
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1444975
ZED (ゼロエネルギーデバイス):自己給電および後方散乱給電による電子・電気機器市場と技術 (2024-2044年)Zero Energy Devices ZED: Self-powered and Backscatter-Powered Electronics and Electrics Markets, Technology 2024-2044 |
||||||
|
|||||||
| ZED (ゼロエネルギーデバイス):自己給電および後方散乱給電による電子・電気機器市場と技術 (2024-2044年) |
|
出版日: 2024年02月29日
発行: Zhar Research
ページ情報: 英文 408 Pages
納期: 即日から翌営業日
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
| レポート統計 | |
|---|---|
| SWOT評価: | 7 |
| 章構成: | 12 |
| 2024-2044年の予測ライン: | 65 |
| 企業数: | 90 |
| インフォグラム・表・グラフ: | 113 |
当レポートでは、ZED (ゼロエネルギーデバイス) の技術および用途を調査し、技術の定義、背景、これまでの成功事例、6G通信におけるZEDの可能性、ワイヤレスセンサー、IoT、その他の電子機器に向けたZEDの進歩、ZEDのためのエネルギーハーベスティングシステムの開発、各種研究パイプラインの概要などをまとめています。
目次
第1章 エグゼクティブサマリー・総論
- 本書の目的と範囲
- 調査手法
- 定義・目的
- 18の主な総論
- 現在のZEDの成功事例
- ZEDに向けた最適な技術戦略
- 電気通信世代の進歩によるZEDの機会が増加
- センサーZEDに向けた進捗状況
- ZEDとその実現技術のロードマップ
- 市場予測
第2章 ゼロエネルギーデバイス (ZED) の定義、例、将来のニーズ
- 概要
- ZEDへの傾向の理由
- ZEDのさまざまな定義
- ZEDの背景:重複および隣接する技術、長寿命エネルギーによる自立の例
- ホスト機器を長寿命化する電気的自律の例
- 電子機器の電力消費量の増加とZED戦略
- 電力消費と電池の問題を削減するための戦略
- ZEDのオンボードエネルギーハーベスティング:軽量化、小型化、コスト削減、故障モードと有害物質の削減のために簡素化されつつある
- グリッドベースの電力に対するエレクトロニクスの需要増加の歯止め
- IoT:失敗の教訓と成功への可能性
- エネルギーハーベスティング入門
- ZEDセンサーが新たなニーズとして注目される理由
- フレキシブル、層状、2Dエネルギーハーベスティングとセンシングの重要性
- 自己給電型センサーと統合型センサー
- 電気通信世代はどのようにZEDの機会を増やしているか
第3章 6G通信のRIS、CPE、クライアントデバイスによるZEDの機会
- 概要
- なぜ6Gが必要なのか?
- 6Gのディスラプティブな側面
- 主要企業の反対意見、今後の課題、目標
- コスト上の課題
- 6G ZEDおよび6G用ワイヤレス給電IoEのオプションに関する3GPPビジョン
- 6G伝送ハードウェアが5Gよりもはるかに優れたパフォーマンスを実現する仕組み
- 6Gを支援する最近のハードウェアの進歩
- 機器とエッジデバイスがZEDになるための6G通信の機会
- 6G通信における特定のZEDニーズ
- 研究パイプラインにおける6G ZED
- 現在わかっている6G通信のSWOT評価
- 6Gの一般ロードマップ
第4章 ワイヤレスセンサー、IoT、パーソナルエレクトロニクス、その他のエレクトロニクスに関するZEDの進歩
- センサーZEDに向けた基本と進歩:概要
- IoTノードと概念
- 市場の進化:測定されるセンサーパラメータは多面的になり、需要は急激に変化する
- センサーZEDへの進歩:自己給電および自己感知デバイス
- スマートセンサーの構造と目的
- 自己給電センサーとZEDセンサーの研究パイプラインの例
- ZEDに向けた進歩:パーソナルエレクトロニクス、産業用およびプロフェッショナルエレクトロニクス
- 電池ベースのZEDパーソナルエレクトロニクスおよびその他の電気・電子機器の例
- ZEDウェアラブルの進歩
第5章 装着するだけの電池不要のZED:実現戦略
- 概要
- 電池の逆風
- ZEDの有効化
- ZED向けのエネルギーハーベスティングシステムの設計
第6章 超低消費電力エレクトロニクス、センサー、電気機器
- 概要
- 超低消費電力エレクトロニクス
- 超低消費電力読み出しインターフェースと多機能エレクトロニクス
- 超低消費電力フォノニックインセンサーコンピューティング
- 6G通信におけるエネルギー効率の向上:欧州委員会のHexa-Xプロジェクト
- ZEDの静的コンテキストヘッダー圧縮と断片化
- その他のエネルギー効率の高いセンシング、処理、IoT向けの新しい電力伝送オプション
- 超低消費電力集積回路
- ナノパワーnPZero
- Everactive:ZED IoT用の超低消費電力回路
- 2nmチップとその先:米国、台湾、中国、日本
- Ericsson ResearchとMITのリチウムイオンチップ
- Move-XのMAMWLE:超低消費電力無線モジュール
- 超低消費電力スマートフォン
- ZEDとしてのメタマテリアルおよびメタサーフェスまたはZEDの有効化
- 定義と範囲
- メタマテリアルZEDウィンドウ
