|
|
市場調査レポート
商品コード
1458501
バイポーラ電池技術開発の現状と将来見通し(2024年)<2024> Current Status and Future Outlook of Bipolar Battery Technology Development |
||||||
|
|||||||
| バイポーラ電池技術開発の現状と将来見通し(2024年) |
|
出版日: 2024年03月29日
発行: SNE Research
ページ情報: 英文 205 Pages
納期: お問合せ
|
全表示
- 概要
- 目次
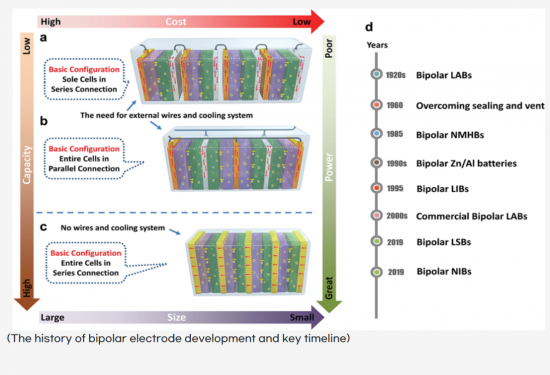
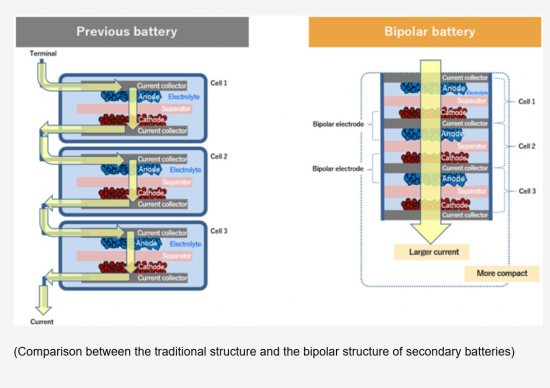
集電体の両面を同じ電極材料で構成したモノポーラ電極からなるシングルセル二次電池は、すべての電極が同じ電解液に浸されています。各電極は外部接続線を用いて並列接続されているため、電池システムにはかなりの量の不活性物質が組み込まれています。その結果、体積エネルギー密度は約40%、重量エネルギー密度は約20%の損失が生じると推定されます。
バイポーラ電池は、電気コネクターやその他の付属品を使用しないため、セルの構成や形状がシンプルです。電池の体積は、個々のユニットセルのスタック厚の合計とユニットセルの基板面積の積に近く、電池の重量は全コンポーネントの総質量に匹敵します。バイポーラ電池の容量はユニットセル1個の容量と同等ですが、バイポーラ電池の出力電圧は、直列に接続されたユニットセルの数と各セルの電圧を掛け合わせた値で決まります。
電池にバイポーラ電極を使用すると、体積エネルギー密度と重量エネルギー密度の両方が大幅に向上します。さらに、用途中心の設計に基づき、電池の形状を容易に調整することができ、ターゲットデバイスの電池収納スペースの利用率を最大化することができます。言い換えれば、電池の体積が減少し、BMSを最小化することで、エネルギー密度の向上と、セルパッケージング材料の使用を最小化することによるコスト削減を同時に追求することができます。これは最終的に、限られた電気自動車の電池搭載スペースにより多くの電池を搭載できることにつながり、航続距離の延長につながる可能性があります。したがって、バイポーラ電極のこれらの利点は、モバイル電子機器や電気自動車に使用される二次電池の設計にとって非常に魅力的です。
バイポーラ電極のもう1つの利点は、電子流が基板を垂直に流れることであり、基板の断面積が大きいと電流密度と電流分布が大きく向上します。そのため、バイポーラ電極を使うことで、安全性に問題がなく、高速動作する二次電池を安全に機能させることができます。
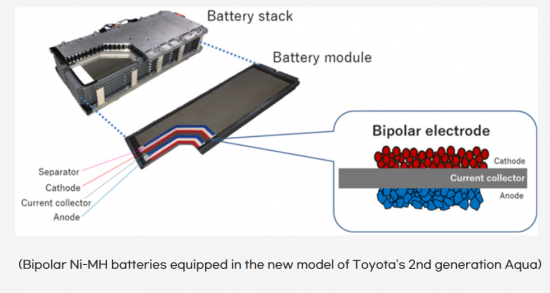
