCoat Technologies, Energy Materials Corporation, Ergis Group, Flexell Space, GCL, Green Science Alliance Co., Ltd., Hangzhou Xianna Optoelectronic Technology Co., Ltd., Hanwha Qcells, Hefei BOE Solar Technology, Helio Display Materials, HETE Photo Electricity, Hiking PV, Homerun Resources, Huasun Energy (Ningxia Huasun New Materials Technology), JA Solar, Jiangsu Xiehang Energy Technology (Fellow Energy/Xiehang Energy), Jinko Solar, Kaneka Corporation, Koreakiyon, LONGi Green Energy Technology, Mellow Energy, Microquanta Semiconductor, Nanolumi, Nexwafe, Opteria, Oxford PV, PEROLED Korea, PeroNova, Perovskia Solar, Power Roll, PXP, Renshine Solar, RISEN, Saule Technologies, SCHOTT, SEI Energy Technology (Jiaxing), Sekisui Chemical Co Ltd, SN Display Co., Ltd., Sofab Inks, Solaronix, Solaveni GmbH, Solaires Enterprises, and more....
- Analysis of their strategies, partnerships, and product offerings
- Regulations and environmental considerations
- Future trends and opportunities
- Tandem solar cells and perovskite-silicon integration
- Flexible and wearable perovskite devices
- Perovskite quantum dots for displays and lighting
- Perovskite-based sensors for IoT and smart cities
- Recyclable and eco-friendly perovskite materials
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- 1.1. Market Overview
- 1.2. Technology roadmap
- 1.3. Market drivers and restraints
- 1.3.1. Market Drivers
- 1.3.1.1. Increasing Demand for Renewable Energy
- 1.3.1.2. Declining Costs of Perovskite Production
- 1.3.1.3. Government Policies and Incentives
- 1.3.1.4. Advancements in Perovskite Stability and Efficiency
- 1.3.2. Market Restraints
- 1.3.2.1. Lead Toxicity Concerns
- 1.3.2.2. Stability and Degradation Issues
- 1.3.2.3. Scalability and Manufacturing Challenges
- 1.3.2.4. Competition from Established Technologies
- 1.3.1. Market Drivers
- 1.4. Market opportunities and future trends
- 1.4.1. Tandem Solar Cells and Perovskite-Silicon Integration
- 1.4.2. Flexible and Wearable Perovskite Devices
- 1.4.3. Perovskite Quantum Dots for Displays and Lighting
- 1.4.4. Perovskite-Based Sensors for IoT and Smart Cities
- 1.4.5. Perovskite Materials for Neuromorphic Computing
- 1.4.6. Recyclable and Eco-Friendly Perovskites
- 1.5. Market forecasts
- 1.5.1. Global Perovskite Materials and Technologies Market Size and Growth Rate
- 1.5.2. Market Forecasts by Application
- 1.5.3. Market Forecasts by Region
- 1.5.3.1. North America
- 1.5.3.2. Europe
- 1.5.3.3. China
- 1.5.3.4. Asia-Pacific
- 1.5.3.5. Rest of World
- 1.6. Regulations
- 1.6.1. Regulations and Standards for Perovskite Materials
- 1.6.2. Toxicity and Environmental Concerns
- 1.6.3. Disposal and Recycling Strategies
- 1.6.4. Occupational Health and Safety Measures
2. INTRODUCTION
- 2.1. What are Perovskites?
- 2.1.1. Perovskite Structure and Composition
- 2.1.2. Types of Perovskites
- 2.1.2.1. Inorganic Perovskites
- 2.1.2.2. Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Perovskites
- 2.1.3. Perovskite Properties
- 2.2. Advantages of Perovskite Materials
- 2.3. Challenges and Limitations
3. PEROVSKITE MATERIALS
- 3.1. Inorganic Perovskites
- 3.1.1. Lead-Based Perovskites
- 3.1.1.1. Methylammonium Lead Triiodide (MAPbI3)
- 3.1.1.2. Formamidinium Lead Triiodide (FAPbI3)
- 3.1.1.3. Cesium Lead Triiodide (CsPbI3)
- 3.1.2. Lead-Free Perovskites
- 3.1.2.1. Tin-Based Perovskites
- 3.1.2.2. Bismuth-Based Perovskites
- 3.1.2.3. Double Perovskites
- 3.1.3. Other Inorganic Perovskites
- 3.1.1. Lead-Based Perovskites
- 3.2. Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Perovskites
- 3.2.1. 3D Hybrid Perovskites
- 3.2.2. 2D Hybrid Perovskites (Ruddlesden-Popper Phases)
- 3.2.3. Quasi-2D Hybrid Perovskites
- 3.2.4. 1D Hybrid Perovskites
- 3.2.5. Perovskite Quantum Dots
- 3.2.5.1. Properties
- 3.2.5.2. Comparison to conventional quantum dots
- 3.2.5.3. Synthesis methods
- 3.2.5.4. Applications
- 3.2.5.5. Companies
4. PEROVSKITE SYNTHESIS AND PROCESSING METHODS
- 4.1. Overview
- 4.2. Solution-Based Methods
- 4.2.1. One-Step Deposition
- 4.2.2. Two-Step Sequential Deposition
- 4.2.3. Anti-Solvent Assisted Crystallization
