|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1565777
リチウムイオン二次電池正極材料の技術動向と市場見通し(~2035年)<2024> Technology Trend and Market Outlook for Cathode Materials of Lithium-ion Secondary Batteries (~2035) |
||||||
|
|||||||
| リチウムイオン二次電池正極材料の技術動向と市場見通し(~2035年) |
|
出版日: 2024年10月07日
発行: SNE Research
ページ情報: 英文 618 Pages
納期: お問合せ
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
リチウムイオン二次電池市場は、小型IT用途から、電気自動車(EV)とエネルギー貯蔵システム(ESS)市場により重点を置く方向にシフトしています。EVに搭載されるリチウムイオン二次電池の需要は急速に増加しており、この用途に使用される正極材料市場の成長を促進しています。
リチウムイオン二次電池のリチウム供給に重要な役割を果たす正極材料には、LiCoO2(LCO)、LiO2(NCM)、Li(Ni1-x+yCoxAly)O2(NCA)、スピネル構造LiMn2O4(LMO)などの層状構造材料があります。近年では、中国のEV市場拡大に牽引され、コスト効率で支持されているLiFePO4(LFP)正極材料も、業界の大きな注目を集めています。
LCOは、その優れた物理的・電気化学的特性と高いエネルギー密度から、モバイルIT機器の正極材料としてしばしば使用されていますが、コバルトの高いコストが大きな欠点となっています。一方、LMOはコスト効率が高く、熱安定性にも優れていますが、可逆容量が低く、高温での寿命が短くなるなどの限界があります。
高放電容量を可能にするNCMは、ニッケル含有量が80%以上で約200mAh/gに達します。韓国の正極材料メーカーは過去10年間、高容量Ni系正極材料の研究を積極的に行っており、NCMやNCMAのような先進の誘導体が市場の主流となっています。
LFPは手頃な鉄ベースの組成で、コスト効率で競争力を獲得しています。コバルトやニッケルといった三元系材料の原材料の価格が近年高騰しているため、LFPのコスト優位性はより顕著になっています。新しい技術であるLMFP(マンガン添加LFP)は、LFPの限界を解決するもので、CATL、BYD、Gotionといった中国の大手メーカーが商業化のために採用しています。LFP電池は、2020年9月以降の中国のEV市場で、NCM(ニッケル、コバルト、マンガン)とNCA(ニッケル、コバルト、アルミニウム)の三元電池のシェアを上回り、2020年の17%から2022年に36%に成長しました。Tesla、Volkswagen、Ford、Stellantisといった世界の自動車メーカーもLFP電池の可能性を探っています。
高電圧中ニッケル(HV Mid-Ni)NCMは、当初Umicoreによって商業化されましたが、材料のクラックや電池寿命の低下などの問題により、高ニッケル代替品の台頭とともに人気を失っています。しかし、単結晶負極材料の進歩と電池技術の向上により、HV Mid-Ni NCMはLFPの有力な競合材料として再浮上しつつあります。高ニッケル材料を使用する韓国企業は、この分野への投資拡大を検討しています。
リチウムイオン二次電池の4大構成要素(正極、負極、電解液、セパレーター)の1つである正極材料は、全体のコストの約30~40%を占める。したがって、大規模なリチウムイオン二次電池を実用化するためには、正極の性能を向上させながらコストを削減することが不可欠です。世界的には、正極材料メーカーは200社以上あり、100~150社程度が積極的に生産を行っています。日本は約20~30社、韓国は約15~30社、中国やその他の地域は約100~150社です。ベルギーの多国籍企業Umicoreもこの部門で注目されています。さらに、正極材料の原材料や前駆体を供給する企業は、世界中に約150社あります。