Furukawa Electricのバイポーラ電極を採用した小型電池を皮切りに、近年ではToyotaがバイポーラNi-MH電池を商品化し、Aqua HEVに搭載しています。Toyotaは2023年6月の発表で、2026年~2027年に量販EV向けバイポーラLFP電池を、2027年~2028年に未来型EV向けバイポーラNi系LIB電池を生産する計画であるとのロードマップを明らかにしました。このロードマップの狙いは、航続距離の向上と、パフォーマンス型LIBに比べたコスト削減です。
近年発売されたToyota Crown CrossoverとLexus RXは、バイポーラNi-MHとして知られる従来のNi-MH電池の改良版を搭載しています。これは、特にハイエンドモデルや低燃費モデルでLIBを使用するという従来の動向からの脱却を意味します。このシフトは、Ni-MH電池の使用をラインアップ全体で徐々に拡大する意図を示唆しており、電池技術採用の戦略的変化を示しています。
当レポートでは、バイポーラ電池市場について調査分析し、近年利用が始まったバイポーラ電極の開発動向と研究開発の現状に関する情報を提供しています。
目次
第1章 二次電池向けバイポーラ電極
- 電池構造最適化の必要性
- バイポーラ電極
- バイポーラ電極の開発
- バイポーラ電極の用途
- バイポーラアルカリ電池
- バイポーラリチウムイオン電池
- バイポーラポストLiB(Li-S、Naイオン)
- 課題と見通し
第2章 バイポーラ固体電池:設計、製造、電気化学
- 概要
- バイポーラプレート
- バイポーラ固体電池の製造と電気化学特性
- 結果と将来見通し
第3章 バイポーラ固体電池:エネルギー密度の設計
- 概要
- 結果と考察
第4章 バイポーラ固体電池:準固体電解質ベース
- 準固体リチウムグライム複合体
- バイポーラ固体LIBの評価
- バイポーラ固体LIBのSEM分析
- 結論
第5章 バイポーラ固体電池:硫化物電解質ベース
- 概要
- 結果と考察
- 結論
第6章 バイポーラ固体電池:多段階印刷製造ベース
- 概要
- イントロダクション
- 実験
- 結果と考察
- 結論
第7章 バイポーラ固体電池:FeOx-LFBOアノードの応用
- 概要
- イントロダクション
- 実験結果
- 結論
第8章 バイポーラLFP/LTO電池:マイクロ/マイルドハイブリッド向けLIB
- 概要
- イントロダクション
- 実験
- 結果と考察
- 結論
第9章 バイポーラNi-MH電池
- 概要
- 電池設計
- ウエハーセルの応用
- HEVへの応用
- PHEVへの応用
- ユーティリティへの応用
第10章 バイポーラ高電圧ナトリウムイオン電池
- 概要
- イントロダクション
- 実験と方法
- 結果
第11章 バイポーラ全ポリマー電池
- 全ポリマー電池の特性
- 全ポリマー電池の生産方式
- 全ポリマー電池の特性
- 全てのポリマー電池の基本構造
- 全てのポリマー電池を直列に積み重ねる
- 安全性を強化したバイポーラ全ポリマー電池
- コアシェル型電極材料
- APB Corporationのバイポーラ全ポリマー電池
- 全ポリマー電池の将来見通し
第12章 バイポーラ鉛蓄電池(Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd.)