- 6G RIS ZEDおよびその他の目的のためのメタサーフェス
- 6G通信RISの機会:SWOT評価
第7章 問い合わせられたときのみデバイスに電力を供給:バックスキャッタ、SWIPT、WIET、EAS用WPT、RFID、IoT、6G通信、その他の電子機器
- 概要:バックスキャッタ、EAS、RFID、6G SWIPT
- アンビエントバックスキャッタ通信のAmBCと群集検出可能なCD-ZED
- ハイブリッドビームフォーミングベースのSWIPT
- ストレージを排除する回路とインフラ:SWOT評価
- さらなる研究:最近の論文47件
第8章 電磁波ハーベスティング:太陽光発電から電力デバイスへ
- 概要
- 周波数別の電磁エネルギーハーベスティングツールキット:太陽光発電
- 単位体積および単位面積あたりの太陽光発電出力を増加させるための戦略
- ZED太陽光発電の重要なパラメータ
- 単一接合効率の限界
- 太陽電池の効率の動向
- コスト削減の経験曲線
- 2024年から2044年にかけて進化するいくつかの形式オプション
- pn接合による太陽光発電と他のオプションとの比較
- ペロブスカイト太陽光発電
- ZEDとして太陽光発電を備えた統合MEMS
- より多くの場所で実現可能かつ手頃な価格の太陽光発電:例
- 電池不要のソーラーZEDへのルート:テープ、IoT、カメラ
- スマートウォッチの透明および不透明太陽光発電
- センシングとIoTのための電池不要のドローン飛行
- ZED向け太陽光発電:SWOT評価
- さらなる研究論文とイベント
第9章 アンビエント電磁波ハーベスティング:既存放射の再利用によるデバイスおよび通信用のRFハーベスティング
- 概要
- 周波数別の電磁エネルギーハーベスティングツールキット:RF
- 人工のアンビエントRF放射を収集して車載電力を生成するデバイス
- ベーシックRFハーベスターRFEH
- RFハーベスタ改善への道筋
- さまざまな形式のRFハーベスタの結果
- RFハーベスティングを使用したセンサーと生体認証アクセス
- ウェアラブル向けのRFハーベスティング
- RFハーベスティングにおけるその他の最近の進歩
第10章 電気力学、圧電、摩擦電気などを使用したデバイス向けメカニカルハーベスティング (音響・振動・直線および回転運動):熱電、焦電、蒸発水力発電、微生物燃料電池 (バイオ燃料ハーベスティング)
- 概要
- 電磁放射ハーベスティングを超えるZEDエネルギーハーベスティング技術
- 機械エネルギー源とハーベスティングオプション
- GeorgiaTechのいくつかのオプションの比較
- 振動ハーベスティング
- 超低周波音のハーベスティング
- Kinetronおよびその他の電気力学 (「動電学」) ハーベスタは通常、超低周波音を収集します
- プッシュボタンハーベスティング
- EnOceanの建物は「ワイヤーなし、電池なし、制限なし」のIoTを制御します
- ゼロエネルギー開発電池レスZED
- 電池不要のセンサー電源用の蒸散動電ハーベスティング
- 音響採取
- 運動の摩擦電気エネルギーハーベスティング
- SWOT評価:熱電発電
- 水力発電ハーベスティング
- フレキシブルエネルギーハーベスティング:バイオ燃料電池皮膚センサーシステム
- 2024年以前の研究パイプライン
第11章 デバイスのマルチモードエナジーハーベスティング
- 概要
- マルチモードおよびマルチソースハーベスティングにより断続性を低減
- 2024年以前のマルチモードハーベスティングの研究パイプライン
- ZED向けマルチモードエナジーハーベスティング:SWOT評価
第12章 電池不要ZEDのためのスーパーキャパシタ、バリアント、無質量エネルギー
- 概要
- キャパシタ、スーパーキャパシタ、バッテリの選択範囲
- リチウムイオンキャパシタの特長
- スーパーキャパシタとその派生品の実際および潜在的な主要用途
- ZED向け電池レス蓄電技術:SWOT評価
- スーパーキャパシタとそのバリアントにより実現されるZEDの例
- 無質量エネルギースーパーキャパシタ構造エレクトロニクス
- 研究パイプライン:スーパーキャパシタ
- 研究パイプライン:ハイブリッドアプローチ
- 研究パイプライン:擬似コンデンサ
| REPORT STATISTICS | |
|---|---|
| SWOT appraisals: | 7 |
| Chapters: | 12 |
| Forecast lines 2024-2044: | 65 |
| Companies: | 90 |
| Infograms, tables, graphs: | 113 |
Some of the questions answered:
- How can I create a $1 billion ZED business?
- Potential competitors, partners, acquisitions?
- Market and technology roadmap for 2024-2044?
- Technology readiness and potential improvement?
- Appraisal of needs and appropriate technology options?
- Market drivers and forecasts of background parameters?
- Market forecasts by technology and application 2024-2044?
- Deep analysis of research pipeline including 2024 with implications?