当レポートでは、世界のリチウムイオン二次電池正極材料市場について調査分析し、NiリッチNCMを中心に、さまざまな正極材料の最新の技術動向を提供しています。
目次
第1章 正極材料技術の現状と開発動向
第1節 イントロダクション
- 正極材料開発の現状
- 設計基準
- イオン結合と共有結合
- モットハバード型と電荷移動型
- 固相における3d遷移における電荷移動反応の概念
- 固相拡散と二相共存反応の概念
- 正極材料に求められる特性
第2節 正極材料の種類
- 層状複合材料
- LiCoO2
- LiNiO2
- LiMO2(M = Fe、Mn)
- Ni-Mn系
- Ni-Co-Mn 3成分系
- Liリッチ層状化合物
- スピネル系複合材料
- LiMn2O4
- LiMxMn2-xO4
- オリビン系複合材料
- LiFePO4
- LiMPO4
- CTP(Cell-to-Pack)技術
- 低コスト電極材料
- NMX:Coフリー正極材料
第3節 その他の正極材料
- フッ化物系複合材料
第2章 NiリッチNCM技術
第1節 イントロダクション
第2節 NiリッチNCMの課題
- 陽イオン混合
- H2-H3フェーズ
- 残留リチウム化合物
第3節 NiリッチNCMの問題に対するソリューション
- 遷移金属ドーピング
- 表面改質
- 濃度勾配構造
- 単結晶アプローチ:単一粒子による長寿命特性
第3章 HV(高電圧)正極技術
第1節 HV正極の現状
- 中国の現状
- 韓国の現状
- 日本の現状
第2節 HV正極活物質
- LMFP(Li(M)FePO4)
- LNMO:LNMO
- LCO(LiCoO2)
- LiリッチマンガンNMC
- HLM:LMNCO
第3節 HV正極活物質の課題
- 表面劣化
- ガス放出
- 相転移
- マイクロクラック
- LCOバルクとインターフェースの劣化
- CEIの形成と進化のメカニズム
- LCOにおける寄生酸化反応
- LNMOにおける遷移金属の溶解
- 表面のひび割れと相変化
- LiリッチマンガンNMC正極の劣化
第4節 HV正極活物質のソリューション
- 元素ドーピング
- 表面コーティング
- 単結晶(SC)製造
- 構造設計(接続勾配)
- 多機能電解質添加剤
第4章 正極材料の製造プロセス
第1節 正極材料(NCM)の製造プロセス
- 混合
- 焼成
- 粉砕
- シーケンシング
- 磁気分離
第2節 正極材料(LFP)の製造プロセス
- 固体合成法
- 液相合成法
- 前駆体法
第3節 前駆体の製造プロセス
- Ni系NCMの製造フロー
- LFP(固体法)の製造フロー
- LFP(液相法)の製造フロー
- ポストリアクター/リアクタープロセス
第4節 正極材料特性の評価
- 化学組成分析
- 比表面積の測定
- 粒子サイズ測定
- タップ密度測定
- 水分含有量の測定
- 残留炭酸リチウムの測定
- 熱分析
- 粒子強度
第5節 正極板の製造プロセス
第5章 世界のLIB市場の見通し(~2035年)
- 1. 世界の二次電池設置の見通し
- 2. 世界の二次電池出荷の見通し
- 3. 世界の二次電池生産の見通し
- 4. 世界の二次電池生産の見通し:サプライヤー別
- 5. 世界の二次電池生産M/Sの見通し:サプライヤー別
- 6. 世界の二次電池生産:正極化学別
- 7. 世界の二次電池生産M/S:正極化学別
第6章 世界の正極供給状況と市場見通し
- 1. 需要見通し:正極用途別(2021年~2035年)
- 2. 需要見通し:正極化学別(2021年~2035年)
- 3. 需要M/Sの見通し:正極化学別(2021年~2035年)
- 4. EV向け需要見通し:正極化学別(2021年~2035年)
- 5. ESS向け需要見通し:正極化学別(2021年~2035年)
- 6. 二次電池正極出荷の詳細(2021年~2024年)
- 7. 二次電池正極出荷の詳細:国別(2021年~2024年)
- 8. ニッケル系CAM出荷(供給)数量:サプライヤー別(2021年~2024年)
- 9. ニッケル系CAM出荷M/S:サプライヤー別(2021年~2024年)
- 10. LFP正極出荷(供給)数量:サプライヤー別(2021年~2024年)