- 世界初の商品化
- 長期電力貯蔵向けESS電池
第13章 バイポーラLIB(Fraunhofer IKTS)
- 概要
- バイポーラ電池の概念
- ウェットプロセス電極製造
- セパレーターコーティング
- バイポーラセル、スタック
- バイポーラ電池向けロールクラッド箔(SCHLENK)
第14章 バイポーラNi-MH電池(TOYOTA)
- バイポーラ電池の特性
- 新しい電池技術
- TOYOTAの電池イノベーション
- TOYOTAの年表
- TOYOTAの製造工程
第15章 バイポーラ電池の特許
- TOYOTA:バイポーラニッケル水素電池
- Hyundai Motor Company:バイポーラ固体電池
- TOYOTA:バイポーラ固体電池
- Samsung SDI:バイポーラ電極と製造
- LG Chem:バイポーラ電池
- LGES:バイポーラLIB
- KITECH:バイポーラ固体電池
- ProLogium:水平複合給電構造
参考文献
A single-cell secondary battery consisted of monopolar electrodes, where both sides of the current collector are composed of the same electrode material, has all electrodes immersed in the same electrolyte. Since each electrode is connected in parallel using external connecting wires, a significant amount of inactive material has been integrated into the battery system. As a result, it is estimated that the volumetric energy density may experience a loss of approximately 40%, and the gravimetric energy density approximately 20%.
The bipolar battery features a simple cell configuration and shape as it does not utilize electrical connectors or other accessories. The volume of the battery is close to the product of the total stack thickness of the individual unit cells and the substrate area of the unit cell, while the weight of the battery is comparable to the total mass of all components. Although the capacity of the bipolar battery is equivalent to that of a single unit cell, the output voltage of the bipolar battery is determined by the number of unit cells connected in series and the voltage of each cell multiplied together.
Using bipolar electrodes in batteries significantly increases both volumetric and gravimetric energy density. Additionally, based on application-centric design, the battery shape can be easily adjusted to maximize the utilization of the battery storage space in the target device. In other words, the battery volume decreases, and by minimizing the BMS, energy density enhancement and cost savings can be simultaneously pursued through minimized use of cell packaging materials. This ultimately translates into the ability to install more batteries in limited electric vehicle battery mounting spaces, potentially leading to increased driving range. Therefore, these advantages of bipolar electrodes are highly attractive for the design of secondary batteries used in mobile electronic devices and electric vehicles.
Another advantage of bipolar electrodes is that electron flow occurs vertically through the substrate, and when the substrate's cross-sectional area is large, current density and distribution are significantly improved. Therefore, using bipolar electrodes allows fast-operating secondary batteries to function safely without any safety issues.
Starting with Furukawa Electric's compact batteries featuring bipolar electrodes, Toyota has recently commercialized bipolar Ni-MH batteries, which were applied to the Aqua HEV. In the announcement at June 2023, Toyota revealed a roadmap stating that they plan to produce bipolar LFP batteries for volume-grade EVs in 2026-2027 and bipolar Ni-based LIBs for future versions of EVs in 2027-2028. This roadmap aims to enhance driving range and reduce costs compared to performance versions of LIBs.
The recently released Toyota Crown Crossover and Lexus RX feature an improved version of the traditional Ni-MH battery, known as the bipolar Ni-MH. This marks a departure from the previous trend of using LIBs, especially in high-end and fuel-efficient models. This shift suggests an intention to gradually expand the use of Ni-MH batteries across the lineup, indicating a strategic change in battery technology adoption.
In this report, we have compiled the history of the development of bipolar electrodes, which have recently begun to be applied, as well as the current status of research and development. We have detailed each development to provide a comprehensive overview, making it easy to understand the overall situation.