- Explanation of trend to "massless energy", and other structural electronics?
- Battery-free, ultra-low power electronics, non-toxic, non-flammable options emerging?
You could call a solar flashlight and an anti-theft tag "zero-energy devices" but the subject is about to take a huge leap forward well beyond these. You can create a billion-dollar business from making the next ZED materials or devices as detailed in the commerclally-oriented 408-page report, "Zero Energy Devices ZED: Self-Powered and Backscatter-Powered Electronics and Electrics Markets, Technology 2024-2044".
Dramatic advances ahead
The day is coming when you never recharge your smart watch or phone and, without need for a battery, they last longer than you do. Internet of Things will be more than a cynical renaming of existing wireless technology because the nodes will genuinely become things-collaborating-with-things and they will be affordable, much smaller, lasting decades and deployable in tens of billions year without pollution. The delights of promised 6G Communications in 2030 will be possible only with ZED metasurfaces enhancing the propagation path and it enabling edge-computing client ZED. You will live longer with ZED inside you. There is much more and you only find it in this deeply insightful, up-to-date report that even scopes research in 2024, future needs and technology evolution. The primary author has created several successful high-tech businesses, so the report is realistic, including warnings concerning dead ends and over-promising.
The big picture
The Executive Summary and Conclusions is sufficient in itself. It has 26 pages of easily- understood infograms and roadmaps followed by 65 forecast lines of ZED and allied technologies and applications. Chapter 2 (25 pages) introduces definitions, context and successes so far including the problem of increasing electricity consumption of electronics with the ZED antidote eliminating power consumption and battery issues. See how on-board energy harvesting is being simplified, saving weight, size, cost, failure modes and toxigens. Can ZED halt the increasing demand of electronics for grid-based electricity? ZED route to success with the Internet of Things? Why are ZED sensors a strong emerging need? Importance of flexible, laminar and 2D energy harvesting and sensing , even self-powered and integrated sensors 2024-2044? See how next telecommunications generations deliver more ZED opportunities.