- 11. LFP正極出荷M/S:サプライヤー別(2021年~2024年)
- 12. CAMサプライヤーの状況の総合分析(2023年現在)
- 13. LFP CAMサプライヤーの状況の総合分析(2023年現在)
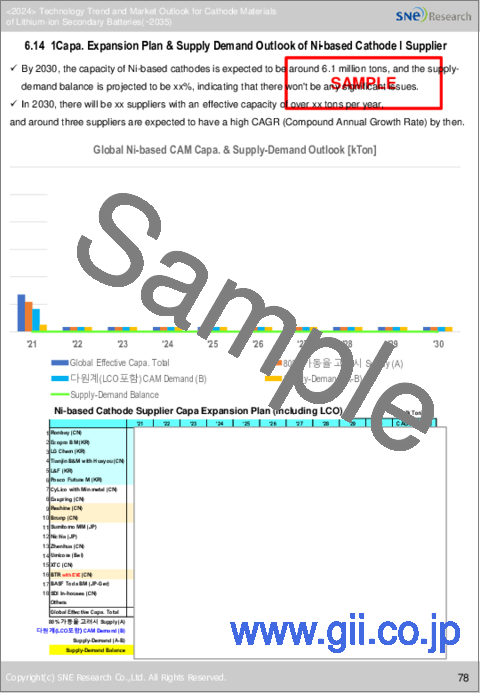
- 14. 多成分正極材料サプライヤーの生産能力拡大計画と需給の見通し(2021年~2030年)
- 15. LFP正極材料サプライヤーの生産能力拡大計画と需給の見通し(2021年~2030年)
- 16. 正極材料の価格の見通し:材料別(2021年~2030年)
- 17. CAMの市場規模の見通し(2021年~2030年)
第7章 正極需要の状況:LIBメーカー別
- 1. CAM需要:用途別、化学別(2021年~2024年)
- 2. CAM需要:LIBメーカー別(2021年~2024年)
- 3. LIBメーカーからのCAM需要:化学別(2021年~2024年)
- 4. 主要LIBメーカーのCAM需要とサプライヤーの状況と見通し
- CATL/LGES/BYD/SDI/SK On/Panasonic/CALB/Guoxuan/EVE/REPT
- 5. 主要企業間の需給の概要
第8章 正極材料メーカーの状況
第1節 韓国の正極材料メーカー
- Ecopro
- L&F
- Posco Future M
- Umicore Korea
- LG Chem
- SDI (STM)
- Cosmo AM&T
- SM Lab
- Top Materials
第2節 日本の正極材料メーカー
- Nichia
- Sumitomo Metal Mining
- Toda Kogyo
- Mitsui Kinzoku
- Nippon Denko
第3節 中国の正極材料メーカー
- Ronbay
- B&M
- XTC
- Reshine
- Easpring
- CY Lico
- ShanShan
- ZEC
- BTR
- Brunp
- LIBODE
- Hunan Yuneng
- Dynanonic
- Hubei Wanrun
- Lopal Technology
- Rongtong Hi-TechV
- Guoxuan (Gotion)
- Youshan
- Hunan Shenghua
- Anda
- Jintang Shidai
- Shengfan
- Pulead
- Terui
第4節 その他の地域の正極材料メーカー
第9章 索引
The lithium-ion secondary battery market is shifting from small IT applications toward a more substantial focus on electric vehicle (EV) and energy storage system (ESS) markets. Demand for lithium-ion batteries in EVs is rapidly increasing, driving growth in the market for cathode materials used in these applications.
Cathode materials, which play a crucial role in supplying lithium in lithium-ion secondary batteries, include layered structure materials such as LiCoO2 (LCO), Li(Ni1-x+yCoxMny)O2 (NCM), Li(Ni1-x+yCoxAly)O2 (NCA), and spinel-structured LiMn2O4 (LMO). Recently, LiFePO4 (LFP) cathode materials, favored for their cost efficiency and driven by China's EV market expansion, have also gained substantial industry attention.