The strong points of this report are as follows:
- 1. ailed coverage of recent technological trends related to bipolar batteries
- 2. ailed coverage of the development history and current status of bipolar battery developers
- 3. centrated coverage of the development status of bipolar batteries at Toyota Motor Corporation
- 4. lysis of bipolar battery's key patent



Table of Contents
1. Bipolar Electrodes for Secondary Batteries
- 1.1. The Necessity of Battery Structure Optimization
- 1.2. Bipolar Electrodes
- 1.3. Development of Bipolar Electrodes
- 1.3.1. History of Bipolar Electrode Development
- 1.3.2. Reduction in Weight, Size, and Cost
- 1.3.3. Improvement in Energy Density/Power Density
- 1.3.4. Requirements and Disadvantages of Bipolar Electrodes
- 1.4. Applications of Bipolar Electrodes
- 1.4.1. Bipolar Lead-Acid Batteries (LAB)
- 1.4.2. Improvement of Bipolar Lead-Acid Batteries
- 1.4.2.1. Surface Modification
- 1.4.2.2. Corrosion Prevention
- 1.4.3. Commercialization of Bipolar Lead-Acid Batteries
- 1.5. Bipolar Alkaline Batteries
- 1.5.1. Bipolar Ni-MH
- 1.5.2. Bipolar Al and Zn Batteries
- 1.6. Bipolar Lithium-Ion Batteries
- 1.7. Bipolar post-LiB(Li-S, Na-ion)
- 1.8. Challenges and Outlook
- 1.8.1. Substrate Materials
- 1.8.2. Electrode Materials
- 1.8.3. Electrolyte Materials
- 1.8.4. Engineering Technologies
- 1.8.5. Outlook of Bipolar Electrode
- 1.8.6. Hurdles to Commercialization
- 1.8.7. Other Bipolar Batteries
- 1.8.8. Bipolar Solid-State Batteries
2. Bipolar Solid-State Batteries: Design, Fabrication, and Electrochemistry
- 2.1. Overview
- 2.1.1. Advantages of Bipolar Solid-State Batteries
- 2.1.2. Technical Challenges of Bipolar Batteries
- 2.1.3. Requirements for Bipolar Materials
- 2.2. Bipolar Plates
- 2.3. Fabrication and Electrochemical Characteristics of Bipolar Solid-State Batteries
- 2.3.1. Free standing Lamination Bipolar Solid-State Batteries
- 2.3.2. Printing Bipolar Solid-State Batteries
- 2.4. Results and Future Outlook
3. Bipolar Solid-State Batteries: Design of Energy Density
- 3.1. Overview
- 3.2. Results and Discussion
- 3.2.1. SolidPAC demo
- 3.2.2. Comparison of Bipolar Stacking and Conventional Stacking
- 3.2.3. Sensitivity Analysis
- 3.2.4. Experimental Data Analysis
4. Bipolar Solid-State Batteries: Based on Quasi-Solid Electrolytes
- 4.1. Quasi-Solid Li-Glyme complex
- 4.2. Evaluation of Bipolar Solid-State LIBs
- 4.3. SEM Analysis of Bipolar Solid-State LIBs
- 4.4. Conclusion
5. Bipolar Solid-State Batteries: Based on Sulfide Electrolytes
- 5.1. Overview
- 5.2. Results and Discussion
- 5.2.1. Manufacturing and Characteristics of Cathode Layers
- 5.2.2. Manufacturing and Characteristics of Anode Layers
- 5.2.3. Manufacturing and Characteristics of Mono cells
- 5.2.4. Characteristics of Bipolar Stacked Solid-State Batteries
- 5.2.5. Comparison of Energy Densities in Bipolar Solid-State Batteries
- 5.3. Conclusion
6. Bipolar Solid-State Batteries: Based on Multistage Printing Manufacturing
- 6.1. Overview
- 6.2. Introduction
- 6.3. Experiment
- 6.3.1. Manufacturing of SWCNT-Coated Electrode Active Material
- 6.3.2. Fabrication of Printed Bipolar LIB
- 6.4. Results and Discussion
- 6.4.1. Solid Gel Composite Electrolyte(GCE)
- 6.4.2. Fabrication and Characteristics of Printed Electrodes
- 6.4.3. GCE and Electrode Paste Control
- 6.4.4. Mechanical Flexibility and Thermal Stability