The heart of the report
The heart of the report consists of three chapters on how to address certain important sectors with ZED then seven chapters on the important ZED enabling technologies emerging 2024-2044 to drive your success. Enjoy close examination of the latest research pipeline and realistic timescales and requirements for commercial success with much distilled into new SWOT appraisals, comparison charts and infograms. This is firm analysis of commercial opportunities not academic obscurity, rambling text or nostalgia.
ZED for 6G Communications
6G Communications is planned for 2030, with a radically improved form in 2035. The 49 pages of Chapter 3 address this, highlighting how it will both need widespread ZED in its infrastructure to succeed and it may enable huge numbers of edge computing ZED client devices.
ZED appearing as wireless sensors, IOT, personal and other electronics
Chapter 4 concerns "ZED progress with wireless sensors, IOT, personal and other electronics" so it takes a full 56 pages to interpret such a broad scope of achievements, opportunities and research approaches. The massive scope for vast numbers of fit-and-forget battery-free sensors gets particular attention. Sensor transducers that are their own source of electricity, ZED wearables including metaverse interfacing, ZED in automotive, medical and more - it is all here. Then come the technology chapters with your best opportunities to participate.
Optimal technology strategies
Chapter 5 "Strategies to achieve fit-and-forget battery-free ZED" in 30 pages presents battery headwinds 2024-2044 and ZED enablement, notably eight ZED enablers that can be combined. See self-healing materials for fit-and-forget then useful specification compromises with energy harvesting. Here is a battery-free perpetual micro-robot. Combining these approaches is brought to life with examples of "Batteryless energy harvesting with demand management" , "Quest for battery less ZED in heterogenous cellular networks", "Wireless sensor networks enable their ZED devices with severe performance compromises", "Oppo view of zero power communications and "ZED lessons from active RFID"
Energy harvesting system design for ZED
Then comes energy harvesting system design for ZED, the elements of a harvesting system and new infograms on energy harvesting system detail with improvement strategies 2024-2044 and on 13 families of energy harvesting technology considered for ZED 2024-2044 followed by more detail. Again, the approach is critical not evangelistic because companies and researchers vary in their approaches from very realistic in our 20-year timeframe to the extremely speculative and unwanted.
Next ultra-low power electronics makes new ZED feasible
Chapter 6 (39 pages) addresses the contribution to the success of ZED from "Ultra-low power electronics, sensors, and electrics". It is broad in scope but, because of their great importance, it particularly covers ultra-low power integrated circuits and metamaterials needing much less electricity so your energy harvesting and backscatter power can operate vastly more forms of device.
Backscatter on steroids
Chapter 7 (19 pages) "Powering devices only when interrogated: backscatter, SWIPT, WIET, WPT for EAS, RFID, IOT, 6G Communications and other electronics" then goes really deeply into that form of ZED enablement. This necessarily includes so-called "ambient backscatter communications AmBC", "crowd-detectable CD-ZED" and much new research. It is followed by three chapters on the all-important energy harvesting technologies evolving for ZED applications.
On-board harvesting options increase and combine
Chapter 8 (23 pages) is "Harvesting electromagnetic waves: photovoltaics to power devices" then Chapter 9 (18 pages) is "9. Harvesting ambient electromagnetic waves: RF harvesting power for devices and communication by recycling existing emissions" and the rest is covered in Chapter 10 (39 pages) "Mechanical harvesting for devices (acoustic, vibration, linear and rotational motion) using electrodynamics, piezoelectrics, triboelectrics etc. Thermoelectrics, pyroelectrics, evaporative hydrovoltaics, microbial fuel cells (biofuel harvesting)".