Due to its superior physical and electrochemical properties and high energy density, LCO is often used as a cathode material for mobile IT devices, though the high cost of cobalt is a significant drawback. LMO, on the other hand, is cost-effective and has excellent thermal stability, though it has limitations such as lower reversible capacity and reduced lifespan at high temperatures.
NCM, which enables high discharge capacity, can reach approximately 200 mAh/g with nickel content over 80%. South Korean cathode material companies have been actively researching high-capacity Ni-based cathode materials over the past decade, making NCM and advanced derivatives like NCMA mainstream in the market.
LFP, with its affordable iron-based composition, has gained a competitive edge in cost-efficiency. With the recent surge in prices of raw materials like cobalt and nickel for ternary materials, LFP's cost advantage has become more pronounced. A novel technology, LMFP (LFP with added manganese), addresses the limitations of LFP and has been adopted by major Chinese manufacturers like CATL, BYD, and Gotion for commercialization. LFP batteries surpassed the share of NCM (nickel, cobalt, manganese) and NCA (nickel, cobalt, aluminum) ternary batteries in China's EV market after September 2020, growing from 17% in 2020 to 36% in 2022. Global automakers such as Tesla, Volkswagen, Ford, and Stellantis are also exploring the potential of LFP batteries.
High Voltage Mid-Nickel (HV Mid-Ni) NCM, initially commercialized by Umicore, fell out of favor with the rise of high-nickel alternatives due to issues such as material cracking and reduced battery life. However, with advancements in single-crystal anode materials and improved battery technologies, HV Mid-Ni NCM is re-emerging as a viable competitor to LFP. South Korean companies that use high-nickel materials are considering expanding their investment in this area.
Cathode materials, one of the four primary components (cathode, anode, electrolyte, separator) of lithium-ion secondary batteries, account for approximately 30-40% of the overall cost. Thus, to commercialize large-scale lithium-ion batteries, improving cathode performance while reducing costs is essential. Globally, there are over 200 cathode material manufacturers, with around 100 to 150 actively engaged in production. Japan has around 20-30 companies, Korea around 15-30, and China and other regions around 100-150. Umicore, a multinational company in Belgium, is also notable in the sector. Additionally, there are approximately 150 companies worldwide that supply raw materials and precursors for cathode materials.
The global cathode materials market is dominated by companies in China, Japan, and Korea. Chinese companies have emerged as leaders, leveraging domestic demand and the growth of major Chinese battery makers, while Japanese firms rely on advanced precursor technologies to compete. Korean companies face intense price competition from Chinese suppliers and technological competition with Japanese firms.
This report provides insights into the latest technical trends across various cathode material types, with a focus on Ni-rich NCM. It also explores cobalt-free cathode technologies and single-particle cathode developments. Additionally, chapters are dedicated to emerging technologies for LFP and LMFP cathodes, high-voltage cathode technologies, and their manufacturing processes.
In-Depth Report Highlights:
- Gain insights into the latest technologies for high-interest LFP and high-voltage (HV) cathode materials.
- Understand the advancements in Ni-rich NCM cathode materials.
- Explore new developments in cobalt-free and single-particle cathode materials.
- Obtain data on production, demand, and capacity expansion plans for cathode materials by major producers and cell manufacturers.
- Access comprehensive information on major cathode producers in China, Korea, and Japan.
- Discover detailed information on the manufacturing processes of ternary and LFP cathodes.
- Analyze supply and demand forecasts for cathode active materials (CAM) by major battery manufacturers, and gain market outlook insights.