- 6.5. Conclusion
7. Bipolar Solid-State Batteries: Application of FeOx-LFBO Anode
- 7.1. Overview
- 7.2. Introduction
- 7.3. Experiment Results
- 7.3.1. Synthesis and Characteristics of FeOx-LFBO
- 7.3.2. Electrochemical Performance of FeOx-LFBO Anode
- 7.3.3. Mechanism Analysis
- 7.3.4. Electrochemical Performance of Cu-free LIB
- 7.4. Conclusion
8. Bipolar LFP/LTO Batteries: LIBs for Micro/Mild Hybrid
- 8.1. Overview
- 8.2. Introduction
- 8.3. Experiments
- 8.4. Results and Discussion
- 8.4.1. LFP, LTO
- 8.4.2. 15Wh Bipolar Battery
- 8.4.3. Safety
- 8.5. Conclusion
9. Bipolar Ni-MH Batteries
- 9.1. Overview
- 9.2. Battery Design
- 9.3. Application of Wafer Cells
- 9.4. Application in HEVs
- 9.5. Application in PHEVs
- 9.6. Application in Utility
- 9.6.1. High-Power Bipolar Batteries
- 9.6.2. High-Energy Bipolar Batteries
10. Bipolar High-Voltage Na-ion Batteries
- 10.1. Overview
- 10.2. Introduction
- 10.2.1. Monopolar 48V Battery System
- 10.2.2. Commercialization Issues of Bipolar Batteries
- 10.3. Experiment and Method
- 10.4. Results
- 10.4.1. Bipolar Batteries with Liquid Electrolytes
- 10.4.2. nS mP(Series-Parallel) Bipolar Batteries
- 10.4.3. Na-ion Bipolar Batteries with Above 5V
- 10.4.4. Custom Cell Voltage Profile Design
11. Bipolar All Polymer Batteries
- 11.1. Characteristics of All Polymer Batteries
- 11.1.1. Advantages of All Polymer Batteries
- 11.1.2. Disadvantages of All Polymer Batteries
- 11.1.3. Energy Density of All Polymer Batteries
- 11.1.4. Manufacturers of All Polymer Batteries
- 11.1.4.1. Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- 11.1.4.2. JFE Chemical
- 11.1.4.3. Teijin
- 11.1.4.4. Gunze/Sanyo Chemical Industries
- 11.2. Manufacturing Methods of All Polymer Batteries
- 11.3. Characteristics of All Polymer Batteries
- 11.3.1. Voltage Increase by Stacking
- 11.3.2. Elimination of Drying Process
- 11.3.3. Improve of Production Speed
- 11.4. Basic Structure of All Polymer Batteries
- 11.5. All Polymer Batteries Stacked in Series
- 11.6. Safety-Enhanced Bipolar All Polymer Batteries
- 11.7. Core-Shell Type Electrode Materials
- 11.8. Bipolar All Polymer Batteries by APB Corporation
- 11.9. Future Outlook of All Polymer Batteries
12. Bipolar Lead-Acid Batteries (Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd.)
- 12.1. World's First Commercialization
- 12.1.1. Structure and Challenges of Bipolar Lead-Acid Batteries
- 12.1.2. Overcoming Challenges with Metal/Polymer Materials
- 12.2. ESS Batteries for Long-Term Power Storage
13. Bipolar LIBs (Fraunhofer IKTS)
- 13.1. Overview
- 13.2. Concept of Bipolar Batteries
- 13.3. Wet Process Electrode Manufacturing
- 13.4. Separator Coating
- 13.5. Bipolar Cells and Stacks
- 13.6. Roll Clad Foil for Bipolar Battery (SCHLENK)
14. Bipolar Ni-MH Batteries (TOYOTA)
- 14.1. Characteristics of Bipolar Batteries
- 14.2. New Battery Technologies
- 14.3. Battery Innovation by TOYOTA
- 14.4. Timeline of TOYOTA
- 14.5. Manufacturing Process by TOYOTA
15. Bipolar Battery Patents
- 15.1. TOYOTA: Bipolar Ni-MH Batteries
- 15.2. Hyundai Motor Company: Bipolar Solid-State Batteries
- 15.3. TOYOTA: Bipolar Solid-State Batteries
- 15.4. Samsung SDI: Bipolar Electrodes and Manufacturing
- 15.5. LG Chem: Bipolar Batteries
- 15.6. LGES: Bipolar LIBs
- 15.7. KITECH: Bipolar Solid-State Batteries
- 15.8. ProLogium: Horizontal Composite Electric Supply Structure