However, an aspect rarely addressed is the combination of these many energy harvesting technologies to reduce and sometimes eliminate the need for on-board energy storage to overcome their intermittency and inability to respond to load variations. Consequently, Chapter 11 (16 pages) covers, "Multi-mode energy harvesting for devices" including its progression into single smart materials. See examples such as "thermoelectric with photovoltaic", "photovoltaic with electrokinetic", "thermoelectric with photovoltaic and movement harvesting" and "push button harvesting with solar power and intermittency tolerant electronics". From 2024 and other research, learn how there is much more to come for smart watches through to medical implants.
Storage that batteries can never achieve
At this stage you will realise that many zero energy devices without storage have been presented throughout the report. You will accept that self-powered devices with long-life batteries can still be considered "ZED". Nonetheless, it is clear that the big opportunity ahead is where alternatives to on-board batteries are used to cover intermittency of energy harvesting and the need to respond to load variation. Chapter 12 (40 pages) therefore analyses, "Supercapacitors, variants and massless energy for battery-free ZED". It explains why supercapacitors and lithium-ion capacitors are the prime candidates but it also discusses others with few or none of the problems of batteries such as life, reliability, toxicity and flammability.
Massless energy will transform ZED
They all take more space and weight than a good battery in a ZED but two escape routes are presented. One is wide area thin formats and the other is what Imperial College London calls "massless energy". Here, a dumb load-bearing structure such as a watch case is replaced with a structural supercapacitor material incurring no increase in space or weight even if it has a photovoltaic overlayer. The report, "Zero Energy Devices ZED: Self-Powered and Backscatter-Powered Electronics and Electrics Markets, Technology 2024-2044" is your essential guide to this large new ZED opportunity.
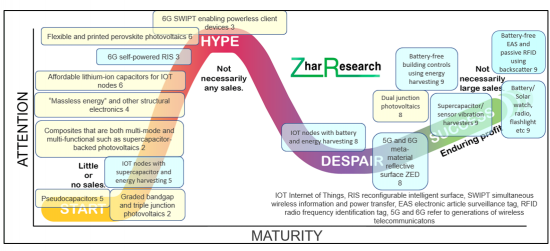
CAPTION Maturity of primary ZED enabling technologies in 2024. Indicated number is technology readiness level TRL - maturity level of a technology throughout its research, development and deployment phase progression on a scale from 1 to 9. ZED is shown blue and ZED enabling technologies are shown yellow. Source Zhar Research report, "Zero Energy Devices ZED: Self-Powered and Backscatter-Powered Electronics and Electrics Markets, Technology 2024-2044".

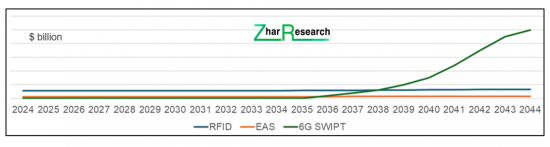
CAPTION Backscatter ZED $ billion 2024-2044. Source: Zhar Research report, "Zero Energy Devices ZED: Self-Powered and Backscatter-Powered Electronics and Electrics Markets, Technology 2024-2044".