- Track the evolution of cathode material trends over the past 3-5 years.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Status of Cathode Material Technology & Development Trend
1. Introduction
- 1.1. Status of Cathode Material Development
- 1.2. Design Criteria
- 1.2.1. Ionic Bonding and Covalent Bonding
- 1.2.2. Mott-Hubbard Type and Charge Transfer Type
- 1.2.3. Concept of Charge transfer Reaction in 3d Transition in Solid Phase
- 1.2.4. Concept of Diffusion in Solid Phase and Two-Phase Coexistence Reaction
- 1.3. Characteristics required in Cathode Materials
2. Types of Cathode Material
- 2.1. Layered Composites
- 2.1.1. LiCoO2
- 2.1.2. LiNiO2
- 2.1.3. LiMO2 (M = Fe, Mn)
- 2.1.4. Ni-Mn Based
- 2.1.5. Ni-Co-Mn 3-Component System
- 2.1.6. Li-rich layered compounds
- 2.2. Spinel based Composites
- 2.2.1. LiMn2O4
- 2.2.2. LiMxMn2-xO4
- 2.3. Olivine based Composites
- 2.3.1. LiFePO4
- 2.3.2. LiMPO4 (M = Mn, Co, Ni)
- 2.3.3. CTP (Cell-to-Pack) Technology
- 2.4. Low-cost electrode materials
- 2.4.1. NMX: Co-free Cathode materials
3. Other cathode material
- 3.1. Fluoride based composites
Chapter 2. Ni-Rich NCM Technology
1. Introduction
2. Issues of Ni-Rich NCM
- 2.1. Cation mixing
- 2.2. H2-H3 Phase
- 2.3. Residual lithium compounds
3. Solution to Ni-Rich NCM Issues
- 3.1. Transition metal doping
- 3.2. Surface modification
- 3.3. Concentration gradient structure
- 3.4. Single crystal approach: Long-Life Characteristics through Single Particles
Chapter 3. HV (High Voltage) Cathode Technology
1. HV Cathode Current state
- 1.1. Current status in China
- 1.2. Current status in Korea
- 1.3. Current status in Japan
2. HV Cathode Active Material
- 2.1. LMFP (Li(M)FePO4)
- 2.2. LNMO : LNMO(LINI0.5MN1.5O4)
- 2.3. LCO (LiCoO2)
- 2.4. Li rich Manganese NMC(L1.2Mn0.54N0.13C0.13O2)
- 2.5. HLM : LMNCO (L1.2Mn0.54N0.13C0.13O2)
3. Issues of HV Cathode Active Material
- 3.1. Surface degradation
- 3.2. Gas release
- 3.3. Phase transformation
- 3.4. Microcracks
- 3.5. Degradation of LCO bulk & interface
- 3.6. Formation & Evolution Mechanism of CEI
- 3.7. Parasitic Oxidation Reaction at LCO
- 3.8. Transition Metal Dissolution at LNMO
- 3.9. Surface Cracks and Phase Changes
- 3.10. Degradation of Li-rich Manganese NMC cathode
4. Solutions to HV Cathode Active Material
- 4.1. Element Doping
- 4.2. Surface Coating
- 4.3. Single Crystal (SC) Favbrication
- 4.4. Structural Design (Connection Gradient)
- 4.5. Multifunctional Electrolyte Additives
Chapter 4. Manufacturing Process of Cathode Materials
1. Manufacturing Process of Cathode Materials (NCM)
- 1.1. Mixing
- 1.2. Calcination
- 1.3. Crushing
- 1.4. Sieving
- 1.5. Magnetic Separation
2. Manufacturing Process of Cathode Materials ((LFP)
- 2.1. Solid-state Synthesis Method
- 2.2. Liquid-phase Synthesis Method
- 2.3. Precursor Method
3. Manufacturing Process of Precursor
- 3.1. Production Flow of Ni-based NCM
- 3.2. Production Flow of LFP (Solid-state Method)
- 3.3. Production Flow of LFP (Liquid-phase Method)
- 3.4. Post Reactor/Reactor Process
4. Evaluation of Cathode Material Characteristics
- 4.1. Chemical Composition Analysis