- 4.2.4. Vapor-Assisted Solution Process
- 4.2.5. Spin Coating
- 4.3. Vapor Deposition Methods
- 4.3.1. Thermal Evaporation
- 4.3.2. Co-Evaporation
- 4.3.3. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
- 4.3.4. Hybrid Chemical Vapor Deposition
- 4.3.5. Aerosol Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition
- 4.3.6. Sputtering
- 4.4. Other Synthesis Methods
- 4.4.1. Mechanochemical Synthesis
- 4.4.2. Combustion Synthesis
- 4.4.3. Hydrothermal Synthesis
- 4.5. Deposition Techniques for Scalable Processing
- 4.5.1. Inkjet Printing
- 4.5.2. Blade Coating
- 4.5.3. Slot-Die Coating
- 4.5.4. Spray Coating
- 4.6. Roll-to-Roll Processing
- 4.6.1. Overview of Roll-to-Roll Printing for Perovskites
- 4.6.2. Advantages for High-Volume Production and Cost Reduction
- 4.6.3. Challenges in Perovskite Film Deposition
- 4.6.4. Examples of Roll-to-Roll Perovskite Device Fabrication
- 4.7. Post-Synthesis Processing Techniques
- 4.7.1. Thermal Annealing
- 4.7.2. Solvent Annealing
- 4.7.3. Pressure-Assisted Annealing
- 4.8. Comparison of Deposition Methods
- 4.8.1. Overview of Method Advantages and Limitations
- 4.8.2. Guidelines for Choosing a Perovskite Deposition Method
5. PEROVSKITE APPLICATIONS AND END-USE MARKETS
- 5.1. Photovoltaics
- 5.1.1. Global solar power market
- 5.1.2. Photovoltaic (PV) commercialization
- 5.1.3. Solar photovoltaic (PV) investment landscape
- 5.1.4. Thin film solar cells
- 5.1.4.1. Thin film solar PV market
- 5.1.4.2. Perovskite photovoltaics (PV)
- 5.1.5. Thin Film Perovskite Solar Cells (PSCs)
- 5.1.5.1. Applications
- 5.1.5.2. The n-i-p and p-i-n configurations
- 5.1.5.3. Mesoporous scaffolds
- 5.1.5.4. Perovskite solar technologies opportunity
- 5.1.5.5. Advantages
- 5.1.5.6. Costs
- 5.1.5.7. PSC Architectures and Device Structures
- 5.1.5.8. Advantages of PSCs over Silicon Solar Cells
- 5.1.5.9. Challenges and Stability Issues
- 5.1.5.10. Degradation
- 5.1.5.11. Additive engineering
- 5.1.5.12. Glass-glass encapsulation
- 5.1.5.13. Polymer encapsulation
- 5.1.5.14. Passivation layers
- 5.1.5.15. Perovskite PV value chain
- 5.1.6. Tandem Solar Cells
- 5.1.6.1. Applications
- 5.1.6.1.1. Building integration
- 5.1.6.1.2. Solar farms
- 5.1.6.2. Properties
- 5.1.6.3. Perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells
- 5.1.6.4. Configurations
- 5.1.6.5. Challenges
- 5.1.6.6. Companies
- 5.1.6.7. All Perovskite Tandem Solar Cells
- 5.1.6.7.1. Overview
- 5.1.6.7.2. Manufacturing
- 5.1.6.7.3. Band gap tuning
- 5.1.6.7.4. Advantages and limitations
- 5.1.6.7.5. Companies
- 5.1.6.1. Applications
- 5.1.7. Materials
- 5.1.7.1. Substrate materials
- 5.1.7.1.1. Rigid glass substrates
- 5.1.7.1.2. Flexible glass substrates
- 5.1.7.1.3. Plastic substrates
- 5.1.7.1.4. Metal Foil Substrates
- 5.1.7.1.5. Transparent conducting films
- 5.1.7.1. Substrate materials
- 5.1.8. Rooftop installation
- 5.1.9. Space and Aerospace Applications
- 5.1.10. Indoor energy harvesting
- 5.1.11. Automotive
- 5.1.12. Agrivoltaics
- 5.1.13. Market players
- 5.1.14. Global perovskite PV market to 2035
- 5.2. Light-Emitting Devices
- 5.2.1. Light emitting diodes market
- 5.2.2. Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes (PeLEDs)
- 5.2.2.1. Applications
- 5.2.3. White Light-Emitting Devices
- 5.2.4. Lasers and Optical Amplifiers
- 5.3. Photodetectors and Sensors
- 5.3.1. Thin film photodetectors market
- 5.3.2. Visible Light Photodetectors
- 5.3.3. X-Ray Detectors
- 5.3.4. Gamma-Ray Detectors
- 5.3.5. Chemical Sensors
- 5.3.6. Humidity Sensors
- 5.4. Transistors and Memory Devices
- 5.4.1. Field-Effect Transistors (FETs)
- 5.4.2. Resistive Random-Access Memory (RRAM)
- 5.5. Catalysis and Photocatalysis
- 5.5.1. Water Splitting and Hydrogen Production
- 5.5.2. CO2 Reduction and Conversion
- 5.5.3. Organic Synthesis
- 5.5.4. Pollutant Degradation
- 5.6. Thermoelectrics
- 5.7. Other Emerging Applications
- 5.7.1. Piezoelectrics
- 5.7.2. Superconductors
- 5.7.3. Spintronics
- 5.7.4. Batteries and Supercapacitors
6. COMPANY PROFILES (65 company profiles)
7. APPENDICES
- 7.1. List of Terms and Abbreviations
- 7.2. Research Methodology