Table of Contents
1. Executive summary and conclusions
- 1.1. Purpose and scope of this report
- 1.2. Methodology of this analysis
- 1.3. Definition and purpose
- 1.4. 18 Primary conclusions
- 1.5. Current ZED successes
- 1.6. Optimal technology strategies for ZED 2024-2044
- 1.7. Progress of telecommunications generations to more ZED opportunities
- 1.8. Progress towards sensor ZED 2024-2044
- 1.9. Roadmap of ZED and its enabling technologies 2024-2044
- 1.10. Market forecasts 2024-2044
- 1.10.1. Backscatter ZED units sold billion RFID, EAS, 6G SWIPT 2024-2044
- 1.10.2. Backscatter ZED $ billion RFID, EAS, 6G SWIPT 2024-2044
- 1.10.3. Energy storage market battery vs batteryless $ billion 2023-2044
- 1.10.4. Batteryless storage short vs long duration 2023-2044
- 1.10.5. Batteryless energy storage vs lithium-ion battery market $ billion 2023-2044: table, graphs, explanation
- 1.10.6. Lithium-ion battery market by three storage levels 2023-2044
- 1.10.7. Batteryless energy storage by three storage levels $ billion 2023-2044: table
- 1.10.8. Batteryless storage market by 13 technology categories $ billion 2023-2044 table
- 1.10.9. 6G infrastructure enabling client devices without storage: global yearly 6G RIS sales by five types and total $ billion 2024-2044
- 1.10.10. Global yearly 6G RIS sales by five types $ billion 2023-2043: area graph with explanation
- 1.10.11. Sensors global value market for seven application sectors $ billion 2023-2044:
- 1.10.12. Sensor value market % by 6 input media 2024, 2034, 2044: table with sub-categories and reasons
- 1.10.13. Sensor value market % by six input media 2024-2044
- 1.10.14. Smartphone sensor market units, unit price, value market $ billion 2023-2044
- 1.10.15. Smartphone units sold globally 2023-2044 if 6G is successful
- 1.10.16. X-reality hardware market with possible 6G impact 2024-2044
2. Definition, examples and future need for zero energy devices
- 2.1. Overview
- 2.2. Reasons for the trend to ZED
- 2.3. Different definitions of zero energy device ZED
- 2.4. Context of ZED: overlapping and adjacent technologies and examples of long-life energy independence
- 2.5. Electrical autonomy examples that last for the life of their host equipment
- 2.6. The increasing electricity consumption of electronics and ZED strategies
- 2.7. Strategies to reduce power consumption and battery issues
- 2.8. On-board energy harvesting for ZED is being simplified to save weight, size, cost and reduce the number of failure modes and toxigens
- 2.9. Stopping the increasing demand of electronics for grid-based electricity
- 2.10. Internet of Things: lessons of failure and possible route to success
- 2.11. Introduction to energy harvesting
- 2.12. Why ZED sensors are a strong emerging need
- 2.13. Importance of flexible, laminar and 2D energy harvesting and sensing 2024-2044
- 2.14. Self-powered and integrated sensors
- 2.15. How telecommunications generations are progressing to more ZED opportunities
3. ZED opportunity with 6G Communications RIS, CPE and client devices
- 3.1. Overview
- 3.2. Why do we need 6G?
- 3.3. Disruptive 6G aspects
- 3.4. Arguments against, challenges ahead and objectives of key players
- 3.5. The cost challenge
- 3.6. 3GPP vision of options for 6G ZED and wireless powered IoE for 6G
- 3.7. How 6G transmission hardware will achieve much better performance than 5G
- 3.8. Recent hardware advances that can aid 6G 2024-2044
- 3.9. 6G Communications opportunities for equipment and edge devices to become ZED
- 3.10. Specific ZED needs in 6G communications
- 3.11. 6G ZED in the research pipeline
- 3.11.1. Machine Type Communication (MTC)
- 3.11.2. Zero-energy air interface for advanced 5G and for 6G
- 3.11.3. Zero-energy devices empowered 6G opportunities
- 3.11.4. First real-time backscatter communication demonstrated for 6G in 2023
- 3.11.5. Further reading-13 other recent research papers relevant to 6G ZED
- 3.12. SWOT appraisal of 6G Communications as currently understood
- 3.13. 6G general roadmap 2024-2044