- 4.2. Measurement of Specific Surface Area
- 4.3. Particle Size Measurement
- 4.4. Tap Density Measurement
- 4.5. Measurement of Moisture Content
- 4.6. Measurement of Residual lithium Carbonate
- 4.7. Thermal Analysis
- 4.8. Particle Strength
5. Manufacturing Process of Cathode Plate
Chapter 5. Outlook for Global LIB Market (~2035)
- 1. Global Secondary Battery Installation Outlook
- 2. Global Secondary Battery Shipment Outlook
- 3. Global Secondary Battery Production Outlook
- 4. Global Secondary Battery Production Outlook by Suppliers
- 5. Global Secondary Battery Production M/S Outlook by Suppliers
- 6. Global Secondary Battery Production by Cathode Chemistry
- 7. Global Secondary Battery Production M/S by Cathode Chemistry
Chapter 6. Global Cathode Supply Status and Market Outlook
- 1. Demand Outlook by Cathode Application ('21~'35)
- 2. Demand Outlook by Cathode Chemistry ('21~'35)
- 3. Demand M/S Outlook by Cathode Chemistry ('21~'35)
- 4. Demand Outlook by Cathode Chemistry for EVs ('21~'35)
- 5. Demand Outlook by Cathode Chemistry for ESS ('21~35)
- 6. Secondary Battery Cathode Shipment Details ('21~24)
- 7. Secondary Battery Cathode Shipment Details by Country (2021~2024)
- 8. Shipment (Supply) Volume by Ni-based CAM Supplier ('21~'24)
- 9. Shipment M/S by Ni-based CAM Supplier ('21~'24)
- 10. Shipment (Supply) Volume by LFP Cathode Supplier ('21~'24)
- 11. Shipment M/S by LFP Cathode Supplier ('21~'24)
- 12. Comprehensive Analysis of CAM Supplier Status (as of 2023)
- 13. Comprehensive Analysis of LFP CAM Supplier Status (as of 2023)
- 14. Capa. Expansion Plan & Supply Demand Outlook of Multi-Component Cathode Material Supplier ('21~'30)
- 15. Capa. Expansion Plan & Supply Demand Outlook of LFP Cathode Material Supplier ('21~'30)
- 16. Price Outlook by Cathode Material ('21~'30)
- 17. CAM Market Size Outlook ('21~'30)
Chapter 7. Cathode Demand Status by LIB Maker
- 1. CAM Demand by Application and Chemistry ('21~'24)
- 2. CAM Demand by LIB Maker ('21~'24)
- 3. Demand for CAM by Chemistry from LIB Maker ('21~'24)
- 4. CAM Demand and Supplier Status and Outlook for Major LIB Makers
- CATL / LGES / BYD / SDI / SK On / Panasonic / CALB / Guoxuan / EVE / REPT
- 5. Supply-Demand Overview Among Key Players
Chapter 8. Status of Cathode Material Manufacturers
1. Korean Cathode Material Manufacturers
- 1.1. Ecopro
- 1.2. L&F
- 1.3. Posco Future M
- 1.4. Umicore Korea
- 1.5. LG Chem
- 1.6. SDI(STM)
- 1.7. Cosmo AM&T
- 1.8. SM Lab
- 1.9. Top Materials
2. Japanese Cathode Material Manufacturers
- 2.1. Nichia
- 2.2. Sumitomo Metal Mining
- 2.3. Toda Kogyo
- 2.4. Mitsui Kinzoku
- 2.5. Nippon Denko
3. Chinese Cathode Material Manufacturers
- 3.1. Ronbay
- 3.2. B&M
- 3.3. XTC
- 3.4. Reshine
- 3.5. Easpring
- 3.6. CY Lico
- 3.7. ShanShan
- 3.8. ZEC
- 3.9. BTR
- 3.10. Brunp
- 3.11. LIBODE
- 3.12. Hunan Yuneng
- 3.13. Dynanonic
- 3.14. Hubei Wanrun
- 3.15. Lopal Technology
- 3.16. Rongtong Hi-TechV
- 3.17. Guoxuan(Gotion)
- 3.18. Youshan
- 3.19. Hunan Shenghua
- 3.20. Anda
- 3.21. Jintang Shidai
- 3.22. Shengfan
- 3.23. Pulead
- 3.24. Terui