4. ZED progress with wireless sensors, IOT, personal and other electronics
- 4.1. Overview of basics and progress towards sensor ZED 2024-2044
- 4.2. IOT nodes and concepts
- 4.3. Market evolution: sensor parameters measured become multi-faceted, demand changes radically
- 4.4. Progress to sensor ZED: self-powered and self-sensing devices
- 4.5. Smart sensor anatomy and purpose
- 4.6. Examples of self-powered sensors and ZED sensor research pipeline in 2024
- 4.7. Progress towards ZED with personal electronics, industrial and professional electronics
- 4.8. Examples of battery-based ZED personal and other electronics and electrics
- 4.9. Progress with ZED wearables
5. Strategies to achieve fit-and-forget battery-free ZED
- 5.1. Overview
- 5.2. Battery headwinds 2024-2044
- 5.3. ZED enablement
- 5.3.1. Eight ZED enablers that can be combined
- 5.3.2. ZED enabler: self-healing materials for fit-and-forget
- 5.3.3. Specification compromise with energy harvesting: battery-free perpetual micro-robot
- 5.3.4. Batteryless energy harvesting with demand management
- 5.3.5. Quest for battery less ZED in heterogenous cellular networks
- 5.3.6. Wireless sensor networks enable their ZED devices with severe performance compromises
- 5.3.7. Oppo view of zero power communications
- 5.3.8. ZED lessons from active RFID
- 5.4. Energy harvesting system design for ZED
- 5.4.1. Elements of a harvesting system
- 5.4.2. Energy harvesting system detail with improvement strategies 2024-2044
- 5.4.3. 13 families of energy harvesting technology considered for ZED 2024-2044
6. Ultra-low power electronics, sensors, and electrics
- 6.1. Overview
- 6.2. Ultra-low power electronics
- 6.2.1. Ultra-low-power readout interfaces and multifunctional electronics
- 6.2.2. Ultra-low-power phononic in-sensor computing
- 6.2.3. Improved energy efficiency in 6G Communications: European Commission Hexa-X Project
- 6.2.4. Static context header compression and fragmentation for ZED
- 6.2.5. Other energy efficient sensing, processing and new power transfer options for IOT
- 6.3. Ultra-low power integrated circuits
- 6.3.1. Nanopower nPZero
- 6.3.2. Everactive ultra-low power circuits for ZED IOT
- 6.3.3. 2nm chips and beyond-USA, Taiwan, China, Japan
- 6.3.4. Ericsson Research and MIT Lithionic chips
- 6.3.5. Move-X's MAMWLE: Ultra-low-power radio module
- 6.4. Ultra-low-power smartphone
- 6.5. Metamaterials and metasurfaces as ZED or enabling ZED
- 6.5.1. Definitions and scope
- 6.5.2. Metamaterial ZED window
- 6.5.3. Metasurfaces for 6G RIS ZED and other purposes
- 6.5.4. SWOT appraisal of 6G Communications RIS opportunities
7. Powering devices only when interrogated: backscatter, SWIPT, WIET, WPT for EAS, RFID, IOT, 6G Communications and other electronics
- 7.1. Overview: backscatter, EAS, RFID, 6G SWIPT
- 7.1.1. Forms of wireless power transfer enabling batteryless and less-battery devices
- 7.1.2. Backscatter communications
- 7.1.3. Evolution of wireless electronic communication devices needing no on-board energy storage 1980-2035
- 7.2. Ambient backscatter communications AmBC and Crowd-detectable CD-ZED
- 7.2.1. View of Aalto University on AmBC and CD-ZED
- 7.2.2. Orange AmBC and CD-ZED
- 7.2.3. Battery-free AmBC: University of California San Diego
- 7.2.4. Crowd-detectable CD-ZED research
- 7.3. Hybrid beamforming-based SWIPT
- 7.4. SWOT appraisal of circuits and infrastructure that eliminate storage
- 7.5. Further research: 47 recent papers
8. Harvesting electromagnetic waves: photovoltaics to power devices
- 8.1. Overview
- 8.2. Electromagnetic energy harvesting toolkit by frequency: photovoltaics
- 8.3. Strategies for increasing photovoltaic output per unit volume and area 2024-2044
- 8.4. Some important parameters for ZED photovoltaics
- 8.5. Limits of single junction efficiency
- 8.6. PV cell efficiency trends
- 8.7. Experience curve of cost reduction
- 8.8. Some format options evolving 2024-2044
- 8.9. Photovoltaics by pn junction compared to other options 2024-2044
- 8.10. Perovskite photovoltaics
- 8.11. Integrated MEMS with photovoltaics as ZED
- 8.12. Photovoltaics feasible and affordable in more places: examples
- 8.13. Routes to battery-free solar ZED: tape, IOT, cameras
- 8.14. Transparent and opaque photovoltaics in smartwatches
- 8.15. Battery-free drone flight for sensing and IOT
- 8.16. SWOT appraisal of photovoltaics for ZED
- 8.17. Further research papers and events in 2024
9. Harvesting ambient electromagnetic waves: RF harvesting power for devices and communication by recycling existing emissions
- 9.1. Overview
- 9.2. Electromagnetic energy harvesting toolkit by frequency: RF
- 9.3. Devices harvesting ambient man-made RF emissions to produce on-board electricity
- 9.4. Basic RF harvester RFEH
- 9.5. Routes to RF harvester improvement
- 9.6. Results for various forms of RF harvester
- 9.7. Sensors and biometric access using RF harvesting
- 9.8. RF harvesting for wearables
- 9.9. Other recent advances in RF harvesting
10. Mechanical harvesting for devices (acoustic, vibration, linear and rotational motion) using electrodynamics, piezoelectrics, triboelectrics etc. Thermoelectrics, pyroelectrics, evaporative hydrovoltaics, microbial fuel cells (biofuel harvesting)
- 10.1. Overview
- 10.2. ZED energy harvesting technology beyond harvesting electromagnetic radiation 2024-2044
- 10.3. Sources of mechanical energy and harvesting options 2024-2044
- 10.4. GeorgiaTech comparison of some options
- 10.5. Vibration harvesting
- 10.5.1. General
- 10.5.2. Hitachi Rail battery-free ZED vibration sensor powered by electrodynamic energy harvesting
- 10.6. Harvesting infrasound
- 10.7. Kinetron and other electrodynamic ("electrokinetic") harvesters typically harvesting infrasound
- 10.8. Push button harvesting
- 10.9. EnOcean building controls "no wires, no batteries, no limits" IOT
- 10.10. Zero Energy Development battery-free ZED
- 10.11. Transpiration electrokinetic harvesting for battery-free sensor power supply
- 10.12. Acoustic harvesting
- 10.13. Triboelectric energy harvesting of motion
- 10.14. Thermoelectric harvesting with SWOT appraisal
- 10.15. Hydrovoltaic harvesting
- 10.16. Flexible energy harvesting: biofuel cell skin sensor system
- 10.16. Research pipeline in 2024 and earlier
11. Multi-mode energy harvesting for devices
- 11.1. Overview
- 11.2. Multi-mode and multiple-source harvesting to reduce intermittency
- 11.2.1. Thermoelectric with photovoltaic
- 11.2.2. Photovoltaic with electrokinetic: Ressence Model 2 watch
- 11.2.3. Thermoelectric with photovoltaic and movement harvesting: DCO, Wurth and Analog Devices products
- 11.2.4. Push button harvesting with solar power and intermittency tolerant electronics BFree
- 11.3. Multi-mode harvesting research pipeline 2024 and earlier
- 11.4. SWOT appraisal of multi-mode energy harvesting for ZED
12. Supercapacitors, variants and massless energy for battery-free ZED
- 12.1. Overview
- 12.2. Spectrum of choice-capacitor to supercapacitor to battery
- 12.3. Lithium-ion capacitor features
- 12.4. Actual and potential major applications of supercapacitors and their derivatives 2024-2044
- 12.5. SWOT appraisal of batteryless storage technologies for ZED
- 12.6. Examples of ZED enabled by supercapacitors and variants
- 12.6.1. Bicycle dynamo with supercapacitor or electrolytic capacitor
- 12.6.2. IOT ZED enabled by LIC hybrid supercapacitor
- 12.6.3. Supercapacitors in medical devices
- 12.7. Massless energy-supercapacitor structural electronics
- 12.7.1. Review
- 12.7.2. Structural supercapacitors for aircraft: Imperial College London, Texas A&M University
- 12.7.3. Structural supercapacitors for boats and other applications: University of California San Diego
- 12.7.4. Structural supercapacitors for road vehicles: five research centers
- 12.7.5. Structural supercapacitors for electronics and devices: Vanderbilt University USA
- 12.7.6. Transparent structural supercapacitors on optoelectronic devices
- 12.8. Research pipeline: Supercapacitors
- 12.9. Research pipeline: Hybrid approaches
- 12.10. Research pipeline: Pseudocapacitors


